Imagine your child has been diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. While the diagnosis may be devastating, there is hope in the form of treatment. However, as you embark on this journey, it is important to understand and manage the potential side effects that may arise from the treatment. This article aims to provide you with valuable information on how to effectively manage and alleviate the various side effects that can occur during the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children.
1. Types of Treatment for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
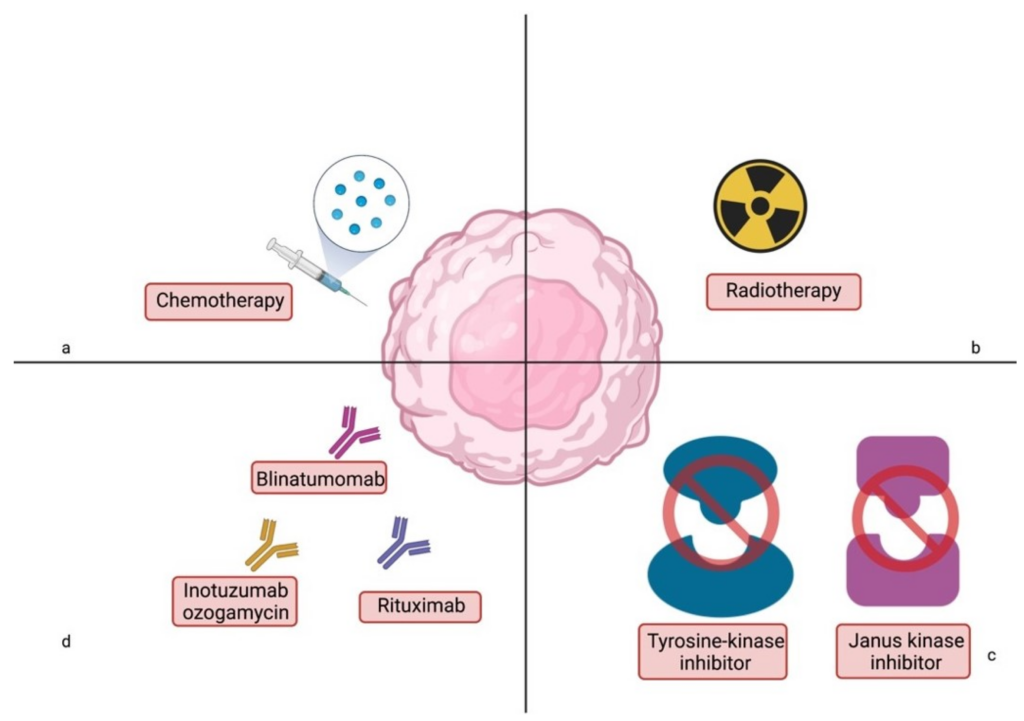
1.1 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the primary treatment option for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children. It involves using powerful drugs to kill the leukemia cells. Chemotherapy can be given through various methods, such as intravenous infusion, oral medications, or injection into the spinal fluid. The goal of chemotherapy is to eliminate the leukemia cells and achieve remission.
1.2 Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells. It is mainly used in specific situations, such as when the leukemia has spread to the brain and spinal cord or when there is a risk of disease recurrence in the central nervous system.
