If you or someone you know is living with an endocrine system disorder, you understand the challenges it can present in everyday life. From hormonal imbalances to metabolic issues, these disorders can greatly impact your overall well-being. Fortunately, there are various medications available that can help manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with these conditions. In this article, we will explore the different types of medication used to treat endocrine system disorders and how they can improve your quality of life. So, let’s dive in and discover how medication can make a positive difference in managing these disorders.
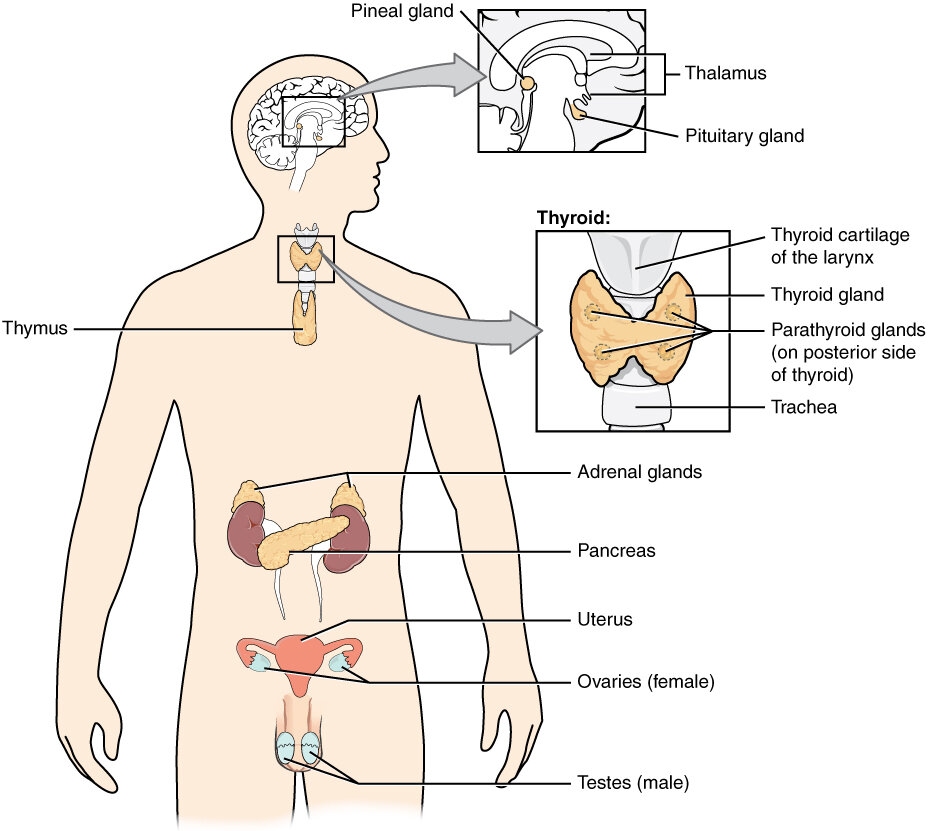
Introduction to the Endocrine System Disorders
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that produce and release hormones, which regulate various bodily functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. However, when there is an imbalance or dysfunction in the endocrine system, it can lead to a variety of disorders. Endocrine system disorders can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being, but with proper diagnosis and management, many of these conditions can be effectively treated.
Types of Endocrine System Disorders
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland that produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. This can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, irritability, and increased sensitivity to heat. Treatment for hyperthyroidism often involves medications called antithyroid drugs, which help to reduce the production of thyroid hormones. Beta-blockers can also be prescribed to manage the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism
On the other hand, hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is underactive and does not produce enough thyroid hormones. This condition can cause fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold. The most common treatment for hypothyroidism is a synthetic thyroid hormone called levothyroxine, which helps to restore normal hormone levels in the body.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body regulates blood sugar levels. There are different types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Managing diabetes typically involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy is often necessary for individuals with type 1 diabetes, while oral medications may be prescribed for those with type 2 diabetes.
Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by the overproduction of cortisol, a hormone that helps regulate metabolism and stress response. Symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome may include weight gain, muscle weakness, mood swings, and thinning skin. Medications such as glucocorticoid receptor antagonists and adrenal enzyme inhibitors can be used to manage the symptoms and reduce cortisol production in the body.
Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, low blood pressure, and darkening of the skin. Medications called glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids are typically used to replace the hormones that the adrenal glands are not producing.
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a rare condition caused by an excess of growth hormone in adults. This can lead to enlarged hands, feet, and facial features. In some cases, it may also cause health problems such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Treatment options for acromegaly include medications that lower the production of growth hormone, surgery to remove tumors, and radiation therapy to destroy tumor cells.
Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the pituitary gland, which controls the production of many hormones in the body. The treatment for pituitary tumors depends on the size and type of the tumor, but options may include medication to shrink the tumor, surgery to remove the tumor, or radiation therapy to destroy tumor cells.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by a variety of symptoms, including irregular menstrual periods, cysts on the ovaries, and elevated androgen levels. While there is no cure for PCOS, medications can be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and manage other symptoms.
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism occurs when the parathyroid glands produce too much parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels in the body. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism may include fatigue, kidney stones, and weakened bones. Treatment often involves evaluating the underlying cause and may include medication to regulate hormone levels or surgery to remove the affected parathyroid gland.
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce sufficient amounts of one or more hormones. This can lead to a range of symptoms depending on which hormones are affected. Hormone replacement therapy is typically used to replace the deficient hormones and manage the associated symptoms.
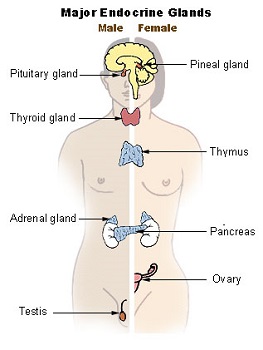
Diagnosis of Endocrine System Disorders
When it comes to diagnosing endocrine system disorders, healthcare professionals employ various methods to determine the underlying cause of symptoms. These may include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history and physical examination are often the first steps in diagnosing an endocrine disorder. Your healthcare provider will ask you about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications or supplements you are taking. They will also perform a physical examination to look for any visible signs or abnormalities.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are essential for evaluating hormone levels and identifying any imbalances. Blood tests can measure hormone levels and assess organ function, while urine tests may be conducted to measure hormone metabolites or assess kidney function. These tests can provide valuable information regarding the functioning of the endocrine system.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs, may be ordered to visualize the endocrine glands and detect any abnormalities or tumors. These tests can help in identifying the location, size, and nature of any growths or lesions within the endocrine system.
Biopsy
In cases where a tumor or abnormal growth is suspected, a biopsy may be performed. A small sample of tissue is taken for examination under a microscope to determine if it is benign or malignant. This information is crucial for determining the course of treatment.
Genetic Testing
In some cases, genetic testing may be recommended to diagnose inherited endocrine disorders or identify genetic mutations that increase the risk of developing certain conditions. Testing for specific genetic mutations can provide valuable information for prognosis, treatment options, and family planning.
Treatment Options for Endocrine System Disorders
Treatment for endocrine system disorders often involves a combination of medication, hormone replacement therapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and lifestyle changes. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type and severity of the disorder, as well as individual circumstances.
Medication
Medications are commonly used to manage endocrine system disorders. They can help regulate hormone levels, alleviate symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. Various medications are available to target specific hormonal imbalances and restore normal function within the endocrine system.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a common treatment option for hormonal deficiencies, such as hypothyroidism or hypopituitarism. HRT involves taking medications that supplement or replace the hormones that the body is not producing in sufficient amounts. This can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Surgery
Surgery is often necessary to remove tumors or growths within the endocrine system. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, minimally invasive techniques or more extensive procedures may be employed. Surgery can be curative in some cases, particularly when a tumor is the underlying cause of the disorder.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be used to destroy tumor cells or reduce the size of a tumor before or after surgery. It involves directing high-energy beams to the affected area to kill or slow down the growth of abnormal cells. Radiation therapy can be an effective treatment option for endocrine system disorders, particularly when tumors are resistant to other forms of treatment.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing endocrine system disorders. Eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, and managing stress levels can all contribute to better hormonal balance and overall well-being. Your healthcare provider may provide guidance on specific lifestyle modifications that can benefit your particular condition.
