Internal bleeding can be a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Whether caused by trauma, medical conditions, or certain medications, internal bleeding can result in severe complications if not treated promptly. In this article, you will discover the essential steps for providing emergency treatment for internal bleeding, including recognizing the symptoms, seeking professional help, and implementing first aid techniques that could potentially save a life. Prepare yourself to become an informed and prepared ally in the face of this perilous situation.
Emergency Treatment for Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. When blood vessels rupture or tear inside the body, it can lead to internal bleeding. This can occur due to accidents, trauma, or medical conditions that affect the blood vessels or organs. Prompt recognition and appropriate emergency treatment are crucial to save lives and prevent complications. In this article, we will discuss the steps to recognize the signs of internal bleeding, when to call for medical help, how to provide first aid, and more.
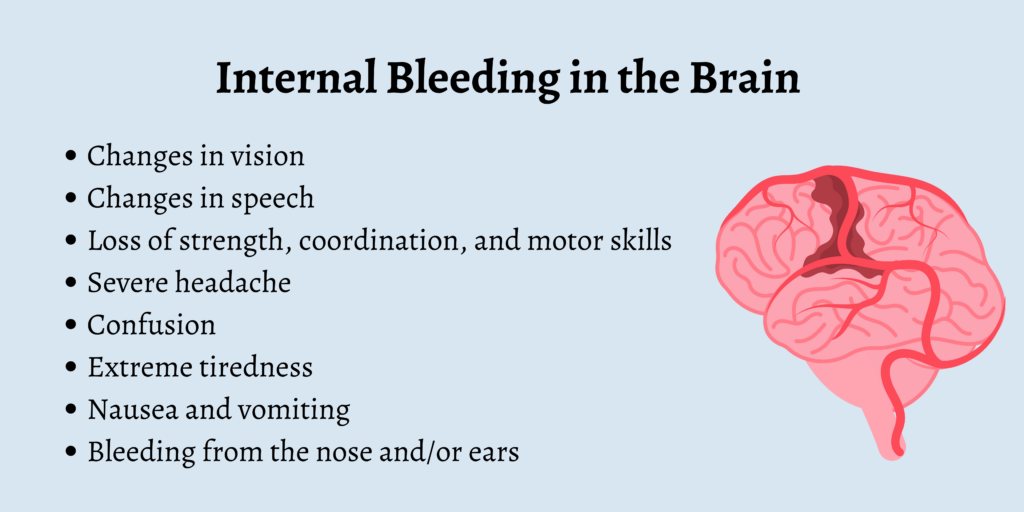
Recognizing the Signs of Internal Bleeding
Recognizing the signs of internal bleeding can be challenging since it occurs inside the body. However, there are certain symptoms that may indicate the presence of internal bleeding. These include:
- Bleeding from orifices: Look for blood in the urine, vomit, or stool.
- Abdominal pain: Sharp, intense pain in the abdomen could be a sign of internal bleeding.
- Bruising: Unexplained bruises or bruising in unusual places may indicate internal bleeding.
- Weakness and dizziness: If you feel weak or dizzy without a clear cause, it may be a result of internal bleeding.
- Pale skin: Internal bleeding can cause a person’s skin to become paler than usual.
Calling for Medical Help
If you suspect someone is experiencing internal bleeding, it is vital to call for medical help immediately. Internal bleeding can be life-threatening, and the person needs to receive medical attention as soon as possible. When calling emergency services, provide them with all the relevant information, including the person’s condition, location, and any details about the incident that may have caused the internal bleeding.

Providing First Aid
While waiting for medical professionals to arrive, there are several first aid measures you can take to help the person experiencing internal bleeding:
- Keep the person calm: Encourage the injured person to stay as calm and still as possible to minimize blood loss and prevent further injury.
- Lay the person down: Have the person lie down on their back and elevate their legs, unless they have a head, neck, spine, or leg injury. This can help increase blood flow to vital organs.
