Imagine a world where the burden of Type 2 Diabetes is finally lifted. This article reveals exciting news about a potential cure that could become a reality by 2023. With millions of people worldwide currently living with this chronic condition, the prospect of a cure is nothing short of life-changing. Stay tuned as we explore the groundbreaking research and promising developments that could transform the lives of those affected by Type 2 Diabetes.
The Global Burden of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence has been steadily increasing over the years, posing a significant health challenge. In 2023, it is estimated that over 400 million people will be living with type 2 diabetes globally. This alarming number highlights the urgent need for effective management and potential breakthroughs in the treatment of this condition.
Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for around 90% of all diabetes cases. It primarily affects adults, but it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals as well. The rise in the number of people with type 2 diabetes can be attributed to various factors, including sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy dietary habits, and a growing aging population. The burden of this disease is particularly high in low and middle-income countries, where resources for prevention and treatment are often limited.
Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Health
Type 2 diabetes has a profound impact on an individual’s health, affecting multiple organ systems and increasing the risk of various complications. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes, as well as kidney failure, blindness, and lower limb amputations. The condition also poses a significant burden on mental health, causing distress, anxiety, and depression. Managing type 2 diabetes is crucial to prevent these complications and ensure individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Economic Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes
The economic burden of type 2 diabetes is substantial, both for individuals and healthcare systems. The cost of medication, regular check-ups, and other healthcare services can be a financial strain for many people living with diabetes. Additionally, the indirect costs, such as loss of productivity and reduced quality of life, further exacerbate the economic impact. It is estimated that by the year 2030, the global healthcare expenditure on diabetes will exceed $800 billion annually. Addressing this issue is crucial to ensure the sustainability of healthcare systems and improve overall socio-economic well-being.
Current Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for managing type 2 diabetes. A combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and insulin therapy can significantly improve blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
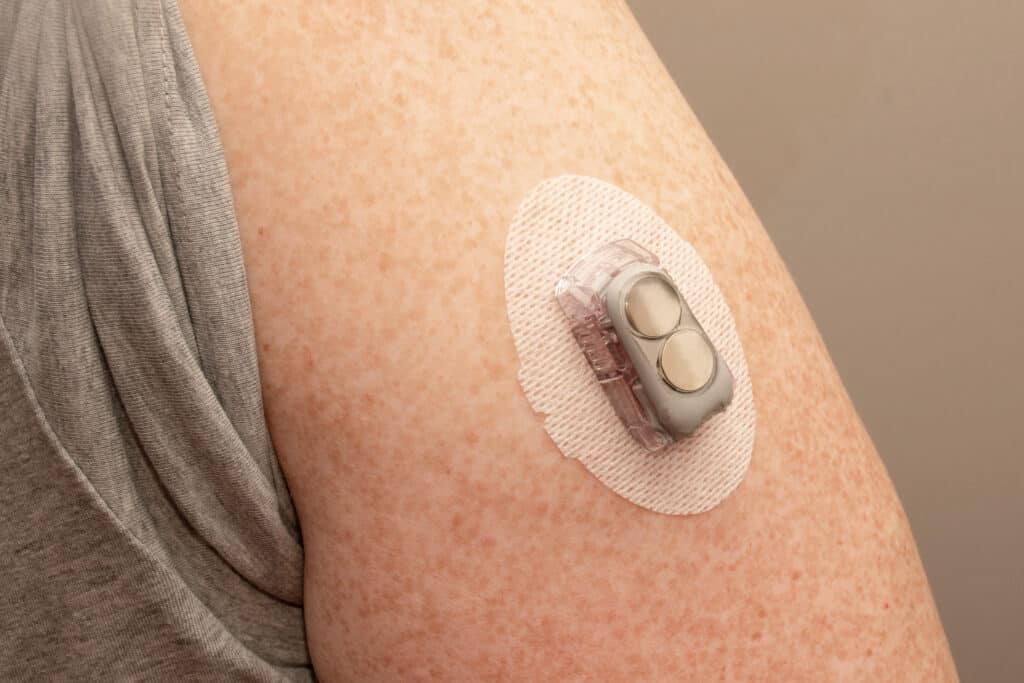
Regular blood glucose monitoring is a key component of diabetes management. It allows individuals to track their glucose levels and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. Monitoring can be done through fingerstick blood glucose testing or by using continuous glucose monitoring systems. These devices provide real-time data and enable individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
Medications
Several classes of medications are available to help manage type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways to lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Commonly prescribed medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT-2 inhibitors. The choice of medication depends on various factors, such as individual characteristics, age, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is often necessary for individuals who have difficulty achieving adequate blood glucose control with oral medications alone. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and it can be administered through injections or insulin pumps. Different types of insulin are available, with varying durations of action. Insulin therapy requires careful dosing and monitoring to avoid hypo- or hyperglycemia.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in the management of type 2 diabetes. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications. A balanced diet that is low in processed sugars and saturated fats, along with regular exercise, can enhance insulin sensitivity and promote overall well-being. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers or dieticians to develop a personalized plan that suits individual needs and preferences.

