In this article, you will learn about the importance of preventing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children. ALL is the most common type of cancer in children, but it is also highly treatable if detected early. By understanding the risk factors and implementing preventative measures, we can significantly reduce the occurrence of ALL and ensure a healthier future for our young ones. Join us as we explore the key steps you can take to protect your child from this devastating disease.

1. Understanding Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
1.1 Definition
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It is characterized by the rapid production of immature white blood cells, known as lymphoblasts, which crowd out healthy blood cells. ALL primarily affects children, although it can occur in adults as well. The condition is considered acute because it progresses rapidly and requires immediate medical attention.
1.2 Prevalence and Impact
ALL is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in children, accounting for approximately 25% of pediatric cancer cases. Each year, thousands of children worldwide are diagnosed with ALL, making it a significant health concern. The impact of ALL extends beyond the affected child, impacting their families, communities, and healthcare systems. The emotional, financial, and psychological burden placed on families dealing with childhood ALL diagnosis is substantial, highlighting the need for preventive strategies.
1.3 Types of ALL
There are different subtypes of ALL based on the type of lymphoblast involved. The two main classifications are B-cell ALL and T-cell ALL. B-cell ALL is the most common subtype, accounting for around 85% of ALL cases in children. T-cell ALL is less common but generally more aggressive. The specific subtype of ALL can impact the prognosis and treatment options available for the affected child.
2. Risk Factors for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
2.1 Genetic Predisposition
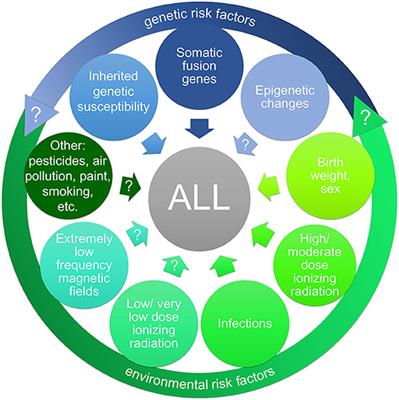
Genetic factors play a role in the development of ALL. Certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, are known to increase the risk of developing ALL. Additionally, certain gene mutations have been identified in individuals with ALL. Understanding the genetic predisposition to ALL can help identify individuals who may be at higher risk and enable targeted preventive measures.
2.2 Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also contribute to the risk of developing ALL. Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as that from X-rays or certain cancer treatments, has been linked to an increased risk of ALL. Other potential environmental factors include exposure to certain chemicals and pesticides, as well as maternal exposure during pregnancy. It is important to identify and reduce these environmental hazards to minimize the risk of ALL.
2.3 Other Possible Risk Factors
In addition to genetic and environmental factors, there are other potential risk factors for ALL. These may include certain infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus or human T-cell leukemia virus, and a history of certain blood disorders or autoimmune conditions. More research is needed to fully understand the role of these factors in the development of ALL.

3. Early Detection and Diagnosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
3.1 Common Symptoms and Signs
Early detection of ALL is crucial for successful treatment and improved outcomes. Recognizing the common symptoms and signs of ALL can aid in early diagnosis. These symptoms may include fatigue, persistent fever, easy bruising or bleeding, bone or joint pain, frequent infections, swollen lymph nodes, and unexplained weight loss. If you notice these symptoms in your child or someone you know, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
3.2 Diagnostic Tests
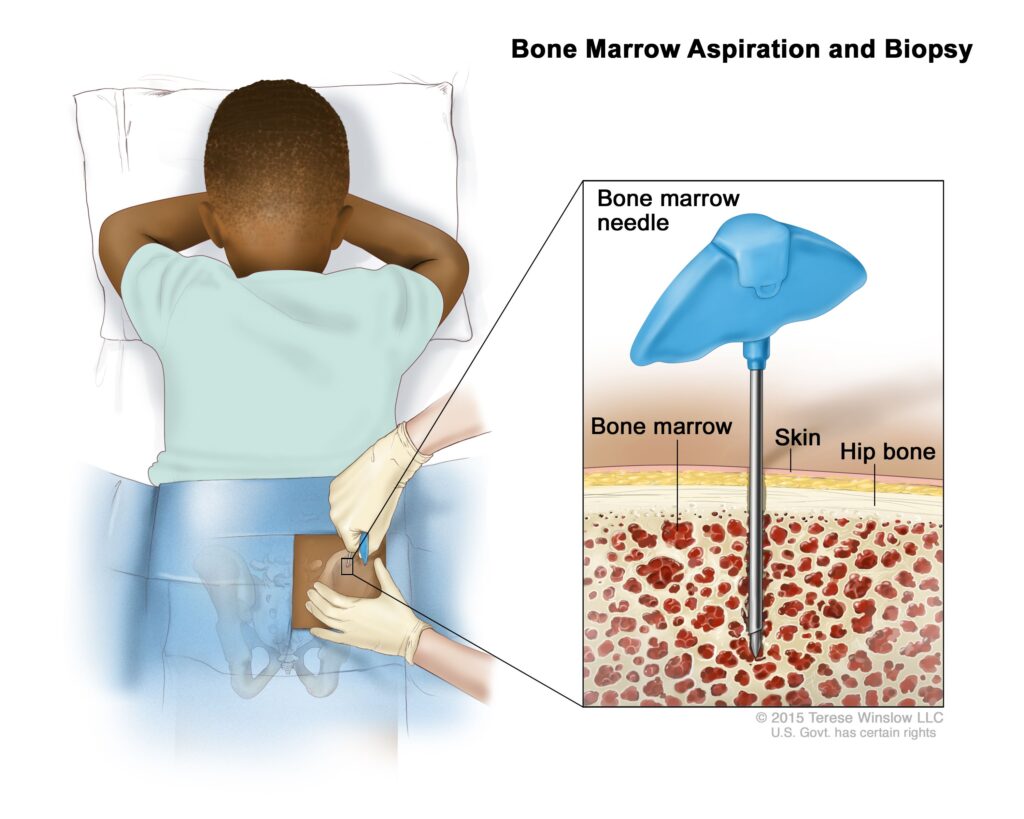
Diagnosing ALL involves various tests and procedures. These may include blood tests to evaluate the number and types of blood cells, bone marrow aspiration, and biopsy to examine the cells in the bone marrow, imaging tests to determine the extent of the disease, and genetic testing to identify specific gene mutations. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential to initiate the appropriate treatment plan for the affected child.
