In this informative article, we will explore the intriguing world of Dermatitis Herpetiformis, uncovering its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a unique skin condition that often leaves its sufferers puzzled and seeking answers. By understanding the factors that contribute to its development, recognizing the telltale signs, and exploring the various treatment options, you will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of Dermatitis Herpetiformis with confidence. So, let’s embark on this journey together to unravel the mysteries of this dermatological phenomenon.

Causes of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Genetic factors
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is known to have a strong genetic component. Research has shown that certain genes are associated with an increased risk of developing the condition. People who have a family history of the disease are more likely to develop it themselves. However, it is important to note that not everyone with these genetic factors will necessarily develop Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
Autoimmune reaction
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is classified as an autoimmune disorder, which means that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. In the case of Dermatitis Herpetiformis, the immune system targets gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This autoimmune reaction triggers an inflammatory response in the skin, leading to the characteristic rash and blisters associated with the condition.
Gluten sensitivity
Individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis are usually sensitive to gluten. When they consume gluten-containing foods, their immune system mounts an attack on the gluten, resulting in the skin rash and other symptoms of the condition. It’s important to note that while gluten sensitivity is a common trigger for Dermatitis Herpetiformis, not all individuals with the condition have gluten sensitivity. Other factors, such as infections or medications, can also trigger Dermatitis Herpetiformis in some cases.
Symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Skin rash and blisters
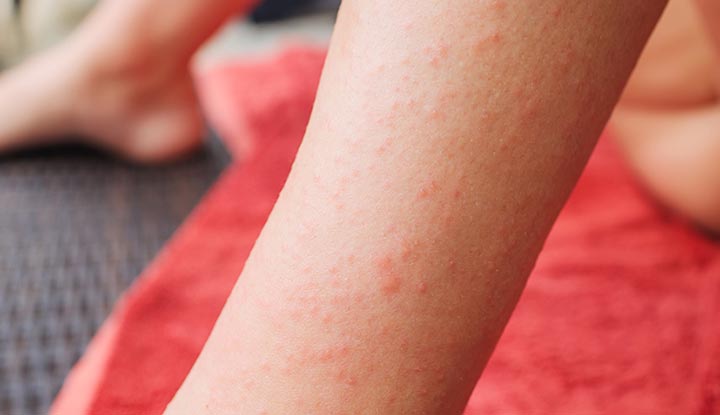
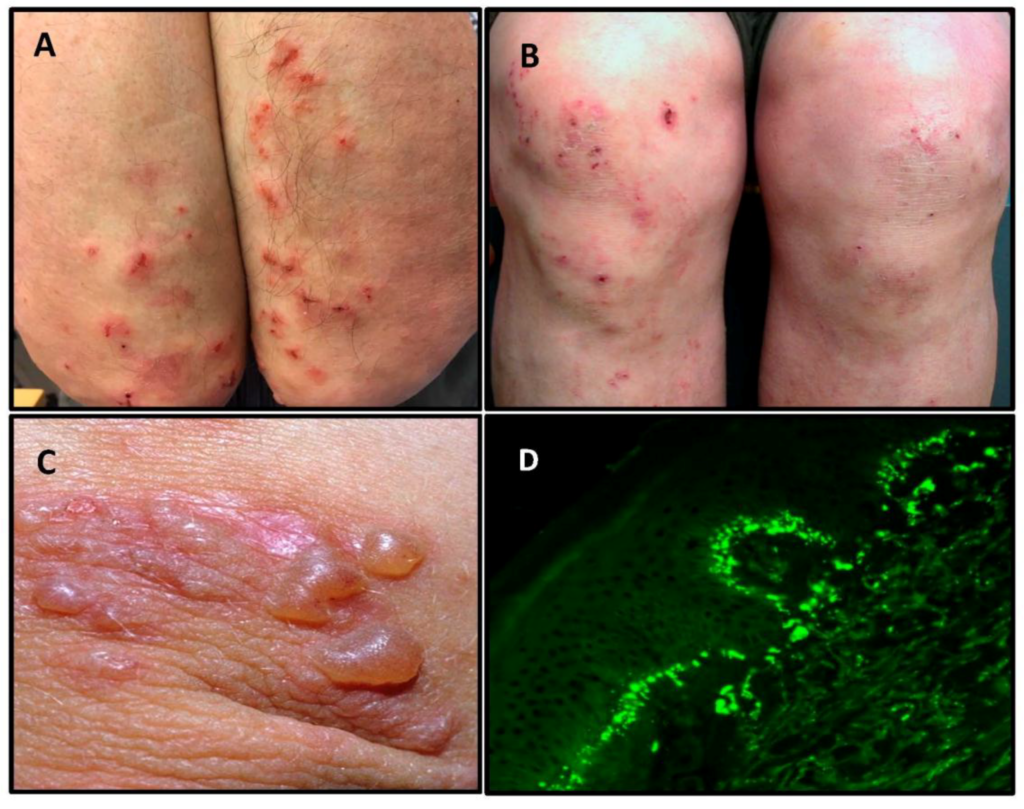
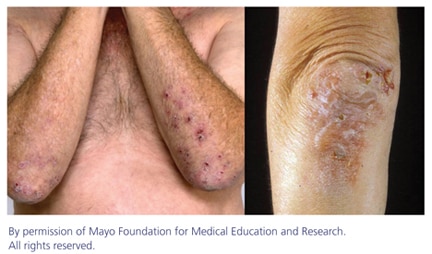
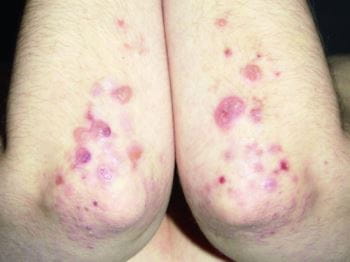
The most common symptom of Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a rash that typically appears on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and back. The rash consists of small, raised red bumps that often develop into blisters. These blisters can be very itchy and may cause a burning sensation. Scratching the blisters can lead to secondary infections and further worsening of the symptoms.