- Do not give fluids: Avoid giving the injured person anything to eat or drink, as they may need immediate surgery.
- Reassure the person: Offer words of comfort and reassurance to help alleviate anxiety and stress.
Positioning the Injured Person
Proper positioning of the injured person can play a crucial role in minimizing further harm and ensuring a stable condition. Depending on the individual’s injuries and symptoms, you may need to position them differently. Remember the following guidelines:
- Head and neck injuries: If there is a possibility of head or neck injuries, avoid moving the person’s head and neck and keep them in a neutral position.
- Severe bleeding with no head or neck injuries: If the injured person is bleeding severely, but there are no head or neck injuries, elevate the person’s legs while keeping their head and torso flat on the ground. This can help improve blood flow to vital organs.
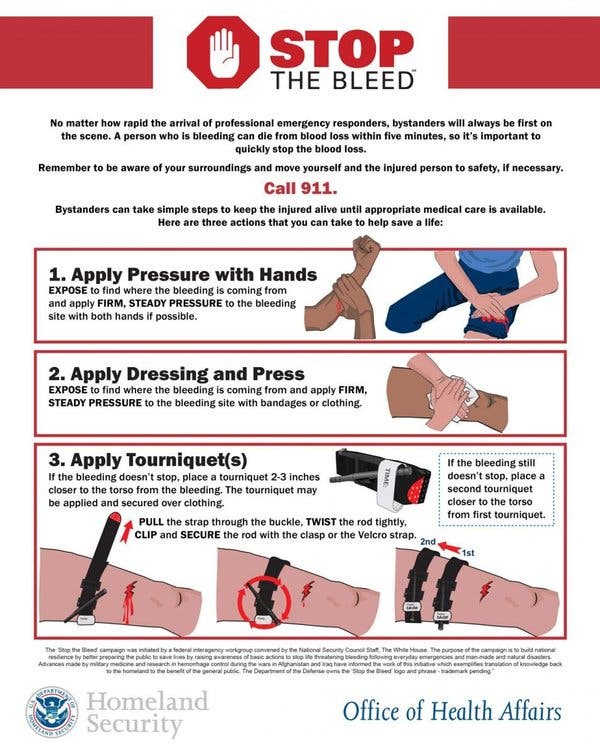
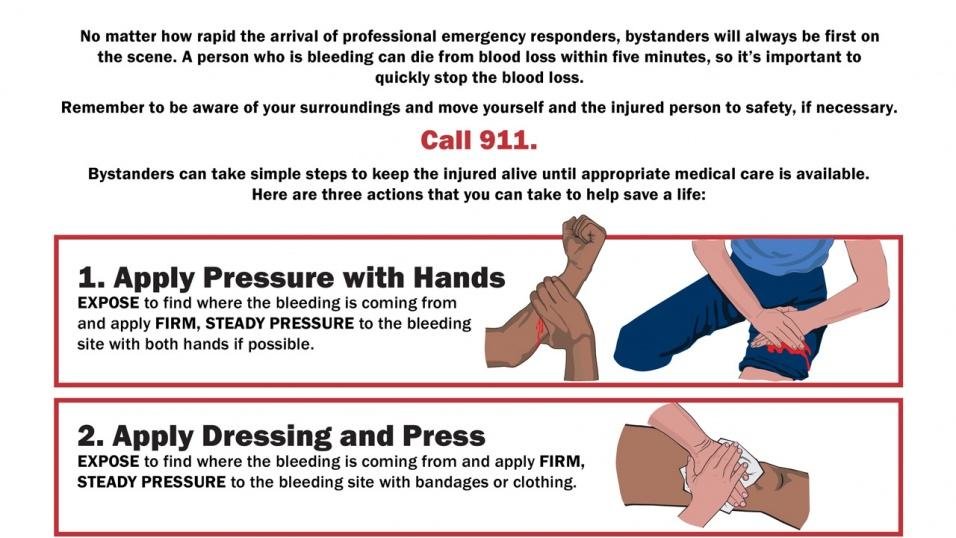
Controlling External Bleeding
While internal bleeding cannot be stopped through first aid, controlling any external bleeding can help minimize blood loss. Follow these steps:
- Apply direct pressure: Use a clean cloth or your hand to apply direct pressure to the bleeding site.
