Are you or someone you know managing Down’s Syndrome? In this article, we will explore the various aspects of managing Down’s Syndrome, from medical interventions and therapies to support networks and lifestyle adjustments. Whether you are a caregiver, a family member, or an individual with Down’s Syndrome, this article aims to provide you with valuable information and resources to help navigate the challenges and celebrate the unique strengths of this condition.

Understanding Down’s Syndrome
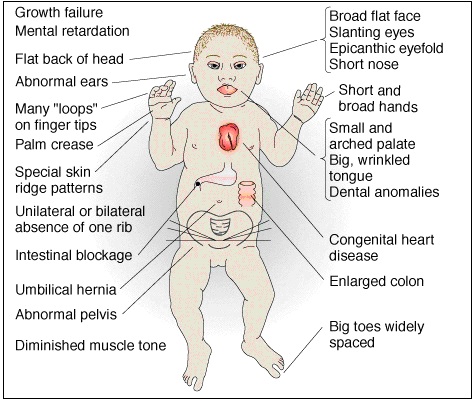
Down’s Syndrome is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and affects various aspects of a person’s physical and intellectual growth. It is important to have a comprehensive understanding of Down’s Syndrome to provide effective support and care for individuals with this condition.
Diagnosis and Medical Management
Prenatal Screening
Prenatal screening is a crucial step in diagnosing Down’s Syndrome during pregnancy. It involves a variety of tests that can help identify the likelihood of the baby having this genetic condition. Tests such as ultrasound, blood tests, and genetic screening can provide valuable information to expectant parents, allowing them to make informed decisions about their pregnancy and plan for future care.
Diagnostic Tests
If prenatal screening suggests a high probability of Down’s Syndrome, further diagnostic tests may be offered. These tests, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, involve obtaining a small sample of cells from the placenta or amniotic fluid for analysis. These diagnostic tests can accurately determine whether a fetus has Down’s Syndrome, providing parents with a definitive diagnosis to guide their decisions and prepare for the future.
Medical Interventions
Once a diagnosis of Down’s Syndrome is confirmed, appropriate medical interventions can be implemented to manage any associated health conditions. These interventions may include regular check-ups, early interventions for potential health issues, and ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal physical health. Medical management is an integral part of supporting individuals with Down’s Syndrome, and a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals and families is vital for their overall well-being.

Early Intervention and Development
Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention programs play a crucial role in supporting the development of children with Down’s Syndrome. These programs provide specialized services tailored to meet the child’s individual needs, focusing on areas such as communication, motor skills, and cognitive development. Early intervention aims to address potential delays and challenges early on, maximizing the child’s developmental potential and improving their overall quality of life.
Speech and Language Therapy
Speech and language therapy is an essential component of early intervention for individuals with Down’s Syndrome. This therapy focuses on improving communication skills, including speech production, language comprehension, and social communication. Speech and language therapists work closely with children and their families to develop personalized strategies and exercises that support the development of effective communication skills.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy helps individuals with Down’s Syndrome develop strong motor skills and improve physical capabilities. Through specialized exercises and therapeutic interventions, physical therapists address issues such as poor muscle tone, delays in gross and fine motor skills, and coordination difficulties. This therapy not only enhances physical abilities but also promotes independence and participation in everyday activities.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on facilitating independent daily living skills and improving fine motor skills in individuals with Down’s Syndrome. By working on activities such as self-care tasks, fine motor manipulation, and sensory integration, occupational therapists help children develop essential life skills. This therapy aims to enhance independence and optimize the individual’s ability to participate in various activities, both at home and in the community.
Behavioural Therapy
Behavioural therapy is an important intervention for individuals with Down’s Syndrome, specifically targeting challenging behaviours and promoting positive social interactions. Behavioural therapists use evidence-based strategies to teach appropriate behaviour, self-regulation, and social skills. By providing individuals with the tools to effectively manage their behaviour and interact positively with others, behavioural therapy fosters healthy relationships and enhances overall well-being.
Educational Support and Inclusion
Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)
Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) are essential tools for supporting the educational needs of individuals with Down’s Syndrome. These personalized plans outline specific goals and strategies to meet the unique learning requirements of each student. IEPs involve collaboration between teachers, parents, and educational specialists to create a supportive and inclusive learning environment that maximizes the individual’s educational potential.
