Living with coeliac disease can be challenging, especially when it comes to figuring out what to eat. However, understanding the nutritional dietary requirements and foods allowed for those with coeliac disease can make the journey much easier. In this article, we will explore the foods that are safe to consume for individuals with coeliac disease, ensuring that you can still enjoy a delicious and wholesome diet while managing your condition.

General guidelines
Understanding coeliac disease
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the small intestine and is triggered by the consumption of gluten. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and it can cause damage to the lining of the small intestine in individuals with coeliac disease. This can lead to various digestive symptoms like diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain. It is important to understand that coeliac disease is a chronic condition, and the only treatment is to follow a strict gluten-free diet.
Importance of a gluten-free diet
Following a gluten-free diet is crucial for individuals with coeliac disease to manage their symptoms and prevent further damage to their intestine. Even small amounts of gluten can cause a negative reaction in individuals with coeliac disease, so it is essential to be diligent about avoiding gluten-containing foods. By sticking to a gluten-free diet, you can alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms, reduce long-term complications, and improve your overall well-being.
Consulting a healthcare professional
If you suspect that you have coeliac disease or if you have been diagnosed with it, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, support, and guidance. A healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or a registered dietitian, can conduct the necessary tests to confirm the diagnosis and provide you with personalized advice on your gluten-free diet. They can also help you understand how to read food labels, recognize hidden sources of gluten, and manage special considerations like cross-contamination.
Gluten-free grains, cereals, and flours
Rice
Rice is a versatile staple grain that is naturally gluten-free and can be used as a substitute for wheat-based products. It can be cooked and enjoyed as a side dish, added to soups, or used as an ingredient in various gluten-free recipes. Whether you opt for brown rice, white rice, or specialty varieties like basmati or jasmine rice, you can feel confident that your meal will be safe and delicious.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a nutritious and protein-packed grain that is also gluten-free. It is a great alternative for individuals with coeliac disease, and it can be used as a substitute for couscous, bulgur, or other gluten-containing grains. Quinoa is not only rich in nutrients, but it also has a delightful nutty flavor and a slightly chewy texture, making it a versatile ingredient for salads, stir-fries, and as a side dish.
Corn
Corn and corn-derived products, such as cornmeal and corn flour, are free from gluten and can be enjoyed by individuals with coeliac disease. Corn can be used in various forms, including fresh corn on the cob, corn tortillas, corn chips, and grits. Its natural sweetness and versatility make it a popular choice for gluten-free cooking and baking.
Buckwheat
Despite its name, buckwheat is not related to wheat and is naturally gluten-free. It is a nutritious grain-like seed that can be ground into flour and used in gluten-free baking or enjoyed as a side dish. Buckwheat has a unique earthy flavor and a rich texture, making it a favorite in dishes like buckwheat pancakes or soba noodles.
Amaranth
Amaranth is a gluten-free pseudo-cereal that has been cultivated for thousands of years. It is a nutrient-dense grain and a good source of protein, fiber, and essential minerals. Amaranth can be cooked and used as a base for grain bowls, added to soups and stews, or ground into flour for baking gluten-free goods.
Sorghum
Sorghum is a gluten-free grain that is widely used in gluten-free baking and cooking. It is a versatile ingredient that can be milled into flour or cooked and enjoyed as a side dish. With its mild flavor and hearty texture, sorghum adds depth and substance to gluten-free recipes.
Millet
Millet is a small, gluten-free grain that is highly nutritious and easily digestible. It can be cooked and enjoyed as a side dish, used as a base for pilafs, or ground into flour for gluten-free baking. Millet has a mild, slightly nutty flavor, and it pairs well with a variety of other ingredients.
Tapioca
Tapioca is a gluten-free starch derived from the cassava root. It is often used as a thickening agent in gluten-free recipes or as a binder in baked goods. Tapioca flour or starch can be used to make gluten-free bread, pizza dough, or even as a coating for fried foods.
Potato flour
Potato flour is a gluten-free flour made from cooked and dried potatoes. It is commonly used as an ingredient in gluten-free baking or as a thickener for soups and sauces. Potato flour adds moisture and a mild potato flavor to gluten-free recipes, making it a versatile option for those with coeliac disease.
Flaxseed meal
Flaxseed meal is a nutritious and gluten-free option for incorporating fiber and omega-3 fatty acids into your diet. It can be used as an egg substitute in baking or added to smoothies and cereals for an extra nutritional boost. Flaxseed meal has a slightly nutty flavor and can enhance both the taste and texture of gluten-free recipes.
