You may have heard about Addison’s Disease, a rare hormonal disorder that occurs when your adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. While the condition itself can be challenging to manage, it is essential to proactively prevent and address potential complications that may arise. By understanding the risks and adopting a comprehensive approach to healthcare, individuals with Addison’s Disease can lead fulfilling and healthy lives. In this article, we will explore some of the common complications associated with Addison’s Disease and provide practical tips on how to prevent and manage them effectively. Keep reading to ensure you have the tools to navigate the complexities of this condition with confidence.
Preventing Addison’s Disease Complications
Living with Addison’s disease requires careful management to prevent complications and ensure optimal health. By understanding the disease, recognizing symptoms, maintaining medication regimens, monitoring cortisol levels, managing stress, preventing adrenal crisis, avoiding infections, and making lifestyle modifications, you can effectively prevent complications associated with Addison’s disease.
Understanding Addison’s Disease
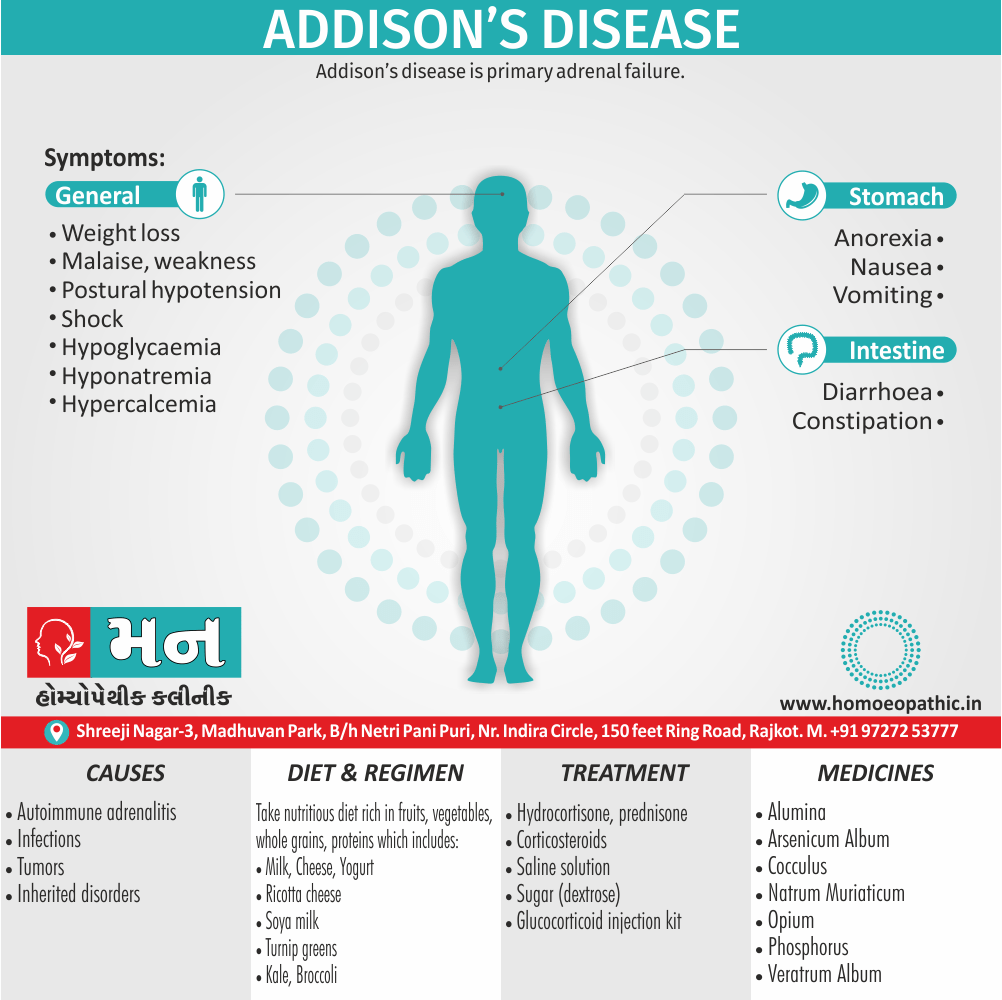
Addison’s disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare condition that affects the adrenal glands, leading to low production of cortisol and aldosterone. This chronic condition is typically caused by an autoimmune response, where the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the adrenal glands. Other causes may include infections, cancer, or certain medications.
