Have you ever experienced that disorienting feeling when the world around you seems to spin uncontrollably? It’s quite common and can leave you feeling nauseous and off-balance. In this article, we will explore the causes of dizziness, from inner ear issues to medication side effects, and provide valuable tips on managing and preventing this unsettling sensation. So, whether you’re seeking relief from occasional bouts of dizziness or looking to support a loved one struggling with it, this article will help you gain a better understanding and equip you with the tools to effectively manage dizziness.
Understanding Dizziness
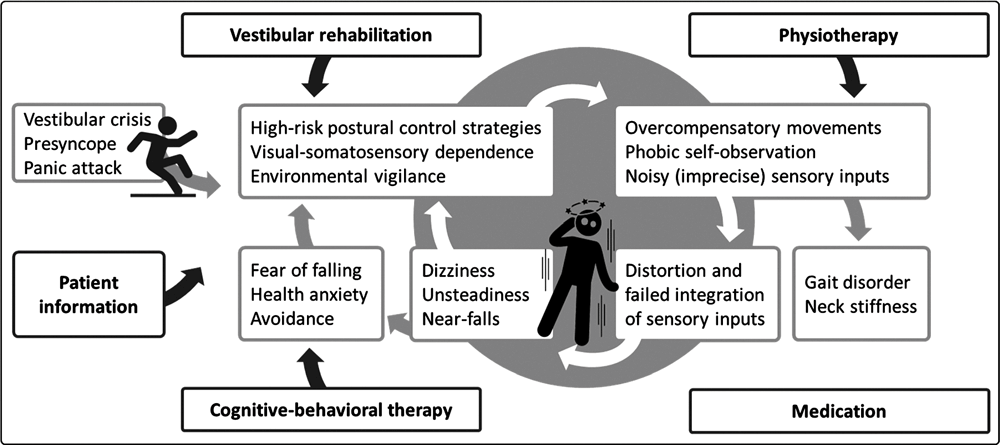
Dizziness is a common symptom that many people experience at some point in their lives. It is a feeling of lightheadedness, unsteadiness, or a sensation that everything around you is spinning. Understanding the causes, types, and symptoms of dizziness is important in order to properly diagnose and manage this condition.
Definition of Dizziness
Dizziness can be defined as a sensation of being off-balance or feeling unstable. It is often accompanied by a feeling of movement, such as spinning or swaying. Dizziness can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, and can be caused by a variety of factors.
Causes of Dizziness
Dizziness can have many different causes, ranging from temporary conditions to more serious underlying medical issues. Some common causes of dizziness include:
-
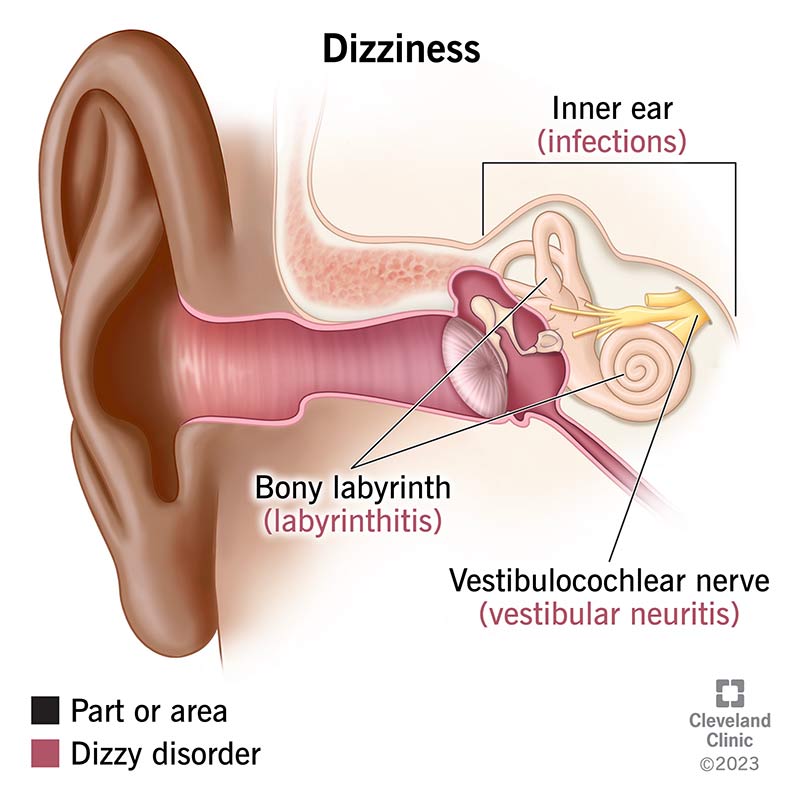
Inner ear problems: The inner ear plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. Conditions such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), labyrinthitis, and Meniere’s disease can all cause dizziness.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure or anxiety, can cause dizziness as a side effect.
