Are you a nurse looking to enhance your knowledge on obesity management? Look no further! This article will provide you with the best nursing considerations and management strategies for addressing obesity. From understanding the factors contributing to obesity to implementing effective interventions, we’ve got you covered. So, grab a cup of tea, sit back, and prepare to learn the essentials of caring for patients with obesity.

Assessment
When it comes to managing obesity, a comprehensive assessment is essential to develop an effective treatment plan. The assessment process involves various components, including the calculation of Body Mass Index (BMI), evaluation of comorbidities, assessment of psychosocial factors, and identification of weight loss goals.
Body Mass Index (BMI) calculation
Calculating the BMI is a fundamental step in assessing obesity. It allows healthcare professionals to determine whether an individual’s weight is within a healthy range. By dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters, the BMI provides a numerical value that can be classified as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. This information helps guide healthcare providers in identifying appropriate interventions and setting realistic weight loss goals for individuals.
Evaluation of comorbidities
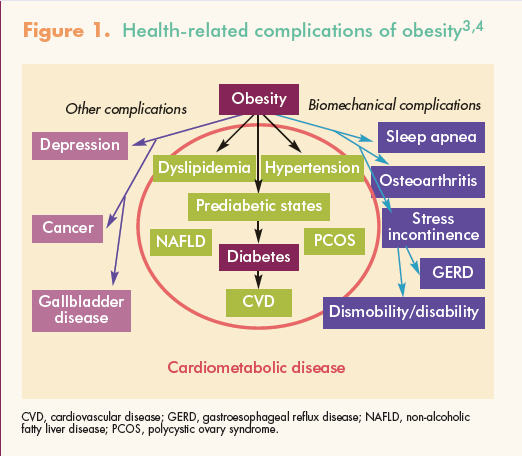
Another crucial aspect of the assessment process is evaluating comorbidities associated with obesity. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and sleep apnea commonly occur alongside obesity. Identifying and addressing these comorbidities is vital for the overall management and improvement of health outcomes in individuals with obesity.
Assessment of psychosocial factors
Obesity is a complex issue that often involves psychosocial factors. It is important to consider an individual’s mental and emotional well-being when developing an obesity management plan. Factors such as stress, depression, anxiety, body image issues, and emotional eating can significantly impact a person’s ability to achieve lasting weight loss. Assessing and addressing these psychosocial factors is crucial for successful obesity management.
Identification of weight loss goals
Setting realistic weight loss goals is an essential part of the assessment process. Working collaboratively with individuals, healthcare providers can help set achievable targets for weight loss. This helps in creating a personalized treatment plan that is tailored to the specific needs, abilities, and preferences of each person. By setting realistic goals, individuals are more likely to stay motivated and achieve long-term success in their weight loss journey.
Nutritional Interventions
Nutritional interventions play a crucial role in the management of obesity. A comprehensive approach to dietary assessment and planning is necessary to address the unique needs and challenges of individuals with obesity.
Dietary assessment and planning
Assessing an individual’s dietary habits and patterns is essential to develop an effective nutritional plan. By understanding their current eating habits, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies for making healthier food choices. This may include evaluating portion sizes, identifying sources of excess calories, and addressing specific dietary preferences or restrictions.
Caloric restriction recommendations
Caloric restriction is often a key component of weight loss interventions. By reducing daily calorie intake, individuals can create an energy deficit that promotes weight loss. Healthcare providers can provide specific recommendations for caloric intake based on each person’s individual needs and weight loss goals. This may involve setting a daily calorie target and providing guidance on portion control and nutrient-dense food choices.
Scheduling regular meals and snacks
Establishing regular meal and snack times can help individuals with obesity maintain a consistent eating pattern and prevent excessive hunger. By spacing out meals and snacks throughout the day, individuals can better manage their energy intake and reduce the likelihood of overeating. Healthcare providers can work with individuals to create a meal schedule that suits their lifestyle and promotes balanced nutrition.
Promotion of balanced and nutritious meals
In addition to caloric restriction, promoting balanced and nutritious meals is essential for long-term weight management. Emphasizing the importance of a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of food groups helps individuals with obesity meet their nutritional needs while also supporting weight loss. Healthcare providers can provide education on the benefits of consuming nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.