Itching and burning sensation
The intense itching and burning sensation are hallmark symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. The itching can be so severe that it interferes with sleep and daily activities. Scratching the itchy skin can provide temporary relief but can also lead to more skin damage and worsening of the condition. It is important to resist the urge to scratch and seek appropriate treatment for itch relief.
Chronic inflammation
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the skin. This inflammation is a result of the autoimmune reaction triggered by gluten. The constant inflammation can cause the skin to become red, swollen, and tender. In some cases, the inflammation may also extend beyond the skin, affecting the deeper layers and causing joint pain.
Grouped and symmetrical lesions
The rash and blisters of Dermatitis Herpetiformis tend to appear in clusters or groups. These lesions are typically symmetrically distributed on both sides of the body. This characteristic pattern of lesions can help distinguish Dermatitis Herpetiformis from other skin conditions. However, it is important to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis, as other skin conditions may also present with similar symptoms.
Scaly and crusty skin
As the blisters of Dermatitis Herpetiformis heal, they may leave behind scaly or crusty patches of skin. These patches can be unsightly and may cause discomfort. Proper skin care, including gentle cleansing and moisturizing, can help alleviate the symptoms and promote healing.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Physical examination
To diagnose Dermatitis Herpetiformis, a dermatologist will conduct a thorough physical examination of the affected skin. They will examine the rash and blisters, take note of their characteristics and distribution patterns, and assess the overall appearance of the skin.
Skin biopsy
A skin biopsy is a definitive diagnostic test for Dermatitis Herpetiformis. During the procedure, a small piece of skin tissue is removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The biopsy helps identify the presence of specific antibodies, known as IgA deposits, in the skin. The presence of these antibodies confirms the diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
Blood tests
Blood tests can also be helpful in diagnosing Dermatitis Herpetiformis. These tests measure the levels of certain antibodies, such as IgA and tissue transglutaminase (TTG) antibodies, in the blood. Elevated levels of these antibodies can indicate an autoimmune reaction to gluten. However, it is important to note that a negative blood test does not necessarily rule out Dermatitis Herpetiformis, as some individuals may have a false-negative result.
