If you’ve ever dealt with sneezing, itching, and congestion during certain times of the year, you’re likely familiar with the frustrations of seasonal allergies. However, as a nurse, you play a vital role in helping patients manage these allergy symptoms and providing the necessary care. In this article, we will explore some important nursing considerations for seasonal allergies, including effective treatment options, patient education, and preventive measures. By incorporating these considerations into your nursing practice, you can improve the quality of life for individuals dealing with seasonal allergies.
1. Understanding Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, are allergic reactions that occur at specific times of the year. These allergies are triggered by certain environmental allergens such as pollen, mold spores, and dust mites. Understanding the causes and symptoms of seasonal allergies is crucial for effective management and treatment.
1.1 Causes of Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergies are primarily caused by the immune system’s overreaction to harmless substances, known as allergens, that are present in the environment during specific seasons. The most common allergens include tree pollen in the spring, grass pollen in the summer, and weed pollen in the fall. These allergens can enter the body through the respiratory system and cause an allergic response.
1.2 Common Symptoms of Seasonal Allergies
The symptoms of seasonal allergies can vary from mild to severe and may include sneezing, itchy or runny nose, nasal congestion, watery eyes, itching or irritation in the throat, and coughing. Some individuals may also experience fatigue, headache, and impaired concentration due to the allergic reaction. It is important to recognize these symptoms to differentiate them from other respiratory conditions and provide appropriate treatment.
1.3 Diagnosing Seasonal Allergies
Diagnosing seasonal allergies involves a thorough assessment of both the patient’s medical history and physical examination. During the medical history, the healthcare provider will ask about any previous instances of allergies, the timing and duration of symptoms, and possible triggers. A physical examination may reveal common signs such as swollen nasal passages and red, watery eyes. Allergy testing, either through skin tests or blood tests, can confirm the specific allergens triggering the allergic reaction.
2. Assessing the Patient
Before initiating any treatment plan, it is important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient to determine the severity of their seasonal allergies and identify any underlying conditions or factors that may impact the management process.
2.1 Medical History
Obtaining a detailed medical history is crucial in understanding the patient’s allergies and any potential complications or comorbidities. The healthcare provider should inquire about the duration and frequency of symptoms, previous treatments, medication use, and any known triggers. Additionally, it is important to ask about the patient’s family history of allergies, as genetics can play a significant role.
2.2 Physical Examination
A physical examination helps identify any physical manifestations of seasonal allergies. The healthcare provider will assess the patient’s nasal passages for signs of inflammation, such as redness or swelling. They may also examine the eyes for redness, itching, or tearing. The examination can help confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the allergies.
2.3 Allergy Testing
Allergy testing is often performed to determine the specific allergens triggering the seasonal allergies. Skin prick tests involve exposing the skin to small amounts of allergens and observing the reaction. Blood tests, such as the specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) test, can also identify specific allergens by measuring the levels of antibodies in the blood. These tests can provide valuable information for developing an effective treatment plan.

3. Treatment Options
When it comes to managing seasonal allergies, several treatment options are available that aim to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. It is important to tailor the treatment plan to each individual’s needs and consider their preferences and medical history.
3.1 Medications for Seasonal Allergies
Medications are often the first line of treatment for seasonal allergies. Antihistamines are commonly used to relieve symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction. Nasal sprays containing corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve nasal congestion. Decongestants, available as oral medications or nasal sprays, can provide temporary relief from congestion. It is essential to use these medications as directed and be aware of potential side effects.
3.2 Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy)
Allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, may be recommended for individuals with severe or persistent allergies. This treatment involves regular injections of small amounts of allergens over a period of time to help desensitize the immune system and reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Allergy shots are typically administered by an allergist and can provide long-term relief for seasonal allergies.
3.3 Alternative Remedies
Some individuals may opt for alternative remedies to manage their seasonal allergies. These can include herbal supplements, acupuncture, and nasal rinses with saline solutions. While these remedies may provide relief for some individuals, it is important to discuss their use with a healthcare provider to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
4. Patient Education
Educating patients about seasonal allergies is an essential aspect of nursing care. By understanding the condition and its management, patients can actively participate in their treatment and make informed decisions regarding their health.
4.1 Explaining Seasonal Allergies
As a healthcare provider, it is important to explain to patients what seasonal allergies are and why their body reacts negatively to certain allergens. Use simple language and visual aids, if necessary, to help patients grasp the concept. Emphasize the importance of identifying their specific triggers and avoiding them when possible.
