Chest pain is a symptom that shouldn’t be taken lightly, as it could potentially indicate an underlying health issue. While it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis, familiarizing yourself with the common causes of chest pain can help calm your worries and prompt you to seek medical attention when necessary. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most prevalent factors contributing to chest pain, shedding light on various conditions ranging from minor and benign to more serious and urgent. With this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to understand your symptoms and make informed decisions about your health.
Musculoskeletal Causes
Chest pain can often be attributed to various musculoskeletal causes. One common cause is costochondritis, which is the inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. This can cause sharp or stabbing pain in the chest area, especially when taking deep breaths or coughing.
Muscle strain is another possible cause of chest pain. Intense physical activity or sudden movements can lead to muscle strains in the chest area, resulting in discomfort or aching pain. These strains can be particularly common in athletes or individuals who perform repetitive motions involving the chest muscles.
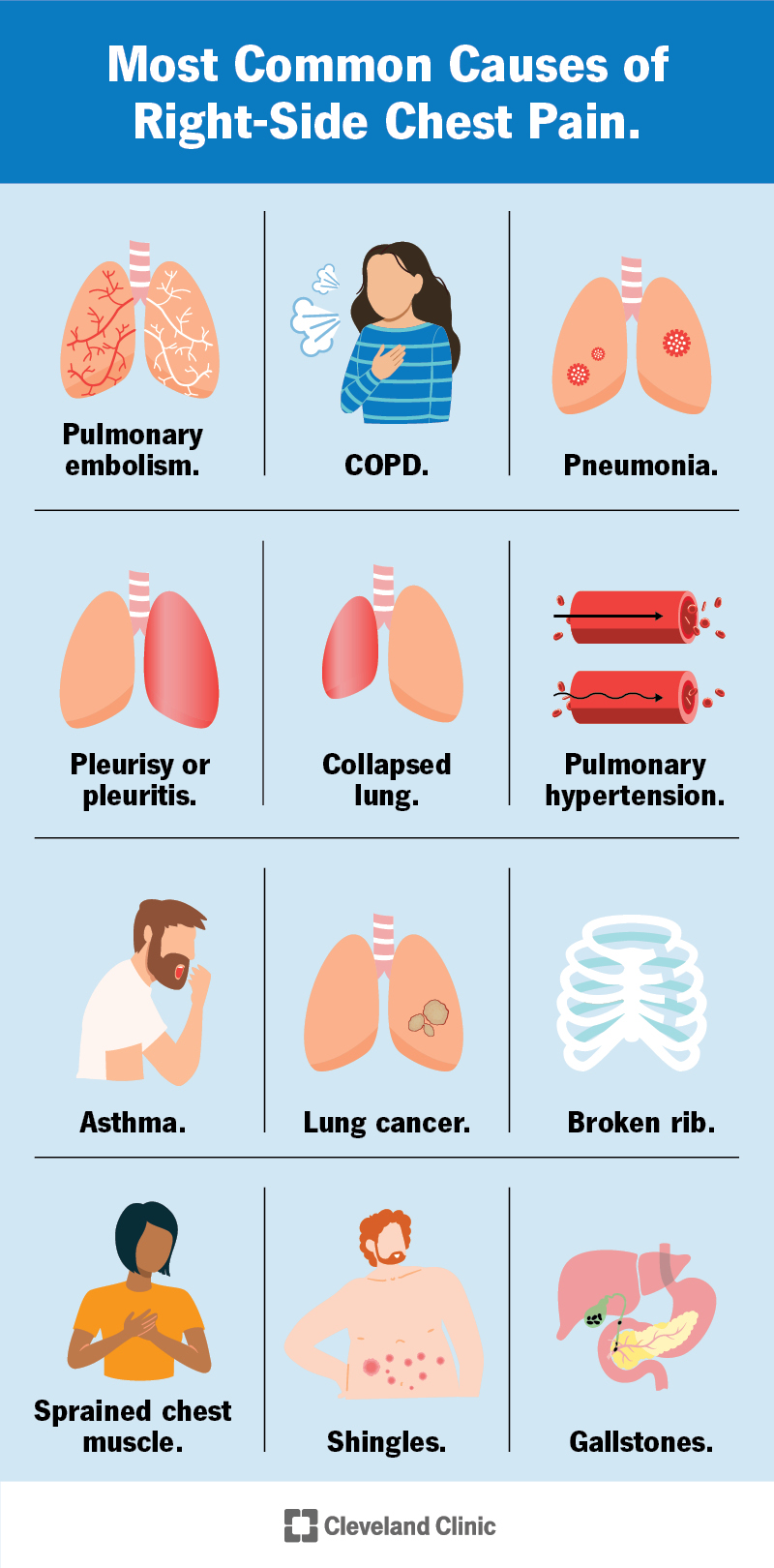
In some cases, a broken or fractured rib can be the source of chest pain. This can occur due to trauma, such as a fall or a direct blow to the chest. Rib fractures can cause severe pain, making breathing or movement difficult. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect a rib fracture.
