Having Dermatitis Herpetiformis can be a challenging condition, but with the right tips and strategies, you can effectively manage it and reduce its impact on your life. This article provides valuable insights and practical advice on how to handle Dermatitis Herpetiformis, from understanding its symptoms and triggers to implementing lifestyle changes and seeking medical treatment. By following these tips and strategies, you can regain control over your skin and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
Understanding Dermatitis Herpetiformis
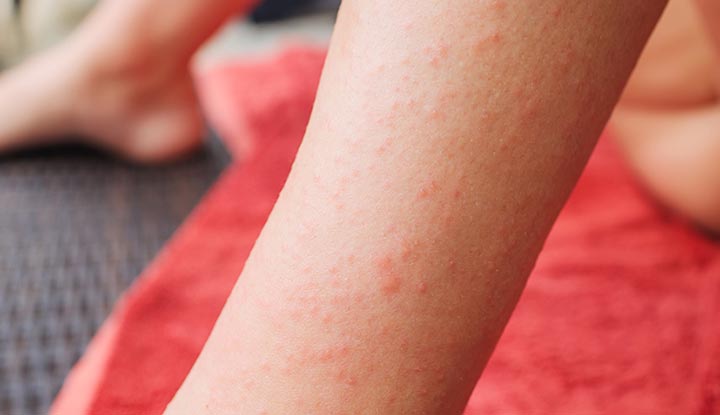
What is Dermatitis Herpetiformis?
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic skin condition that is characterized by itchy, blistering rashes. Although the word “herpetiformis” may be misleading, DH is not related to herpes at all. The name comes from the blister-like appearance of the rashes, which resembles herpes sores. DH is actually a manifestation of celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption. While celiac disease primarily affects the small intestine, DH predominantly affects the skin.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of DH is not fully understood, but it is known to be related to an immune system reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. For individuals with DH, consuming gluten triggers an immune response that leads to the formation of antibodies, specifically immunoglobulin A (IgA), which accumulate beneath the skin. These antibodies cause inflammation and damage to the skin, resulting in the characteristic blisters and intense itching.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
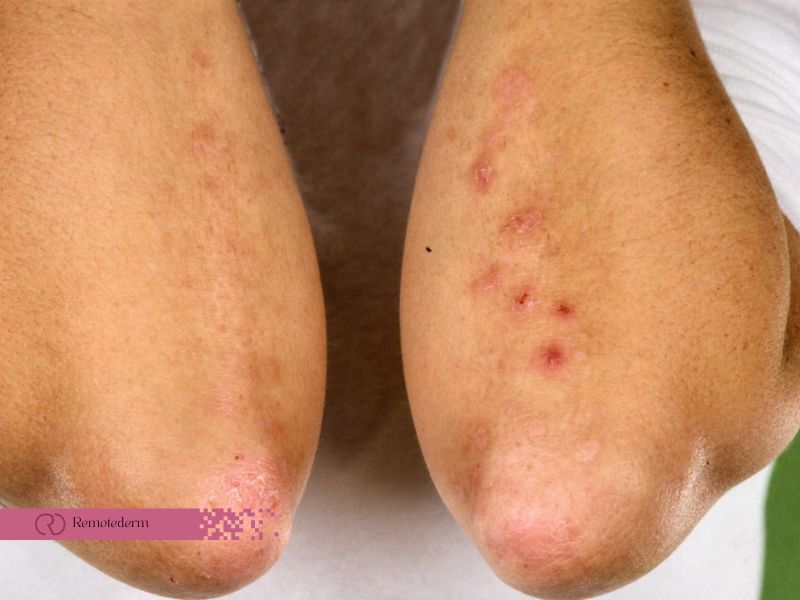
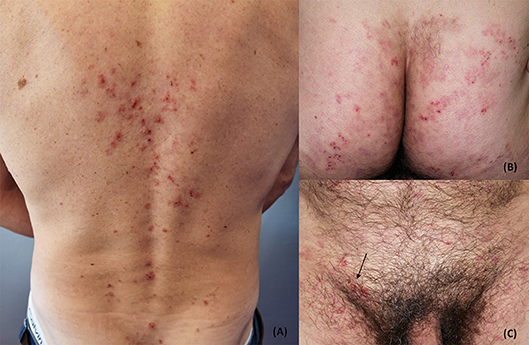
The most common symptom of DH is the presence of a red, itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters. These blisters often appear on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and back, but can occur in any area of the body. The itching can be relentless and may interfere with daily activities and quality of life. Other symptoms may include a burning sensation, stinging, or a feeling of heat in the affected areas.
