Are you struggling to manage your insulin resistance? In this article, we will explore the various lifestyle changes and medications that can help you effectively control insulin resistance. By making small adjustments to your daily routine and incorporating the right medications into your treatment plan, you can take charge of your health and minimize the risk of complications associated with insulin resistance. With a focus on friendly guidance and practical advice, this article aims to empower you to make informed decisions about your well-being. So, let’s dive in and discover the tools and strategies that will transform your life for the better.
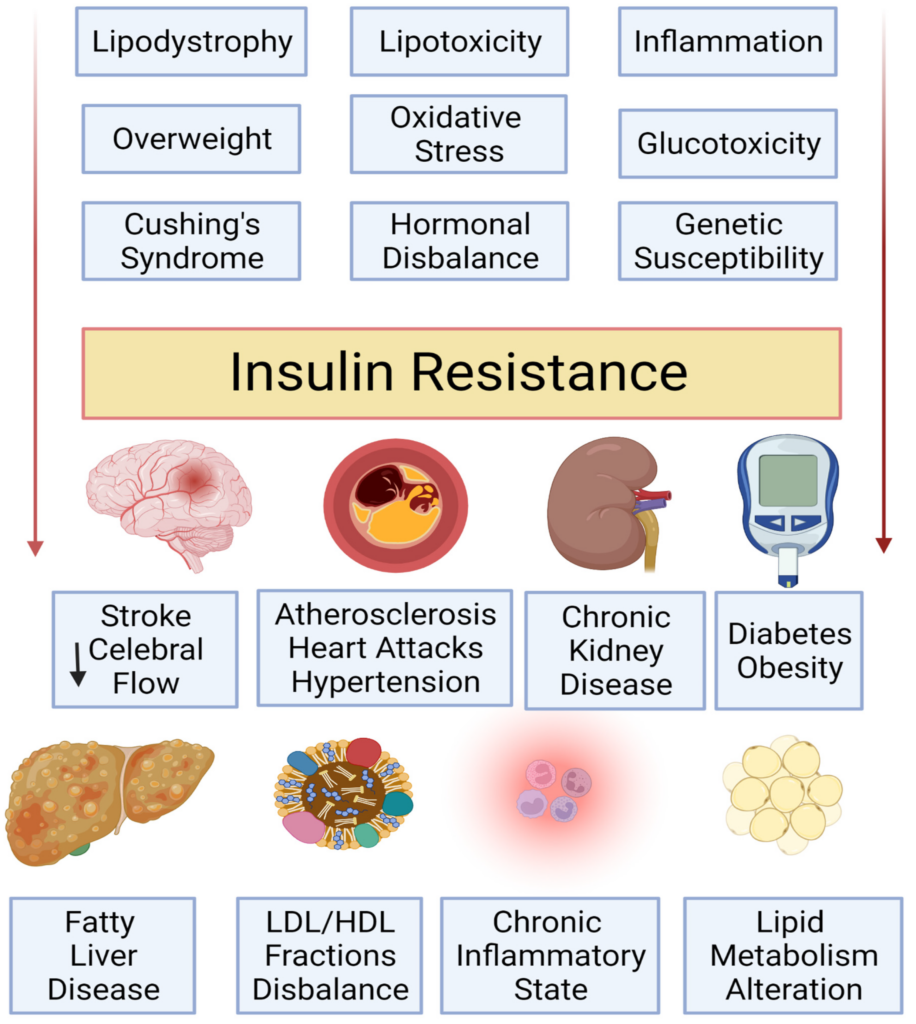
1. Understanding Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition where your body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When your cells become resistant to insulin, it can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can have a negative impact on your overall health. Understanding insulin resistance is crucial in order to take necessary steps to manage and prevent further complications.
1.1 What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is produced by the pancreas and plays a vital role in regulating the amount of glucose (sugar) in your blood. It allows glucose to enter your cells, where it is used as a source of energy. However, in cases of insulin resistance, your cells become less sensitive to the effects of insulin, resulting in elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream. This can eventually lead to the development of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and other health issues.
1.2 Causes of Insulin Resistance
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of insulin resistance. One of the primary causes is excess body weight, particularly excess abdominal fat. This type of fat releases chemicals that can interfere with insulin’s ability to function effectively. Other factors include a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet (high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars), genetics, and certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and Cushing’s syndrome.
1.3 Impact on the Body
Insulin resistance can have a profound impact on various systems in your body. When cells are resistant to insulin, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, leading to abnormally high levels in the blood. This can result in increased fat storage, especially around the waist, and contribute to weight gain. Over time, high insulin levels can lead to chronic inflammation, high blood pressure, and an increased risk of heart disease. Insulin resistance is also closely associated with other metabolic conditions, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and certain types of cancer.
