Ever wondered about the important nursing considerations when it comes to prosthetic eyes? Look no further! In this article, we explore the various aspects of nursing management for patients with a prosthetic eye. From proper cleaning techniques to ensuring secure placement, we dive into the crucial factors that can greatly impact the comfort and well-being of these individuals. So join us as we navigate through the key nursing considerations for prosthetic eyes and discover how nurses can play a vital role in providing optimal care for their patients.
Assessment
Patient’s understanding of prosthetic eye
Assessing the patient’s understanding of the prosthetic eye is an essential part of the nursing process. It is important to gauge their knowledge and perception of the procedure, as well as any concerns or misconceptions they may have. By conducting open and non-judgmental conversations, nurses can create a safe space for patients to express their thoughts and feelings. It is crucial to address any questions or fears they may have, providing clear and concise explanations to ensure their understanding.
Availability of support system
Assessing the availability of a support system for the patient is crucial in determining the level of assistance they will have in coping with the insertion of a prosthetic eye. It is important to identify whether the patient has family or friends who can provide emotional support during this time. Additionally, evaluating the patient’s access to resources such as support groups or counseling services can help improve their overall psychological well-being. By understanding the patient’s support system, nurses can tailor their care to meet the individual’s needs and provide the necessary emotional support throughout the process.
Physical examination of the eye socket
Conducting a thorough physical examination of the eye socket is an essential nursing consideration when preparing for prosthetic eye insertion. This examination allows healthcare professionals to assess the condition of the eye socket, including any potential abnormalities or complications. By carefully observing the socket for signs of infection, inflammation, or discharge, nurses can identify any issues that need to be addressed before the insertion procedure. Accurate documentation of the physical examination findings is crucial for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the patient’s progress.
Evaluation of the patient’s overall health
When considering the insertion of a prosthetic eye, it is imperative to evaluate the patient’s overall health status. This evaluation helps identify any pre-existing medical conditions or medications that may influence the procedure or subsequent care. Nurses should review the patient’s medical history, including any chronic diseases, allergies, or previous surgeries. Additionally, assessing the patient’s current medications is vital to ensure there are no contraindications or potential interactions. By evaluating the patient’s overall health, nurses can provide individualized care that accounts for their specific medical needs and minimizes potential risks.
Preparation
Educating the patient about the procedure
One of the key roles of a nurse in the preparation phase of prosthetic eye insertion is to educate the patient about the procedure. It is essential to provide clear and concise information regarding the steps involved, potential risks and complications, and expected outcomes. Explaining the process in a friendly and understandable manner helps alleviate any anxieties or fears the patient may have. Visual aids, such as diagrams or videos, can also be utilized to enhance their understanding. By ensuring the patient is well-informed, nurses can empower them to make informed decisions and actively participate in their own care.
Assisting in obtaining necessary supplies
Assisting the patient in obtaining the necessary supplies is another crucial aspect of nursing preparation. This may include providing information about where to purchase the prosthetic eye, necessary cleaning solutions, and storage containers. By helping the patient gather these supplies, nurses contribute to their overall preparedness and ensure they have everything they need to care for their prosthetic eye. Additionally, providing proper instructions on the use and maintenance of these supplies is essential for the patient’s long-term comfort and well-being.
Coordinating with ophthalmologist
Coordinating with the ophthalmologist is vital to ensure effective collaboration between healthcare professionals involved in the prosthetic eye insertion. Nurses play a crucial role in communicating the patient’s needs, concerns, and medical history to the ophthalmologist. They can also assist in scheduling appointments, facilitating the sharing of information, and coordinating any additional procedures or assessments that may be required. By maintaining open lines of communication, nurses contribute to the seamless coordination of care and the best possible outcomes for the patient.
Addressing emotional concerns of the patient
Addressing the emotional concerns of the patient during the preparation phase is essential for their overall well-being and successful adjustment to the prosthetic eye. Nurses should create a safe and supportive environment where patients can freely express their emotions and fears. Active listening and empathetic communication are key in understanding their emotional needs and providing appropriate support. By addressing their concerns, nurses can help alleviate anxiety, promote a positive mindset, and facilitate the patient’s emotional readiness for the procedure.

