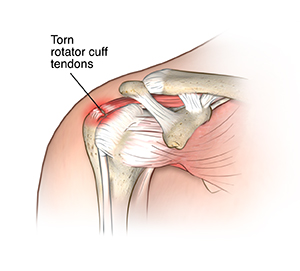
In this article, we will explore the key nursing considerations and nursing management for individuals experiencing a rotator cuff injury. A rotator cuff injury can cause significant pain and limitations in daily activities, making it crucial for nurses to have a comprehensive understanding of the condition and necessary interventions. From assessing pain levels to implementing rehabilitation strategies, nurses play a vital role in promoting patient recovery and optimizing their quality of life. By implementing these key nursing considerations, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care and support to individuals with a rotator cuff injury.

Assessment
History taking
When assessing a patient with a potential rotator cuff injury, a thorough history is essential. It is important to gather information about the patient’s occupation, hobbies, and activities to determine any potential causes of injury. Additionally, asking about the onset and duration of symptoms, any previous injuries or surgeries, and any existing medical conditions will help to provide a complete picture of the patient’s situation.
Physical examination
After taking a comprehensive history, a physical examination is necessary to assess the extent of the rotator cuff injury. The healthcare provider will perform a range of motion assessment, checking for any limitations in movement and any signs of pain or discomfort. Strength testing and palpation of the shoulder area will also be conducted to gauge the severity of the injury. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be ordered to further evaluate the injury if necessary.
Diagnostic tests
In some cases, diagnostic tests may be required to confirm the presence of a rotator cuff injury and to determine its severity. These tests can include ultrasound or MRI, which will provide detailed images of the shoulder area. These images will help clinicians assess the integrity of the tendons and muscles in the rotator cuff and guide treatment decisions.
Patient Education
Explanation of injury
When a patient is diagnosed with a rotator cuff injury, it is crucial to provide them with a clear and concise explanation of their injury. This includes discussing the specific tendons and muscles involved, as well as the potential causes and risk factors. By understanding their injury, patients are better equipped to participate in their own care, make informed decisions, and follow the recommended treatment plan.
Pain management techniques
Managing pain effectively is a key aspect of nursing care for patients with a rotator cuff injury. Various techniques can be employed to help alleviate pain, including the use of over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids, as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Additionally, non-pharmacological approaches such as heat therapy, cold therapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may also be employed to provide relief.
Activity modification
Patients with a rotator cuff injury may need to modify their daily activities to avoid exacerbating their symptoms or worsening their injury. Nurses play a crucial role in educating patients about proper body mechanics, lifting techniques, and ergonomic principles. This includes demonstrating safe lifting practices, explaining the importance of maintaining good posture, and providing tips for adapting their work environment to reduce strain on the shoulder.

Pain Management
Medications
Medications can play an important role in managing pain associated with a rotator cuff injury. Depending on the severity of the pain, non-prescription pain relievers such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs may be recommended. In more severe cases, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger pain medications or muscle relaxants to help alleviate discomfort.
Physical therapy modalities
Physical therapy modalities are often employed as part of a comprehensive pain management plan. Techniques such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and manual therapy can help decrease pain, reduce inflammation, and improve blood flow to the affected area. These modalities are typically administered by a skilled physical therapist and can be tailored to meet each patient’s specific needs.
Ice and heat therapy
Ice and heat therapy are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation associated with a rotator cuff injury. Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected area can help decrease swelling and numb pain. On the other hand, the application of heat, such as using heating pads or warm towels, can help relax muscles and increase blood flow, promoting healing and reducing stiffness.
Range of Motion Exercises
Passive range of motion exercises
Passive range of motion exercises are often initiated in the early stages of rehabilitation for a rotator cuff injury. These exercises involve the therapist or caregiver moving the patient’s arm and shoulder through a full range of motion without the patient actively participating. This helps maintain joint flexibility and prevent stiffness while the injured area heals.
Active range of motion exercises
As the patient’s pain and inflammation decrease, active range of motion exercises can be introduced. These exercises involve the patient moving their shoulder and arm independently, gradually increasing the range of motion. This promotes muscle strength, coordination, and helps restore function to the injured shoulder.
Stretching exercises
Stretching exercises are important for maintaining and improving flexibility in the shoulder joint. This can help prevent future injuries and improve overall joint function. Healthcare providers or physical therapists can guide patients through a variety of stretching exercises that target the muscles and tendons of the rotator cuff. These exercises should be performed in a pain-free range and gradually increased in intensity over time.