2. Diagnosing Insulin Resistance
Recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance and undergoing appropriate diagnostic tests can help determine if you are experiencing this condition. Early detection is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
2.1 Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Symptoms of insulin resistance can vary from person to person and may be subtle in the early stages. However, some common signs include persistent fatigue, frequent hunger or cravings, increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight gain. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, so it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
2.2 Diagnostic Tests for Insulin Resistance
There are several tests that can be conducted to diagnose insulin resistance. One commonly used test is the fasting blood glucose test, which measures your blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. Another test, the oral glucose tolerance test, involves consuming a glucose solution and measuring blood sugar levels at specific intervals afterwards. Additionally, a test called the HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance) can provide an estimate of your insulin resistance based on fasting glucose and insulin levels.
2.3 Identifying Underlying Conditions
In some cases, insulin resistance can be a symptom or a result of an underlying medical condition. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common cause of insulin resistance in women. Identifying and addressing these underlying conditions is crucial for managing insulin resistance effectively. Your healthcare provider may recommend further tests or refer you to a specialist for a more comprehensive evaluation.
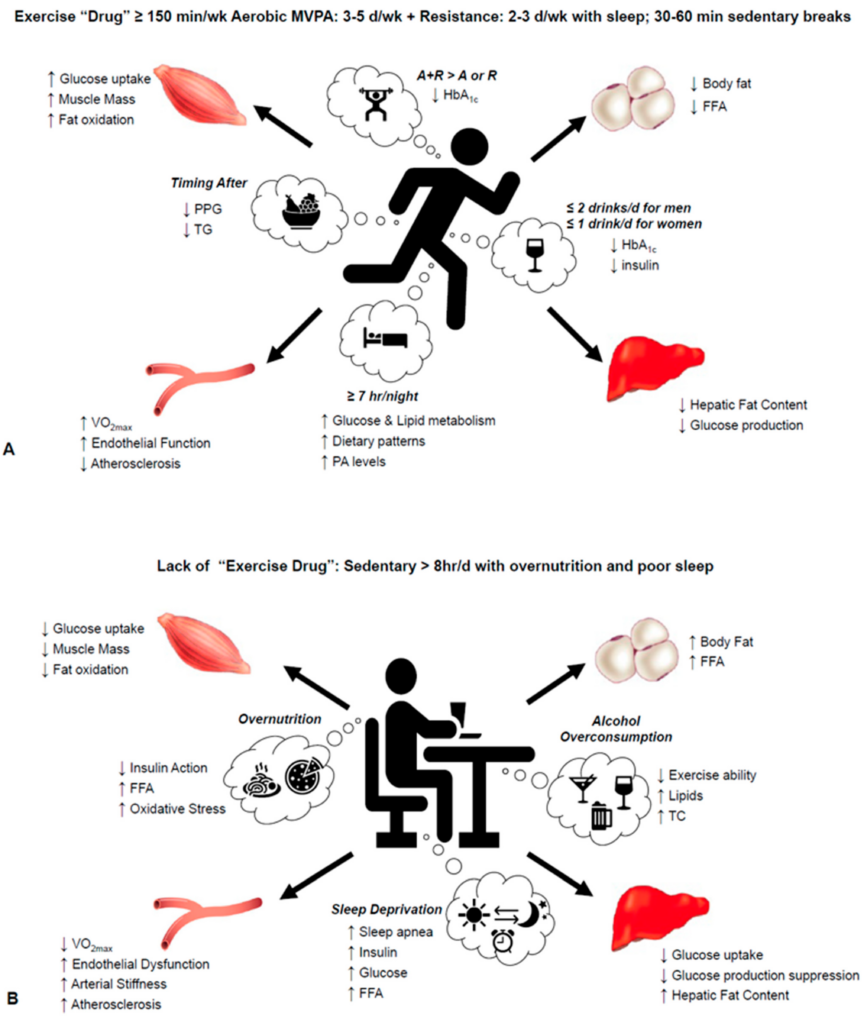
3. Lifestyle Changes for Managing Insulin Resistance
Making specific lifestyle changes is key to managing insulin resistance and improving your overall health. It is important to adopt a well-rounded approach that includes dietary modifications, regular physical activity, weight management strategies, stress reduction techniques, and prioritizing adequate sleep.
3.1 Importance of Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is crucial in managing insulin resistance. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in fiber, lean protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. Avoid or limit foods that are high in refined sugars and carbohydrates, as they can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and sources of lean protein to promote stable blood sugar levels and aid in weight management.