- Elevate the injury: Elevate the injured body part above the heart level, if possible, to help reduce blood flow to the area.
- Use pressure points: If direct pressure does not stop the bleeding, apply pressure to the corresponding pressure point between the bleeding site and the heart, if known.
- Apply a tourniquet as a last resort: Only use a tourniquet as a last resort if all other attempts fail to control the bleeding. It should be tightly tied above the bleeding site.
Monitoring Vital Signs
Monitoring the injured person’s vital signs can provide crucial information to both emergency medical personnel and yourself. Keep an eye on the following vital signs:
- Breathing rate: Observe the person’s breathing rate. Rapid or irregular breathing may indicate shock or complications.
- Heart rate: Check the person’s pulse. A fast or weak pulse can be a sign of internal bleeding.
- Skin color and temperature: Monitor the person’s skin color and temperature. Paleness or cool and clammy skin may suggest internal bleeding.
- Level of consciousness: Observe the person’s level of consciousness. Confusion, drowsiness, or loss of consciousness may indicate severe internal bleeding or shock.
Administering CPR if Necessary
In some cases, internal bleeding can lead to cardiac arrest. If the injured person is not responsive and not breathing, CPR may be necessary to maintain circulation until professional help arrives. If you are trained in CPR, follow the appropriate steps to administer it safely. If you are not trained, focus on providing support until trained personnel arrive.
Assessing the Severity of the Bleeding
Assessing the severity of internal bleeding can help medical professionals determine the appropriate treatment options. While you may not have the necessary equipment or expertise to make a definitive assessment, you can still gather information to assist the healthcare professionals. Take note of:
- Severity of external bleeding: Assess and communicate the severity of any external bleeding to medical professionals, as it may provide insight into the extent of internal bleeding.
- Pain and tenderness: Ask the injured person about any pain or tenderness they are experiencing. This information can help healthcare professionals determine the potential sources of internal bleeding.
- Abnormal vital signs: Provide medical professionals with any abnormal vital signs you’ve observed, such as rapid heart rate or low blood pressure.

Treating Shock
Internal bleeding can result in shock, a life-threatening condition where the body struggles to maintain adequate blood flow. If you suspect the injured person is in shock, follow these steps:
- Keep the person lying down: Continue to keep the injured person flat on their back, with their legs elevated, unless contraindicated.
- Cover the person: Use a blanket or clothing to keep the person warm and prevent loss of body heat.
- Do not give fluids: Unless instructed otherwise by medical professionals, avoid giving the injured person anything to eat or drink.
- Reassure and support: Provide emotional support and reassurance to the injured person to help alleviate anxiety and stress.
Preparing for Emergency Medical Transport
Emergency medical professionals will determine the most appropriate mode of transportation for the injured person. While awaiting their arrival, take the following steps:
- Clear the area: Clear the area around the injured person to provide a safe and accessible space for the medical professionals to work.
- Gather essential information: Collect any relevant medical information, such as allergies, pre-existing conditions, or medications, to share with the medical professionals when they arrive.
- Prepare personal belongings: Gather the injured person’s personal belongings, such as identification and insurance cards, to accompany them during transportation.
- Stay with the injured person: If possible, stay with the injured person until the medical professionals arrive and provide any necessary assistance or support.
Remember, emergency treatment for internal bleeding requires trained medical professionals. While it is important to provide initial first aid and support, always seek professional medical help as soon as possible. Early intervention greatly increases the chances of a positive outcome and reduces the risk of complications.