If you’ve been struggling with lower back pain, you’re not alone. Many people suffer from discomfort in this area, which can greatly impact their daily lives. The good news is that there are various exercises you can do to strengthen your lower back and alleviate the pain. In this article, we will explore some of these exercises and how they can benefit you. So, let’s get started on your journey to a stronger and pain-free lower back!

Overview of Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain is a common issue that affects many individuals at some point in their lives. It is characterized by discomfort, stiffness, or pain in the lower part of the back, and can range from mild to severe. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial in managing and alleviating lower back pain effectively.
Causes of lower back pain
Lower back pain can be caused by various factors, including muscle strain or sprain, poor posture, herniated discs, spinal abnormalities, arthritis, and even stress. In some cases, certain lifestyle habits, such as a sedentary lifestyle or improper lifting techniques, can also contribute to lower back pain.
Symptoms of lower back pain
The symptoms of lower back pain may vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include a dull or sharp ache, muscle stiffness, difficulty standing or sitting, limited range of motion, and radiating pain that may travel down the legs or buttocks. In severe cases, lower back pain can even lead to numbness or tingling sensations.
Prevention of lower back pain
Preventing lower back pain involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and practicing good ergonomics. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly to strengthen the back muscles, practicing proper posture, using ergonomic furniture, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing. Taking these preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing lower back pain.
Importance of Strengthening Lower Back
Strengthening the lower back is crucial for maintaining a healthy spine and reducing the risk of injury. A strong lower back provides stability and support, ultimately enhancing overall core strength and posture.
Benefits of a strong lower back
Having a strong lower back offers numerous benefits. It helps to improve balance and flexibility, reduces the likelihood of muscle imbalances, and enhances overall physical performance. Additionally, a strong lower back can alleviate pressure on the spine, leading to reduced pain and discomfort.
Reducing the risk of lower back injury
Strengthening the lower back muscles can significantly reduce the risk of incurring injuries, such as muscle strains or sprains. Strong muscles better support the spine, reducing the impact and stress placed on it during physical activity or daily movements. This is particularly important for individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive motions, heavy lifting, or high-impact movements.
Improving posture
A strong lower back contributes to improved posture. It helps to align the spine properly and counteracts the tendency to slouch or hunch forward. By maintaining a good posture, individuals can reduce strain on the back, neck, and shoulders, while also promoting better breathing and overall well-being.

Seeking Medical Advice
While self-care measures can be effective for managing lower back pain, it is important to seek medical advice if the pain persists or worsens. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide a more accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Consulting a healthcare professional
If you experience persistent lower back pain, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional, such as a physician or physical therapist. They can evaluate your condition, review your medical history, and perform relevant tests or examinations to determine the underlying cause of the pain. This will enable them to recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Determine underlying causes of lower back pain
Understanding the root cause of lower back pain is essential for effective treatment. A healthcare professional can help identify any underlying conditions or factors that may be contributing to the pain. This may involve diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays or MRIs, to assess the structure of the spine and identify any abnormalities or injuries.
Getting proper diagnosis and advice
Seeking medical advice ensures that you receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate advice for managing your lower back pain. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on pain management techniques, recommend specific exercises or physical therapies, prescribe medications if necessary, and refer you to other specialists if needed. This personalized approach is crucial for effectively addressing lower back pain and preventing further complications.
Exercises for Lower Back Strength
Regular exercise is key to strengthening the lower back muscles and reducing the risk of pain or injury. Incorporating a variety of exercises that target the back muscles can help improve overall strength, flexibility, and stability.
Exercise 1: Pelvic Tilt
The pelvic tilt is an effective exercise for strengthening the lower back muscles. To perform this exercise, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Slowly tilt your pelvis upward, pressing your lower back into the floor, and hold for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat this movement for several repetitions.
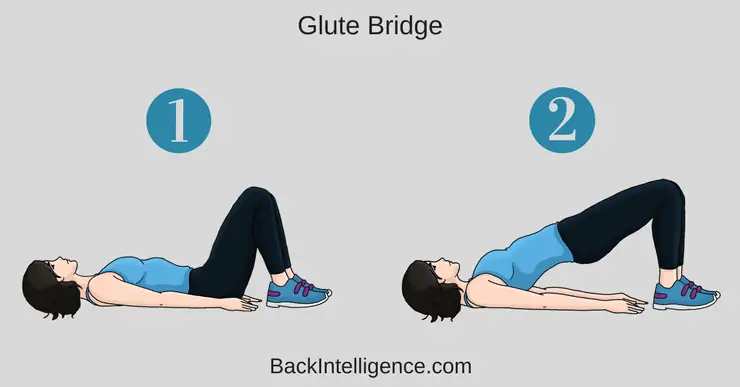
Exercise 2: Bridge
The bridge exercise focuses on the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. Start by lying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Press your heels into the ground and lift your hips off the floor, creating a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. Hold this position for a few seconds, then lower your hips back down. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise 3: Superman
The Superman exercise targets the entire back, including the lower back muscles. Begin by lying on your stomach with your arms extended overhead. Simultaneously lift your arms, chest, and legs off the floor, using your back muscles. Hold this position for a few seconds, then lower back down. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise 4: Deadlift
The deadlift is a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, including the lower back. Stand with your feet hip-width apart and hold a weight or barbell in front of you. Keeping your back straight, hinge at the hips and lower the weight towards the ground, then lift back up using your glutes and lower back muscles. Repeat for several repetitions, ensuring proper form and technique.