3.2 Role of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is vital for managing insulin resistance. Engaging in exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing your cells to utilize glucose more efficiently. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling, and strength training exercises to build lean muscle mass. Consult with a healthcare professional or a certified fitness trainer to develop an exercise plan that suits your individual needs and abilities.
3.3 Weight Management Strategies
Maintaining a healthy weight is an essential aspect of managing insulin resistance. Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can exacerbate insulin resistance. Incorporating portion control, mindful eating, and regular physical activity can aid in weight management. Work with a registered dietitian or a nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan and develop healthy habits.
3.4 Stress Reduction Techniques
Chronic stress can negatively impact insulin sensitivity and contribute to insulin resistance. Implementing stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies, can help manage stress levels. Prioritizing self-care and finding healthy ways to cope with stress can have a significant positive impact on your overall well-being.
3.5 Sleep and Insulin Resistance
Adequate sleep is crucial in managing insulin resistance. Poor sleep quality or inadequate sleep duration can disrupt hormonal balance, including insulin regulation. Strive for 7-9 hours of high-quality sleep per night. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a conducive sleep environment can promote better sleep habits.
4. Medications for Insulin Resistance
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage insulin resistance. Medications may be prescribed to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication options based on your individual needs and health status.
4.1 Insulin Sensitizers
Insulin sensitizers are medications that help improve the body’s response to insulin. They work by increasing insulin sensitivity in the cells, allowing for better glucose uptake. One commonly prescribed insulin sensitizer is metformin, which is typically used to manage insulin resistance and prediabetes. It helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin action in the liver and muscles.
4.2 Metformin
Metformin is a medication commonly prescribed for individuals with insulin resistance and prediabetes. It helps lower blood sugar levels by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving the body’s response to insulin. Metformin may also support weight management and decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication to discuss potential side effects and individual suitability.
4.3 Thiazolidinediones
Thiazolidinediones, also known as TZDs, are another class of medications used to improve insulin sensitivity. They work by targeting specific receptors in the body, enhancing the uptake and utilization of glucose by the cells. While effective, these medications can have some side effects and are usually prescribed when other treatment options have not been successful or are not suitable. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider is important while taking thiazolidinediones.
4.4 GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists are injectable medications that stimulate the production of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). GLP-1 helps regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production and decreasing the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar. These medications are typically used in individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes to improve blood sugar control and promote weight loss. Discuss the potential benefits and any necessary precautions with a healthcare provider.
4.5 DPP-4 Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors are oral medications that work by preventing the breakdown of a hormone called incretin. Incretin helps stimulate insulin release and suppresses the release of glucagon, which can lower blood sugar levels. This class of medications is often prescribed for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes who cannot tolerate other medications or who require additional control of blood sugar levels. As with any medication, it is important to review potential side effects and interactions with a healthcare provider.
4.6 Other Medications
In certain cases, healthcare providers may prescribe other medications to manage insulin resistance, particularly if there are underlying medical conditions contributing to the resistance. These medications may include anti-diabetic drugs such as sulfonylureas, meglitinides, or SGLT-2 inhibitors. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs.
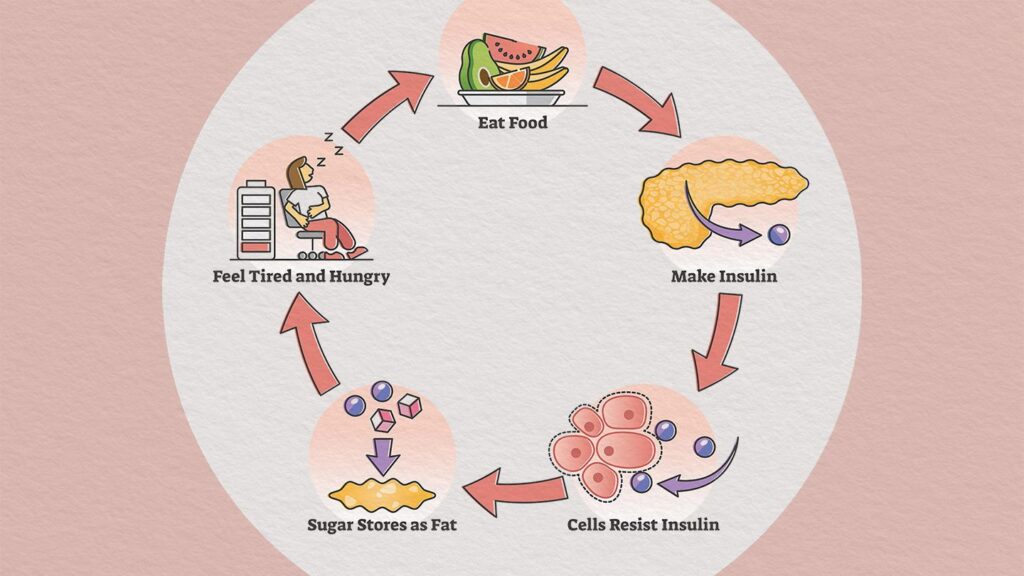
5. Combination Therapies
Depending on the severity of insulin resistance, multiple medications or a combination of medications and lifestyle changes may be prescribed. Combination therapies can target different aspects of insulin resistance and provide more effective management. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
5.1 Using Multiple Medications
In some cases, using multiple medications to manage insulin resistance may be necessary. Combining medications with different mechanisms of action, such as insulin sensitizers and incretin-based medications, can provide better blood sugar control and improve insulin sensitivity. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable combination of medications based on your individual needs.
