In “Understanding Juvenile Diabetes,” you will gain a comprehensive understanding of this condition that affects many young individuals. Juvenile diabetes, also known as type 1 diabetes, is a chronic illness that occurs when the pancreas no longer produces insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Through this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to manage this condition effectively. Whether you are a parent, caregiver, or someone interested in learning more about juvenile diabetes, this article will provide you with the necessary knowledge to navigate this complex condition.
Causes
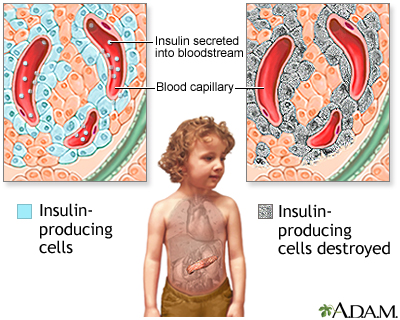
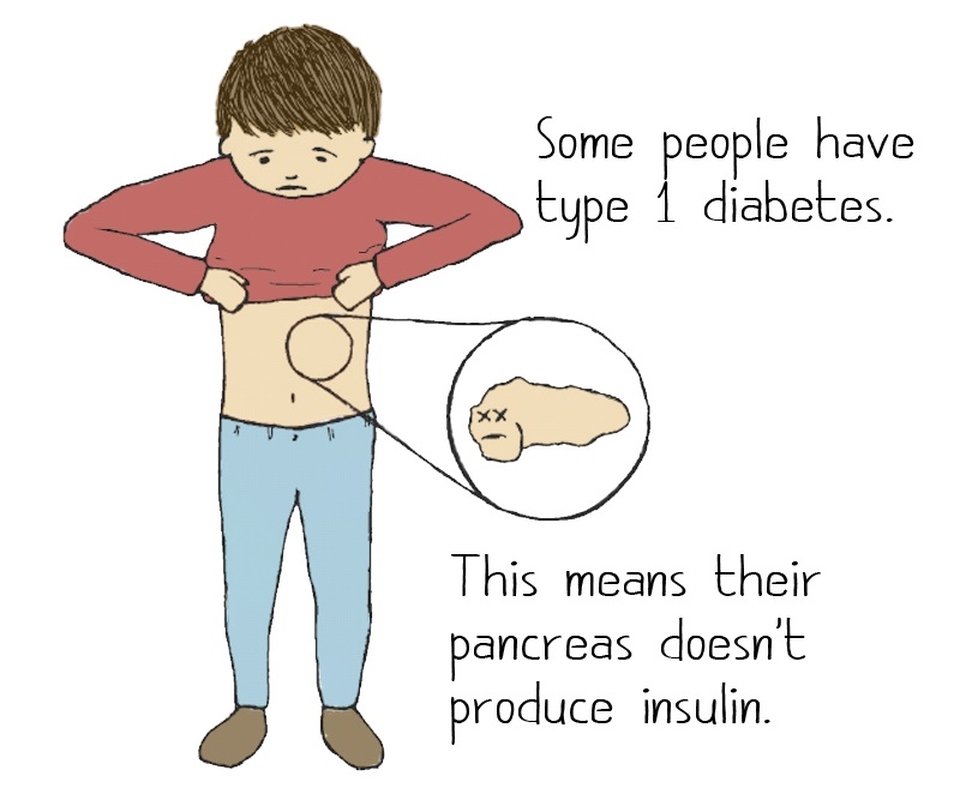
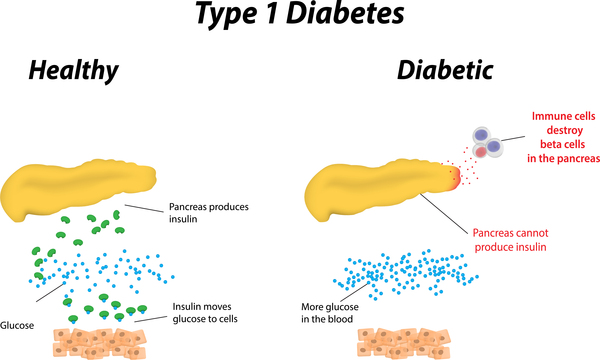
Autoimmune disorder
Juvenile diabetes, also known as type 1 diabetes, is caused by an autoimmune disorder. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Without sufficient insulin, the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels properly. The exact triggers for this autoimmune response are still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of juvenile diabetes. Individuals with a family history of the disease are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Certain genes are associated with an increased susceptibility to autoimmune disorders, including type 1 diabetes. However, having these genetic markers does not guarantee the development of the disease, as environmental factors also play a crucial role.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors are thought to trigger the autoimmune response in genetically susceptible individuals. These factors could include viral infections, such as the Coxsackie virus or respiratory infections. Additionally, certain dietary factors, such as the timing and type of introduction of specific foods during infancy, have been investigated as potential environmental triggers. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complex interactions between genes and the environment in the development of juvenile diabetes.