Prosthetic Eye Insertion
Ensuring a sterile environment
Maintaining a sterile environment during the prosthetic eye insertion procedure is crucial to prevent infections and complications. Nurses should ensure that the patient is positioned correctly and that all necessary equipment and supplies are sterile and readily available. Adhering to proper hand hygiene and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) contributes to the prevention of contamination. Nurses should closely follow infection control protocols and monitor the environment throughout the procedure to minimize the risk of infection.
Assisting the ophthalmologist during the procedure
Assisting the ophthalmologist during the prosthetic eye insertion procedure is an essential role for nurses. This may involve providing instruments and supplies, assisting with the placement and alignment of the prosthesis, and ensuring adequate lighting and visibility. Nurses should be prepared to anticipate the needs of the ophthalmologist and provide support in a timely and efficient manner. Clear communication and teamwork are essential during the procedure to ensure patient safety and the successful insertion of the prosthetic eye.
Monitoring patient’s vital signs
Monitoring the patient’s vital signs is a crucial nursing consideration during the prosthetic eye insertion procedure. Regularly assessing the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate allows for the early detection of any changes or complications. Any significant deviations from baseline vital signs should be promptly reported to the ophthalmologist for further evaluation. Nurses should be prepared to respond quickly and appropriately to any emergent situations that may arise, ensuring the patient’s safety and well-being throughout the procedure.
Providing emotional support during the process
Providing emotional support during the prosthetic eye insertion process is an essential role for nurses. This procedure can be emotionally challenging for patients, as it involves a significant change in their physical appearance and body image. Nurses should maintain a calm and reassuring presence, offering words of encouragement and comfort. Active listening and empathetic communication help create a safe space for patients to express their emotions and concerns. By acknowledging their feelings and providing emotional support, nurses contribute to the patient’s overall well-being and successful adaptation to the prosthesis.
Post-Insertion Care
Monitoring for signs of infection
Monitoring for signs of infection is a critical nursing consideration in the post-insertion care of a prosthetic eye. Nurses should closely observe the eye socket for any signs of redness, increased discharge, swelling, or abnormal odor. Additionally, monitoring the patient’s temperature can help detect early signs of infection. Any concerning changes should be promptly reported to the healthcare team for further evaluation and appropriate intervention. By vigilantly monitoring for signs of infection, nurses help ensure the patient’s safety and prevent potential complications.