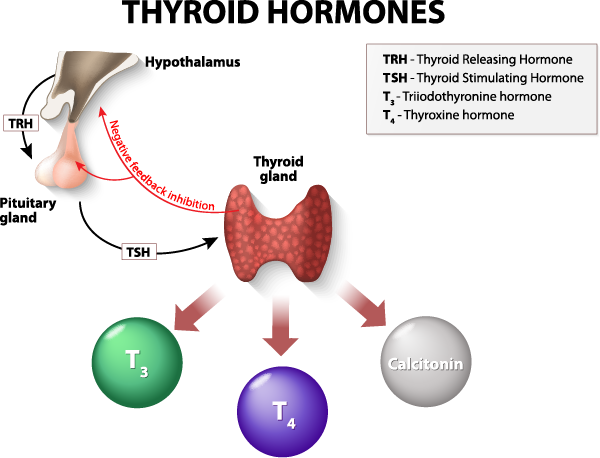
Managing Hyperthyroidism with Medication
Antithyroid Drugs
Antithyroid drugs are commonly used to manage hyperthyroidism by reducing the production of thyroid hormones. These medications work by interfering with the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones. Methimazole and propylthiouracil are the two main types of antithyroid drugs prescribed. Regular monitoring of thyroid function is necessary when taking antithyroid drugs to ensure proper management of the condition.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are medications that can help alleviate the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism. These medications work by blocking the effects of the hormone adrenaline, which can help control symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and nervousness. Beta-blockers are usually prescribed as a temporary measure until other treatments, such as antithyroid drugs, take effect.
Managing Hypothyroidism with Medication
Synthetic Thyroid Hormone
The primary treatment for hypothyroidism is synthetic thyroid hormone medication, typically levothyroxine. This medication is an exact replica of the hormone produced by the thyroid gland and helps to replace the deficient hormone levels in the body. It is important to take the medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider and undergo regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust the dosage if necessary.
Managing Diabetes with Medication
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may also be required for some individuals with type 2 diabetes when blood sugar levels cannot be adequately controlled through other means. Insulin is typically administered through injections or an insulin pump, and the dosage and schedule will be determined based on individual needs.
Oral Medications
Different classes of oral medications are available to manage type 2 diabetes. These medications work in various ways to help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, or reduce glucose production by the liver. Your healthcare provider will determine which medication or combination of medications is most suitable for your condition.
Managing Cushing’s Syndrome with Medication
Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonists
Glucocorticoid receptor antagonists are medications that work by blocking the effects of cortisol, the hormone that is excessively produced in Cushing’s syndrome. By inhibiting cortisol’s action, these medications can help alleviate the symptoms associated with the condition.
Adrenal Enzyme Inhibitors
Adrenal enzyme inhibitors are a type of medication that can reduce cortisol production by interfering with certain enzymes involved in the synthesis of cortisol. By inhibiting these enzymes, these medications help to lower cortisol levels and manage the symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome.
Managing Addison’s Disease with Medication
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are the mainstay of treatment for Addison’s disease as they help to replace the deficient cortisol levels. These medications are taken orally and provide the necessary cortisol replacement. Regular monitoring and adjustments of medication dosage are necessary to ensure optimal control of the condition.
Mineralocorticoids
In addition to glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoid replacement therapy is often required in individuals with Addison’s disease. Mineralocorticoids, such as fludrocortisone, help regulate salt and water balance in the body, which is essential for maintaining blood pressure and overall hydration.
Managing Hypopituitarism with Medication
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is the primary mode of treatment for hypopituitarism. The goal is to replace the deficient hormones using synthetic hormones that closely mimic natural hormone levels. Depending on which specific hormones are deficient, hormone replacement therapy may involve medications such as corticosteroids, thyroid hormone, sex hormones, or growth hormone.
In conclusion, the endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, and disorders within this system can have a significant impact on your health. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, many endocrine system disorders can be effectively managed. Medication, hormone replacement therapy, surgical intervention, radiation therapy, and lifestyle changes are all valuable tools in treating and managing these conditions. If you suspect you may have an endocrine system disorder, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan to help you live a healthy and balanced life.