Elimination diet
In some cases, an elimination diet may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. This involves completely avoiding foods that contain gluten for a period of time. If the symptoms improve or disappear during the elimination diet, it indicates a gluten sensitivity and supports the diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
Treatment Options for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Gluten-free diet
The cornerstone of treatment for Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a strict gluten-free diet. This involves completely avoiding foods that contain gluten, such as wheat, barley, and rye. Following a gluten-free diet can help prevent the immune system from reacting to gluten, thereby reducing inflammation and alleviating the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. It is important to work with a registered dietitian to ensure proper nutrient intake and to learn how to read food labels to identify hidden sources of gluten.
Dapsone medication
Dapsone is a medication commonly prescribed to individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis. It helps to control the symptoms by suppressing the immune response and reducing inflammation. Dapsone is typically taken orally and should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist. It is important to note that dapsone does not cure Dermatitis Herpetiformis but provides symptomatic relief.
Other medications
In cases where dapsone is not well tolerated or if the symptoms are not adequately controlled, other medications may be prescribed. These may include sulfapyridine, colchicine, tetracyclines, or corticosteroids. Each medication works differently to help reduce inflammation and manage the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. The specific medication and dosage will depend on individual factors and should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Skin care and itch relief
In addition to dietary and medication management, proper skin care is essential in managing Dermatitis Herpetiformis. Gentle cleansing with mild, fragrance-free products can help prevent further skin irritation. Moisturizing creams containing ingredients like ceramides or hyaluronic acid can help soothe and hydrate the skin. Cooling measures, such as applying cold compresses or taking cool showers, can provide temporary relief from itching and burning sensations.
Gluten-Free Diet
Eliminating gluten-containing foods
Adopting a gluten-free diet is crucial for managing Dermatitis Herpetiformis. This means avoiding foods that contain wheat, barley, and rye. Common sources of gluten include bread, pasta, cereals, and baked goods. It is important to read food labels carefully, as gluten can also be found in processed foods, sauces, and condiments. Opting for naturally gluten-free foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and gluten-free grains (e.g., rice, quinoa) can help ensure a balanced and varied diet.
Reading food labels
When following a gluten-free diet, it is important to familiarize yourself with reading food labels. Look for labels that clearly state “gluten-free” or “certified gluten-free.” Additionally, be aware of ingredients and food additives that may contain gluten, such as malt flavoring, modified food starch, and certain thickeners. By understanding how to decipher food labels, you can make informed choices and avoid accidental gluten consumption.
Finding gluten-free substitutes
Fortunately, there are now numerous gluten-free substitutes available for common gluten-containing foods. Gluten-free bread, pasta, and cereals can be found in most grocery stores. These products are often made from alternative grains, such as rice, corn, or quinoa, or from gluten-free flours like almond or coconut flour. Experimenting with different brands and recipes can help you find substitutes that you enjoy and that fit into your gluten-free lifestyle.
Dapsone Medication
How dapsone works
Dapsone is an oral medication that belongs to a class of drugs called sulfones. It works by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation. Dapsone helps alleviate the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis by reducing the intensity of the autoimmune reaction triggered by gluten. It can provide significant relief from itching, burning, and skin lesions, although it does not address the underlying cause of the condition.
Potential side effects
Like any medication, dapsone can have potential side effects. The most common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, and allergic reactions. Additionally, dapsone can cause anemia and a decrease in white blood cell count, so it is important to have regular blood tests to monitor these levels. Some individuals may also experience a skin rash or other skin reactions. It is important to report any side effects to a healthcare professional.
Monitoring and dosage
When prescribed dapsone, it is essential to have regular check-ups with a healthcare professional to monitor its effectiveness and any potential side effects. Blood tests may be necessary to assess liver and kidney function, as well as blood cell counts. The dosage of dapsone may vary depending on the individual and the severity of symptoms. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and not make any changes without consulting a healthcare professional.
Other Medications
Sulfapyridine
Sulfapyridine is an antibiotic medication that can be used as an alternative to dapsone for managing Dermatitis Herpetiformis. It helps reduce inflammation and control the symptoms associated with the condition. Sulfapyridine is typically taken orally and may be used in combination with other medications, such as corticosteroids, to achieve optimal symptom control.
Colchicine
Colchicine is another medication that may be prescribed for individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis. It is primarily used to treat gout, but it has also been found to have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis. Regular blood tests are necessary when taking colchicine to monitor for potential side effects.
Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines, such as doxycycline, may be prescribed to help alleviate the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. These antibiotics have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the inflammation in the skin. Tetracyclines are typically taken orally and require regular monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a type of medication that can help reduce inflammation and control the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. They may be prescribed as topical creams or ointments for localized symptoms or taken orally for more widespread or severe symptoms. Corticosteroids can have significant side effects when used long-term, so they are typically used for short periods or in combination with other medications.
Skin Care and Itch Relief
Gentle cleansing
Proper skin care is essential for managing symptoms and promoting healing in Dermatitis Herpetiformis. When cleansing the affected skin, it is important to use mild, fragrance-free cleansers that will not further irritate the skin. Avoid harsh soaps or cleansers that contain potential irritants. Gently pat the skin dry instead of rubbing, which can cause additional skin damage.
Moisturizing creams
Moisturizing the skin regularly is crucial for individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis. Moisturizers help soothe and hydrate dry, irritated skin. Look for moisturizers that are fragrance-free and hypoallergenic. Creams or ointments that contain ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or dimethicone can provide additional relief and protection for the skin.
Cooling and soothing measures
To relieve the intense itching and burning sensations associated with Dermatitis Herpetiformis, cooling measures can be helpful. Applying cold compresses or taking cool baths or showers can temporarily numb the skin and provide relief. Avoid hot water or harsh scrubbing, as these can further irritate the skin. After bathing, gently pat the skin dry and apply a moisturizer to lock in moisture.
Lifestyle and Coping Strategies
Educating oneself about the condition
Understanding Dermatitis Herpetiformis is key to managing the condition effectively. Take the time to educate yourself about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available. Speak with healthcare professionals, read reputable sources, and join support groups or online communities to connect with others who have similar experiences. By empowering yourself with knowledge, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare and take an active role in managing your condition.
Seeking support and joining support groups
Living with Dermatitis Herpetiformis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It can be helpful to seek support from others who understand what you are going through. Support groups, whether in-person or online, provide a safe space to share experiences, exchange tips, and receive encouragement. Building a support network can help you navigate the ups and downs of living with Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
Minimizing stress and triggers
Stress and certain triggers can exacerbate the symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. It is important to identify your personal triggers, which may include stress, certain foods, or environmental factors, and take steps to minimize their impact. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in activities you enjoy can help reduce stress levels. Additionally, staying vigilant about your gluten-free diet and avoiding other known triggers can help keep symptoms under control.
Adhering to treatment plans
Strict adherence to the prescribed treatment plan is essential for managing Dermatitis Herpetiformis effectively. This includes following a gluten-free diet, taking medications as prescribed, and practicing proper skin care. Skipping medication doses, consuming gluten-containing foods, or neglecting skin care can result in a worsening of symptoms. It is important to communicate openly with your healthcare team and address any concerns or challenges you may face in adhering to the treatment plan.
Possible Complications of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Secondary infections
Scratching the rash and blisters associated with Dermatitis Herpetiformis can lead to breaks in the skin, which can become infected. Bacterial infections, such as impetigo or cellulitis, are common complications of Dermatitis Herpetiformis. These infections can cause further skin damage and may require additional treatment with antibiotics. Proper skin care, including gentle cleansing and avoiding scratching, can help prevent secondary infections.
Nutritional deficiencies
Following a strict gluten-free diet can sometimes lead to nutritional deficiencies, especially if a person’s dietary choices are limited. Gluten-containing grains are a source of important nutrients, such as fiber, B vitamins, and iron. When eliminating these grains from the diet, it is important to ensure adequate intake of these nutrients through alternative sources or supplementation. Working with a registered dietitian can help ensure a well-balanced diet and prevent nutritional deficiencies.
Psychological impact
Living with a chronic skin condition like Dermatitis Herpetiformis can have a significant psychological impact. It can affect body image, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. Dealing with symptoms like intense itching, pain, and discomfort can be emotionally distressing. It is important to seek support from healthcare professionals, therapists, or support groups to address any emotional or psychological challenges. Developing coping strategies and practicing self-care can also help improve overall mental well-being.