1.3 Stem Cell Transplantation
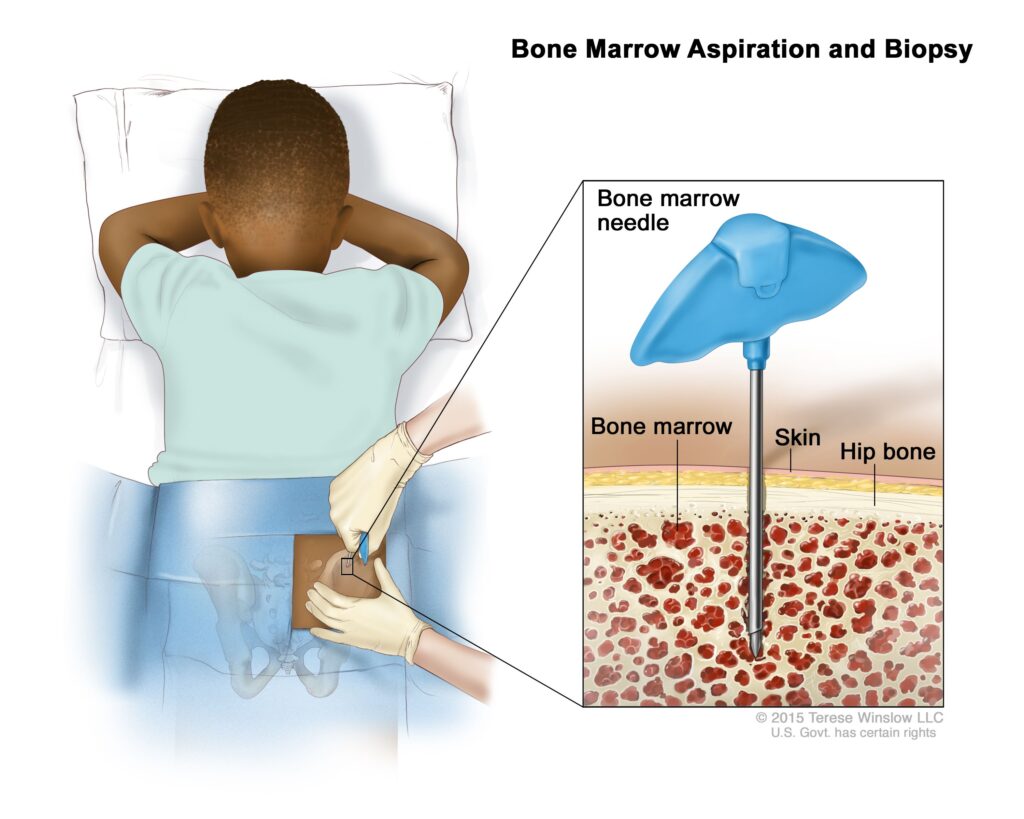
Stem cell transplantation, also known as a bone marrow transplant, involves replacing the unhealthy bone marrow with healthy stem cells obtained from a donor or the patient themselves. This procedure is typically used in high-risk cases or when the leukemia reoccurs after initial treatment. It aims to restore the normal production of blood cells.
1.4 Targeted Therapy
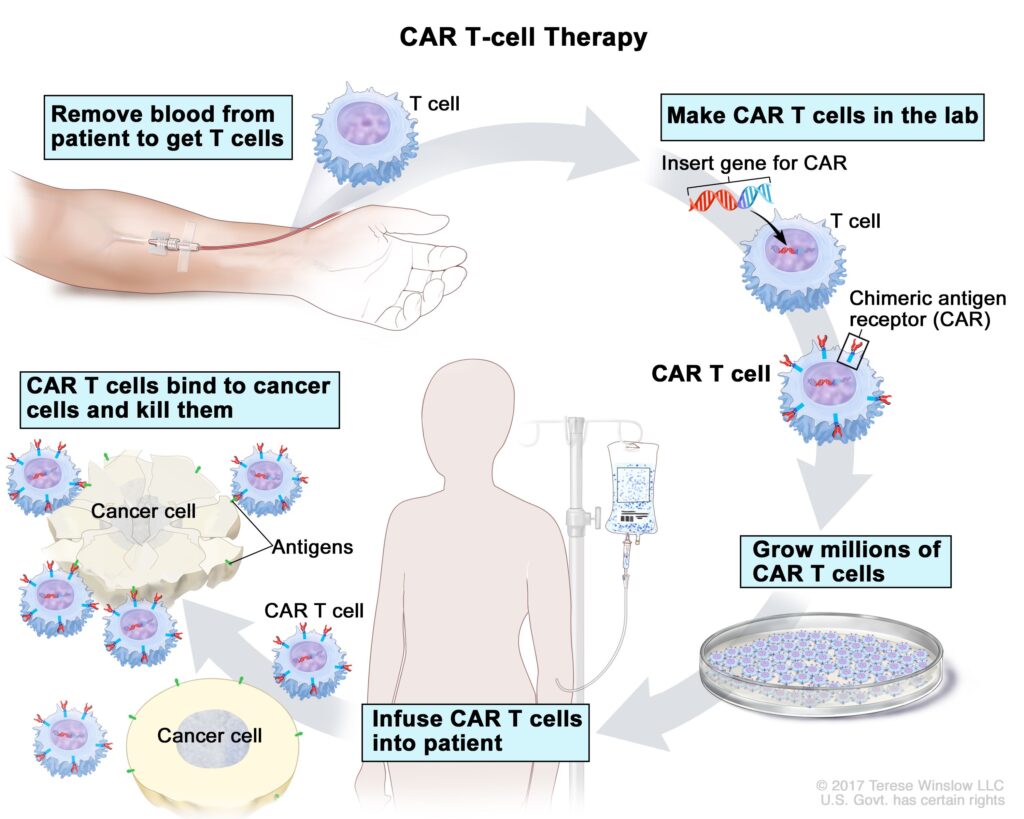
Targeted therapy uses specially designed drugs that specifically target certain molecules or genes in leukemia cells. These drugs work by interfering with the growth and division of cancer cells, causing them to die. Targeted therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of ALL, especially in cases where other treatments have been unsuccessful.