Diagnosing DH usually involves a combination of clinical examination, skin biopsy, and blood tests. A dermatologist will typically examine the rash and may perform a skin biopsy to confirm the presence of IgA deposits. Blood tests for specific antibodies related to celiac disease, such as tissue transglutaminase antibodies (tTG-IgA), can also be helpful in determining the underlying cause of the skin condition.
Medical Treatments for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Topical Medications
Topical medications are often prescribed to manage the symptoms of DH. These may include corticosteroid creams or ointments, which help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. Prescription-strength corticosteroids can be particularly effective in providing relief. In some cases, topical antibiotics may be prescribed to address any secondary bacterial infections that may occur due to scratching and broken skin.
Oral Medications
For more severe cases of DH or those that do not respond well to topical treatments, oral medications may be necessary. Dapsone is the most commonly prescribed medication for DH. It helps suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation, thus relieving itching and promoting the healing of skin lesions. However, it is important to note that dapsone can have side effects, including anemia and liver toxicity, so it should be used under careful medical supervision.
Gluten-Free Diet
The primary and most effective treatment for DH is adhering to a strict gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten from your diet can help prevent further damage to the skin and alleviate symptoms. It is important to completely avoid foods that contain gluten, as even small amounts can trigger a reaction. This means avoiding wheat, barley, rye, and any products that contain these grains. Gluten can hide in unexpected places, such as sauces, dressings, and even medications, so it is crucial to read labels carefully and be vigilant.
Skin Care Tips for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Gentle Cleansing and Bathing
When managing DH, it is essential to maintain proper skin hygiene without aggravating the condition. Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid harsh soaps or hot water, as these can strip the skin’s natural oils and further irritate the rash. Gently pat the skin dry after bathing instead of rubbing, as excessive friction can exacerbate itching. It is also advisable to limit bathing time and use lukewarm water to prevent excessive drying of the skin.
Moisturizing and Soothing the Skin
Moisturizing the skin regularly is crucial for individuals with DH. Choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers that are suitable for sensitive skin. Applying moisturizer immediately after bathing or showering can help lock in moisture and soothe dry, itchy skin. If the rash is particularly severe, a cool compress or an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream may provide some relief.
Avoiding Irritants and Allergens
To prevent flare-ups and minimize skin irritation, it is important to identify and avoid potential irritants and allergens. Avoiding harsh chemicals, such as laundry detergents and fabric softeners, that can irritate sensitive skin is recommended. Additionally, it may be helpful to wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing made of natural fibers, like cotton, to minimize skin irritation and promote airflow.
Dietary Strategies to Manage Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Gluten-Free Diet
As mentioned earlier, sticking to a strict gluten-free diet is crucial for managing DH. This means avoiding foods such as bread, pasta, cakes, cookies, and most processed snacks that contain gluten. Instead, focus on consuming naturally gluten-free foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains like rice or quinoa. It is essential to read food labels carefully and be aware of hidden sources of gluten, such as certain sauces or seasonings.
Identifying Hidden Sources of Gluten
While eliminating obvious sources of gluten is a good start, it is important to be aware of hidden sources of gluten that may be present in certain products. Some food items may contain gluten due to cross-contamination during manufacturing or the use of gluten-based additives. It is always advisable to check ingredient labels and look for gluten-free certification logos whenever possible. When dining out, communicating your dietary restrictions to restaurant staff can help ensure that your meal remains gluten-free.
Supplementing with Vitamins and Minerals
A gluten-free diet can sometimes result in nutrient deficiencies, as many fortified food products contain gluten. Therefore, it may be necessary to supplement your diet with vitamins and minerals. Consult with a healthcare professional to identify any potential deficiencies and discuss appropriate supplements. Common supplements for individuals with DH may include iron, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folic acid.
Stress Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Reducing Stress Levels
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of DH, so it is important to find healthy ways to manage and reduce stress levels. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or practicing mindfulness, can help promote a sense of calm and reduce stress. Regular physical exercise, such as yoga, tai chi, or walking, can also be beneficial for both physical and mental well-being.
Improving Sleep Quality
Proper sleep is essential for overall health and can significantly impact the management of DH. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can promote better sleep quality. Avoiding stimulating activities, such as using electronic devices, right before bed can also contribute to improved sleep.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity can provide numerous benefits for individuals with DH. Exercise promotes blood circulation, which can aid in the healing process of skin lesions. It can also help manage stress, improve mood, and strengthen the immune system. However, it is important to choose low-impact activities that do not further irritate the skin, such as swimming, cycling, or gentle yoga.