Symptoms
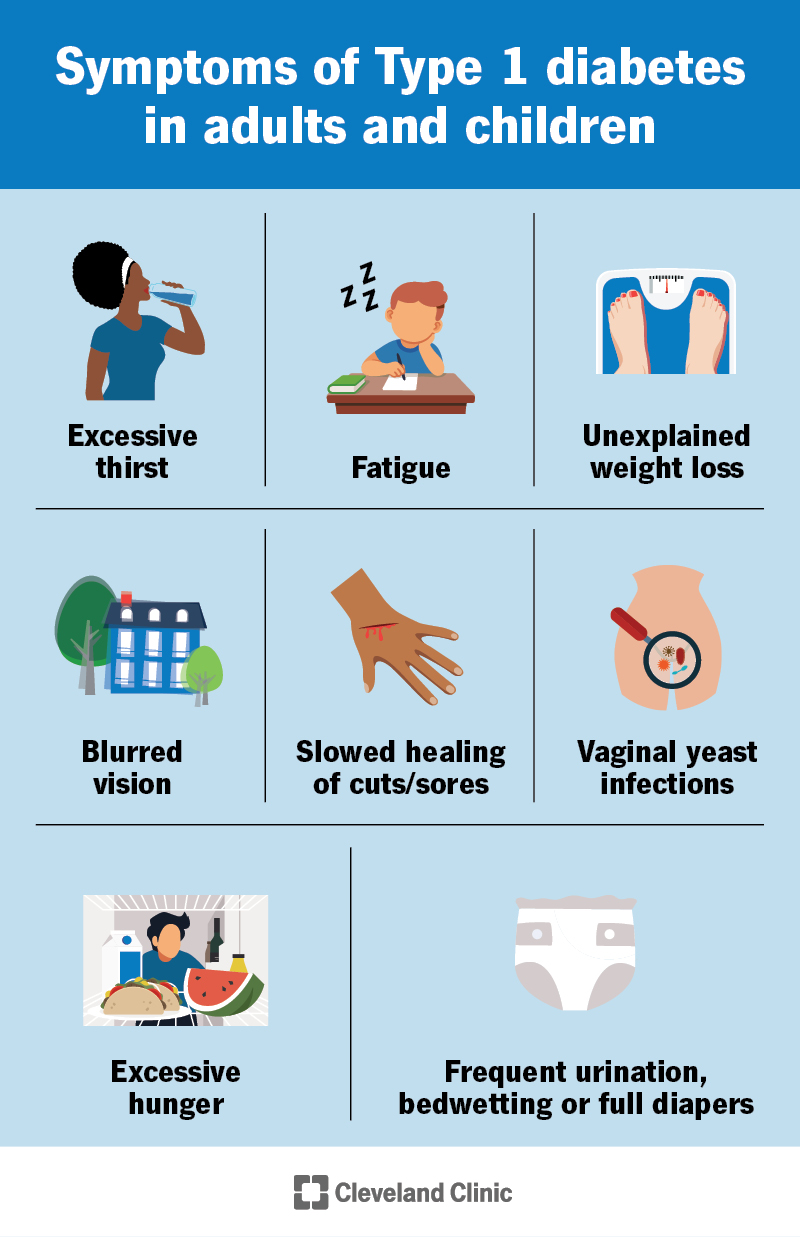
Excessive thirst
One of the primary symptoms of juvenile diabetes is excessive thirst, also known as polydipsia. The increased levels of sugar in the blood cause dehydration, leading to an intense feeling of thirst. Individuals may find themselves constantly needing to drink large amounts of fluids to quench their thirst.
Frequent urination
Frequent urination, or polyuria, is another common symptom of juvenile diabetes. The excess sugar in the blood cannot be properly absorbed by the body’s cells, so it is excreted through the urine. As a result, individuals with the condition may need to urinate more frequently than usual, including during the night.
Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is often an early sign of juvenile diabetes. The body is unable to utilize the glucose from food due to the lack of insulin, leading to the breakdown of fat and muscle tissues for energy. This can result in significant weight loss despite normal or increased food intake.
Fatigue
Fatigue or extreme tiredness is a symptom commonly experienced by individuals with juvenile diabetes. The lack of insulin prevents glucose from entering cells to be converted into energy. As a result, the body struggles to maintain its energy levels, leading to a constant feeling of fatigue.
Blurred vision
Blurred vision can be a consequence of high blood sugar levels in individuals with juvenile diabetes. When there is an excess of sugar in the blood, it can create imbalances in the fluids of the body, including the lenses of the eyes. This can impair the ability to focus properly, resulting in blurred vision.

Diagnosis
Blood glucose test
Diagnosing juvenile diabetes involves measuring blood glucose levels. This can be done through a blood glucose test, which involves pricking the finger to obtain a small blood sample. The sample is then tested using a glucose meter to determine the concentration of sugar in the blood. Persistent high blood sugar levels indicate the presence of juvenile diabetes.
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test
The glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test provides a broader picture of a person’s average blood sugar levels over the past few months. This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is attached to sugar molecules. A higher A1C level indicates poorer blood sugar control and can help diagnose juvenile diabetes.
Random blood sugar test
In some cases, a random blood sugar test may be conducted. This test measures blood glucose levels at any given time, regardless of when the individual last ate. If the blood sugar level is significantly elevated, it can be indicative of juvenile diabetes.
Management
Blood sugar monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing juvenile diabetes. This involves using a glucose meter to regularly test blood sugar levels throughout the day. By tracking these levels, individuals can adjust their insulin dosage and make necessary dietary and lifestyle modifications to keep their blood sugar within target ranges.
Insulin therapy
Insulin therapy is a key component of managing juvenile diabetes. Since the body is unable to produce sufficient insulin, individuals with the condition need to manually administer insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. This can be done through insulin injections or by using an insulin pump. The type and dosage of insulin required vary for each individual and may change over time.
Healthy eating
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is essential for managing juvenile diabetes. A registered dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan that takes into account an individual’s specific needs and preferences. The goal is to consume a variety of nutrient-rich foods while properly managing carbohydrate intake, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity
Engaging in regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with juvenile diabetes. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and improving glucose uptake by the muscles. It can also aid in weight management, reduce the risk of heart disease, and enhance overall well-being. However, it is important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to ensure they remain within the target range.
Complications
Heart disease
People with juvenile diabetes have an increased risk of developing heart disease later in life. Elevated blood sugar levels over an extended period can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing them and increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke. Maintaining good control of blood sugar levels, along with managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Nerve damage
Chronic high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the nerves, a condition known as neuropathy. This can result in various symptoms, including numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet. Proper management of blood sugar levels is essential to prevent or delay nerve damage.
Kidney damage
The kidneys can be affected by juvenile diabetes, leading to a condition called diabetic nephropathy. Consistently high blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste from the blood effectively. Regular monitoring of kidney function and maintaining good control of blood sugar levels can help prevent or delay kidney damage.
Eye damage
Untreated or poorly managed juvenile diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition known as diabetic retinopathy. This can result in vision problems, including blurry or distorted vision and, in severe cases, vision loss. Regular eye examinations and optimal blood sugar control are important in preventing or managing eye complications.
Psychological Impact
Emotional distress
Being diagnosed with juvenile diabetes can cause emotional distress. The challenges of managing a chronic condition, including constant blood sugar monitoring, insulin injections, and dietary restrictions, can be overwhelming. Individuals may experience feelings of frustration, anger, or sadness, which can impact their overall well-being.
Anxiety
Anxiety is a common psychological concern for individuals with juvenile diabetes. The unpredictability of blood sugar levels and the potential for developing complications can lead to heightened anxiety levels. Implementing effective stress management techniques and seeking support from healthcare professionals can help individuals better cope with these anxieties.
Depression
Living with juvenile diabetes can increase the risk of developing depression. The daily demands of managing the condition, coupled with the potential impact on quality of life and the fear of complications, can contribute to feelings of sadness or hopelessness. It is important for individuals to seek support and professional help if they experience symptoms of depression.
Social isolation
Juvenile diabetes can sometimes lead to social isolation, particularly in situations where individuals feel different or isolated due to their condition. The need to manage blood sugar levels and make dietary adjustments may create challenges when participating in social activities. Encouraging open communication and educating friends, family, and peers about the condition can help alleviate feelings of isolation and promote inclusivity.