Special Education Services
Special education services are crucial in providing tailored support to individuals with Down’s Syndrome who require additional assistance in their educational journey. Special education teachers are trained to address the individual needs of students with Down’s Syndrome, implementing appropriate teaching methodologies, and adapting curriculum materials to meet their specific learning styles. These services ensure that individuals receive the necessary support and accommodations to thrive academically.
Inclusive Classrooms
Inclusive classrooms promote a sense of belonging and foster social interactions between individuals with and without Down’s Syndrome. By integrating individuals with Down’s Syndrome into mainstream classrooms, inclusive education creates opportunities for meaningful relationships, enhances social skills, and encourages peer support. Inclusive classrooms benefit not only individuals with Down’s Syndrome but also their typically developing peers, as they learn the value of diversity and inclusive practices.
Adapting Teaching Strategies
Teachers play a crucial role in adapting teaching strategies to address the unique learning needs of individuals with Down’s Syndrome. They may utilize visual aids, hands-on activities, and multi-sensory approaches to enhance comprehension and engagement. By modifying lesson plans and instructional methods, teachers can create an inclusive learning environment that accommodates the diverse learning styles of individuals with Down’s Syndrome.
Social and Emotional Development
Building Relationships
Building relationships is a fundamental aspect of social and emotional development for individuals with Down’s Syndrome. Encouraging positive social interactions and fostering meaningful connections with peers and family members are essential for their overall well-being. Parents, teachers, and caregivers can support the development of relationships by providing opportunities for social engagement, teaching social skills, and promoting inclusive environments.
Developing Social Skills
Individuals with Down’s Syndrome may struggle with certain social skills due to cognitive and developmental differences. It is crucial to provide targeted support to develop these skills, which may include effective communication, active listening, collaboration, and conflict resolution. Social skills training, group activities, and role-playing exercises can aid in the development of these important abilities, enhancing individuals’ social interactions and promoting positive relationships.
Managing Emotions
Emotional regulation and self-management can be challenging for individuals with Down’s Syndrome, potentially leading to difficulties in expressing and managing their emotions. Providing guidance and support in understanding emotions, coping strategies, and self-advocacy skills is vital. By teaching individuals with Down’s Syndrome to recognize and manage their emotions effectively, we empower them to navigate social situations and maintain healthy emotional well-being.
Supporting Cognitive Development
Structured Learning Activities
Structured learning activities play a crucial role in supporting cognitive development in individuals with Down’s Syndrome. These activities provide a predictable routine, clear instructions, and opportunities for repetition and reinforcement. By engaging in structured learning, individuals can enhance their cognitive abilities, improve attention span, and develop problem-solving skills. This form of learning promotes independence and builds a strong foundation for lifelong learning.
Memory and Learning Strategies
Individuals with Down’s Syndrome often experience challenges with memory and learning. Implementing specific strategies, such as visual aids, mnemonic techniques, and repetition, can aid in memory retention and improve learning outcomes. Memory and learning strategies are tailored to each individual’s strengths and weaknesses, empowering them to overcome cognitive barriers and achieve their full potential.
Problem-solving Skills
Promoting problem-solving skills is essential for individuals with Down’s Syndrome to navigate daily challenges and make independent decisions. By providing opportunities for problem-solving in various contexts, individuals can enhance their critical thinking abilities, creativity, and decision-making skills. Problem-solving activities encourage individuals to analyze situations, generate solutions, and evaluate the outcomes, fostering a sense of autonomy and self-confidence.

Nutrition and Health
Balanced Diet and Nutritional Needs
Maintaining a balanced diet and meeting the nutritional needs of individuals with Down’s Syndrome is crucial for their overall health and well-being. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients and promote optimal growth and development. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to address any specific dietary concerns or considerations associated with Down’s Syndrome.
Weight Management
Individuals with Down’s Syndrome may have a higher risk of developing weight-related issues, such as obesity. It is important to monitor and manage weight through healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and guidance from healthcare professionals. Encouraging a balanced lifestyle that emphasizes nutritious food choices and maintaining an active lifestyle benefits individuals with Down’s Syndrome and promotes optimal overall health.
Healthcare and Preventive Measures
Regular healthcare check-ups and preventive measures play a crucial role in managing the health of individuals with Down’s Syndrome. Routine examinations, immunizations, and screenings can help identify potential health concerns early on and prevent complications. Collaborating with healthcare professionals to address specific medical needs and following recommended healthcare guidelines ensure individuals with Down’s Syndrome receive the necessary care to maintain their well-being.