Strengthening Exercises
Isometric exercises
Isometric exercises involve contracting the muscles without any visible movement in the joint. These exercises can help strengthen the muscles of the rotator cuff and provide stability to the shoulder joint. Isometric exercises are often performed against resistance, such as pushing against a wall or holding a stable object, and should be performed within a pain-free range.
Resistance band exercises
Resistance band exercises are a popular and effective way to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles. These exercises involve using an elastic band to provide resistance during various movements. They can be easily modified to accommodate a wide range of fitness levels and can be performed both in a clinical setting and at home. Resistance band exercises can help improve muscle strength and control, promoting overall shoulder stability.
Weight training
In more advanced stages of rehabilitation, weight training exercises can be added to the treatment plan. These exercises involve using dumbbells or other weights to provide resistance during movements that target the muscles of the rotator cuff. Weight training can help build muscle strength, increase joint stability, and improve overall functional capacity.
Activity Modification
Lifting techniques
Lifting heavy objects or improper lifting techniques can put excessive stress on the shoulder and increase the risk of further injury to the rotator cuff. Nurses play a crucial role in educating patients on proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees and using leg muscles rather than relying solely on the shoulders and arms. Teaching patients to distribute weight evenly and avoid sudden or jerky movements can help prevent re-injury and facilitate proper healing.
Avoiding overhead activities
Engaging in activities that require repeated overhead movements can strain the rotator cuff and contribute to ongoing pain and dysfunction. Nurses should advise patients to avoid or modify such activities to prevent exacerbation of symptoms. By providing alternative strategies or suggesting adaptations, nurses can empower patients to participate in activities that they enjoy while protecting their shoulder from further harm.
Workplace ergonomics
Workplace ergonomics is an important consideration for patients with a rotator cuff injury, particularly if their work involves repetitive or strenuous movements. Nurses can provide guidance on proper desk and chair setup, positioning of computer monitors, and utilizing ergonomic tools such as adjustable keyboards and chairs. These modifications can help reduce strain on the shoulder and promote proper alignment, allowing for more comfortable and efficient work.
Surgical Considerations
Pre-operative care
For patients who require surgery to repair a severe rotator cuff injury, pre-operative care is essential to ensure optimal outcomes. As a nurse, you will play a crucial role in educating patients about the surgical procedure, including what to expect before, during, and after the operation. This includes providing information about fasting requirements, pre-operative tests, and any necessary preparations or medications.
Post-operative care
After surgery, patients require careful monitoring and support to facilitate a smooth recovery. Nurses will assist with pain management, wound care, and mobility exercises to prevent complications such as post-operative infection, stiffness, or joint instability. Close collaboration with the healthcare team, including surgeons and physical therapists, is important to ensure a coordinated and effective post-operative care plan.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a critical component of the recovery process following rotator cuff surgery. Nurses will work closely with physical therapists and occupational therapists to ensure that patients are properly guided through their rehabilitation program. This may involve range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and functional activities to restore shoulder function and improve overall quality of life. Education and support throughout the rehabilitation process are essential to optimize outcomes and facilitate a successful return to daily activities.
Wound Care
Incision care
Proper wound care is crucial to minimize the risk of infection and promote optimal healing following rotator cuff surgery. Nurses will provide instructions on how to keep the surgical incision clean and dry, as well as how to change dressings. Emphasizing the importance of hand hygiene and using sterile techniques when dressing the wound can help prevent contamination and reduce the risk of complications.
Dressing changes
Depending on the surgeon’s preferences, patients may require regular dressing changes following rotator cuff surgery. Nurses will assess the incision site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage, and ensure that the dressings are applied correctly and securely. Education about signs and symptoms of infection and when to seek medical attention is essential for patients to monitor their wound’s progress and report any concerns promptly.
Infection prevention
Preventing infection is a crucial aspect of nursing care for patients with a rotator cuff injury. This includes providing thorough education about proper wound care, hygiene practices, and recognizing signs of infection. Encouraging patients to adhere to prescribed antibiotics and promptly report any signs or symptoms of infection can help prevent complications and promote optimal healing.

Psychosocial Support
Coping strategies
A rotator cuff injury can often have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life, limiting their ability to participate in daily activities and potentially causing emotional distress. Nurses play a vital role in providing psychosocial support by implementing coping strategies. These strategies may include encouraging patients to engage in relaxation techniques, counseling them on stress management, and connecting them to appropriate resources such as support groups or mental health services.
Emotional support
Emotional support is crucial for patients with a rotator cuff injury, as they may experience frustration, anxiety, or sadness due to their pain or limitations. Nurses can offer empathetic listening, validate their feelings, and provide encouragement. By acknowledging and addressing emotional concerns, nurses can help patients feel supported and empowered throughout their recovery journey.
Encouragement
Nurses should provide consistent encouragement to patients with a rotator cuff injury. This includes acknowledging their progress, celebrating milestones, and reinforcing the importance of adherence to treatment plans. By being a source of positivity and motivation, nurses can help patients maintain their dedication to their rehabilitation program and facilitate a successful recovery.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Providers
Orthopedic surgeon
Collaboration with the orthopedic surgeon is vital in the care of patients with a rotator cuff injury. Nurses should maintain clear and open communication with the surgeon to ensure cohesive and coordinated care. This includes sharing important patient information, discussing treatment plans, and seeking clarification or further guidance when necessary.
Physical therapists
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the rehabilitation of patients with a rotator cuff injury. Nurses should work collaboratively with physical therapists to ensure patients receive appropriate and individualized therapy sessions. This can involve sharing information about the patient’s progress, providing updates on any changes in the patient’s condition, and communicating any concerns or difficulties that arise during therapy sessions.
Occupational therapists
Occupational therapists focus on helping patients regain independence in their daily activities. Nurses should collaborate closely with occupational therapists to support the achievement of functional goals and facilitate a successful return to work and other activities. Sharing information about the patient’s progress, discussing specific functional needs, and coordinating therapies can help ensure a holistic and individualized approach to care.
In conclusion, nursing considerations for patients with a rotator cuff injury are multifaceted. From comprehensive assessment and patient education to pain management techniques, activity modification, and collaboration with other healthcare providers, nurses play a crucial role in facilitating healing and promoting optimal recovery. By providing compassionate and knowledgeable care, nurses can empower patients, improve outcomes, and enhance their overall quality of life.