5.2 Complementary Approaches
Complementary approaches, such as herbal supplements or alternative therapies, may be considered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for insulin resistance. However, it is important to approach these options with caution and consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating them into your treatment regimen. Some supplements or therapies may interact with medications or have potential side effects.
5.3 Personalized Treatment Plans
Each individual’s experience with insulin resistance is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to their specific needs. Personalized treatment plans take into account the individual’s medical history, overall health, lifestyle factors, and preferences. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a comprehensive and adaptable plan that incorporates lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring.
6. Monitoring and Managing Insulin Resistance
Consistent monitoring and proactive management are vital in effectively controlling insulin resistance and reducing the risk of complications. Here are some key aspects to consider:
6.1 Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
Monitoring your blood glucose levels is crucial in managing insulin resistance. Regularly measuring your blood sugar levels using a glucometer can provide valuable insights into how well your treatment plan is working and if any adjustments are necessary. Your healthcare provider will guide you on target blood sugar ranges and frequency of monitoring.
6.2 Tracking Physical Activity and Diet
Keeping track of your physical activity and diet is an essential part of managing insulin resistance. Recording your exercise routines, food intake, and portion sizes can help identify patterns and make necessary adjustments. Various mobile apps and tools are available to assist in tracking and monitoring these aspects.
6.3 Communication with Healthcare Provider
Maintaining open and regular communication with your healthcare provider is key in managing insulin resistance. Report any changes in symptoms, side effects of medications, or difficulties in adhering to the treatment plan. Your healthcare provider can guide you through any necessary modifications to your treatment and provide ongoing support.
6.4 Adjusting Medications and Dosages
Medications may need to be adjusted over time to ensure optimal management of insulin resistance. Your healthcare provider may recommend dosage changes or modifications in medication types based on your individual response and evolving health needs. It is important to follow their instructions and keep them informed of any changes or concerns.
6.5 Lifestyle Modification Reviews
Regularly reviewing your lifestyle modifications with your healthcare provider is crucial in maintaining long-term success in managing insulin resistance. Assessing the impact of dietary changes, physical activity, stress reduction techniques, and sleep habits can guide further adjustments and ensure that your treatment plan is effective in the long run.
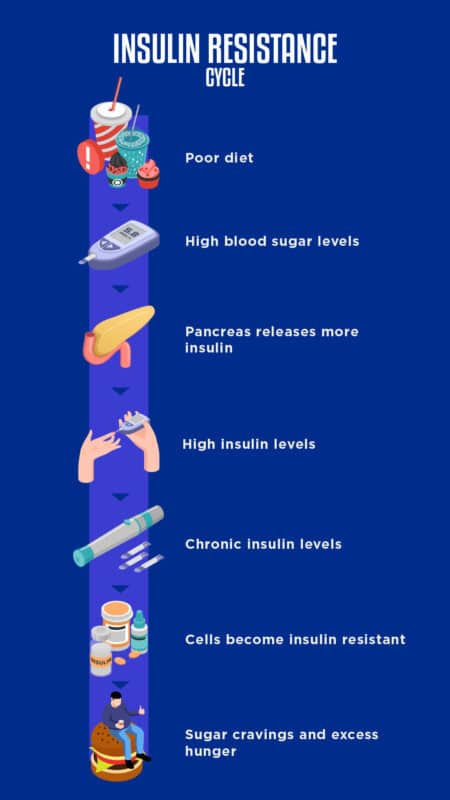
7. Risks and Complications of Insulin Resistance
Untreated or poorly managed insulin resistance can have serious long-term health consequences. Understanding the risks and potential complications associated with this condition is essential in taking proactive steps towards prevention and effective management.