4.2 Avoidance Strategies
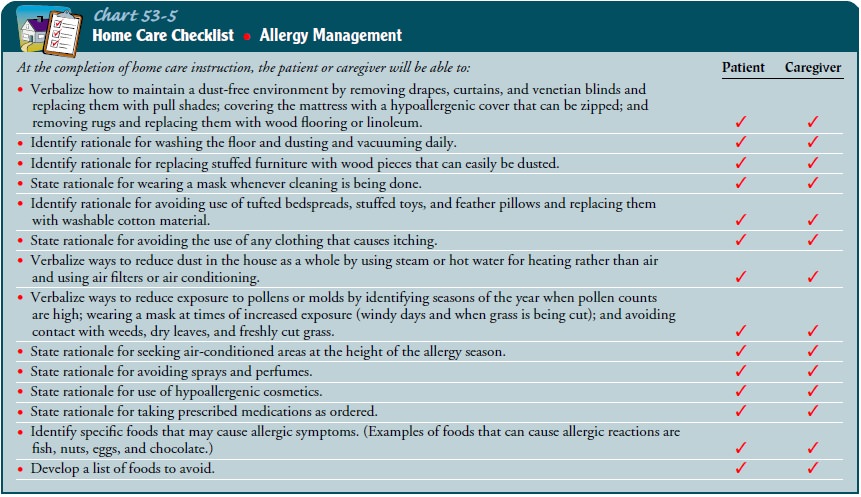
Teach patients about effective strategies to minimize exposure to allergens. This may include staying indoors during peak pollen times, keeping windows closed, using air purifiers, and wearing protective clothing when outdoors. Instructing patients on proper cleaning techniques to reduce dust mites and mold spores in the home environment can also be beneficial.
4.3 Proper Medication Use
Proper medication use is crucial for managing seasonal allergies effectively. Educate patients on the different types of medications available, including their proper administration, potential side effects, and when to seek medical advice. Emphasize the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment plans and following up with healthcare providers regularly.

5. Symptom Management
Symptom management is a key component of nursing care for patients with seasonal allergies. By providing guidance on various treatment modalities, nurses can help patients find relief from their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
5.1 Antihistamines
Antihistamines are commonly used to manage the symptoms of seasonal allergies. Advise patients on the appropriate dosage and timing of antihistamine medications. Educate them about the potential side effects, such as drowsiness or dry mouth, and how to manage them effectively. Encourage patients to report any adverse reactions to their healthcare provider.
5.2 Nasal Sprays
Nasal sprays containing corticosteroids can provide relief from nasal congestion and inflammation associated with seasonal allergies. Instruct patients on the proper administration technique, emphasizing the importance of regular use to achieve maximum effectiveness. Advise patients to consult their healthcare provider if they experience any nasal irritation or bleeding.
5.3 Eye Drops
Eye drops can be an effective way to relieve itching, redness, and watering of the eyes caused by seasonal allergies. Explain the proper method of applying eye drops and remind patients to wash their hands before and after use. It is important to recommend preservative-free eye drops for patients who experience eye irritation or allergies to certain preservatives.
5.4 Decongestants
Decongestants can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion caused by seasonal allergies. However, it is important to educate patients about the potential side effects of decongestants, such as increased blood pressure and heart rate. Advise patients to use decongestants for short durations only and to consult their healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.
6. Monitoring and Follow-up
Monitoring and follow-up are essential in managing seasonal allergies effectively. Regular assessment and communication with the patient can help identify any changes in symptoms, medication effectiveness, or potential adverse effects.
6.1 Tracking Symptoms
Encourage patients to keep a record of their symptoms, including the type, severity, duration, and frequency. This information can help healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments. Additionally, instruct patients to note any triggers or environmental factors that may exacerbate their symptoms.
6.2 Adverse Effects of Medications
Inform patients about the potential adverse effects of the medications they are prescribed. Discuss common side effects and instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms or reactions. Remind patients not to discontinue medications without consulting their healthcare provider.
6.3 Adjusting Treatment Plan
As seasonal allergies can vary in severity and presentation, it may be necessary to adjust the treatment plan based on the patient’s response to therapy. Regular follow-up appointments should be scheduled to assess the effectiveness of the current treatment and make any necessary modifications. Engage in open communication with patients to ensure their concerns are addressed and treatment goals are met.