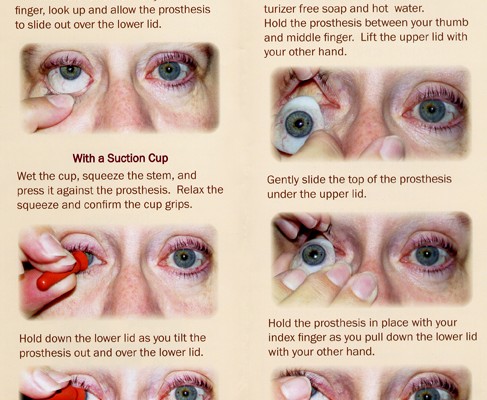
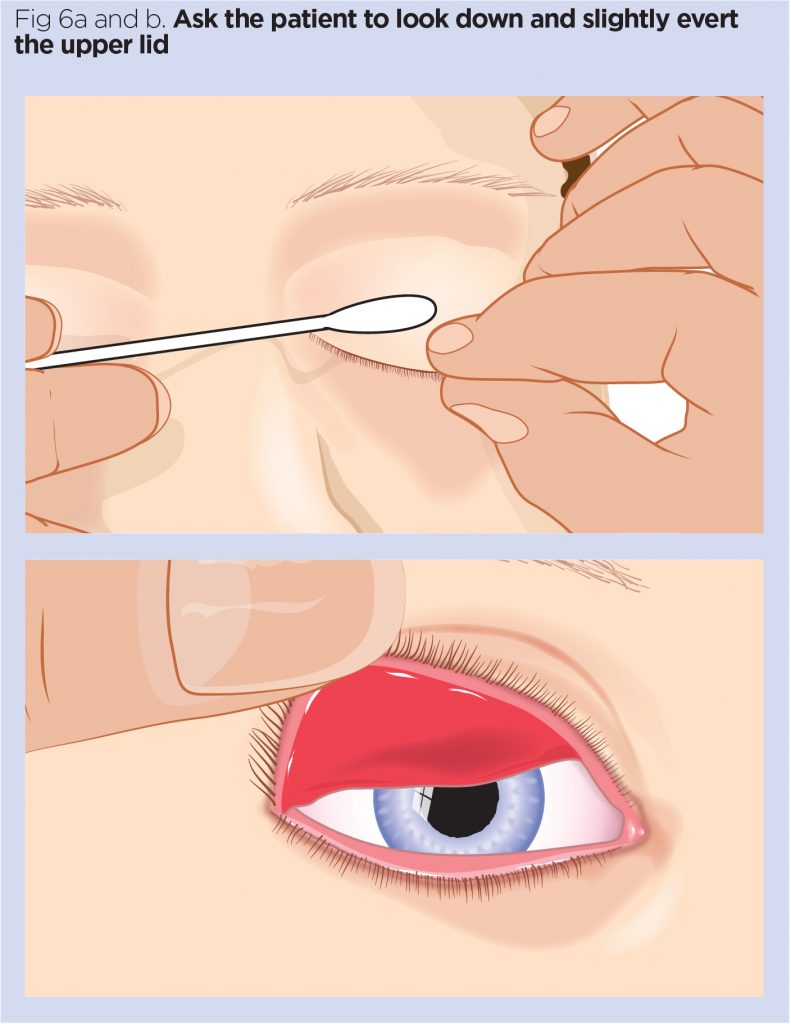
Maintaining proper hygiene of the prosthetic eye
Maintaining proper hygiene of the prosthetic eye is essential for preventing infections and ensuring the patient’s comfort. Nurses should educate the patient on appropriate cleaning techniques and provide clear instructions on how to safely handle and care for their prosthesis. Regular cleaning and disinfection, using recommended cleaning solutions, help remove debris and minimize the risk of infection. Nurses should also emphasize the importance of avoiding contact with harmful substances or excessive moisture, as these can damage the prosthetic eye. By promoting proper hygiene practices, nurses contribute to the long-term success and comfort of the patient’s prosthetic eye.
Assessing the fit and comfort of the prosthesis
Regular assessment of the fit and comfort of the prosthesis is an essential nursing consideration in post-insertion care. Nurses should closely monitor the patient’s feedback regarding any discomfort, pain, or pressure sensations related to the prosthesis. They should also assess the fit and appearance of the prosthesis, ensuring that it aligns with the patient’s natural eye and eyelids. Any concerns or issues should be documented and promptly communicated to the ophthalmologist for further evaluation and possible adjustments. By assessing the fit and comfort of the prosthesis, nurses help optimize the patient’s quality of life and satisfaction with their visual appearance.
Educating the patient on daily care and removal
Patient education on daily care and removal of the prosthetic eye is a crucial nursing consideration in post-insertion care. Nurses should provide clear and detailed instructions on how to safely remove and reinsert the prosthesis, emphasizing proper hand hygiene and handling techniques. They should also educate the patient on the frequency of cleaning, recommended cleaning solutions, and storage techniques. Reinforcing the importance of regular follow-up appointments with the ophthalmologist ensures ongoing evaluation and adjustment when necessary. By educating the patient on daily care and removal, nurses empower them to independently manage their prosthesis and maintain optimal eye health.

Psychosocial Support
Addressing body image concerns
Addressing body image concerns is an important aspect of psychosocial support in prosthetic eye care. Nurses should create a non-judgmental and empathetic environment where patients can express their feelings and concerns about their changed appearance. Active listening, validation, and reassurance are key in acknowledging their struggles and providing emotional support. Nurses can offer advice on makeup techniques, hairstyles, or accessories that may enhance the patient’s self-confidence and help them feel more comfortable with their new prosthetic eye. By addressing body image concerns, nurses contribute to the patient’s psychological well-being and successful adaptation.