Physical Activity
Incorporating physical activity into the management of obesity is crucial for achieving and maintaining weight loss. Regular exercise not only helps burn calories but also offers numerous health benefits.
Evaluation of current activity level
Assessing an individual’s current activity level is essential to determine the appropriate starting point for physical activity interventions. This involves evaluating the frequency, duration, and intensity of exercise, as well as any barriers or limitations individuals may face. Understanding their baseline activity level allows healthcare providers to develop an exercise plan that is safe, realistic, and achievable.
Development of personalized exercise plan
Creating a personalized exercise plan is key to supporting individuals in their weight loss journey. Healthcare providers can collaborate with individuals to design an exercise regimen that aligns with their preferences and goals. This may include incorporating activities they enjoy, such as walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing. The plan should also take into consideration their fitness level and any medical conditions or physical limitations that may affect their ability to exercise.
Guidance on incorporating aerobic exercises
Aerobic exercises, also known as cardiovascular exercises, are particularly beneficial for weight management. These activities increase heart rate and breathing, helping individuals burn calories and improve cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers can offer guidance on incorporating aerobic exercises into a person’s exercise plan, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or participating in group fitness classes.
Recommendations for strength training
Strength training exercises are essential for building and maintaining muscle mass, which can help increase metabolism and support weight loss efforts. Healthcare providers can provide recommendations on incorporating strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance training, into an individual’s exercise routine. It is important to ensure that exercises are performed safely and properly to minimize the risk of injury.
Behavioral Modifications
Addressing behavioral factors that contribute to obesity is a critical part of its management. Behavior modification techniques aim to identify and change unhealthy habits and patterns, promoting sustainable lifestyle changes.
Identification of triggers for overeating
Identifying triggers for overeating is an essential step in behavior modification. Triggers can be emotional, environmental, or situational factors that lead to excessive food consumption. By recognizing these triggers, individuals can develop strategies to manage their responses and adopt healthier coping mechanisms.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques are commonly utilized in obesity management. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to unhealthy behaviors. Healthcare providers can assist individuals in developing positive coping strategies, improving self-esteem, and promoting a healthier relationship with food and body image.
Support for emotional eating and stress management
Emotional eating is a common response to stress, anxiety, or other emotional triggers. It can contribute to weight gain and hinder weight loss efforts. Healthcare providers can offer support and guidance in managing emotions and stressors without relying on food. This may involve exploring alternative coping mechanisms, such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, or engaging in activities that provide emotional fulfillment.
Encouragement of self-monitoring
Self-monitoring is a valuable tool for behavior modification and weight management. Encouraging individuals to keep a food diary or track their physical activity can help increase awareness and accountability. Healthcare providers can provide resources and guidance on effective self-monitoring techniques, such as using smartphone applications or journals. Regularly reviewing progress can motivate individuals and facilitate adjustments to their treatment plan.
Medication Management
In certain cases, medications may be considered as part of the treatment plan for obesity. Medications for weight loss should be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and increased physical activity.
Evaluation of medication history
Before prescribing weight-loss medications, healthcare providers must evaluate an individual’s medication history. This evaluation helps identify any potential contraindications or drug interactions that may affect the choice of medication. It is important to consider an individual’s overall health, medical conditions, and current medication regimen to ensure the safe and appropriate use of weight-loss medications.
Prescription of weight-loss medications
Prescribing weight-loss medications should be done judiciously and in accordance with relevant guidelines and protocols. Healthcare providers can assess an individual’s eligibility for medication management and discuss the available options. Medications may include appetite suppressants, lipase inhibitors, or combination drugs that target different aspects of weight loss. The choice of medication is based on factors such as an individual’s BMI, medical history, and specific weight loss goals.
Monitoring for side effects and drug interactions
Regular monitoring for side effects and potential drug interactions is essential when utilizing weight-loss medications. Healthcare providers should closely monitor individuals for any adverse effects and adjust the treatment plan accordingly. This involves conducting regular check-ups and educating individuals about potential side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, cardiovascular effects, or changes in mood or behavior.
Education on adherence to medication regimen
Adherence to the prescribed medication regimen is crucial for achieving optimal results. Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive education and counseling on the appropriate use of weight-loss medications. This includes information on dosage, administration, potential interactions with other medications or supplements, and any precautions or warning signs that individuals should be aware of. Regular follow-up appointments can help reinforce adherence and address any concerns or issues.