-
Low blood sugar: When your blood sugar drops too low, it can lead to feelings of dizziness.
-
Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can cause dehydration, which can in turn lead to dizziness.
-
Anxiety and stress: Emotional factors can contribute to dizziness, especially in individuals who are prone to anxiety or panic attacks.
Types of Dizziness
There are several different types of dizziness that individuals may experience. These include:
-
Vertigo: Vertigo is a specific type of dizziness characterized by a spinning sensation. It is often caused by inner ear problems and can be accompanied by nausea and a loss of balance.
-
Presyncope: Presyncope is the feeling of lightheadedness or faintness, often associated with a drop in blood pressure. It can be caused by various factors, such as standing up too quickly or from prolonged sitting or lying down.
-
Disequilibrium: Disequilibrium is a general feeling of unsteadiness or imbalance. It can be caused by inner ear problems, musculoskeletal issues, or neurological conditions.
-
Non-specific dizziness: Non-specific dizziness refers to a general feeling of being off-balance without a specific sensation of spinning or lightheadedness. It may be caused by various factors, such as medications or anxiety.
Common Symptoms of Dizziness
In addition to the specific sensations associated with different types of dizziness, there are some common symptoms that individuals may experience. These include:
-
Nausea or vomiting: Dizziness can often be accompanied by feelings of nausea or the urge to vomit.
-
Loss of balance: Many people with dizziness may have difficulty maintaining their balance and feel unsteady on their feet.
-
Blurred vision: Dizziness can sometimes cause blurred vision or difficulty focusing on objects.
-
Sweating: Individuals with dizziness may experience excessive sweating, especially if the cause is related to anxiety or stress.
-
Feeling faint: Dizziness can sometimes progress to a feeling of faintness or near-fainting.
Diagnosing Dizziness
When experiencing dizziness, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Diagnostic methods for dizziness include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your doctor will first ask about your medical history and any previous episodes of dizziness. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your balance, coordination, and reflexes. Additionally, they may ask about any medications you are currently taking or any recent changes in your lifestyle or diet.
Diagnostic Tests for Dizziness
Depending on the suspected cause of your dizziness, your doctor may order certain diagnostic tests. These may include:
-
Blood tests: Blood tests can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your dizziness, such as low blood sugar or anemia.
-
Audiometry: Audiometry is a hearing test that can help determine if any inner ear problems are causing your dizziness.
-
Electronystagmography (ENG): ENG is a test that measures eye movements to assess the function of the inner ear and the vestibular system, which plays a crucial role in balance.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): In some cases, an MRI may be ordered to rule out any structural abnormalities in the brain or inner ear.
Distinguishing Dizziness from Vertigo
Dizziness and vertigo are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different sensations. Dizziness is a broad term that encompasses various forms of the condition, while vertigo specifically refers to a spinning sensation. Differentiating between dizziness and vertigo is important, as the underlying causes and treatment approaches may vary.
Managing Dizziness
Managing dizziness involves addressing the underlying cause, as well as implementing various strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve overall balance and stability. The following methods can be effective in managing dizziness:
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Making certain lifestyle and dietary changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of dizziness episodes. These may include:
-
Staying hydrated: Ensuring adequate fluid intake can help prevent dehydration, which can contribute to dizziness.
-
Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that may lead to dizziness, such as certain foods, alcohol, or stressful situations.
-
Managing stress and anxiety: Reducing stress and anxiety levels through relaxation techniques, counseling, or other coping mechanisms.