2. Common Side Effects of Treatment
2.1 Nausea and Vomiting
Chemotherapy medications can cause nausea and vomiting as side effects. These symptoms can be managed with anti-nausea medications prescribed by your healthcare team. Eating small, frequent meals and avoiding strong smells or foods that trigger nausea can also help minimize these side effects.
2.2 Fatigue
Fatigue is a common side effect of ALL treatment. It can be overwhelming and affect your daily activities. It is important to prioritize rest and conserve your energy. Taking short naps, engaging in light exercise, and asking for help when needed can all help manage fatigue.
2.3 Hair Loss
Chemotherapy can often result in temporary hair loss. While losing your hair can be emotionally challenging, remember that it is a temporary side effect. Consider using wigs, scarves, or hats to cover your head if it bothers you, and remember that it will grow back once treatment is complete.
2.4 Increased Risk of Infections
Leukemia treatment can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. To minimize the risk, it is important to practice good hygiene, wash your hands frequently, and avoid close contact with individuals who are sick. Your healthcare team may also recommend vaccines, antibiotics, or antifungal medications to further protect you.
2.5 Anemia
Anemia is a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry sufficient oxygen to the organs and tissues. ALL treatment can sometimes cause anemia as a side effect. Your healthcare team may prescribe iron supplements or recommend blood transfusions to help manage anemia and improve your energy levels.
2.6 Mucositis
Mucositis refers to the inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes lining the mouth and digestive tract. Chemotherapy drugs can cause mucositis, resulting in painful mouth sores and difficulty eating or swallowing. Maintaining good oral hygiene, using prescribed mouthwashes, and consuming soft, non-irritating foods can help alleviate these symptoms.
2.7 Growth Problems
ALL treatments, especially radiation therapy, can sometimes cause growth problems in children. Regular monitoring of growth, maintaining proper nutrition, and considering growth hormone therapy may be necessary to address any growth concerns.
2.8 Cognitive Issues
Some children undergoing ALL treatment may experience cognitive issues, such as difficulty with memory, attention, and learning. Educational support, cognitive rehabilitation programs, and accommodations at school can help mitigate these challenges and ensure academic success.
2.9 Emotional and Behavioral Changes
Dealing with a cancer diagnosis and its treatments can cause emotional and behavioral changes in children. It is essential to provide psychosocial support through counseling, therapy, and support groups. Open communication with your child’s healthcare team and involving a multidisciplinary approach can greatly assist in managing these changes.