Surgical Interventions
For individuals with severe obesity or those who have not achieved sustained weight loss through non-surgical interventions, bariatric surgery may be considered. Bariatric surgery is a significant decision that demands careful assessment, pre-operative preparation, and post-operative care.
Assessment of eligibility for bariatric surgery
Determining eligibility for bariatric surgery involves a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s medical history, BMI, comorbidities, and previous weight management efforts. This assessment helps identify individuals who may benefit from surgical interventions. Healthcare providers work closely with individuals to explain the surgical options available, associated risks, benefits, and expected outcomes. Additionally, psychological evaluations and nutritional assessments are conducted to ensure individuals are prepared for the surgical process.
Pre-operative preparation
Preparing individuals for bariatric surgery involves physical, psychological, and nutritional preparation. Healthcare providers educate individuals on the surgical process, potential complications, expected recovery, and necessary lifestyle changes. They may also recommend pre-operative weight loss to reduce surgical risks and optimize outcomes. Coordination with nutritionists and psychologists helps individuals understand and adhere to pre-operative dietary modifications and address any psychological concerns or emotional factors.
Post-operative care and monitoring
Post-operative care is crucial for successful recovery and long-term weight management. Healthcare providers closely monitor individuals in the immediate post-operative period to ensure proper healing and to address any complications. They provide guidance on post-surgical dietary modifications, incorporate physical activity gradually, and offer support for emotional adjustment post-surgery. Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor progress, address concerns, and help individuals navigate the lifestyle changes required after bariatric surgery.
Support for lifestyle changes after surgery
Bariatric surgery necessitates significant lifestyle changes to support long-term weight loss and overall well-being. Healthcare providers offer continuous support and education to individuals, helping them adopt healthy eating habits, engage in regular physical activity, and manage psychosocial factors. They may recommend participation in support groups or counseling services to provide emotional support and encourage sustainable lifestyle changes.

Psychosocial Support
Psychosocial support is vital in obesity management to address the emotional and mental well-being of individuals. A holistic approach to care includes counseling, evaluation and treatment of underlying mental health conditions, support groups, and referral to specialized therapists.
Counseling for body image issues
Body image issues are common among individuals with obesity and can significantly impact their self-esteem and mental well-being. Healthcare providers offer counseling and support to address these concerns, helping individuals develop a positive body image and improve their self-confidence. Counseling sessions may focus on promoting self-acceptance, challenging negative thoughts, and developing coping strategies to navigate societal pressures and stereotypes.
Evaluation and treatment of underlying mental health conditions
Obesity is often associated with underlying mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or binge eating disorder. Healthcare providers conduct evaluations to identify and assess these conditions, providing appropriate treatment or referrals to specialized therapists when necessary. Integrated care, involving collaboration with mental health professionals, ensures that individuals receive comprehensive support to address the interplay between mental health and obesity.
Support groups and peer counseling
Participation in support groups and peer counseling can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with obesity. These avenues offer a sense of community, shared experiences, and emotional support from others facing similar challenges. Healthcare providers provide information on local support groups, online communities, and counseling services, helping individuals connect with resources that foster a supportive environment.
Referral to specialized therapists
In some cases, individuals may require specialized therapy to address specific psychological or behavioral factors contributing to obesity. Healthcare providers can refer individuals to therapists experienced in cognitive-behavioral therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, or other evidence-based practices. Collaborative care between healthcare providers and therapists ensures comprehensive support for individuals, allowing them to address underlying issues that may hinder weight management efforts.
Family Involvement
Family involvement is crucial in obesity management. Inclusion of family members in the treatment process offers support, encourages lifestyle changes, and helps improve overall family dynamics.
Education on the impact of obesity on family dynamics
Healthcare providers educate families about the impact of obesity on family dynamics and emphasize the importance of a supportive environment. They provide information on how obesity affects not only the individual but also the family as a whole, including potential challenges, emotional factors, and changes in daily routines. By understanding these dynamics, family members can better support individuals in their weight loss journey.
Support for family members in making lifestyle changes
Obesity management is often more effective when lifestyle changes are made collectively within the family unit. Healthcare providers offer support and resources to family members who may also benefit from adopting healthier habits. This may involve providing guidance on healthy meal planning, offering suggestions for incorporating physical activity into family routines, and addressing any unique challenges or barriers faced by the family as a whole.