Challenges in Treating Type 2 Diabetes
Despite the availability of treatment options, managing type 2 diabetes poses several challenges. These challenges range from the lack of long-term efficacy of current treatments to issues related to patient compliance and access to healthcare.
Lack of Long-term Efficacy
While current treatments can effectively lower blood glucose levels in the short term, their long-term efficacy is often limited. Many individuals with type 2 diabetes experience a gradual decline in treatment effectiveness over time, leading to the need for additional medications or insulin therapy to achieve adequate glycemic control. Finding interventions with sustainable long-term efficacy has been a major challenge in diabetes research.
Adverse Effects of Medications
Some medications used to manage type 2 diabetes can have adverse effects on individuals. For example, certain medications may cause gastrointestinal issues, weight gain, or hypoglycemia. These side effects can impact treatment adherence and quality of life. Developing medications with a better safety profile and fewer adverse effects is a priority for researchers and healthcare providers.
Patient Compliance
Achieving optimal glycemic control requires strict adherence to treatment plans, including medication schedules, regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications. However, many individuals struggle with treatment compliance due to various reasons, such as forgetfulness, difficulties with self-management, or psychological barriers. Improving patient education, support systems, and simplifying treatment regimens are essential in enhancing treatment adherence and patient outcomes.
Access to Healthcare
Access to healthcare services is a significant challenge for many individuals with type 2 diabetes, especially in low and middle-income countries. Limited healthcare resources, including healthcare providers, medications, and monitoring devices, hinder optimal diabetes management. Addressing healthcare disparities and improving access to affordable and quality care is crucial to ensure that everyone has an equal opportunity to manage their condition effectively.
Emerging Technologies for Type 2 Diabetes Management
Advancements in technology have paved the way for innovative solutions in type 2 diabetes management. These emerging technologies aim to provide individuals with better tools for monitoring blood glucose levels and simplifying treatment regimens.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time glucose readings throughout the day. These systems consist of a small wearable device that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid and transmits the data to a smartphone or receiver. CGM systems help individuals make immediate adjustments to their treatment plan based on their glucose trends, reducing the risk of hypo- or hyperglycemia.
Artificial Pancreas
The development of an artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop system, is a significant breakthrough in type 2 diabetes management. This device combines CGM technology with an insulin pump to automatically deliver the right amount of insulin based on real-time glucose readings. The goal of the artificial pancreas is to mimic the function of the natural pancreas and provide individuals with better glucose control and increased treatment convenience.
Closed-loop Insulin Delivery Systems
Closed-loop insulin delivery systems, similar to the artificial pancreas, aim to automate insulin administration based on glucose levels. However, these systems do not incorporate CGM technology and instead rely on algorithms to adjust insulin dosing. Closed-loop insulin delivery systems can potentially offer a more user-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional insulin therapy.
Smart Insulin Pens
Smart insulin pens are pen-like devices that incorporate digital technology to record and transmit insulin dosing data to a smartphone app. These pens can provide individuals with better visibility into their insulin usage, reminders for medication adherence, and insights on their glucose patterns. Smart insulin pens can help enhance treatment compliance and facilitate communication between individuals and healthcare providers.

Potential Breakthroughs in Type 2 Diabetes Cure
While current treatments aim to manage type 2 diabetes and prevent complications, researchers are actively exploring potential breakthroughs that could offer a cure for this condition. These breakthroughs involve novel treatment approaches targeting gene therapy, stem cell therapy, immunotherapy, and microbiome-targeted therapies.