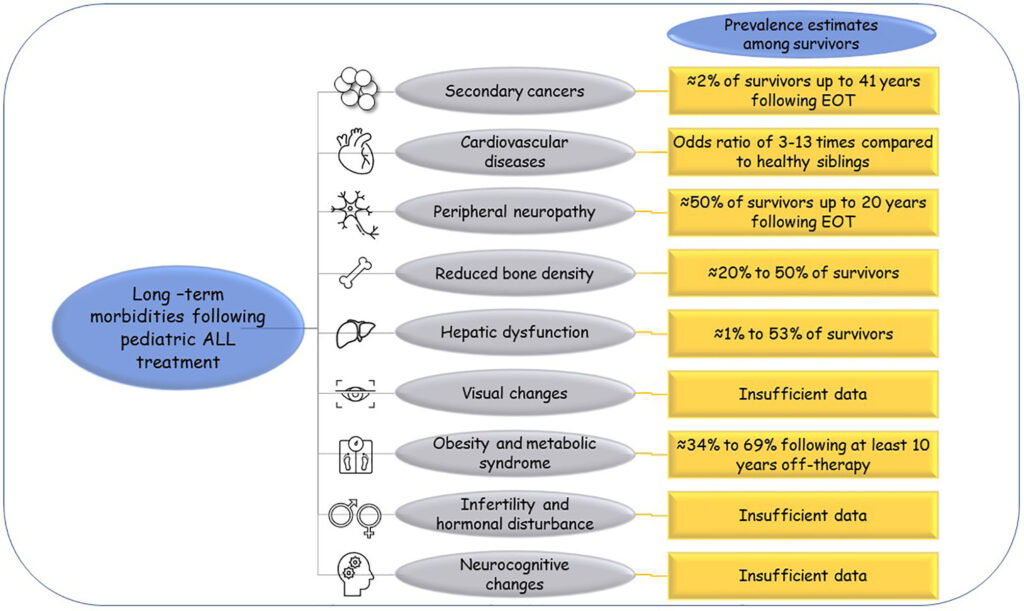
2.10 Long-Term Effects
It is important to be aware of the potential long-term effects of ALL treatments. Some individuals may experience late effects, such as heart problems, fertility issues, or secondary cancers. Regular follow-up care, screening, and survivorship programs can help detect and manage these long-term effects.
3. Coping Strategies for Managing Side Effects
3.1 Medications for Nausea and Vomiting
Prescribed anti-nausea medications can effectively manage chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It is crucial to take these medications as instructed by your healthcare team and to communicate any changes in symptoms to them.
3.2 Energy Conservation Techniques
To manage fatigue, incorporating energy conservation techniques into your daily routine can be beneficial. Prioritizing rest, pacing yourself throughout the day, and delegating tasks can help preserve energy levels and prevent exhaustion.
3.3 Wearing Wigs or Scarves
For children experiencing hair loss, wearing wigs or scarves can help boost confidence and manage the impact of this side effect. Consult with a stylist who specializes in wigs to find the best fit and style for your child.
3.4 Frequent Hand Washing and Avoiding Illness
To reduce the risk of infections, practicing frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick is essential. Encourage your child to follow good hygiene practices and educate their immediate circle on the importance of these precautions.
3.5 Blood Transfusions and Iron Supplements
To manage anemia, your healthcare team may recommend blood transfusions or iron supplements. These interventions can help improve red blood cell levels and alleviate symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
3.6 Maintaining Oral Hygiene
Adhering to proper oral hygiene practices is crucial for managing mucositis and preventing mouth sores. Regularly brushing teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using prescribed mouthwashes or rinses, and avoiding certain foods that may aggravate oral tissue can help alleviate discomfort.
3.7 Nutritional Support and Growth Hormone Therapy
Working with a registered dietitian can ensure that your child receives adequate nutrition during and after treatment. In cases of growth problems, growth hormone therapy might be recommended to support your child’s physical development.
3.8 Educational Support and Cognitive Rehabilitation
Children experiencing cognitive issues may benefit from educational support tailored to their needs. Collaborating with educators, schools, and specialists can ensure that appropriate accommodations are in place for optimal learning and cognitive development.
3.9 Psychosocial Support for Emotional and Behavioral Changes
Dealing with emotional and behavioral changes requires a comprehensive approach involving psychosocial support. Individual or family counseling, therapy, and participation in support groups can provide a nurturing environment for emotional healing and adjustment.
3.10 Regular Follow-Up and Survivorship Care
After completing treatment, regular follow-up visits with your healthcare team are important for monitoring and managing potential long-term effects. Survivorship care plans ensure a comprehensive approach to post-treatment care, addressing physical, emotional, and social well-being.
4. Supportive Care for Managing Side Effects
4.1 Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the symptoms and side effects of ALL treatments. It aims to improve the quality of life for both the child and their family. Palliative care can be provided alongside curative treatments and can help manage pain, nausea, discomfort, and other symptoms.
4.2 Pain Management
Pain management strategies, including medications and alternative therapies, can help alleviate pain during treatment. Consult with your healthcare team to develop an individualized pain management plan tailored to your child’s needs.
4.3 Physical Therapy and Exercise
Engaging in physical therapy and exercise, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and overall physical well-being. It can also aid in managing fatigue and improve mood.
