Hey, did you know that there’s been some exciting new research on juvenile diabetes? It’s like a breath of fresh air for those who are affected by this condition. This research focuses on finding more effective treatment options and potential cures, improving the lives of countless young individuals living with diabetes. From breakthroughs in insulin therapy to cutting-edge technologies, this article will dive into the latest advancements and how they can positively impact the lives of those with juvenile diabetes. So get ready to be amazed by the incredible progress being made in the field of diabetes research!
Definition of Juvenile Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Juvenile diabetes, also known as Type 1 diabetes, is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly targets and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to a deficiency in insulin, a hormone that is essential for regulating blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is commonly associated with lifestyle factors, Type 1 diabetes is not preventable and is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence.
Age of Onset
The term “juvenile diabetes” refers to the fact that this type of diabetes often manifests during childhood or adolescence. However, it is important to note that Type 1 diabetes can also develop in adulthood. In fact, about 5% to 10% of all individuals with Type 1 diabetes are diagnosed as adults. The age of onset can vary, with some individuals developing symptoms as young as a few months old, while others may not experience them until their late twenties. Regardless of age, the impact of this condition can be significant and requires lifelong management.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
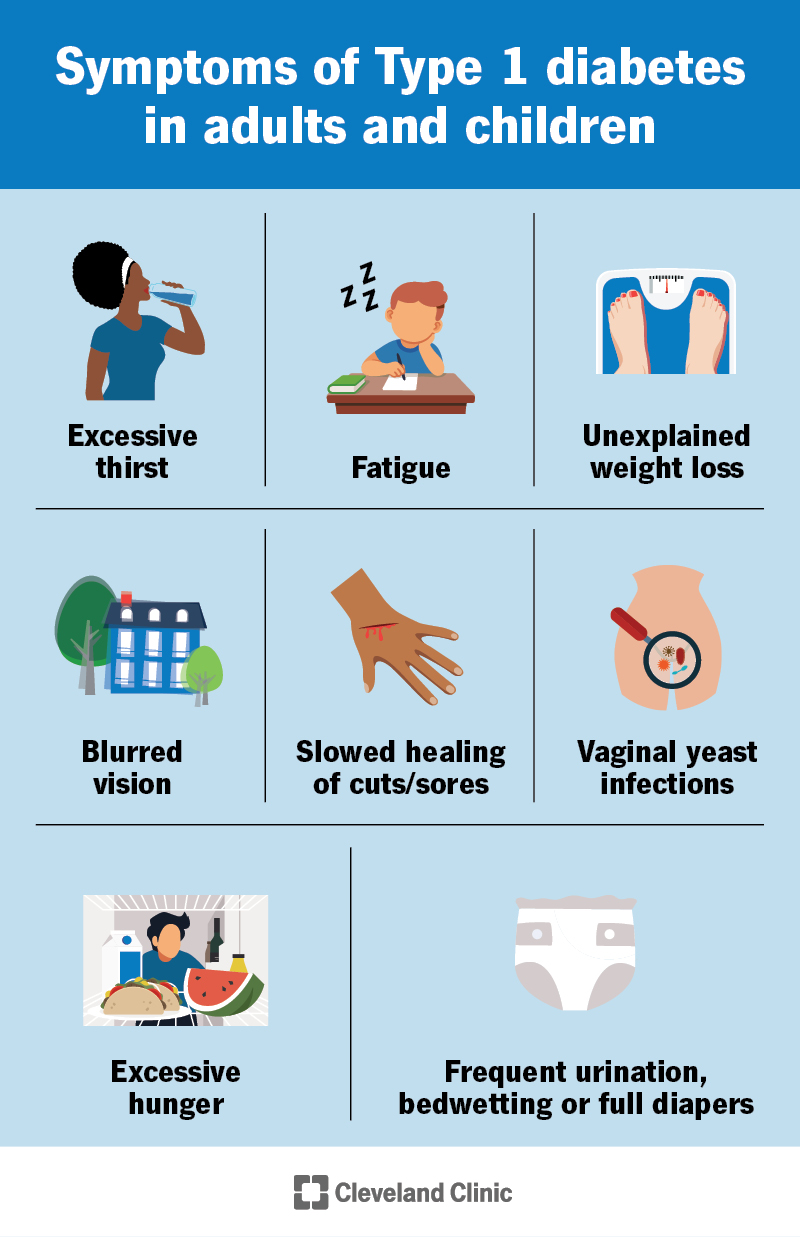
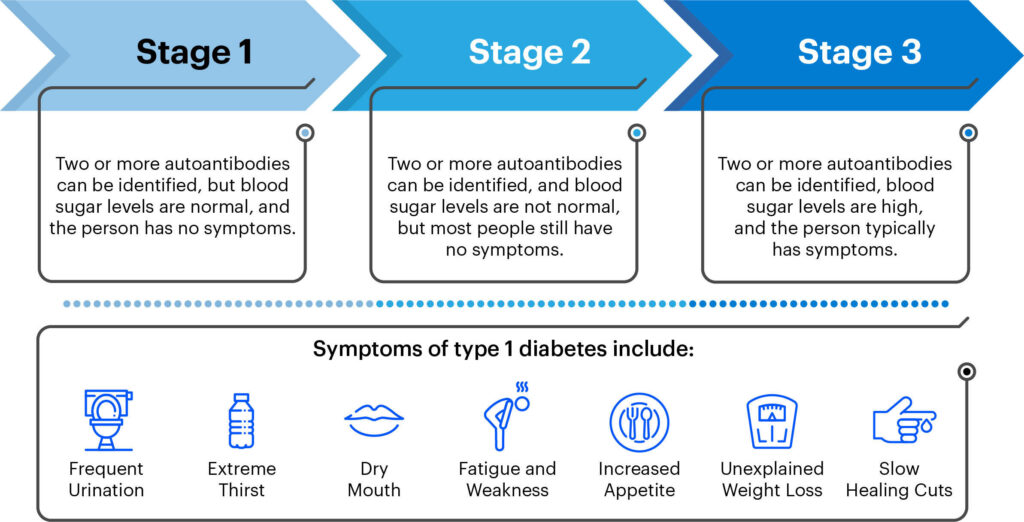
Recognizing the symptoms of juvenile diabetes is crucial for early detection and proper treatment. Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of wounds. If you or your loved one experiences these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosis Methods
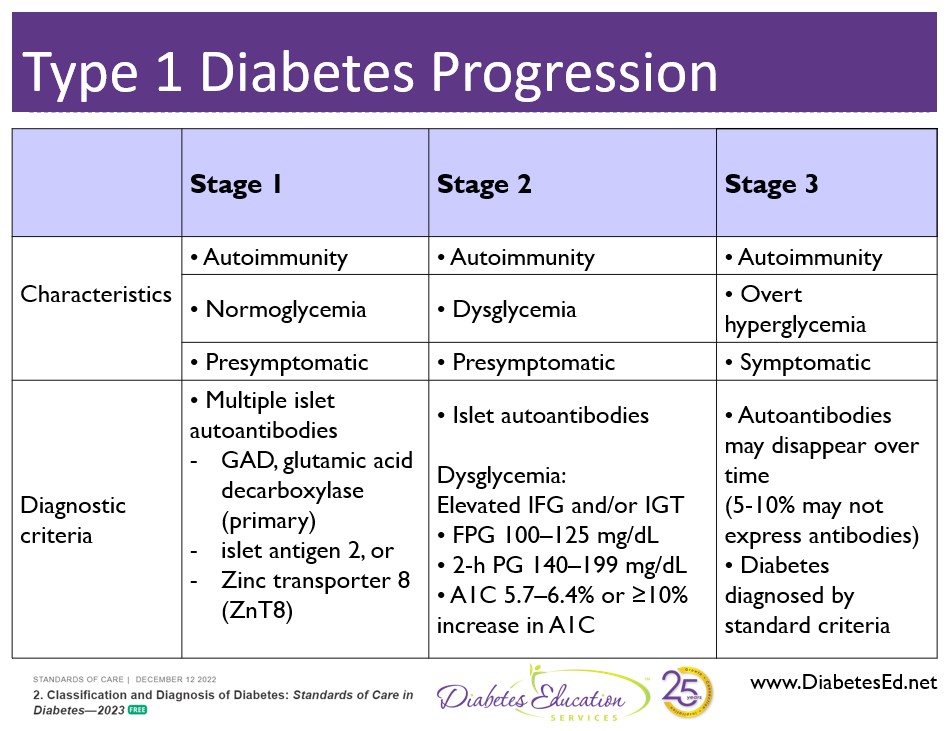