7.1 Long-term Health Consequences
Insulin resistance can increase the risk of developing serious health conditions. Chronic inflammation, high blood pressure, and dyslipidemia (abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides) are common consequences of uncontrolled insulin resistance. These factors can contribute to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
7.2 Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance is a primary risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. When insulin resistance progresses, the pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin to compensate, leading to persistently high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can result in the development of diabetes, which requires ongoing management and can have significant health implications.
7.3 Cardiovascular Disease
Insulin resistance is closely linked to cardiovascular disease. High insulin levels and persistent elevation of blood sugar can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis (build-up of plaque in the arteries), heart attack, and stroke. Managing insulin resistance can help reduce the risk of developing these cardiovascular complications.
7.4 Other Associated Conditions
Insulin resistance is associated with several other medical conditions. These include non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, certain forms of cancer (such as breast and colorectal cancer), sleep apnea, and infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). By diligently managing insulin resistance, you can help reduce the risk and severity of these associated conditions.
8. Support and Resources for Managing Insulin Resistance
Managing insulin resistance can sometimes feel overwhelming, but there are numerous resources available to provide support and guidance on this journey.
8.1 Diabetes Education Programs
Diabetes education programs offer valuable resources and support to individuals with insulin resistance and diabetes. These programs provide information on managing blood sugar levels, making lifestyle changes, and understanding medication options. They may also offer guidance on monitoring and preventive measures. Consult your healthcare provider or local healthcare organizations to locate diabetes education programs in your area.
8.2 Support Groups
Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and understanding, as you connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges with insulin resistance. These groups may be facilitated by healthcare professionals, such as diabetes educators or counselors, and can offer a platform to share experiences, ask questions, and get emotional support. Local community centers, hospitals, or online platforms are excellent resources for finding support groups.
8.3 Online Resources and Apps
Numerous online resources and mobile applications are specifically designed to assist individuals in managing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. These platforms offer educational materials, tracking tools, meal planning assistance, and even virtual coaching. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine reputable and reliable sources of information and tools.
8.4 Working with Registered Dietitians
Registered dietitians are valuable professionals who can help develop personalized meal plans, provide guidance on portion control, and address nutritional concerns related to insulin resistance. They can support you in making sustainable dietary changes and offer ongoing support and accountability. Consult your healthcare provider or local health clinics to find registered dietitians with expertise in diabetes and insulin resistance management.

9. Prevention and Risk Reduction Strategies
While insulin resistance may have genetic and hormonal components, there are several strategies you can implement to reduce your risk or prevent its onset.
9.1 Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of insulin resistance can significantly impact its management and prevention of complications. Regular health check-ups, including blood glucose tests, can help identify insulin resistance at an early stage. If you experience any symptoms of insulin resistance, such as increased thirst or unexplained weight gain, consult with a healthcare provider promptly for assessment and appropriate interventions.
9.2 Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle from an early age is crucial in preventing insulin resistance. Focus on consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and prioritizing quality sleep. A healthy lifestyle not only reduces the risk of insulin resistance but also promotes overall well-being.
9.3 Regular Health Checkups
Routine health checkups play a crucial role in monitoring your overall health and identifying any underlying medical conditions contributing to insulin resistance. Regular screenings, including blood glucose and lipid panels, can help detect insulin resistance in its early stages. Collaborate with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized health checkup schedule based on your individual risk factors and medical history.
9.4 Family History and Genetic Factors
If you have a family history of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, or other related conditions, it is important to be proactive in managing your risk. Genetics can influence your predisposition to insulin resistance, but lifestyle modifications and preventive measures can still be effective in reducing your risk. Communicate your family history to your healthcare provider, as they can provide personalized guidance and recommendations.
9.5 Targeting High-Risk Groups
Certain populations, such as those with a history of gestational diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or a sedentary lifestyle, are at higher risk of developing insulin resistance. Identifying these high-risk groups and implementing targeted preventive strategies, such as early screening and personalized interventions, can help reduce the incidence and impact of insulin resistance.
10. Conclusion
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition that requires proactive management in order to prevent complications and promote overall health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and impacts of insulin resistance, as well as implementing lifestyle changes and potentially medications, you can effectively manage this condition. Regular monitoring, proactive communication with your healthcare provider, and utilization of available support and resources are essential to successfully navigate the challenges of insulin resistance. By taking control and implementing necessary precautions, you can lead a healthy and fulfilling life while managing insulin resistance effectively.