3.3 Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of ALL offers several benefits. It allows for prompt initiation of treatment, which increases the chances of a favorable outcome. Early detection also helps prevent the progression of the disease, reducing the risk of complications and the need for extensive treatment. Regular pediatric check-ups and awareness of the signs and symptoms of ALL can contribute to early diagnosis and improved prognosis.
4. Prevention Strategies for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
4.1 Promotion of Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is an essential part of preventing ALL. Encouraging regular physical activity, maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and promoting good sleep habits can contribute to overall health and strengthen the body’s immune system. These lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk of developing ALL and other diseases.
4.2 Avoidance of Risk Factors
Avoiding known risk factors for ALL is crucial. Minimizing exposure to ionizing radiation, whether through medical procedures or other sources, can significantly reduce the risk. Limiting exposure to harmful chemicals and pesticides, both in the household and the environment, is also important. Taking steps to prevent infections, such as practicing good hygiene and following recommended vaccination schedules, can further reduce the risk of ALL.
4.3 Protective Measures
In certain situations, additional protective measures may be necessary to prevent ALL. For individuals with a genetic predisposition to ALL, genetic counseling can help assess the risk and provide guidance on preventive strategies. Pregnant women should receive proper prenatal care and follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations to minimize potential risks to the developing fetus. By implementing these protective measures, the risk of ALL can be mitigated.
5. Vaccinations and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Prevention
5.1 Role of Vaccinations
Vaccinations play a crucial role in preventing various diseases, including ALL. By stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, vaccines can reduce the risk of infections that could potentially lead to ALL or other types of leukemia. Vaccinations are a safe and effective way to protect individuals, particularly children, from harmful diseases.
5.2 Recommended Vaccines
Several vaccines are recommended to prevent infections that have been associated with an increased risk of ALL. These include vaccines against hepatitis B, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella (chickenpox), and human papillomavirus (HPV). Ensuring that children receive all recommended vaccines according to the age-specific immunization schedule is essential for their overall health and well-being.
5.3 Importance of Timely Vaccination
Timely vaccination is crucial for the prevention of ALL. Childhood vaccinations are typically administered during specific age ranges to maximize their effectiveness. By ensuring that children receive their vaccinations on time, parents and healthcare providers can help protect against infections that may contribute to the development of ALL. Adhering to the recommended vaccination schedule is a vital preventive measure.
6. Genetic Counseling and Screening
6.1 Identifying Genetic Predisposition
Genetic counseling and screening can help identify individuals who may be at higher risk of developing ALL due to inherited genetic factors. A genetic counselor can assess an individual’s family history, evaluate potential risk factors, and provide personalized guidance on preventive strategies. Genetic screening tests can further identify specific genetic mutations associated with ALL, enabling targeted prevention efforts.
6.2 Benefits of Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling offers several benefits, including providing individuals and families with a better understanding of their risk for ALL. It can also help them make informed decisions about preventive measures, such as lifestyle modifications, regular screenings, or the consideration of prophylactic therapies. Genetic counseling provides support and empowers individuals to take proactive steps in reducing their risk of ALL.
6.3 Role of Genetic Screening
Genetic screening has an important role in identifying specific gene mutations associated with ALL. By detecting these mutations early on, individuals can be vigilant about preventive measures and undergo regular screenings to detect any signs of leukemia at its earliest stages. Genetic screening helps tailor prevention strategies and enhances the overall management of individuals at increased risk of developing ALL.