Home Remedies for Dizziness
There are several home remedies that can provide relief from dizziness. These include:
-
Deep breathing: Taking slow, deep breaths can help calm your nervous system and alleviate dizziness.
-
Head positioning exercises: Certain head positioning exercises, such as the Epley maneuver, can help reposition displaced crystals in the inner ear and relieve symptoms of vertigo.
-
Ginger: Consuming ginger in various forms, such as tea or capsules, is believed to have anti-nausea properties and can help alleviate dizziness.
Medications for Dizziness
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage dizziness. These may include:
-
Antiemetics: Antiemetics are medications that can help alleviate nausea and vomiting associated with dizziness.
-
Antihistamines: Antihistamines can be used to treat dizziness caused by allergies or inner ear problems.
-
Vestibular suppressants: Vestibular suppressants can help reduce vertigo symptoms by suppressing the activity of the inner ear.
Physical Therapy and Vestibular Rehabilitation
Physical therapy and vestibular rehabilitation can be beneficial for individuals with chronic dizziness. These therapies focus on exercises and techniques to improve balance, coordination, and overall vestibular function. Your healthcare provider may refer you to a physical therapist who specializes in vestibular rehabilitation for further evaluation and treatment.
Preventing Dizziness
While it may not always be possible to prevent dizziness entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of experiencing frequent or severe dizziness episodes. These include:
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Take note of any triggers that have been associated with your dizziness episodes and try to avoid them when possible. Common triggers may include certain foods, stress, fatigue, or specific physical movements.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for overall well-being and can help minimize the occurrence of dizziness. Some key lifestyle factors include:
-
Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and overall balance.
-
Healthy diet: Maintain a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients to support proper bodily function.
-
Sufficient sleep: Aim for an adequate amount of quality sleep each night to ensure proper rest and rejuvenation.
Exercises for Balance and Posture
Incorporating exercises that focus on balance and posture into your routine can improve overall stability and reduce the risk of dizziness. Examples of such exercises include yoga, tai chi, or specific balance-training exercises recommended by a healthcare professional.
When to Seek Medical Help
While dizziness is often a temporary and benign symptom, there are instances where it may indicate a more serious underlying condition. It is important to be aware of certain red flags and seek medical help when necessary. Some red flags for dizziness may include:
Red Flags for Dizziness
-
Sudden onset and severe dizziness without an apparent cause.
-
Loss of consciousness or fainting episodes.
-
Chest pain or pressure associated with dizziness.
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech along with dizziness.
-
Dizziness accompanied by severe headache or a head injury.
When Dizziness Requires Urgent Medical Attention
Seek urgent medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms along with dizziness:
-
Sudden severe headache.
-
Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
-
Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body.
-
Loss of vision or changes in vision.
-
Difficulty breathing.
Remember, it is always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical help if you are unsure about the severity or underlying cause of your dizziness.
Living with Dizziness
Living with dizziness can be challenging, especially for individuals who experience chronic or recurrent episodes. However, there are coping strategies and support resources available to help manage the condition more effectively.
Coping Strategies for Dizziness
-
Keep a symptom journal: Keeping track of your dizziness episodes, triggers, and any associated symptoms can help identify patterns and provide valuable information for healthcare providers.
-
Practice relaxation techniques: Learning relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help reduce stress and anxiety levels, which may contribute to dizziness.
-
Use assistive devices: For individuals with balance issues, using assistive devices such as canes or walkers can provide added stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Support and Resources for Individuals with Chronic Dizziness
It can be helpful to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges. Support groups, either in-person or online, provide a safe space to share experiences, learn coping strategies, and receive support from individuals who understand what you are going through.
Additionally, there are various resources available that provide information and guidance on managing dizziness. These may include reputable websites, books, and educational materials that can help individuals better understand their condition and navigate their treatment journey.
In conclusion, understanding dizziness is crucial for effectively managing this common symptom. By recognizing the causes, types, and symptoms of dizziness, seeking appropriate medical help, implementing lifestyle changes, and accessing support and resources, individuals can navigate the challenges of living with dizziness and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources and strategies available to help you effectively manage your dizziness.