Exercise 5: Pelvic Lifts
Pelvic lifts are a great exercise for strengthening the lower back and core muscles. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place your hands on your hips and lift your pelvis off the floor, creating a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. Hold this position for a few seconds, then lower back down. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise 6: Prone Press-up
The prone press-up exercise targets the lower back and can help alleviate pain and stiffness. Begin by lying on your stomach, placing your hands under your shoulders. Press through your hands, lifting your upper body off the floor while keeping your hips grounded. Hold this position for a few seconds, then lower back down. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise 7: Quadruped Opposite Arm and Leg Raise
Quadruped opposite arm and leg raises help to strengthen the lower back, core, and stabilizer muscles. Start on all fours with your hands positioned under your shoulders and knees under your hips. Simultaneously extend one arm forward and the opposite leg backward, while keeping your back straight. Hold this position for a few seconds, then return to the starting position and switch sides. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise 8: Cat-Camel Stretch
The cat-camel stretch is a gentle exercise that promotes flexibility and releases tension in the lower back. Start on all fours with your hands positioned under your shoulders and knees under your hips. Slowly round your back upward like a cat, tucking your chin towards your chest. Hold this position for a few seconds, then arch your back downward, lifting your chin upward like a camel. Repeat this movement for several repetitions, focusing on the fluidity of the spine.
Exercise 9: Wall Sits
Wall sits are a beneficial exercise for strengthening the lower back and legs. Stand with your back against a wall and slide down until your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Hold this position for a few seconds, engaging your lower back and core while keeping your back against the wall. Slowly stand back up and repeat for several repetitions.
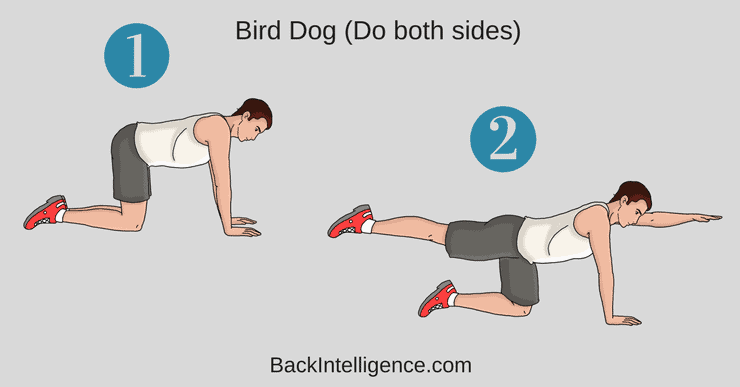
Exercise 10: Bird Dogs
Bird dogs are a dynamic exercise that targets the lower back, core, and stabilizer muscles. Begin on all fours with your hands positioned under your shoulders and knees under your hips. Extend one arm forward while simultaneously extending the opposite leg backward, maintaining a straight line from your fingertips to your toes. Hold this position for a few seconds, then return to the starting position and switch sides. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercise Precautions
While exercise is beneficial for strengthening the lower back, it is important to take certain precautions to prevent further injury or pain.
Knowing your limits and capabilities
Before starting any exercise program, it is crucial to assess your fitness level and capabilities. Listen to your body and only perform exercises that are within your physical limits. Pushing yourself too hard or performing exercises that are too advanced may increase the risk of injury.
Using proper form and technique
Using proper form and technique is essential to effectively strengthen the lower back and prevent strain or injury. Pay attention to your posture, engage the correct muscles, and avoid any excessive movements or compensations. If necessary, consult a fitness professional to learn the proper form for each exercise.
Not pushing through pain
If you experience any pain or discomfort during an exercise, it is important to stop immediately. Pain is an indication that something is wrong, and continuing to exercise through pain may worsen the condition or cause further damage. Listen to your body and adjust the intensity or range of motion to a level that is comfortable and pain-free.
Warm-Up and Cooling Down
Proper warm-up and cool-down sessions are essential for preparing the body before exercise and aiding in recovery afterward. Taking the time to warm up and cool down can significantly reduce the risk of muscle strain or soreness.
Importance of warm-up exercises
Warm-up exercises help to gradually increase blood flow to the muscles, increase body temperature, and prepare the body for physical activity. By warming up before exercise, you can improve muscle elasticity and joint mobility, and reduce the risk of muscle strains or injuries.
