Myositis, a condition that causes inflammation of the muscles, can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. As a nurse, it is crucial to understand the key considerations and effective nursing management strategies for individuals with myositis. From providing personalized care plans to monitoring medication effectiveness, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to support and improve the well-being of patients with myositis.
Assessment and Diagnosis
Patient History
During the assessment and diagnosis phase, obtaining a thorough patient history is crucial in order to understand the specific details of the individual’s condition. Gathering information about the onset and progression of symptoms, any potential triggers or exacerbating factors, and any previous medical treatments or interventions can provide valuable insight into the patient’s current health status. Additionally, exploring the patient’s family history for any genetic predispositions or similar conditions can help guide the diagnostic process.
Physical Examination
Conducting a comprehensive physical examination is an essential component of assessing and diagnosing myositis. The physical examination should focus on evaluating muscle strength, range of motion, and any noticeable muscle abnormalities such as weakness or atrophy. Assessing the skin for any rash or changes in color is also important, as certain types of myositis can present with characteristic dermatological findings. Furthermore, performing a thorough neurological examination can help identify any associated neurological deficits or complications.
Laboratory Tests
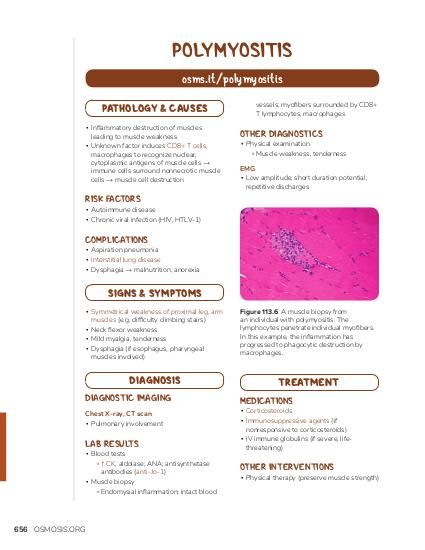
Laboratory tests play a crucial role in diagnosing myositis and evaluating the extent of the disease. Blood tests such as creatine kinase (CK) levels can help assess the degree of muscle inflammation and damage. Other laboratory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and antinuclear antibodies (ANA), may also be ordered to rule out other underlying conditions and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s overall health status.
Imaging Studies
In addition to physical examination and laboratory tests, imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound can be valuable tools in the assessment and diagnosis of myositis. These imaging modalities can help visualize muscle inflammation, identify areas of muscle damage, and assess the extent of the disease. Imaging studies can also be used to monitor disease progression and response to treatment over time.
Treatment and Medications
Immunosuppressive Drugs
Immunosuppressive drugs are a cornerstone of treatment for myositis. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, which helps to reduce inflammation and prevent further muscle damage. Commonly prescribed immunosuppressive drugs include corticosteroids, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil. The specific choice and dosage of immunosuppressive drugs will depend on the individual patient’s condition and response to treatment.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are widely used in the treatment of myositis due to their potent anti-inflammatory properties. These medications help to control inflammation in the muscles and alleviate symptoms. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can be associated with significant side effects, such as osteoporosis, weight gain, and an increased risk of infection. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to closely monitor patients who are taking corticosteroids and adjust the dosage as needed to minimize side effects.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of myositis. A skilled physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to help improve muscle strength, increase range of motion, and enhance functional abilities. Physical therapy sessions may include stretching exercises, resistance training, and aerobic conditioning. Additionally, physical therapists can provide education on proper body mechanics and teach patients energy conservation techniques to optimize their physical functioning.
Pain Management
Pain is a common symptom experienced by individuals with myositis, and effective pain management strategies are essential to enhance patients’ quality of life. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, stronger pain medications such as opioids may be necessary to control severe pain. Additionally, non-pharmacological approaches such as heat or cold therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and relaxation techniques can also be beneficial in managing pain.
Assistive Devices
For individuals with significant muscle weakness or functional limitations, assistive devices can be invaluable in promoting independence and improving quality of life. Devices such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs can provide stability and support during ambulation. Adaptive equipment, such as utensils with built-up handles or reachers, can assist individuals with activities of daily living. Occupational therapists and physical therapists play a crucial role in evaluating the specific needs of each patient and recommending appropriate assistive devices.
Monitoring and Management
Vital Signs
Regular monitoring of vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature, is important to assess the patient’s overall health status and detect any potential complications. Changes in vital signs can indicate infection, cardiovascular compromise, or other systemic problems that may require immediate intervention.
Symptom Assessments
Ongoing assessment of symptoms is essential in managing myositis. Monitoring and documenting the patient’s pain levels, muscle strength, range of motion, and overall functional status can help identify trends and guide treatment adjustments. Assessing symptoms such as fatigue, skin changes, and respiratory difficulties can also provide valuable information about disease progression and help identify any potential complications.