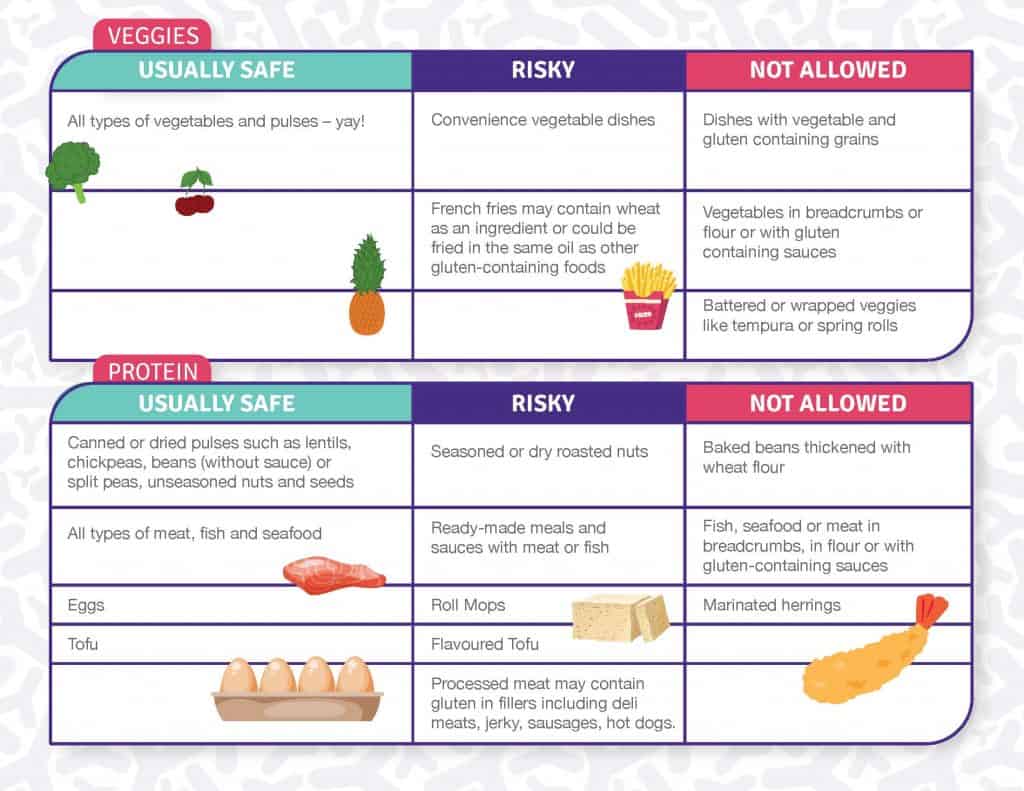
Protein sources
Fresh meat and poultry
Fresh meat and poultry are naturally gluten-free and are excellent sources of high-quality protein. Whether you prefer chicken, beef, pork, or lamb, you can enjoy these protein-rich foods without worrying about gluten. However, it is important to check for any marinades, seasonings, or coatings, as some may contain gluten.
Fish and seafood
Fish and seafood are not only delicious but also excellent sources of lean protein and essential omega-3 fatty acids. Fresh fish like salmon, tuna, and cod, as well as shellfish like shrimp and crab, are naturally gluten-free. You can enjoy them grilled, baked, or sautéed, and enhance their flavor with a variety of gluten-free sauces and seasonings.
Legumes
Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are nutritious plant-based sources of protein that are naturally gluten-free. They are also rich in fiber and various vitamins and minerals. Legumes can be used in a wide range of gluten-free dishes, including soups, stews, salads, and curries, providing both nutrition and satisfaction.
Eggs
Eggs are a versatile and affordable source of protein that can be enjoyed by individuals with coeliac disease. Whether you prefer them scrambled, fried, boiled, or incorporated into a recipe, eggs are a nutrient-dense option that can keep you feeling full and energized.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only a great source of protein but also provide healthy fats, fiber, and essential nutrients. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds are all nutritious options that can be enjoyed as a snack, added to salads or smoothies, or used as ingredients in gluten-free baking.
Dairy and alternatives
Milk (lactose-free or plant-based)
Milk is an excellent source of calcium and essential vitamins, but individuals with coeliac disease may need to choose lactose-free or plant-based options to avoid gluten contamination. Lactose-free cow’s milk and plant-based milk alternatives, such as almond milk, soy milk, or coconut milk, are suitable choices for those following a gluten-free diet.