The adrenal glands are small, triangle-shaped endocrine glands located on top of the kidneys. They play a crucial role in the body’s stress response and produce hormones like cortisol and aldosterone. In Addison’s disease, the adrenal glands cannot produce sufficient amounts of these hormones, leading to a range of symptoms and potential complications.
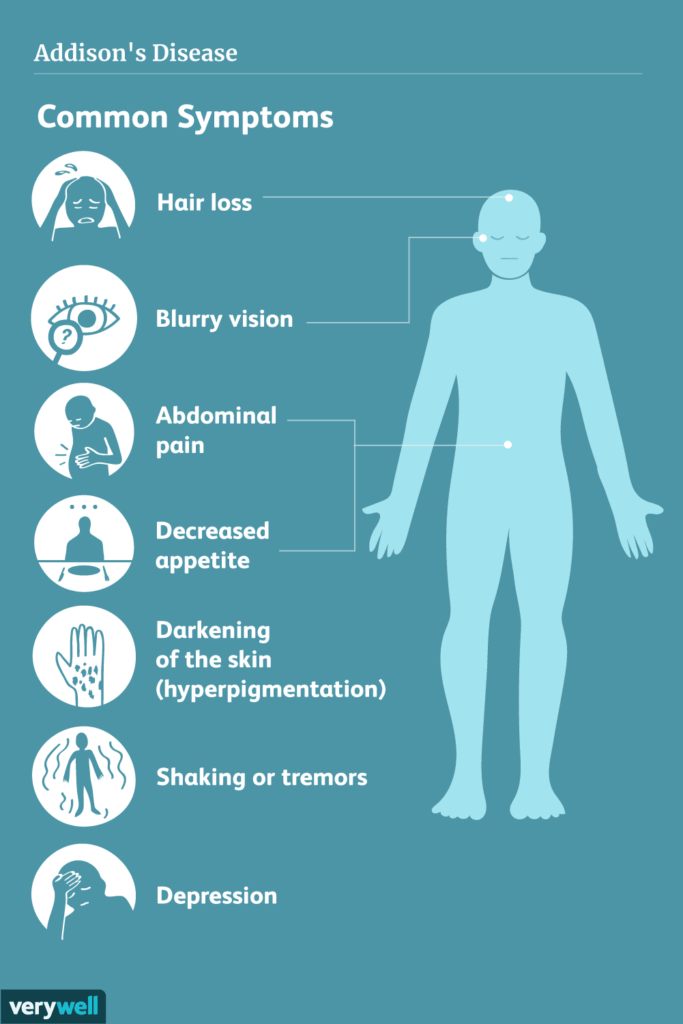
Recognizing the Symptoms
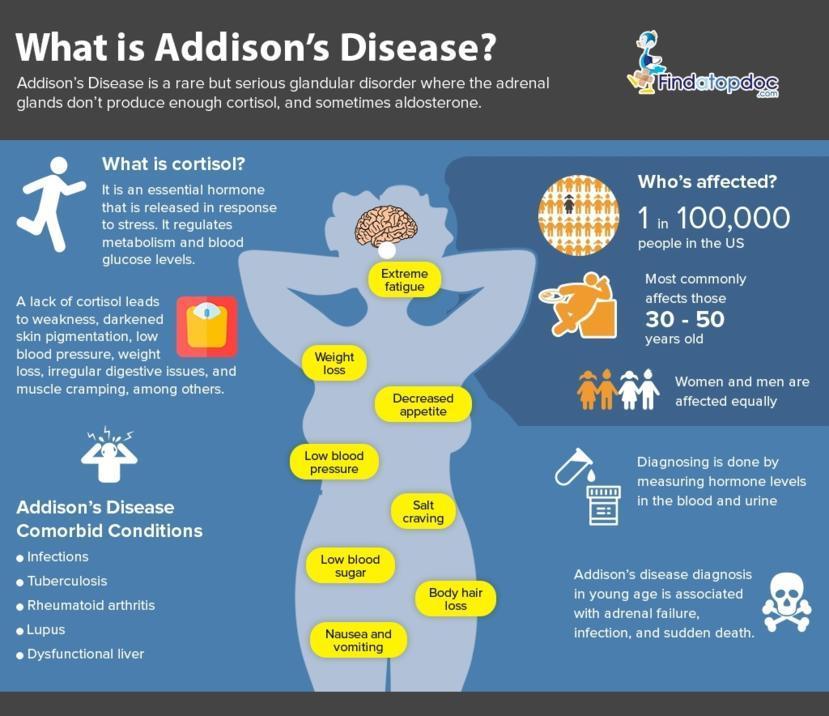
Recognizing the symptoms of Addison’s disease is essential for early diagnosis and proper management. The symptoms may vary from person to person, but common indicators include fatigue and weakness, weight loss, decreased appetite, gastrointestinal issues like nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure, salt cravings, hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin), and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels).