7. Pregnancy and ALL Prevention
7.1 Maternal Factors and Impact
Maternal factors during pregnancy can influence the risk of ALL in the child. Maternal exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, or infections during pregnancy may increase the risk. Additionally, certain conditions such as gestational diabetes or obesity have been associated with an elevated risk of childhood ALL. It is crucial for expectant mothers to prioritize their health and follow appropriate prenatal care to minimize potential risks.
7.2 Importance of Prenatal Care
Comprehensive prenatal care is essential for both the mother’s and child’s health and well-being. Regular prenatal visits provide healthcare professionals with opportunities to monitor the pregnancy, identify any potential risks, and offer appropriate interventions or screenings. Proper prenatal care can help optimize the health of the mother and reduce the risk of complications that could contribute to the development of childhood ALL.
7.3 Strategies for Reducing Risk
To reduce the risk of childhood ALL, expectant mothers can implement several strategies. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and radiation, managing gestational diabetes if present, and following their healthcare provider’s recommendations for prenatal care. By prioritizing maternal health and well-being, mothers can contribute to preventing ALL and ensuring the best possible start for their children.
8. Environmental Hazards and Children’s Health
8.1 Identifying Environmental Hazards
Identifying and addressing environmental hazards is vital for protecting children’s health and preventing ALL. Chemicals such as benzene, a known carcinogen, and certain pesticides have been associated with an increased risk of leukemia. Industrial pollution and exposure to second-hand smoke are also considered environmental hazards that can impact children’s health. By recognizing and addressing these hazards, we can create safer environments for children.
8.2 Reducing Exposure
Reducing exposure to environmental hazards is essential in preventing ALL. This can be accomplished through various measures, such as implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions, promoting clean energy sources, and advocating for smoke-free environments. Education and awareness initiatives can also empower families to minimize exposure to harmful chemicals and ensure their homes are free from potential hazards.
8.3 Creating Safe Living Spaces
Creating safe living spaces is crucial for children’s health and well-being. This includes ensuring homes and schools are free from environmental hazards such as lead-based paint, asbestos, and mold. Providing access to clean drinking water, maintaining proper ventilation, and promoting good hygiene practices all contribute to a safer living environment. By prioritizing the creation of safe spaces, we can protect children from potential risks, including the development of ALL.
9. Education and Awareness Programs
9.1 Importance of Education
Education and awareness programs play a central role in preventing ALL. By providing accurate and accessible information about ALL risk factors, early detection, and prevention strategies, these programs empower individuals and communities to take proactive steps in reducing the burden of the disease. Education also helps dispel myths and misconceptions, enabling informed decision-making to prevent ALL.
9.2 Initiatives and Campaigns
Numerous initiatives and campaigns are dedicated to raising awareness about ALL and its prevention. These efforts aim to reach both the general public and healthcare professionals, providing them with the necessary knowledge to identify risk factors, advocate for preventive measures, promote early detection, and support affected families. Collaborating with organizations, schools, and community leaders ensures the widespread dissemination of information and fosters a collective approach to ALL prevention.
9.3 Engaging Communities and Schools
Engaging communities and schools is vital in implementing successful prevention strategies. Community-based initiatives can facilitate access to education and resources, encouraging individuals to adopt healthy lifestyles, reduce exposure to environmental hazards, and follow preventive guidelines. Schools also play a crucial role by integrating health education into curricula, promoting healthy behaviors, and organizing awareness campaigns. By involving communities and schools, we can create a supportive and informed environment for preventing ALL.
10. Research and Advances in ALL Prevention
10.1 Current Studies and Findings
Ongoing research is dedicated to understanding the factors contributing to the development of ALL and identifying effective prevention strategies. Studies are exploring genetic markers associated with increased risk, environmental exposures, and the impact of lifestyle factors. Additionally, advancements in genetic testing targeted therapies, and immunotherapies are revolutionizing the field and offering new avenues for prevention and treatment.
10.2 Future Directions
Future research directions aim to further refine our understanding of ALL and develop more precise preventive measures. Continued investigation into genetic markers and their interactions with environmental factors can enhance risk assessment and inform personalized prevention strategies. Additionally, advancements in technology and data analysis are expected to improve early detection methods, leading to better outcomes for children at risk of developing ALL.
10.3 Collaborative Efforts for Progress
Collaborative efforts among researchers, healthcare providers, advocacy groups, and policymakers are essential for advancing ALL prevention. By sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise, these collaborations can accelerate progress in research, education, and policy development. International networks and partnerships can facilitate the exchange of best practices and enable a global approach to preventing ALL in children. Through collaborative efforts, we can strive towards a future where the incidence of ALL is significantly reduced, and children can live healthier lives.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Preventing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children
How To Prevent Childhood Leukemia, How To Prevent Leukemia In Babies, Prevention Of Leukemia In Child