Transition to Adulthood
Vocational Training and Employment Opportunities
Preparing individuals with Down’s Syndrome for adulthood involves providing vocational training and exploring employment opportunities. Vocational training programs equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to engage in meaningful employment, fostering independence and self-sufficiency. Identifying inclusive workplaces that facilitate the inclusion of individuals with Down’s Syndrome promotes their integration into the workforce and enhances their overall quality of life.
Independent Living Skills
Promoting independent living skills is crucial for individuals with Down’s Syndrome as they transition to adulthood. Life skills training, such as managing personal finances, cooking, cleaning, and transportation skills, empower individuals to live as independently as possible. By fostering self-care and self-sufficiency, individuals with Down’s Syndrome can have greater control over their lives and participate more actively in their communities.
Community Support and Resources
Accessing community support and resources is essential for individuals with Down’s Syndrome as they transition to adulthood. Community organizations, support groups, and specialized services can provide valuable assistance, guidance, and social connections. By leveraging community resources, individuals with Down’s Syndrome and their families can find the support they need to navigate the challenges and opportunities of adulthood.

Family Support and Advocacy
Parent Support Groups
Parent support groups play a significant role in providing emotional support, guidance, and community for families of individuals with Down’s Syndrome. These groups offer a safe space for parents to share experiences, seek advice, and connect with others who understand the unique challenges and joys of raising a child with Down’s Syndrome. By joining parent support groups, families can access valuable resources, build meaningful relationships, and draw strength from a supportive community.
Educating Family Members and Friends
Educating family members and friends about Down’s Syndrome is crucial for fostering understanding, acceptance, and support. By providing accurate information, debunking myths, and sharing personal experiences, families can contribute to a more inclusive and compassionate society. Educating family members and friends helps create a supportive network that empowers individuals with Down’s Syndrome to thrive and reach their full potential.
Advocacy Organizations
Advocacy organizations play a vital role in raising awareness, promoting inclusivity, and advocating for the rights of individuals with Down’s Syndrome. These organizations work tirelessly to ensure equal opportunities for individuals with Down’s Syndrome, influencing policy, and driving positive change. Supporting and getting involved with advocacy organizations contributes to a more inclusive society that values and embraces diversity.
Legal Rights and Protections
Understanding the legal rights and protections available to individuals with Down’s Syndrome is essential for their well-being and inclusion. Laws such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provide safeguards against discrimination and ensure access to education, employment, and public accommodations. Familiarizing oneself with these legal rights empowers individuals with Down’s Syndrome and their families to advocate for their needs and protect their rights.
Embracing Diversity and Inclusion
Promoting Acceptance and Respect
Promoting acceptance and respect is crucial for creating an inclusive society that celebrates diversity. By fostering a culture of acceptance, we empower individuals with Down’s Syndrome to be appreciated for their unique abilities and contributions. Encouraging open dialogue, educating others, and challenging stereotypes creates an environment where individuals with Down’s Syndrome can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.
Challenging Stereotypes
Challenging stereotypes associated with Down’s Syndrome is essential to promote a more positive and inclusive narrative. By dispelling misconceptions and showcasing the strengths and capabilities of individuals with Down’s Syndrome, we can reshape societal perceptions. Celebrating achievements, sharing success stories, and emphasizing the diverse talents of individuals with Down’s Syndrome contribute to a more accurate and inclusive understanding of this condition.
Creating Inclusive Communities
Creating inclusive communities involves active participation and collaboration among individuals, organizations, and institutions. By ensuring physical accessibility, providing equal opportunities, and fostering a welcoming environment, communities can empower individuals with Down’s Syndrome to participate fully in all aspects of life. Inclusive communities value diversity, embrace differences, and cultivate an atmosphere that celebrates the uniqueness and contributions of every individual.
In conclusion, understanding Down’s Syndrome is essential for providing effective support and care for individuals with this genetic condition. By addressing the various aspects of diagnosis, medical management, early intervention, education, social and emotional development, cognitive development, nutrition and health, transitioning to adulthood, family support and advocacy, and embracing diversity and inclusion, we can create a world where individuals with Down’s Syndrome can thrive and reach their full potential. Through collaboration, education, and empathy, we can build a society that values and embraces the diversity of all individuals, including those with Down’s Syndrome.