7. Allergy Emergency Response
While most cases of seasonal allergies can be managed with proper treatment and avoidance strategies, it is important to be prepared for emergency situations, such as anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening.
7.1 Recognizing Anaphylaxis
Educate patients and their caregivers about the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis, which can include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. Instruct them to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms after exposure to an allergen.
7.2 Administering Epinephrine
Patients at risk for anaphylaxis should be prescribed an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an EpiPen. Train patients and their caregivers on how to properly administer the epinephrine in case of an emergency. Emphasize the importance of seeking further medical care even after administering epinephrine.
8. Working with Other Healthcare Providers
Collaboration with allergists/immunologists and primary care physicians is essential for comprehensive care of patients with seasonal allergies. Communication and coordination between healthcare providers contribute to the management of allergies and optimal patient outcomes.
8.1 Collaboration with Allergists/Immunologists
Allergists/immunologists are specialists in the diagnosis and treatment of allergies. Collaborate with these healthcare professionals to develop an evidence-based treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific allergens and symptoms. Share relevant patient information and maintain open communication regarding treatment effectiveness and any necessary adjustments.
8.2 Coordinating Care with Primary Care Physicians
Primary care physicians play a vital role in the ongoing management of patients with seasonal allergies. Ensure proper communication with primary care physicians regarding the patient’s diagnosis, treatment plan, and any changes in medication. This collaboration helps ensure continuity of care and avoids duplication of efforts.
9. Special Considerations
Certain patient populations, such as pediatric, elderly, pregnant, and those with comorbidities, require special considerations when managing seasonal allergies. Tailoring treatment plans and education to meet the unique needs of these patients is essential.
9.1 Pediatric Patients
Pediatric patients with seasonal allergies may require modified treatment plans and age-appropriate education. Educate parents or caregivers on proper medication administration techniques and potential side effects in children. Emphasize the importance of creating an allergen-free environment at home and school.
9.2 Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may have additional comorbidities and medication regimens, which can complicate the management of seasonal allergies. Conduct a thorough assessment of these patients to identify any potential interactions or contraindications with their current medications. Provide clear and concise education, considering any sensory impairments or cognitive limitations that may be present.
9.3 Pregnant Patients
Pregnant patients may have concerns about the safety of medications and the potential impact of allergies on their pregnancy. Work closely with obstetricians to identify safe treatment options for pregnant patients. Emphasize non-pharmacological strategies, such as avoidance techniques, to reduce exposure to allergens.
9.4 Patients with Comorbidities
Patients with comorbidities, such as asthma or cardiovascular disease, may require a multidisciplinary approach to manage their seasonal allergies effectively. Collaborate with relevant healthcare professionals to ensure the treatment plan does not exacerbate underlying conditions or interact with other medications. Provide patient education that integrates the management of both allergies and comorbidities.
10. Impact of Seasonal Allergies on Daily Life
Seasonal allergies can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, affecting their sleep, work or school performance, and emotional well-being. Understanding and addressing these impacts are crucial for comprehensive care.
10.1 Sleep Disturbances
Seasonal allergies can cause sleep disturbances due to nasal congestion, coughing, or itching. These disturbances can result in daytime fatigue, decreased productivity, and reduced quality of life. Encourage patients to follow their treatment plan consistently and explore non-pharmacological strategies, such as using hypoallergenic bedding or keeping the bedroom windows closed.
10.2 Impaired Work/School Performance
Symptoms of seasonal allergies can impair work and school performance, leading to reduced productivity and absenteeism. Educate patients about strategies to minimize exposure to allergens in these environments, such as using air purifiers in offices or classrooms. Encourage open communication with employers or school administrators to address any specific accommodations that may be necessary.
10.3 Emotional Impact
Living with chronic seasonal allergies can have emotional implications, including frustration, irritability, and decreased motivation. Encourage patients to seek support from friends, family, or support groups to cope with the emotional impact of their allergies. Provide validation for their feelings and offer resources for stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or counseling services.
In conclusion, nursing considerations for seasonal allergies encompass various aspects, including understanding the causes and symptoms, assessing the patient, providing education, managing symptoms, monitoring and follow-up, identifying emergency responses, collaborating with other healthcare providers, considering special populations, and addressing the impact of allergies on daily life. By incorporating these considerations into nursing practice, healthcare professionals can ensure optimal care and improved quality of life for patients with seasonal allergies.