Gene Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Gene therapy involves manipulating an individual’s genes to correct or modify the underlying causes of a disease. In the context of type 2 diabetes, gene therapy aims to modify gene expression related to insulin production, insulin sensitivity, or glucose metabolism. While this approach is still in the early stages of development, several promising studies have demonstrated the potential of gene therapy in improving glycemic control and reducing the reliance on external insulin.
Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Stem cell therapy holds immense promise in the field of regenerative medicine and potential cures for various diseases, including type 2 diabetes. The goal of stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes is to develop functional pancreatic beta cells that can produce insulin in response to glucose levels. Researchers are exploring different sources of stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells, and refining protocols to differentiate these cells into mature beta cells. Early-stage clinical trials have shown promising results, with some individuals achieving insulin independence after receiving stem cell therapy.
Immunotherapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Immunotherapy involves modulating the immune system to target the underlying autoimmune response in type 2 diabetes. In some individuals, the immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreatic beta cells, leading to reduced insulin production and the development of diabetes. Immunotherapy aims to suppress the aberrant immune response and preserve or restore beta cell function. Various immunomodulatory drugs and biologics are being investigated in clinical trials, with the potential to induce beta cell regeneration and remission of type 2 diabetes.
Microbiome-targeted Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
The gut microbiome, a collection of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract, has been linked to various aspects of health and disease, including type 2 diabetes. Microbiome-targeted therapies aim to modulate the gut microbiota composition to improve glucose metabolism and enhance insulin sensitivity. Approaches such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), which involves transferring healthy microbiota from a donor to a recipient, and the use of probiotics and prebiotics, show promise in influencing gut microbiota diversity and metabolic health.
Gene Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Introduction to Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a promising approach that involves modifying an individual’s genetic material to treat or prevent diseases. In the context of type 2 diabetes, gene therapy aims to target specific genes involved in insulin production, insulin sensitivity, or glucose metabolism. By modifying these genes, researchers hope to restore normal glucose regulation and potentially cure the disease.
Gene Editing and Type 2 Diabetes
Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, provide researchers with precise tools to modify specific genes. In the field of type 2 diabetes, gene editing can be used to correct or modify genetic variants associated with insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, or other factors contributing to the development of the disease. Researchers are actively exploring the feasibility and safety of gene editing approaches in preclinical and early-stage clinical studies.
Challenges and Future Directions
While gene therapy holds immense potential, several challenges need to be addressed before it becomes a viable treatment option for type 2 diabetes. Safety concerns, such as off-target effects and immune reactions, need to be thoroughly evaluated. Furthermore, the delivery of therapeutic genes to the target tissues poses technical challenges, as well as ethical considerations, particularly regarding germline editing. Collaborative efforts among researchers, regulators, and ethical committees are essential to overcome these challenges and ensure the responsible development of gene therapies for type 2 diabetes.

Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Stem Cells and Type 2 Diabetes
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into specialized cell types. In the context of type 2 diabetes, stem cell therapy aims to replace or regenerate pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production and are often dysfunctional in individuals with the disease. Stem cells can potentially differentiate into functional beta cells, providing a renewable source of insulin-producing cells and potentially restoring normal glucose regulation.
Differentiation of Stem Cells into Pancreatic Beta Cells
Researchers are exploring different sources of stem cells for the development of functional pancreatic beta cells. Embryonic stem cells derived from early-stage embryos can differentiate into various cell types, including beta cells. However, ethical concerns and safety considerations limit the widespread use of embryonic stem cells. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), generated from adult cells through a process called reprogramming, offer a promising alternative. Researchers can coax iPSCs to differentiate into beta-like cells, which can mature and secrete insulin in response to glucose levels.
Clinical Trials and Success Stories
Early-stage clinical trials have shown promising results in the field of stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes. Some individuals who received stem cell transplants have achieved insulin independence or significantly reduced their reliance on external insulin. However, larger and more comprehensive clinical trials are needed to determine the long-term safety, efficacy, and scalability of stem cell-based therapies. Understanding the optimal conditions for stem cell differentiation, immune compatibility, and long-term integration into the host pancreas is crucial for the successful translation of this therapy into clinical practice.