Cheese (gluten-free varieties)
Cheese is a delicious and versatile dairy product that can be safely consumed by individuals with coeliac disease. Most natural cheeses are gluten-free, but it is important to check for any added ingredients or flavorings that may contain gluten. Common gluten-free cheese options include cheddar, mozzarella, feta, and Swiss.
Yogurt (gluten-free varieties)
Yogurt is a nutritious and probiotic-rich food that can be part of a gluten-free diet. Opt for plain yogurt or gluten-free varieties, and avoid any yogurts with added gluten-containing ingredients, such as granola or cookie pieces. You can enjoy yogurt as a snack, add it to smoothies, or use it as a base for dressings and dips.
Plant-based milk alternatives (e.g., almond, soy, coconut)
Plant-based milk alternatives are a popular choice for individuals with coeliac disease or those following a vegan lifestyle. Almond milk, soy milk, and coconut milk are gluten-free options that can be used in place of cow’s milk in a wide range of recipes, including baking, cooking, and beverages.
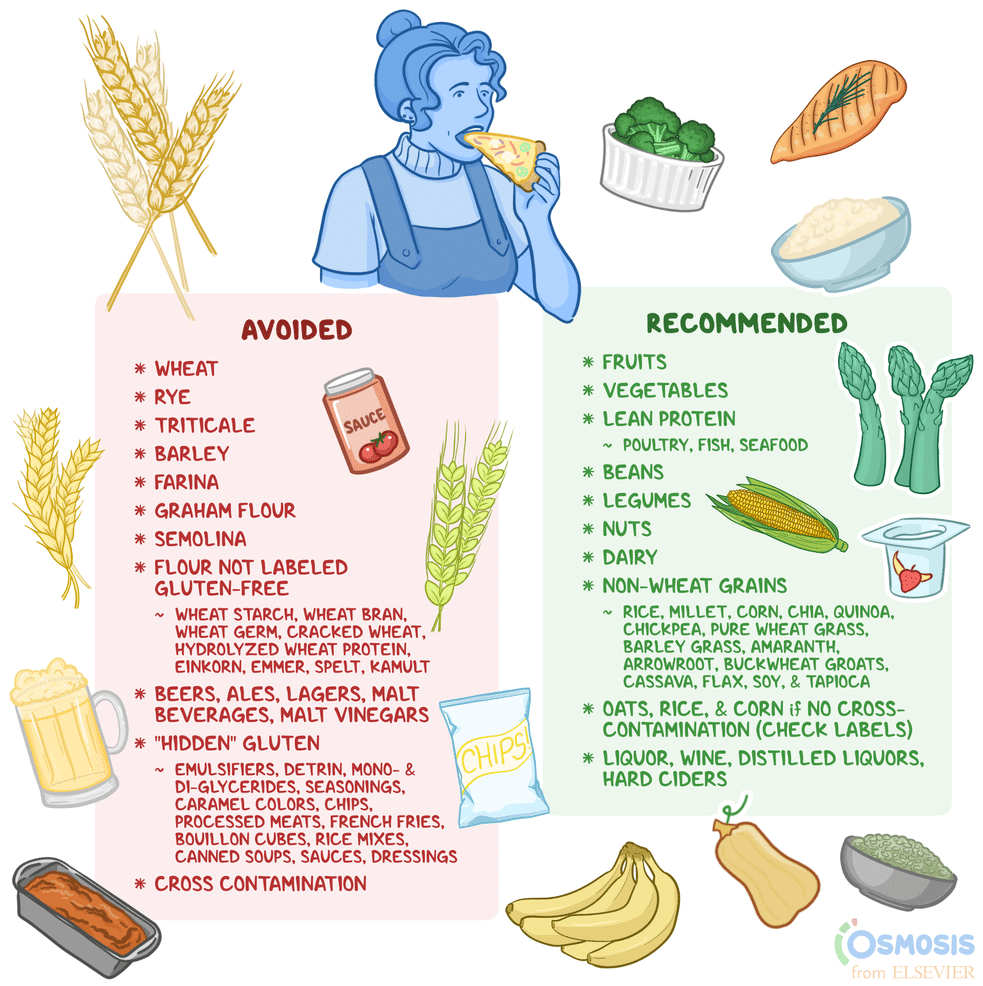
Fruits and vegetables
All fresh fruits
Fresh fruits are naturally gluten-free and can be enjoyed by individuals with coeliac disease. Whether you prefer apples, bananas, berries, or citrus fruits, the options are endless. Not only are fresh fruits packed with essential vitamins and minerals, but they also add natural sweetness and flavor to your meals and snacks.