Medication Adherence
Ensuring medication adherence is critical in managing myositis effectively. Patient education regarding the importance of taking medications as prescribed, understanding potential side effects, and the risks associated with non-adherence is crucial. Healthcare providers should regularly assess and address any barriers to medication adherence and collaborate with patients to develop strategies to enhance compliance. Tools such as pill organizers, medication reminders, and involving family members or caregivers can also support medication adherence.
Patient Education
Empowering patients with knowledge and understanding about their condition is a vital component of managing myositis. Providing comprehensive patient education regarding the disease process, treatment options, potential complications, and self-management strategies can help individuals take an active role in their healthcare. Patients should be informed about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, adhering to medication regimens, managing symptoms, and when to seek medical assistance. Additionally, providing educational materials and resources can further support patients in their journey with myositis.
Preventing Complications
Infection Control
Infection control measures are particularly important for patients with myositis due to their increased susceptibility to infections. Educating patients about proper hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and avoiding close contact with individuals who have an active infection is crucial. Additionally, ensuring adherence to appropriate vaccination schedules, including annual influenza and pneumonia vaccines, can help prevent infectious complications.
Skin Care
Individuals with myositis are vulnerable to skin problems, including dermatomyositis-specific rashes and pressure ulcers. Implementing a comprehensive skin care plan is essential to maintain skin integrity and prevent complications. Regular assessment of the skin for any signs of breakdown or infection, proper hygiene practices, and the use of moisturizers can support skin health. Educating patients on the importance of protecting their skin from excessive sun exposure and using appropriate sunscreens can also minimize the risk of skin-related complications.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Prophylaxis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a potential complication of myositis, especially in individuals with immobility and prolonged bed rest. Implementing measures to prevent DVT, such as early mobilization, leg exercises, and intermittent pneumatic compression devices, can help reduce the risk. Educating patients about the signs and symptoms of DVT, including pain and swelling in the lower extremities, is essential to facilitate early detection and prompt treatment.
Respiratory Support
Respiratory complications can occur in individuals with myositis, particularly in those with involvement of the respiratory muscles. Monitoring respiratory function through regular assessments, including measuring oxygen saturation levels and assessing lung sounds, is important in detecting any respiratory deterioration. Providing respiratory support, such as supplemental oxygen therapy or non-invasive positive pressure ventilation, may be necessary to maintain adequate oxygenation and prevent respiratory failure.

Psychosocial Support
Emotional Support
Living with a chronic condition like myositis can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being. Providing emotional support to patients and their families is crucial to address the psychosocial aspects of the disease. Nurses can play an active role in offering empathy, active listening, and validation of patients’ feelings and concerns. Referring patients to support groups, counseling services, or mental health professionals can also be beneficial in promoting emotional well-being.
Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies is essential for individuals with myositis to manage the challenges associated with the condition. Nurses can help patients explore and implement various coping mechanisms, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness exercises, and stress management strategies. Encouraging patients to engage in hobbies, activities they enjoy, and maintaining social connections can also contribute to their overall well-being and resilience.
Social Work Referral
Social workers play a vital role in addressing the complex social and practical issues that may arise for individuals with myositis. Referring patients to social workers can help address financial concerns, connect patients with community resources, facilitate support group participation, and provide assistance with navigating the healthcare system. Social workers can also address important psychosocial factors, such as housing stability, employment issues, and caregiver support, to enhance patients’ overall quality of life.
Dietary Considerations
Nutritional Assessment
Assessing the nutritional status of individuals with myositis is important to identify potential deficiencies and optimize their overall health. Conducting a comprehensive nutritional assessment, including dietary intake, weight history, and body composition analysis, can help identify any nutritional imbalances or barriers to a healthy diet. Collaboration with a registered dietitian is beneficial in developing personalized nutrition plans tailored to the individual’s specific needs and nutritional goals.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with myositis, as excessive weight can place additional strain on weakened muscles and joints. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can help develop personalized weight management plans that take into consideration the individual’s specific nutritional needs, physical abilities, and preferences. Encouraging a balanced diet, portion control, and regular exercise can support healthy weight management.
Supplement Recommendations
Supplements may be recommended for individuals with myositis to address specific nutritional deficiencies or support overall health. Collaborating with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can help identify any necessary supplementation and ensure appropriate dosages. Common supplements that may be considered include vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and calcium, depending on the individual’s specific needs and lab results.

Patient Safety
Fall Prevention
Individuals with myositis are at an increased risk of falls due to muscle weakness and balance impairments. Implementing fall prevention strategies is essential to minimize the risk of injuries. This may include removing hazards from the environment, ensuring adequate lighting, installing handrails, and encouraging the use of assistive devices. Promoting regular exercise to maintain muscle strength and balance, as well as providing patient education regarding fall prevention techniques, can also be beneficial.