Immunotherapy for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
Targeting Autoimmunity in Type 2 Diabetes
While type 2 diabetes is traditionally considered a metabolic disorder, emerging evidence suggests that autoimmune mechanisms also play a role in its development. In some individuals, the immune system mistakenly recognizes pancreatic beta cells as foreign and launches an autoimmune attack, leading to reduced insulin production. Immunotherapy aims to modulate the immune response and suppress the autoimmunity associated with type 2 diabetes, potentially preserving or restoring beta cell function.
Immunomodulatory Drugs and Type 2 Diabetes
Immunomodulatory drugs are designed to modify the activity or function of the immune system. In type 2 diabetes, these drugs can target specific immune cells or signaling pathways involved in the autoimmune response. For example, drugs targeting B cells, such as rituximab, aim to deplete these cells to reduce inflammation and autoantibody production. Other immunomodulatory drugs, such as anti-inflammatory cytokines or T cell modulators, also hold promise in restoring immune balance and potentially inducing beta cell regeneration.
Progress and Considerations
While immunotherapy holds promise, several considerations need to be addressed to optimize its potential for type 2 diabetes treatment. The heterogeneity of type 2 diabetes and the diversity of immune responses present challenges in identifying appropriate patient subgroups that would benefit the most from immunotherapy. Additionally, the long-term safety, efficacy, and potential side effects of immunomodulatory drugs need to be carefully evaluated in large-scale clinical trials. Collaborative efforts in precision medicine, biomarker identification, and personalized immunotherapy are crucial to advancing this field.
Microbiome-targeted Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Cure
The Gut Microbiome and Type 2 Diabetes
The gut microbiome, composed of trillions of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract, has a significant influence on human health and disease. In the context of type 2 diabetes, alterations in the gut microbiota composition have been observed, including a decrease in beneficial bacteria and an increase in potentially harmful bacteria. These changes are associated with metabolic dysregulation, low-grade inflammation, and insulin resistance. Targeting the gut microbiome through microbiome-targeted therapies offers a novel approach to manage and potentially cure type 2 diabetes.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor to a recipient to restore a healthy gut microbiota composition. FMT has been successful in treating certain gastrointestinal conditions, such as recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, and shows promise in the field of type 2 diabetes. Early studies have demonstrated improvements in glycemic control and insulin sensitivity following FMT in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, more research is needed to determine optimal donor selection, treatment protocols, and long-term effects.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Both probiotics and prebiotics can modulate the gut microbiota, promote microbial diversity, and improve metabolic health. Several studies have shown that specific strains of probiotics and prebiotics can improve glycemic control, reduce inflammation, and enhance insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, optimizing treatment protocols and identifying the most effective strains and dosages are areas of ongoing research.
Future Implications
Microbiome-targeted therapies for type 2 diabetes hold great promise, but several challenges need to be addressed. The complexity and individual variability of the gut microbiome make it difficult to determine precise cause-and-effect relationships between specific microbial changes and disease outcomes. Additionally, the potential long-term effects and safety of microbiota modulation need to be thoroughly investigated. Developing standardized protocols, identifying biomarkers, and tailoring treatments based on individual gut microbiota profiles are areas of ongoing research that will shape the future of microbiome-targeted therapies in type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
The future of type 2 diabetes management and potential cure is filled with promise. Advances in technology have led to the development of innovative treatment options, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, artificial pancreas devices, closed-loop insulin delivery systems, and smart insulin pens. These technologies offer individuals with type 2 diabetes better tools for managing their condition and simplifying treatment regimens.
Further breakthroughs in type 2 diabetes cure may come in the form of gene therapy, stem cell therapy, immunotherapy, and microbiome-targeted therapies. Gene therapy holds the potential to correct or modify the underlying genetic causes of the disease, while stem cell therapy aims to regenerate functional pancreatic beta cells. Immunotherapy seeks to suppress the autoimmune response associated with type 2 diabetes, and microbiome-targeted therapies aim to modulate the gut microbiota to promote metabolic health.
Addressing the existing challenges in type 2 diabetes management, such as the lack of long-term efficacy, adverse effects of medications, patient compliance, and access to healthcare, is essential in improving treatment outcomes and reducing the global burden of this disease.
With ongoing research, collaborative efforts, and advancements in healthcare, there is hope for a future free from the burden of type 2 diabetes. The potential for a cure for type 2 diabetes is within reach, offering individuals the prospect of leading healthy and fulfilling lives without the constraints of this chronic condition.