Skeletal abnormalities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, may also contribute to chest pain. These conditions involve abnormal curvature of the spine, which can put strain on the muscles and joints in the chest area. The resulting discomfort can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the abnormalities.
Gastrointestinal Causes
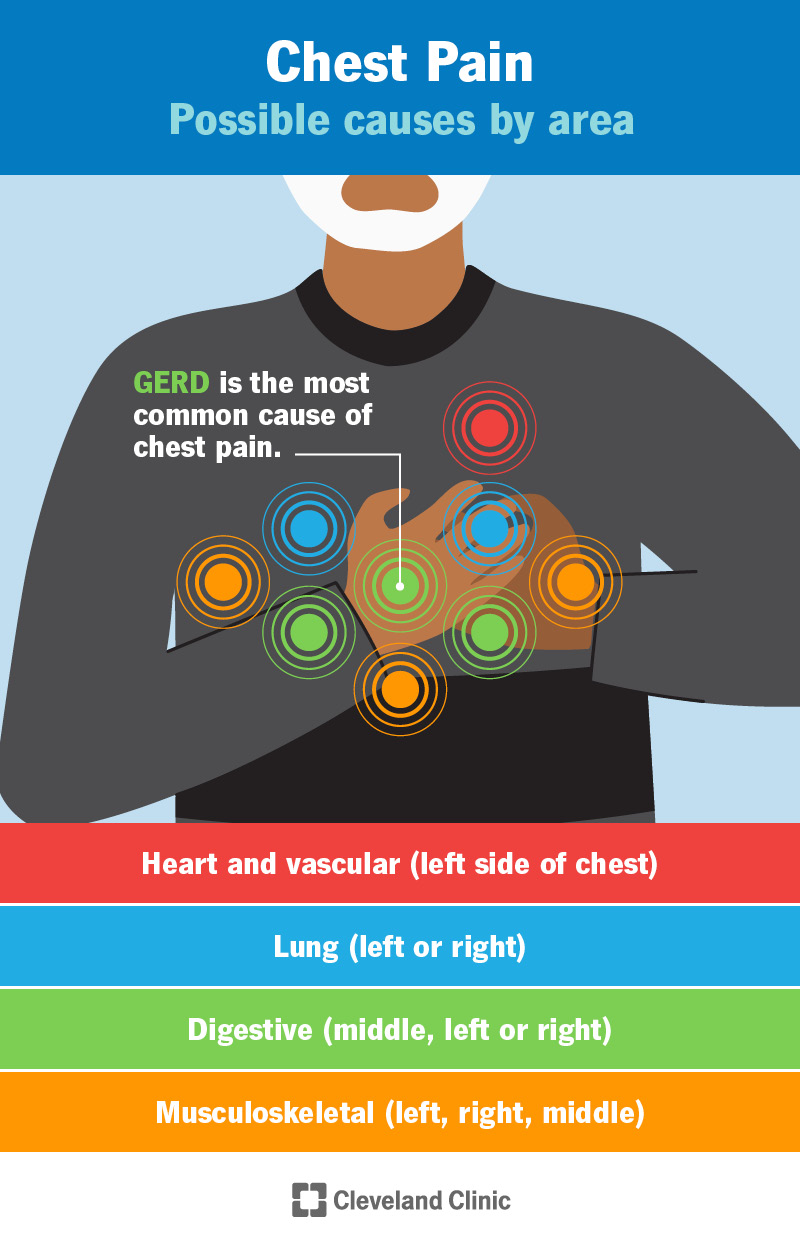
Chest pain can also originate from the gastrointestinal system. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a common digestive disorder that causes acid from the stomach to flow back into the esophagus, resulting in chest pain known as heartburn. This pain is often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest and throat.
Peptic Ulcer Disease, which occurs when there are open sores in the lining of the stomach or the small intestine, can also cause chest pain. The pain is usually described as a gnawing or burning sensation and can be felt in the upper abdomen and chest.
Gallstones, small hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, can cause sudden and severe chest pain. The pain is typically located in the upper right side of the abdomen and may radiate to the chest and back. If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition called acute pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis, inflammation of the pancreas, can also result in chest pain. The pain is often felt in the upper abdomen and may radiate to the back or chest. Pancreatitis can be caused by gallstones, heavy alcohol consumption, or certain medications.

Cardiac Causes
Chest pain is commonly associated with cardiac causes, and it is important to distinguish these causes from other conditions. Angina is chest pain or discomfort that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough blood flow. It is often described as a squeezing or pressure-like sensation in the chest and can be triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress.
Myocardial Infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when the blood supply to the heart is blocked, leading to the death of heart muscle cells. Chest pain during a heart attack is typically severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, and sweating. Prompt medical attention is crucial in this situation.
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the sac-like tissue surrounding the heart. This condition can cause sharp chest pain that worsens with deep breaths or when lying down. The pain may also radiate to the back or neck.