Providing emotional support for adjustment
Providing emotional support for adjustment is crucial for patients adapting to a prosthetic eye. Nurses should be attentive to the patient’s emotional needs and offer empathy and understanding throughout the adjustment process. This may involve regular check-ins, open communication, and addressing any emotional challenges the patient may be facing. Nurses should celebrate small victories and milestones with their patients, reinforcing their resilience and adaptability. By providing ongoing emotional support, nurses play a vital role in helping patients navigate the emotional complexities of living with a prosthetic eye.
Referring to support groups or counseling
Referring patients to support groups or counseling services can greatly enhance their psychosocial support and overall adjustment to a prosthetic eye. These resources provide patients with the opportunity to connect with others who have undergone similar experiences, share their stories and emotions, and receive guidance and advice from professionals. Nurses should provide patients with information about local support groups or online communities where they can find comfort, encouragement, and practical tips for daily living. By facilitating these connections, nurses help foster a sense of belonging and empower patients to seek additional support when needed.
Encouraging open communication
Encouraging open communication is crucial in providing psychosocial support for patients with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should create a safe and non-judgmental space where patients feel comfortable expressing their feelings, concerns, and questions. Active listening, empathy, and validation are essential in building trust and fostering open communication. By encouraging patients to share their experiences, nurses gain valuable insight into their emotional well-being and can provide appropriate support and guidance. Regularly discussing any challenges or successes helps patients feel understood and reinforces their coping abilities.
Complications and Troubleshooting
Infection of the eye socket
Infection of the eye socket is a potential complication following prosthetic eye insertion. Nurses should closely monitor the patient for signs of infection, as mentioned earlier, and promptly report any abnormalities to the healthcare team. If an infection is suspected or diagnosed, appropriate interventions such as antibiotic therapy may be initiated. Nurses should also reinforce the importance of following proper hygiene practices and seeking medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. By identifying and addressing infections early, nurses contribute to the patient’s overall recovery and long-term eye health.
Prosthesis dislodgement or retention issues
Dislodgement or retention issues with the prosthetic eye are other potential complications that may occur. Nurses should carefully assess the fit and stability of the prosthesis during post-insertion care and follow-up appointments. Any concerns or issues reported by the patient should be documented and promptly communicated to the ophthalmologist for further evaluation and adjustment. Nurses should educate the patient on the appropriate actions to take if the prosthesis becomes dislodged or uncomfortable. By addressing these complications, nurses help ensure the patient’s comfort, safety, and satisfaction with their prosthetic eye.
Allergic reactions to the prosthetic material
Allergic reactions to the prosthetic material can occur in some individuals. Nurses should be vigilant in monitoring the patient for any signs of an allergic reaction, such as redness, itching, or swelling. If an allergic reaction is suspected, the patient should be promptly evaluated by the ophthalmologist to determine the appropriate course of action. Nurses should educate the patient on potential allergens and advise them on how to minimize exposure to substances that may trigger an allergic response. By recognizing and addressing allergic reactions, nurses contribute to the patient’s overall comfort and well-being.
Abnormal discharge or discomfort
Abnormal discharge or discomfort related to the prosthetic eye should be carefully monitored by nurses. These symptoms may indicate an underlying issue such as infection or poor fit. Nurses should regularly assess the patient for any concerning changes in discharge, pain, or discomfort and promptly report these findings to the healthcare team. Collaboration with the ophthalmologist is essential in determining the cause of these symptoms and implementing appropriate interventions. By addressing abnormal discharge or discomfort, nurses help ensure the patient’s comfort and promote optimal eye health.

Patient Education
Proper prosthesis handling and cleaning techniques
Patient education on proper prosthesis handling and cleaning techniques is crucial for maintaining the cleanliness and integrity of the prosthetic eye. Nurses should provide clear instructions on how to safely handle, insert, remove, and clean the prosthesis. This includes emphasizing the importance of proper hand hygiene, using recommended cleaning solutions, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances. Nurses should demonstrate the techniques, allow the patient to practice, and provide feedback and guidance as needed. By educating patients on proper handling and cleaning techniques, nurses empower them to independently care for their prosthetic eye and reduce the risk of complications.