To diagnose juvenile diabetes, healthcare professionals typically perform several tests. These may include a blood test to measure blood sugar levels, a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) test to assess blood sugar control over the previous few months, and an oral glucose tolerance test to evaluate how the body responds to a glucose drink. Additionally, individuals may undergo tests to check for the presence of autoantibodies, which are markers of an autoimmune response against insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Causes and Risk Factors
Autoimmune Response
The exact cause of juvenile diabetes is unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One of the primary factors is an autoimmune response, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells. The triggers for this autoimmune response are still not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic susceptibility and exposure to certain environmental factors, such as viral infections or dietary factors during early life.
Genetics
Genetics also play a role in the development of juvenile diabetes. Certain genes related to the immune system and the functioning of the pancreas may increase the risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. However, it is important to note that not everyone with these genetic markers will develop the disease. Genetic susceptibility, combined with other factors, contributes to the overall risk.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are thought to play a significant role in the development of juvenile diabetes. Viral infections, particularly enteroviruses, have been associated with an increased risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. Additionally, early childhood dietary factors, such as the timing of introducing certain foods or breastfeeding practices, may also influence the likelihood of developing the disease. Research into these environmental factors is ongoing to better understand their impact on disease development.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
Global Prevalence
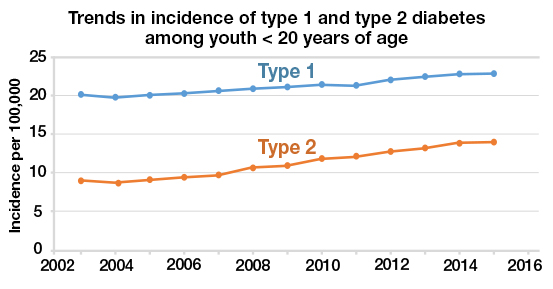