Support Systems and Coping Strategies
Joining Support Groups
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with DH can be immensely helpful. Joining support groups or online communities can provide a platform to share experiences, exchange advice, and find emotional support. It can also serve as a valuable resource for learning about coping strategies and staying up-to-date on the latest research and treatment options.
Seeking Professional Help
Dealing with a chronic skin condition like DH can sometimes take a toll on mental health. If you find yourself struggling to cope with the emotional impact of the condition, do not hesitate to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can provide guidance and support in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with DH.
Educating Family and Friends
Educating your family and friends about DH can help foster understanding and provide much-needed support. Explain the nature of the condition, its triggers, and the dietary restrictions involved in managing DH. Encourage them to learn about the condition themselves and ask any questions they may have. By building awareness, you can create a supportive environment that minimizes misunderstandings and promotes empathy.
Preventing Flare-ups of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Identifying Triggers
Understanding your personal triggers can help prevent future flare-ups of DH. Keep a diary to track any patterns or correlations between your rash outbreaks and potential triggers. Common triggers may include certain foods, stress, exposure to extreme temperatures, or certain skincare products. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Avoiding Excessive Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can worsen the symptoms of DH, leading to increased itching and inflammation. Protect your skin by wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade whenever possible, and using protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves. Be cautious when using sunscreen and choose products that are labeled as “sensitive skin” or “dermatologist-tested” to minimize the risk of skin irritation.
Taking Care of Overall Health
Maintaining overall good health is essential in managing DH and preventing flare-ups. This includes getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and practicing good hygiene. It is also important to manage any underlying health conditions, such as celiac disease, to ensure overall wellness. By taking care of your general health, you can support your immune system and minimize the impact of DH on your skin.
Recognizing Complications and Seeking Medical Attention
Potential Complications
Although DH mainly affects the skin, it is important to be vigilant for any potential complications. In rare cases, DH can be associated with other autoimmune disorders, such as thyroid disease or type 1 diabetes. Additionally, long-term inflammation and blistering can lead to scarring or changes in skin pigmentation. If you notice any unusual symptoms or changes in your skin, consult with a dermatologist for further evaluation.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you suspect you have DH, it is important to seek medical attention from a dermatologist. A dermatologist can properly diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. If you already have a diagnosis of DH but experience worsening symptoms, or if new symptoms arise, it is also crucial to consult with a dermatologist. They can assess any changes, adjust your treatment plan if necessary, and address any concerns you may have.
Monitoring Overall Health
In addition to regular dermatologist visits, it is important to monitor your overall health while managing DH. Stay in touch with your primary care physician and any other specialists involved in your care to ensure a comprehensive approach to your health. Regular blood tests can help monitor any related conditions, such as celiac disease or nutrient deficiencies. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team can help optimize your management of DH.