All fresh vegetables
Like fresh fruits, all fresh vegetables are naturally gluten-free and provide a wide range of nutrients. Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, and colorful peppers are all nutritious options that can be incorporated into various gluten-free recipes. From salads to stir-fries to roasting, the possibilities to enjoy gluten-free vegetables are endless.
Frozen fruits and vegetables (without sauces or seasonings)
Frozen fruits and vegetables are convenient options to have on hand, especially when fresh produce is not readily available. When purchasing frozen fruits and vegetables, make sure to choose varieties without sauces or seasonings to avoid any potential sources of gluten. Frozen produce can be used in smoothies, soups, stews, and stir-fries, providing both nutrition and convenience.
Fats and oils
Olive oil
Olive oil is a heart-healthy fat that can be used in various cooking methods, including sautéing, roasting, and dressing. It adds a distinctive flavor to dishes and provides a source of monounsaturated fats. Olive oil is naturally gluten-free and can enhance the taste and texture of your gluten-free meals.
Coconut oil
Coconut oil is a versatile and flavorful fat that is derived from the fruit of the coconut palm. It has a unique taste and a high smoke point, making it suitable for baking, cooking, and frying. Coconut oil is naturally gluten-free and provides healthy medium-chain triglycerides.
Avocado oil
Avocado oil is a nutrient-rich oil that is derived from the flesh of avocados. It has a mild flavor and a high smoke point, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking methods. Avocado oil is naturally gluten-free and a good source of monounsaturated fats, which can benefit heart health.
Ghee (clarified butter)
Ghee is a type of clarified butter that is commonly used in traditional Indian cuisine. It is made by heating butter to remove the milk solids and water, leaving behind the clarified butterfat. Ghee has a higher smoke point than regular butter and imparts a rich, nutty flavor to dishes. While ghee is derived from dairy, the clarification process removes most of the lactose and casein, making it generally well-tolerated by individuals with coeliac disease.
Butter (if tolerated)
Butter is a tasty and versatile fat that can add flavor and richness to gluten-free dishes. While butter is naturally gluten-free, some individuals with coeliac disease may need to exercise caution, as cross-contamination can occur during production. If you tolerate butter without any adverse reactions, it can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a gluten-free diet.
Mayonnaise (gluten-free varieties)
Mayonnaise is a popular condiment that can be used in a wide range of dishes, from sandwiches to salads to dips. Most commercially available mayonnaise brands are gluten-free, but it is always important to check the label for any hidden sources of gluten. With gluten-free options readily available, you can enjoy mayonnaise without compromising your gluten-free lifestyle.
Beverages
Water
Water is the ultimate gluten-free beverage and is essential for hydration. It is important to stay well-hydrated throughout the day to support overall health and well-being. Opt for plain water or infused water with fruits or herbs to add a refreshing twist.
Herbal teas
Herbal teas are a soothing and caffeine-free option that can be enjoyed by individuals with coeliac disease. Whether you prefer chamomile, peppermint, or ginger tea, herbal teas provide a comforting beverage that can be enjoyed hot or cold. It is important to read the labels of herbal tea blends that may contain gluten-containing ingredients.
Coffee (without additives)
Coffee is a popular beverage that is naturally gluten-free and can be enjoyed by individuals with coeliac disease. However, it is important to be cautious of any additives, such as flavored syrups or coffee creamers, which may contain gluten. Opt for plain, black coffee or use gluten-free additives like dairy or plant-based milk.
Fruit and vegetable juices (without additives)
Fruit and vegetable juices can be a refreshing way to incorporate essential vitamins and minerals into your diet. Choose juices without any additives or additional sweeteners, as they may contain hidden sources of gluten. It is always a good idea to check the labels of canned or bottled juices to ensure they are gluten-free.
Condiments and spices
Salt
Salt is a staple ingredient that is used to enhance the flavor of your meals. It is naturally gluten-free and can be used in various cooking methods and recipes. Whether you prefer sea salt, Himalayan salt, or kosher salt, you can season your gluten-free dishes without any concerns.
Pepper
Pepper is a versatile spice that can add heat and depth to your gluten-free recipes. Whether you choose freshly ground black pepper, white pepper, or chili flakes, you can enjoy the piquant flavor without worrying about gluten.