Avoiding activities that could damage the prosthesis
Educating patients about activities that could potentially damage the prosthetic eye is essential for their long-term care. Nurses should provide clear guidelines on activities to avoid, such as swimming in chlorinated water, rubbing the eye vigorously, or participating in contact sports without protective eyewear. Emphasizing the importance of protecting the prosthesis from trauma or excessive force helps prevent damage and prolong its lifespan. Nurses should also provide information on appropriate protective measures, such as wearing safety glasses or goggles in certain situations. By educating patients on avoiding damaging activities, nurses help promote the longevity and functionality of the prosthetic eye.
Recognizing signs of infection or complications
Educating patients on recognizing signs of infection or complications is crucial for their ongoing care and early intervention. Nurses should clearly explain the common signs and symptoms of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, discharge, or pain, and emphasize the need for prompt medical attention if any of these occur. Additionally, patients should be educated on other potential complications and their associated warning signs, such as prosthesis dislodgement, discomfort, or changes in vision. By empowering patients to recognize and report signs of infection or complications, nurses contribute to their overall safety and well-being.
Importance of regular follow-up appointments
Emphasizing the importance of regular follow-up appointments is vital in patient education for prosthetic eye care. Nurses should educate patients on the need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation by the ophthalmologist to ensure the prosthesis is functioning properly and to address any potential issues. Regular check-ups allow for adjustments to be made if necessary, ensuring optimal fit, comfort, and visual appearance. Nurses should provide clear instructions on scheduling appointments and assist patients in overcoming potential barriers to attendance. By stressing the importance of regular follow-up appointments, nurses help ensure the long-term success and satisfaction of patients with their prosthetic eye.
Collaboration with the Healthcare Team
Communicating with the ophthalmologist and ocularist
Effective communication with the ophthalmologist and ocularist is essential for the optimal care and management of patients with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should maintain open lines of communication, sharing patient updates, concerns, and any changes in the condition of the eye socket or prosthesis. Regular dialogue allows for collaborative decision-making and ensures coordinated care for the patient. Nurses should actively seek clarification or additional information from the healthcare team when needed, demonstrating their commitment to quality patient care. By fostering a collaborative relationship with the ophthalmologist and ocularist, nurses contribute to the comprehensive and individualized care of the patient.
Coordinating care with other healthcare providers
Coordinating care with other healthcare providers is crucial in ensuring the holistic management of patients with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should collaborate with other professionals, such as primary care physicians, pharmacists, or physical therapists, to address the patient’s overall health needs. Sharing relevant information and updates allows for a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s care and facilitates appropriate interventions or adjustments. Nurses should actively engage in interdisciplinary meetings or discussions to contribute their expertise and advocate for the patient’s best interests. By coordinating care with other healthcare providers, nurses promote a multidisciplinary approach to patient care and improve patient outcomes.
Sharing patient updates and progress
Sharing patient updates and progress is an important aspect of collaboration with the healthcare team in prosthetic eye care. Nurses should provide regular updates to the ophthalmologist, ocularist, and other involved healthcare professionals regarding the patient’s condition, any changes or concerns, and the effectiveness of the current care plan. This information ensures that everyone involved is working with the most accurate and up-to-date data, allowing for appropriate adjustments to the patient’s care. Nurses should also document these updates and progress in the patient’s medical records, ensuring continuity of care and serving as a valuable resource for future reference.
Participating in interdisciplinary meetings
Participating in interdisciplinary meetings is essential for effective collaboration and shared decision-making in the care of patients with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should actively engage in these meetings, contributing their expertise, observations, and insights related to the patient’s progress, challenges, and goals. Collaboration with various healthcare professionals, such as ophthalmologists, ocularists, psychologists, or social workers, helps provide a comprehensive care plan that addresses the patient’s physical, emotional, and social needs. By participating in interdisciplinary meetings, nurses promote effective teamwork, enhance communication, and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Documentation
Accurate recording of patient information
Accurate recording of patient information is vital in prosthetic eye care. Nurses should ensure that all pertinent information, including the patient’s medical history, assessments, interventions, and outcomes, is documented in a clear and concise manner. Detailed documentation allows for accurate communication and continuity of care among the healthcare team. Nurses should use standardized documentation tools and follow institutional guidelines to ensure consistency and completeness. By maintaining accurate records, nurses contribute to the comprehensive understanding of the patient’s care and facilitate accountability and informed decision-making.