Juvenile diabetes, or Type 1 diabetes, is a global health issue. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 1.1 million children and adolescents worldwide are living with Type 1 diabetes. The prevalence of the disease varies across countries, with some regions experiencing higher rates than others. Europe and North America have the highest incidence rates, while regions such as Africa have lower rates. However, the overall prevalence is increasing worldwide.
Increase in Cases
The incidence of Type 1 diabetes has been steadily rising over the past few decades. The reasons for this increase are not yet fully understood but may involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Factors such as changes in diet, sedentary lifestyles, and changes in breastfeeding practices have been suggested as possible contributors to the rising incidence. Ongoing research is crucial to understanding the underlying causes and developing strategies for prevention and management.
Treatment Options
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for juvenile diabetes. Since the body no longer produces sufficient insulin, it needs to be replaced through injections or an insulin pump. The dosage and type of insulin required vary for each individual and may change over time. Healthcare professionals work closely with patients to determine the appropriate insulin regimen to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for managing juvenile diabetes. This involves regularly testing blood sugar levels using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system. By monitoring levels, individuals can make informed decisions about insulin dosage, diet, and physical activity to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to insulin therapy, alternative therapies are being explored to improve the management of juvenile diabetes. Some of these include closed-loop systems, also known as artificial pancreas systems, which combine continuous glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery. Dietary interventions, such as low-carbohydrate or low-glycemic index diets, are also being studied for their potential benefits in blood sugar control.