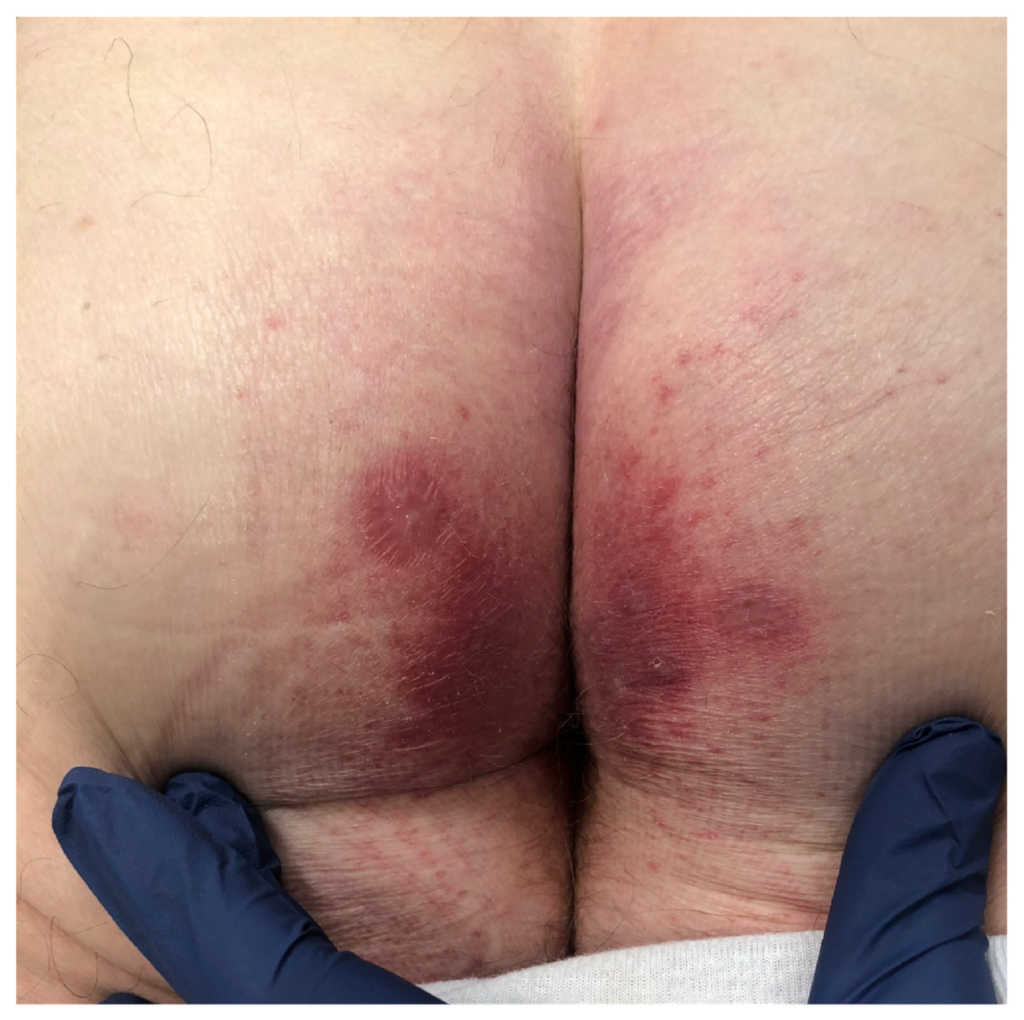
Living with Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dealing with Depression and Anxiety
Living with a chronic skin condition like DH can sometimes lead to feelings of depression, anxiety, or social isolation. It is important to recognize and address these emotions to maintain overall well-being. Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, and practicing self-care activities can all help alleviate these emotional challenges. Remember that it is normal to have ups and downs, and seeking help is a sign of strength.
Building a Supportive Network
Building a supportive network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial in managing the emotional impact of DH. Lean on your loved ones for understanding and support. Engage in activities that bring you joy and make time for hobbies and interests outside of your condition. Actively reaching out to build connections and maintain relationships can make a significant difference in your mental and emotional well-being.
Adopting a Positive Mindset
While living with DH may have its challenges, maintaining a positive mindset can help in coping with the condition. Focus on the aspects of life that bring you joy and gratitude. Practice self-compassion and remind yourself that you are doing your best in managing your health. Celebrate small victories and acknowledge your resilience. By adopting a positive mindset, you can cultivate a stronger sense of self and face challenges with optimism.
Future Developments and Research
Advancements in Treatment Options
As medical research advances, there is ongoing exploration of new treatment options for DH. Researchers are investigating alternative medications, such as oral immunosuppressants or topical calcineurin inhibitors, that may provide additional options for managing the condition. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as targeted drug delivery systems or novel topical formulations, may further improve the efficacy and convenience of treatments for DH.
Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
Although DH is associated with celiac disease, there is still much to learn about the underlying mechanisms of the condition. Further research is needed to better understand how gluten triggers the immune response in the skin and why some individuals develop DH while others with celiac disease do not. Understanding these mechanisms may lead to more targeted approaches to treatment and potentially even prevention in the future.
Clinical Trials and Studies
Participating in clinical trials and studies is a crucial way to advance the understanding and treatment of DH. By volunteering for these research endeavors, individuals with DH can contribute to the development of new therapies and benefit from access to potentially innovative treatments. Discuss with your healthcare team if there are any ongoing studies or clinical trials that you may be eligible to participate in, as they may provide new opportunities for improved management of DH.
In conclusion, managing dermatitis herpetiformis requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses medical treatments, skin care tips, dietary strategies, stress management, support systems, and a proactive approach to preventing flare-ups. By understanding the condition, adopting healthy lifestyle modifications, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with DH can live fulfilling and enjoyable lives while effectively managing their symptoms. With ongoing research and advancements, the future holds promise for improved treatment options and a deeper understanding of this complex skin condition.