Documenting changes in the condition of the eye socket
Documenting changes in the condition of the eye socket is a critical aspect of nursing documentation in prosthetic eye care. Nurses should carefully observe and record any changes in the eye socket, such as redness, swelling, discharge, or signs of infection. Accurate and timely documentation allows for consistent monitoring and tracking of the patient’s progress and provides valuable information for making informed decisions about their care. Nurses should utilize standardized assessment tools and terminology when documenting changes in the condition of the eye socket, ensuring clear communication among the healthcare team.
Maintaining a record of patient education provided
Maintaining a record of patient education provided is essential in prosthetic eye care. Nurses should document the education topics covered, the methods used, and any additional educational resources provided to the patient. This documentation serves as a reference for the patient and the healthcare team, ensuring that important information is easily accessible and reinforcing the importance of ongoing education. Nurses should also document the patient’s understanding and progress in learning the necessary skills and knowledge related to their prosthetic eye care. By maintaining a record of patient education, nurses promote continuity of care and enhance patient empowerment and self-care.
Recording communication with the healthcare team
Recording communication with the healthcare team is crucial for effective collaboration and continuity of care in prosthetic eye management. Nurses should document any verbal or written communication they have with the ophthalmologist, ocularist, or other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care. This includes discussions, consultations, recommendations, or any important decisions made collaboratively. Clear and accurate documentation ensures that the entire healthcare team has access to the same information and promotes transparent communication among professionals. By recording communication, nurses contribute to the ongoing coordination of care and the seamless exchange of crucial information.
Empathy and Cultural Sensitivity
Understanding the patient’s cultural beliefs
Understanding the patient’s cultural beliefs is essential in providing empathetic and culturally sensitive care for individuals with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should be knowledgeable and respectful of various cultural practices, traditions, and beliefs related to body image, appearance, and healthcare. Actively seeking to understand the patient’s cultural background and values helps create a safe and inclusive environment. By considering cultural beliefs in the care plan, nurses can adapt their approach and foster a trusting and respectful nurse-patient relationship.
Respecting personal and religious practices
Respecting personal and religious practices is crucial in promoting empathetic and culturally sensitive care for individuals with a prosthetic eye. Nurses should be mindful of any personal or religious practices that may impact the patient’s care and adjustment to the prosthesis. This includes considerations related to clothing choices, personal grooming, or specific rituals that the patient may engage in. Nurses should demonstrate respect and sensitivity, accommodating these practices whenever possible and appropriate. By respecting personal and religious practices, nurses contribute to the patient’s overall well-being and create a care environment that aligns with their values and beliefs.
Adapting care to individual preferences
Adapting care to individual preferences is an important aspect of providing patient-centered and empathetic care in prosthetic eye management. Recognizing that each patient has unique needs, preferences, and priorities allows nurses to tailor their care approach accordingly. This may involve offering choices or alternatives, creating a care plan that respects the patient’s personal values, or adjusting care activities to accommodate their preferences. By adapting care to individual preferences, nurses promote a sense of autonomy and empower patients to actively participate in their own care.
Being sensitive to emotional and psychological needs
Being sensitive to the emotional and psychological needs of individuals with a prosthetic eye is essential in providing holistic and compassionate care. Nurses should be attentive to the emotional challenges and psychological impact of living with a changed appearance. By demonstrating empathy and understanding, nurses create a safe space for patients to express their emotions and concerns. Addressing emotional and psychological needs may involve actively listening, validating their experiences, providing appropriate support, or referring to mental health professionals. By being sensitive to emotional and psychological needs, nurses contribute to the overall well-being and successful adaptation of patients with a prosthetic eye.