4.4 Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Complementary and alternative medicine practices, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements, can provide additional support in managing side effects. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare team before incorporating these practices to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
4.5 Integrative Oncology
Integrative oncology combines conventional medical treatments with complementary approaches to provide comprehensive care. This approach may include mind-body therapies, nutritional support, and stress management techniques to enhance overall well-being.
4.6 Supportive Counseling
Supportive counseling can help children and their families navigate the emotional challenges associated with ALL treatment. Meeting with a licensed counselor or psychologist can provide a safe space to express feelings, cope with stress, and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
4.7 Support Groups and Peer Support
Participating in support groups or connecting with peers who are going through similar experiences can be immensely helpful. These platforms allow children and their families to share their journey, gain insights, and find support from others who understand their unique challenges.
4.8 Financial and Social Services
Cancer treatment can be financially and socially challenging for families. Seeking assistance from social workers or financial counselors can help alleviate some of these burdens. These professionals can guide you in accessing available resources and programs for financial and social support.
4.9 Nutrition and Diet
A well-balanced and nutritious diet plays a vital role in managing the side effects of ALL treatments. Working with a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized nutrition plan to meet your child’s specific dietary needs during and after treatment.
4.10 Sleep Management
Ensuring adequate sleep is important for overall well-being. Establishing a bedtime routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and addressing any sleep disturbances with your healthcare team can help promote better sleep quality.
5. Communication and Collaboration with the Healthcare Team
5.1 Open and Honest Communication
Maintaining open and honest communication with your child’s healthcare team is crucial throughout their treatment journey. Clear and effective communication ensures that all concerns are addressed promptly, allowing for better management of side effects and overall treatment experience.
5.2 Regularly Discussing Side Effects
Regularly discussing and reporting side effects to your healthcare team is essential for timely intervention and management. Be vigilant in observing any changes in your child’s well-being and communicate them promptly to your healthcare provider.
5.3 Reporting and Monitoring Symptoms
Keeping track of your child’s symptoms and reporting any new or worsening symptoms is important for their care. This information allows your healthcare team to closely monitor their condition and adjust treatment strategies as necessary.
5.4 Seeking Second Opinions
If you have concerns or uncertainties about your child’s treatment plan, seeking a second opinion can provide additional insights and peace of mind. Consulting with another expert in pediatric oncology can help you make informed decisions about your child’s care.
5.5 Researching and Advocating for Best Practices
Being proactive in researching the latest developments and best practices in ALL treatments can empower you as an advocate for your child. Stay informed and engage in discussions with your healthcare team to ensure the best possible care.
5.6 Involving Psychosocial Team in Treatment
Including a psychosocial team, such as social workers, psychologists, or child life specialists, in your child’s treatment can provide invaluable support. These professionals can address emotional, social, and psychological needs and help your child navigate the challenges of ALL treatment.
5.7 Collaborating with School and Teachers
Maintaining open lines of communication with your child’s school and teachers is crucial for educational continuity during treatment. Collaborate with the school to establish appropriate accommodations and support services tailored to your child’s specific needs.
5.8 Engaging in Shared Decision-Making
Engaging in shared decision-making with your healthcare team ensures that all parties have a voice in the treatment plan. It promotes collaboration, mutual understanding, and the best possible outcomes for your child.
5.9 Participating in Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can offer access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancing the field of pediatric oncology. Discuss with your healthcare team if participating in a clinical trial is a viable option for your child.
5.10 Transitioning to Survivorship Care
As your child completes their treatment, transitioning to survivorship care is crucial for long-term wellness. Collaborate with your healthcare team to develop a survivorship care plan that addresses ongoing healthcare needs, monitoring for late effects, and psychosocial support.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Managing Side Effects of Treatment for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children
How Long Can You Live With Leukemia With Treatment, Long-term Side Effects Of Leukemia Treatment, Side Effects Of Arsenic Treatment For Leukemia, Side Effects Of Chemotherapy For Leukemia, Side Effects Of Leukemia Treatment, Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy For Leukemia, Side Effects Of Radiation Treatment For Leukemia, Side Effects Of Targeted Therapy For Leukemia, Side Effects Of Treatment For Leukemia, Side Effects Treatment Childhood Leukemia