Herbs (fresh or dried)
Herbs are aromatic and flavorful additions to gluten-free dishes. Whether you prefer fresh herbs like basil, parsley, or rosemary, or dried herbs like oregano, thyme, or sage, you can enhance the taste and aroma of your meals without adding any gluten.
Spices (gluten-free varieties)
Spices are versatile ingredients that can transform your gluten-free cooking. Most spices, such as turmeric, cinnamon, cumin, and paprika, are naturally gluten-free. However, it is essential to check spice blends and seasonings for any added ingredients that may contain gluten. Choose single ingredient spices or gluten-free spice blends to flavor your meals.
Vinegar (except malt vinegar)
Vinegar, except malt vinegar, is typically gluten-free and can be a flavorful addition to dressings, marinades, and sauces. Common gluten-free vinegars include white vinegar, apple cider vinegar, balsamic vinegar, and rice vinegar. It is important to avoid malt vinegar, as it is derived from barley and contains gluten.
Gluten-free soy sauce or tamari
Soy sauce is a condiment that is commonly used in Asian cuisine and can add depth and umami to your gluten-free dishes. Regular soy sauce is traditionally made with wheat, but gluten-free options like tamari or gluten-free soy sauce are available. These alternatives provide the same savory flavor without the addition of gluten.

Snacks
Fresh fruits
Fresh fruits are not only nutritious but also make excellent gluten-free snacks. Whether you reach for an apple, a handful of berries, or a sliced melon, fresh fruits provide natural sweetness, vitamins, and fiber.
Raw vegetables with gluten-free dips
Raw vegetables, such as carrot sticks, cucumber slices, or bell pepper strips, can be paired with gluten-free dips for a satisfying and healthy snack. Hummus, guacamole, or dairy or plant-based yogurt dips are all delicious options that add flavor and nutrition to your snack time.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are crunchy and satisfying snacks that are packed with protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients. Whether you choose almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, or sunflower seeds, they make excellent gluten-free snacks that can be enjoyed on their own or combined with dried fruits for a trail mix.
Popcorn (plain, without added seasonings)
Popcorn is a classic and gluten-free snacking option. Enjoy it plain or lightly salted for a low-calorie and crunchy treat. However, be cautious of flavored or microwave popcorn, as they may contain gluten-containing additives or seasonings.
Gluten-free crackers or rice cakes
Gluten-free crackers or rice cakes are convenient snacks that can be enjoyed on their own or paired with toppings like cheese, nut butter, or gluten-free spreads. They provide a satisfying crunch and are widely available in various flavors and textures.
Special considerations
Cross-contamination
Cross-contamination is a concern for individuals with coeliac disease, as even small traces of gluten can trigger a reaction. It is important to ensure that gluten-free foods are stored, prepared, and cooked separately from gluten-containing foods. Use separate utensils, cookware, and cutting boards, and be cautious of shared surfaces and appliances. Additionally, when dining out or traveling, communicate your dietary needs to ensure proper precautions are taken.
Reading food labels
When following a gluten-free diet, reading food labels becomes essential. Look for labels that clearly state “gluten-free” or “certified gluten-free” to ensure the product meets the necessary standards. Familiarize yourself with ingredients that may contain hidden gluten, such as malt, hydrolyzed wheat protein, or modified food starch. Always err on the side of caution and contact the manufacturer if you are unsure about a product’s gluten content.
Hidden sources of gluten
Gluten can hide in various unexpected places, making it important to stay vigilant. Some common hidden sources of gluten include sauces, gravies, dressings, and marinades that may contain wheat-based thickeners or soy sauce. Processed foods like soups, sausages, and deli meats can also contain hidden gluten. Always check the ingredients list and be aware of potential cross-contamination.
Eating out and traveling
Eating out and traveling can pose challenges for individuals with coeliac disease, but with proper planning and communication, it is possible to enjoy gluten-free meals. Research restaurants in advance and ask about their gluten-free options or their ability to accommodate dietary restrictions. When traveling, pack gluten-free snacks or meals to ensure you have safe and convenient options. Communicate your needs to waitstaff, chefs, or airline personnel, and consider carrying a restaurant card that explains your dietary requirements in the local language if needed.
Following a gluten-free diet is essential for individuals with coeliac disease to manage their condition and maintain a healthy lifestyle. By understanding coeliac disease, choosing appropriate foods, and being mindful of hidden sources of gluten, you can confidently navigate your gluten-free journey. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and support, as they can guide you in making informed dietary choices and managing your coeliac disease effectively.