Support and Resources
Education and awareness programs
Education and awareness programs are essential for individuals with juvenile diabetes and their families. These programs provide valuable information about the condition, its management, and the potential complications that can arise. They also offer guidance on how to lead a healthy lifestyle and provide updates on the latest advancements in diabetes care.
Support groups
Support groups can be a valuable resource for individuals with juvenile diabetes. Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging, understanding, and emotional support. Support groups often offer a platform for sharing tips, strategies, and coping mechanisms for managing the challenges of the condition.
Counseling services
Counseling services can help individuals and their families navigate the emotional and psychological challenges associated with juvenile diabetes. Professional counselors can provide guidance and support in coping with the daily demands of the condition, managing emotions, and addressing any mental health concerns that may arise.
Financial assistance
Managing juvenile diabetes can come with significant financial burdens, including the cost of medications, blood glucose monitoring equipment, and regular healthcare visits. Financial assistance programs and organizations can provide support and resources to individuals in need, ensuring that they can access the necessary treatments and manage their condition effectively.
Prevention
No known prevention strategies
Currently, there are no known prevention strategies for juvenile diabetes. The autoimmune nature of the condition makes it challenging to prevent its development entirely. However, ongoing research may provide insights into potential preventive measures in the future.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in managing juvenile diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. This includes adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep. A healthy lifestyle can help individuals maintain optimal blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Early detection and management
Early detection and management of juvenile diabetes are essential in preventing long-term complications. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly increases the chances of obtaining an accurate diagnosis and receiving appropriate treatment. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and routine medical check-ups are essential for effective management.
Research and Advances
Artificial pancreas
The development of an artificial pancreas is an exciting advancement in the management of juvenile diabetes. This technology aims to mimic the function of a healthy pancreas by continuously monitoring blood sugar levels and automatically delivering insulin as needed. The artificial pancreas has the potential to greatly improve blood sugar control and reduce the burden of daily diabetes management.
Gene therapy
Gene therapy is an area of active research for juvenile diabetes. It involves modifying or replacing faulty genes responsible for the autoimmune response that leads to the destruction of insulin-producing cells. By targeting and correcting these genetic abnormalities, researchers hope to prevent or reverse the development of juvenile diabetes.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy explores the use of medications to modulate the immune system and prevent or slow the progression of juvenile diabetes. Various approaches, such as immune tolerance induction and the use of immune-modulating drugs, are being investigated to regulate the immune response and preserve the insulin-producing cells.
Public Health Perspective
Epidemiology
Juvenile diabetes is a significant public health concern worldwide. It affects individuals of all ages but is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults. According to the World Health Organization, the global prevalence of diabetes is increasing rapidly, with an estimated 1.9 million cases of type 1 diabetes among individuals under the age of 20.
Burden on healthcare systems
Juvenile diabetes places a considerable burden on healthcare systems due to the lifelong management required for the condition. This includes regular medical visits, access to affordable medications and supplies, and the need for specialized healthcare professionals. Public health initiatives and policies are necessary to ensure the provision of adequate resources and support for individuals with juvenile diabetes.
Health policies and funding
Health policies and funding play a crucial role in addressing the impact of juvenile diabetes on public health. Governments and healthcare organizations must prioritize the development and implementation of policies that support early detection, comprehensive management, and ongoing research for the condition. Adequate funding is essential to improve access to healthcare services, promote awareness, and support advancements in diabetes care.
In conclusion, juvenile diabetes, or type 1 diabetes, is an autoimmune condition with a genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. It is characterized by symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. Diagnosis is typically done through blood glucose tests, glycated hemoglobin tests, and random blood sugar tests. Management includes blood sugar monitoring, insulin therapy, healthy eating, and regular physical activity. Complications can arise in the form of heart disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, and eye damage. The psychological impact of juvenile diabetes can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Support and resources, including education programs, support groups, counseling services, and financial assistance, are available to help individuals and their families. While there are no known prevention strategies, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and early detection and management are crucial. Advances in research include the development of an artificial pancreas, gene therapy, and immunotherapy. From a public health perspective, juvenile diabetes poses a significant burden, and health policies and funding are necessary to address its impact on healthcare systems. By understanding and addressing the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, management, complications, and psychological impact of juvenile diabetes, we can work towards improving the lives of individuals living with this condition.