Advancements in Insulin Delivery
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small devices that deliver insulin continuously throughout the day. They consist of a reservoir of insulin, a programmable computer, and a catheter that is inserted under the skin to deliver the insulin. These pumps offer precise and customizable insulin delivery, mimicking the natural insulin release by the pancreas. They have revolutionized diabetes management, providing convenience and flexibility for individuals with juvenile diabetes.
Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop systems, or artificial pancreas systems, are an emerging technology in the management of juvenile diabetes. These systems combine continuous glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery. The glucose sensor continuously measures blood sugar levels, and the insulin pump adjusts the insulin delivery based on the real-time data. This closed-loop approach aims to maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.

Current Research on Immunotherapies
Immunotherapy Trials
Immunotherapies are being actively investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of juvenile diabetes. These therapies aim to modulate the immune system and prevent the destruction of insulin-producing cells. Some approaches focus on suppressing the autoimmune response, while others aim to induce immune tolerance to prevent the immune system from attacking the pancreatic cells. These trials hold promise for potentially slowing down or halting the progression of the disease.
Targeting Autoimmune Response
Research on immunotherapies aims to specifically target the autoimmune response responsible for the destruction of insulin-producing cells. One approach involves using monoclonal antibodies to selectively neutralize the immune cells involved in the attack. Another approach is to develop vaccines that stimulate the immune system to recognize the insulin-producing cells as “self” rather than foreign. These innovative therapies are still in the experimental stage but offer hope for more targeted and effective treatments in the future.
Genetic Studies and Personalized Medicine
Identifying Genetic Markers
Advancements in genetic studies have allowed scientists to identify specific genetic markers associated with the risk of developing juvenile diabetes. By studying these markers, researchers hope to gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of the disease and develop more personalized treatment approaches. Identifying individuals at high risk through genetic screening may also enable early intervention and prevention strategies.
Tailoring Treatment Plans
Personalized medicine aims to tailor treatment plans to an individual’s unique characteristics, including their genetic profile. By understanding the genetic factors that contribute to the development and progression of juvenile diabetes, healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions that address the specific needs of each patient. This approach holds great potential for improving outcomes and optimizing the management of the disease.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Diabetes Management
Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies are increasingly being used in diabetes management. Predictive analytics algorithms can analyze large datasets, such as blood sugar levels, insulin dosages, and dietary information, to predict future glucose levels and provide recommendations for insulin dose adjustments or lifestyle modifications. This real-time analysis can help individuals with juvenile diabetes make informed decisions to optimize their blood sugar control.
Smart Insulin Pens
Smart insulin pens, equipped with digital technology, are another innovation in diabetes management. These pens can accurately track insulin doses, time of administration, and blood sugar readings. Some smart pens can even sync with smartphone apps to provide real-time data and feedback. These devices empower individuals to manage their diabetes more effectively by providing valuable insights and simplifying the tracking of insulin usage.
Outlook and Future Developments
Potential Cure
While there is currently no cure for juvenile diabetes, ongoing research holds promise for potential breakthroughs in the future. Advances in immunotherapies, genetic studies, and regenerative medicine approaches may eventually lead to a cure or a way to prevent the disease. Investments in research and collaboration among scientists and healthcare professionals worldwide are crucial to advancing our understanding of juvenile diabetes and developing curative strategies.
Preventive Strategies
In addition to seeking a cure, efforts are also underway to develop preventive strategies for juvenile diabetes. Early identification of individuals at high risk, implementation of lifestyle interventions, and targeted immunotherapies may help delay or prevent the onset of the disease. Public health initiatives that promote healthy diets, physical activity, and education about the warning signs of diabetes can also contribute to reducing the incidence of juvenile diabetes.
As research continues to expand our understanding of juvenile diabetes, ongoing advancements in treatment options, technological innovations, and personalized medicine offer hope for improved management and better quality of life for individuals living with this chronic condition. With continued support, awareness, and collaboration, we can work towards a future where juvenile diabetes is effectively managed, and ultimately, prevented or cured.