Involvement of family in meal planning and activities
Incorporating family members in meal planning and activities helps create a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with obesity. Healthcare providers encourage families to engage in joint meal planning, ensuring the inclusion of healthy and nutritious options that meet the needs of everyone. Family involvement in physical activities, such as walks, bike rides, or sports, promotes a more active and healthier lifestyle for all family members.
Assessment and referral for family counseling
In some cases, the challenges associated with obesity may require additional support through family counseling. Healthcare providers can assess the need for family counseling and make appropriate referrals. Counseling sessions provide families with the opportunity to address communication issues, develop strategies for supporting each other’s goals, and enhance overall family cohesion.

Education
Education plays a vital role in obesity management, empowering individuals with knowledge, skills, and resources to make informed decisions and sustain healthy lifestyle changes.
Providing information on the risks and complications of obesity
Healthcare providers educate individuals about the risks and complications associated with obesity, highlighting the impact on overall health and well-being. They explain the increased risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and sleep apnea. By providing this information, individuals are motivated to take action and make positive changes to reduce their risk of obesity-related health issues.
Teaching about healthy eating habits
Education on healthy eating habits is essential in obesity management. Healthcare providers teach individuals about portion control, balanced nutrition, and the importance of consuming nutrient-dense foods. They provide information on food labels, healthy cooking methods, and strategies for making healthier choices when dining out or grocery shopping. By empowering individuals with knowledge, healthcare providers enable them to make informed decisions regarding their dietary choices.
Promoting the importance of physical activity
Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of regular physical activity for overall health and weight management. They educate individuals on the benefits of exercise, including increased calorie expenditure, improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mood, and increased energy levels. Through education and motivational support, healthcare providers encourage individuals to incorporate physical activity as an essential component of their lifestyle.
Providing resources for ongoing education
To support long-term success, healthcare providers provide individuals with resources for ongoing education. This may include recommending books, websites, or reputable online sources that offer evidence-based information on nutrition, exercise, behavior modification, and psychological support. By equipping individuals with these resources, healthcare providers enable them to continue learning and stay informed about the latest advancements in obesity management.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Monitoring and follow-up are essential components of obesity management, ensuring that individuals stay on track with their treatment plan and make necessary adjustments to achieve their weight loss goals.
Regular weight and BMI assessments
Regular weight and BMI assessments allow healthcare providers to monitor an individual’s progress and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed. By regularly tracking weight and BMI, healthcare providers can identify trends, assess the effectiveness of interventions, and provide timely support and guidance. These assessments provide individuals with tangible markers of their progress and serve as a motivation to continue their weight loss journey.
Monitoring of comorbidities
In addition to monitoring weight and BMI, healthcare providers must also monitor coexisting medical conditions associated with obesity. Regular assessments of blood pressure, blood glucose levels, lipid profiles, and other relevant parameters help identify any changes or complications that may require additional interventions or adjustment of treatment plans. Monitoring comorbidities supports overall health management while addressing the interconnectedness between obesity and associated health conditions.
Evaluation of adherence to treatment plan
Consistent evaluation of an individual’s adherence to the treatment plan is crucial for ongoing success in obesity management. Healthcare providers assess whether individuals are following dietary recommendations, engaging in regular physical activity, and implementing behavior modifications. Identifying areas of non-adherence allows for targeted interventions and reinforcement of self-management strategies.
Modification of interventions as needed
Obesity management is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and interventions may need to be modified over time. Healthcare providers regularly review and modify the treatment plan based on individual progress, changes in health status, and personal preferences. Flexibility and open communication ensure that interventions remain effective and relevant, supporting individuals in achieving their weight loss goals and maintaining long-term success.
In conclusion, effective obesity management requires a comprehensive and multidimensional approach. Nurses play a crucial role in assessing individuals, developing personalized treatment plans, and providing ongoing support and education. By addressing factors such as nutrition, physical activity, behavioral modifications, medication management, surgical interventions, psychosocial support, family involvement, education, and monitoring, healthcare providers can facilitate lasting weight loss and overall well-being. Through a collaborative and empathetic approach, nurses can support individuals in their journey towards a healthier lifestyle and improved quality of life.