Effective warm-up exercises for the lower back
To warm up the lower back, incorporate dynamic movements that gently stretch and activate the relevant muscles. Examples of effective warm-up exercises for the lower back include standing side bends, gentle torso twists, back extensions, and hip circles.
Cooling down exercises to prevent muscle soreness
Cooling down exercises are important for gradually reducing the heart rate and allowing the muscles to recover after exercise. Engaging in gentle stretches or low-intensity movements can aid in the removal of waste products, such as lactic acid, and prevent the onset of muscle soreness. Some effective cooling down exercises for the lower back include standing forward bends, seated spinal twists, and child’s pose.
Incorporating Exercise into Daily Routine
Making exercise a part of your daily routine is key to maintaining a strong lower back and overall physical well-being. By setting realistic goals, creating a balanced workout plan, and scheduling exercise time, you can ensure consistency and maximize the benefits of regular exercise.
Setting realistic goals
When incorporating exercise into your daily routine, it is important to set realistic and achievable goals. Start by assessing your fitness level and determining what you would like to accomplish. Whether it’s improving flexibility, increasing strength, or reducing lower back pain, setting realistic goals allows for measurable progress and keeps you motivated.
Creating a balanced workout plan
A balanced workout plan should incorporate a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups, including the lower back. It should consist of cardiovascular activities, strength training exercises, and flexibility exercises. Consult a fitness professional to help create a personalized workout plan that fits your needs and goals.
Scheduling exercise time
To ensure consistency, it is beneficial to schedule dedicated exercise time throughout the week. Whether it’s early mornings, lunch breaks, or evenings, find a time that works best for you and make exercise a priority. Treat it as an appointment with yourself and commit to sticking to your scheduled exercise sessions.
Additional Tips for Stronger Lower Back
In addition to regular exercise, there are other lifestyle habits and tips that can contribute to a stronger lower back and overall spinal health.
Maintaining a healthy diet and weight
Eating a balanced diet that includes foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can promote overall health, including the health of your bones and muscles. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain placed on your lower back and minimizes the risk of developing back pain or injury.
Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing
Sitting or standing for long periods can put excessive pressure on the lower back, leading to pain and discomfort. If your work requires prolonged sitting or standing, make an effort to take breaks and incorporate short walks or stretches throughout the day. This helps to relieve tension on the lower back and promotes better circulation.
Avoiding heavy lifting
Improper lifting techniques, particularly lifting heavy objects, can strain the lower back and lead to injury. When lifting, remember to bend at the knees and use your leg muscles to lift rather than relying solely on the back. If an object is too heavy to lift on your own, seek assistance to avoid unnecessary strain.
Improving ergonomics at work and home
Ergonomics refers to the design and arrangement of your work or home environment to promote optimal posture and reduce strain on your body. Ensure that your workspace is set up correctly, with a supportive chair and desk that allow for proper alignment of the spine. Use ergonomic tools or equipment to minimize repetitive strain on the lower back.

Exercises to Avoid
While exercise is generally beneficial for the lower back, there are certain exercises that may strain the area and should be avoided, particularly if you have pre-existing lower back pain or injuries. Examples of exercises to avoid include heavy squats, weighted standing toe touches, full sit-ups, and exercises that involve excessive twisting or hyperextension of the lower back.
Exercises that strain the lower back
Certain exercises, such as heavy deadlifts or back extensions with heavy weights, place excessive strain on the lower back and may exacerbate existing pain or injuries. It is important to listen to your body and avoid exercises that cause discomfort or pain in the lower back.
Exercises with improper form or technique
Performing exercises with improper form or technique can also strain the lower back. It is essential to learn the correct form for each exercise and pay attention to maintaining proper alignment throughout the movement. If you are unsure about the correct form, seek guidance from a fitness professional to ensure you are performing exercises safely and effectively.
When to Stop and Seek Medical Assistance
While it is normal to experience minor soreness or discomfort after exercise, it is important to recognize the signs of worsening pain or injury and seek medical assistance when necessary.
Recognizing signs of worsening pain or injury
If you experience severe or persistent pain that does not improve with rest, over-the-counter pain medication, or other self-care measures, it may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition. Other signs to watch for include numbness or tingling sensations, weakness in the legs, difficulty controlling bowel or bladder function, or pain that is accompanied by fever or unexplained weight loss. Any of these symptoms should warrant immediate medical attention.
Knowing when to rest and recover
Rest and recovery are essential components of any exercise program, especially when it comes to the lower back. If you feel excessive fatigue, muscle soreness that lasts for more than a few days, or if your lower back pain worsens during or after exercise, it is a sign that you may need to rest and allow your body to recover.
Getting medical assistance when needed
If home remedies and self-care measures do not provide relief or if your symptoms worsen, it is important to seek medical assistance. A healthcare professional can assess your condition, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include physical therapy, medication, or other interventions. Remember, seeking medical assistance is crucial for effectively managing lower back pain and preventing further complications.