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm a diagnosis of Addison’s disease, various tests are used to measure cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels, assess adrenal function, and identify potential underlying causes. The ACTH stimulation test is commonly used, which involves injecting synthetic ACTH and measuring cortisol levels before and after. Other tests may include blood tests to measure cortisol and ACTH levels, antibody tests to detect autoimmune causes, and imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI to assess the adrenal glands.
Maintaining Medication Regimen
Managing Addison’s disease involves hormone replacement therapy to replace the deficient cortisol and aldosterone. It’s crucial to take medication regularly as prescribed by your healthcare provider to maintain stable hormone levels. Adhering to the medication regimen helps prevent complications and improves overall well-being. Adjustments in medication dosages may be required during times of illness, stress, or surgery, so communication with your healthcare provider is vital in ensuring the appropriate dosages.
Monitoring Cortisol Levels
Regular monitoring of cortisol levels is necessary to ensure proper hormone replacement and avoid over or under-dosing. Blood tests are commonly used to measure cortisol levels, and your healthcare provider may recommend specific intervals for testing. During times of increased stress, such as illness or surgery, stress dose steroids may be required to supplement cortisol levels. Additionally, wearing a cortisol bracelet or using self-monitoring techniques can provide valuable information for managing medication dosages effectively.
Managing Stress
Stress can have a significant impact on cortisol levels and overall well-being for individuals with Addison’s disease. Learning stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help manage stress levels. Psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, can also provide a valuable outlet for coping with the challenges of living with the disease. Striving for balance, rest, and avoiding overexertion are essential to prevent excessive stress on the body.
Preventing Adrenal Crisis
An adrenal crisis is a life-threatening condition characterized by a sudden drop in hormone levels, resulting in a medical emergency. Recognizing the warning signs, such as severe fatigue, dizziness, vomiting, and dehydration, is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. To prevent adrenal crisis, individuals with Addison’s disease should always carry an emergency injection kit containing intramuscular hydrocortisone for self-administration. Wearing an emergency medical bracelet stating the condition can also help alert healthcare professionals in case of an emergency. Educating family members, friends, and colleagues about the signs and actions during an adrenal crisis can provide additional support and ensure prompt medical intervention when needed.
Avoiding Infections
As Addison’s disease can weaken the immune system, it’s important to take measures to avoid infections. Ensuring up-to-date vaccinations, practicing good hygiene, frequent handwashing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals are essential preventive measures. Prompt treatment of infections, including respiratory tract or urinary tract infections, is crucial to prevent complications and maintain overall health.

Managing Blood Pressure
Individuals with Addison’s disease often experience low blood pressure due to the decreased production of aldosterone. Monitoring and maintaining blood pressure within the optimal range is vital for preventing complications. Regular blood pressure checks, lifestyle modifications such as reducing salt intake, adequate fluid intake, and medication adjustments as prescribed by your healthcare provider are crucial in managing blood pressure effectively.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical management, making certain lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to preventing complications in Addison’s disease. A balanced diet that includes nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and provide energy. Regular exercise, as recommended by your healthcare provider, promotes cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and mental well-being. Adequate sleep is crucial for hormone regulation and overall health, so ensuring sufficient rest is essential. Additionally, practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and maintaining social connections, contributes to a healthier and happier life with Addison’s disease.
By understanding the disease, recognizing symptoms, adhering to medication regimens, and making lifestyle modifications, individuals with Addison’s disease can effectively prevent complications, optimize their well-being, and lead fulfilling lives. Regular communication with healthcare providers, staying informed about the latest research and therapies, and seeking support from Addison’s disease community can provide valuable resources in managing the condition. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with proper care and support, you can overcome the challenges of Addison’s disease and live a fulfilling life.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Preventing and Managing Addison’s Disease Complications
Can Addison’s Disease Be Cured, Can Addison’s Disease Go Away, Can You Reverse Addison’s Disease, How To Live With Addison’s Disease, How To Manage Addison’s Disease, Managing Addison’s Disease, Managing Addison’s Disease In Dogs