In rare cases, chest pain may be a result of aortic dissection, which is a tear in the lining of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. This condition requires immediate medical intervention as it can be life-threatening. Chest pain from aortic dissection is often described as a tearing or ripping sensation.
Pulmonary Causes
Various pulmonary conditions can lead to chest pain. Pneumonia, an infection that causes inflammation in the lungs, can result in chest pain. The pain is usually sharp and worsens with deep breaths or coughing. Other symptoms of pneumonia include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
Pulmonary Embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks a blood vessel. This condition can cause sudden-onset chest pain, often accompanied by shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, and lightheadedness. Immediate medical attention is necessary for this potentially life-threatening condition.
Pleural Effusion, the buildup of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, can cause chest pain. The pain is commonly described as a dull ache and may be accompanied by difficulty breathing, coughing, or a fever.
Lung Cancer is another possible cause of chest pain. The pain can be due to the tumor putting pressure on surrounding structures or spreading to nearby tissues. Lung cancer-related chest pain may be persistent and worsen over time. Other symptoms may include coughing up blood, persistent cough, and unexplained weight loss.

Respiratory Causes
Respiratory conditions can also contribute to chest pain. Asthma, a chronic lung disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, can cause chest tightness and discomfort. The pain is often accompanied by wheezing and shortness of breath.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), a progressive lung condition that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, can result in chest pain. The pain may be due to the underlying inflammation and damage to the lungs. COPD-related chest pain can be aggravated by coughing or deep breathing.
Pulmonary Hypertension, high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs, can cause chest pain as a result of the increased strain on the heart. This pain may be felt as a pressure-like sensation in the chest and can worsen with physical activity or exertion.
Pleurisy, inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the lungs, can lead to chest pain. The pain is typically sharp and worsens with deep breaths or coughing. It is often associated with an underlying respiratory infection or other inflammatory conditions.
Psychological Causes
Psychological factors can also contribute to chest pain. Anxiety is a common psychological cause, and the physical symptoms of anxiety can manifest as chest pain. The chest pain associated with anxiety is often described as a tightness or heaviness.
Panic Disorder, a type of anxiety disorder, can cause recurrent panic attacks. These attacks can include intense chest pain, often accompanied by palpitations, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom.
Depression, a mood disorder that affects millions of people, can present with various physical symptoms, including chest pain. The pain may be associated with feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or anhedonia (loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities).
Stress, whether it be related to work, relationships, or other factors, can also contribute to chest pain. Stress-induced chest pain is often described as a dull ache or pressure-like sensation.

Cardiovascular Causes
Several cardiovascular conditions can lead to chest pain. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can cause chest discomfort due to the increased strain on the heart and blood vessels. The pain may be experienced as a tightness or squeezing sensation in the chest.
Coronary Artery Disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. Chest pain, often referred to as angina, is a common symptom. It is typically described as a pressure or squeezing sensation in the chest and may be triggered by physical activity or emotional stress.
Cardiomyopathy, a disease that affects the heart muscle, can cause chest pain. The pain may be due to the weakened heart’s reduced ability to pump blood effectively. Other symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, and swollen legs or ankles.
Valvular Heart Disease, which involves abnormalities in the heart valves, can lead to chest discomfort. The pain may be felt as a pressure-like sensation and can be associated with symptoms such as fatigue, palpitations, and shortness of breath.
Digestive Causes
Several digestive conditions can cause chest pain. In addition to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) mentioned earlier, gastritis is another common cause. Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach and can cause chest pain, along with abdominal pain, nausea, and indigestion.
Esophageal Spasm, a condition characterized by uncoordinated contractions of the esophagus, can result in chest pain. The pain is often described as a squeezing or burning sensation and may be exacerbated by swallowing.
Esophageal Cancer, although relatively rare, can cause chest pain. The pain may be felt as a persistent and worsening discomfort, particularly during swallowing. Other symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, unintended weight loss, and chronic coughing.
Panic Attacks
Panic attacks are intense episodes of fear or anxiety that can cause various physical symptoms, including chest pain. Panic Disorder, a condition characterized by recurrent panic attacks, can lead to frequent experiences of chest pain. The pain is often accompanied by a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom.
Anxiety Disorders, which encompass a range of conditions related to excessive worrying and fear, can also contribute to chest pain. The pain may be a result of heightened physical arousal due to anxiety or panic.
Hyperventilation, rapid and shallow breathing that often occurs during periods of anxiety or panic, can lead to chest pain. This pain is typically described as a sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest and may be accompanied by dizziness or tingling sensations.
Lung-related Causes
Various lung-related conditions can cause chest pain. As mentioned earlier, pneumonia and pulmonary embolism can contribute to chest discomfort. Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) can also result in chest pain due to the underlying inflammation and obstruction of the airways.
It is important to note that while chest pain can be attributed to these causes, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Chest pain should never be ignored or self-diagnosed, as it can indicate a serious underlying condition. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe or persistent chest pain, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, dizziness, or fainting.