Assistance with Activities of Daily Living
Assisting individuals with myositis in activities of daily living (ADLs) is important to promote their safety and independence. Collaborating with occupational therapists can help identify any areas of difficulty in self-care tasks such as bathing, dressing, and meal preparation. Occupational therapists can provide valuable recommendations on adaptive equipment and techniques to maximize independence and functional abilities.
Multidisciplinary Team Collaboration
Physicians
Effective collaboration with physicians is crucial in managing myositis comprehensively. Regular communication and coordination with the medical team can help ensure optimal treatment plans, coordinate medication adjustments, and address any emerging concerns or complications. Nurses can serve as advocates for patients, facilitating open lines of communication between patients and physicians to promote continuity of care.
Physical Therapists
Physical therapists are integral members of the multidisciplinary team involved in the care of individuals with myositis. Collaborating closely with physical therapists allows for individualized exercise programs and rehabilitation strategies to be designed to address muscle weakness, improve mobility, and enhance overall physical functioning. Nurses can work collaboratively with physical therapists to help patients adhere to recommended exercise regimens and monitor their progress.
Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists play a vital role in addressing the functional limitations and challenges associated with myositis. Collaborating with occupational therapists can help assess and address any difficulties with activities of daily living, work-related tasks, and leisure activities. Working together, nurses and occupational therapists can develop strategies to enhance patient independence and improve their ability to engage in meaningful activities.
Pharmacists
Pharmacists collaborate closely with the healthcare team, including nurses, in managing medication regimens for individuals with myositis. They play a crucial role in medication management, including medication reconciliation, monitoring for drug interactions, and providing patient education on medication administration. Communication between nurses and pharmacists is essential to ensure patient safety, optimize medication therapy, and address any medication-related concerns.
Social Workers
Social workers provide valuable psychosocial support and assistance to individuals with myositis and their families. Collaborating with social workers allows for comprehensive assessment and addressing of social, emotional, and practical needs. Social workers can provide counseling, connect patients with community resources, navigate insurance and financial concerns, and facilitate support group participation. Nurses can collaborate with social workers to ensure holistic care and support for patients.
Dietitians
Collaborating with registered dietitians can help address nutritional considerations and optimize the dietary management of individuals with myositis. Dietitians can perform comprehensive nutritional assessments, provide education on healthy eating habits, and develop personalized nutrition plans tailored to the individual’s needs. Nurses can work collaboratively with dietitians to ensure patients receive appropriate dietary guidance and support to promote optimal health outcomes.
Patient Advocacy
Respecting Patient’s Autonomy
Respecting the autonomy of patients with myositis is essential in providing patient-centered care. Nurses can advocate for patients’ rights to make informed decisions about their care and treatment options. This includes ensuring patients have access to comprehensive information, fostering open and honest communication, and respecting their preferences and values. Encouraging shared decision-making and involving patients in care planning can help empower individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey.
Ensuring Informed Decision-Making
Ensuring that patients have access to accurate and comprehensive information is key to promoting informed decision-making. Nurses can play a vital role in providing education, answering questions, and addressing any concerns or misconceptions that patients may have. Ensuring that patients understand the potential risks and benefits of treatment options, as well as potential alternatives, can help them make informed decisions about their care.
Facilitating Communication with Healthcare Team
Effective communication with the healthcare team is crucial in ensuring optimal care and outcomes for individuals with myositis. Nurses can serve as advocates for patients by facilitating communication between the patient and the multidisciplinary team. This may involve relaying patient concerns, sharing relevant information, and ensuring that all members of the healthcare team are informed about the patient’s condition and treatment plan. Open lines of communication among all team members are essential to promote collaborative decision-making and comprehensive care.
Research and Education
Participating in Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can be a valuable opportunity for individuals with myositis to contribute to scientific knowledge and potentially access innovative treatments. Nurses can play a role in providing information about ongoing clinical trials and facilitating patient enrollment. Collaborating with the research team, nurses can ensure patients are well-informed about the study objectives, potential benefits, and risks involved, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their participation.
Continuing Education
Continuing education is essential for healthcare professionals involved in caring for patients with myositis. Nurses can seek out professional development opportunities, such as attending conferences, workshops, and webinars, to stay up-to-date with the latest research, treatment guidelines, and nursing considerations. By maintaining a strong knowledge base, nurses can provide evidence-based care and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Patient Support Groups
Patient support groups can be a valuable resource for individuals with myositis, providing a sense of community, emotional support, and an opportunity to share experiences with others who understand their journey. Nurses can provide information about local or online support groups, facilitate connections, and encourage patients to participate in support group activities. Support groups can provide valuable psychosocial support, educational resources, and an avenue for advocacy and empowerment for patients.
