Imagine living in a world where people don’t have to worry about the Ebola virus disease spreading like wildfire. Picture a society where the fear of this deadly virus is a thing of the past. In this article, we will explore the essential steps you can take to prevent the spread of the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) and ensure the safety and well-being of yourself and those around you. From proper hygiene practices to education and awareness, together we can make significant strides in eradicating this devastating disease.
Understanding the Ebola Virus Disease
Introduction to Ebola
Ebola is a severe viral illness known as Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) that affects both humans and non-human primates. It is caused by the Ebola virus, which was first identified in 1976. The most common species of the virus that causes EVD is the Zaire ebolavirus. Ebola outbreaks have occurred primarily in Central and West African countries, with occasional transmission to other parts of the world. Understanding the nature of the Ebola virus and its transmission is crucial in effectively combating the disease.
Ebola transmission
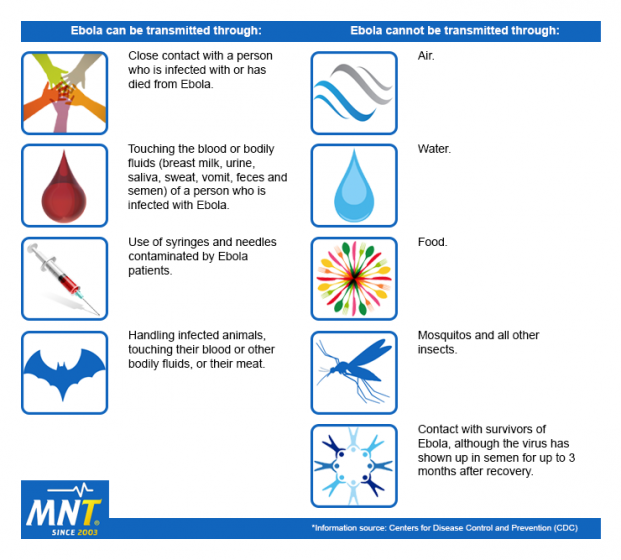
The Ebola virus is primarily transmitted to humans from wild animals and spreads through human-to-human transmission. It is believed that fruit bats are the natural hosts of the Ebola virus and play a crucial role in sustaining the virus in the environment. Direct contact with the blood, secretions, and body fluids (such as urine, saliva, feces, vomit, and breast milk) of infected animals or humans can lead to infection. Ebola can also be spread through contaminated surfaces and materials, such as needles and syringes. It is important to understand these modes of transmission to implement effective preventive measures.
Symptoms of Ebola
The symptoms of Ebola typically appear between 2 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. The early symptoms may include high fever, headache, joint and muscle aches, weakness, and fatigue. These initial symptoms are often followed by diarrhea, vomiting, rash, impaired kidney and liver function, and in some cases, internal and external bleeding. The severity of symptoms can vary, and it is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have been exposed to individuals or areas affected by Ebola.
Ebola diagnosis
Diagnosing Ebola requires specialized laboratory testing. Since the early symptoms of Ebola are similar to those of other diseases, it is essential for healthcare professionals to consider the possibility of Ebola in individuals who have been exposed to the virus or have traveled to affected regions. Blood samples are collected and analyzed for the presence of Ebola virus antigens or genetic material. Rapid diagnostic tests are also being developed to enable quicker and more accessible diagnosis, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Treatment options for Ebola
Currently, there is no specific licensed treatment for Ebola. However, supportive care is vital in managing the symptoms and complications associated with the disease. This includes providing intravenous fluids and electrolytes, maintaining oxygen levels, treating any bacterial infections that may occur, and providing pain relief and fever reduction. Early and aggressive treatment is critical to improving survival rates. Experimental treatments and therapies, such as monoclonal antibody treatments and antiviral drugs, are being researched and evaluated for their effectiveness in treating Ebola.
Preventive Measures to Control Ebola
Importance of prevention
Preventing the spread of Ebola is crucial for controlling outbreaks and minimizing the impact of the disease on individuals and communities. Prevention measures not only protect individuals from contracting Ebola but also help to break the chain of transmission. Recognizing the importance of preventive measures is essential to ensure the health and safety of everyone.
Public health measures
Public health interventions play a vital role in controlling Ebola outbreaks. These measures include timely detection and reporting of suspected cases, contact tracing to identify individuals who may have been exposed to Ebola, and isolation of confirmed cases to prevent further transmission. Additionally, public health authorities implement measures to ensure a timely and effective response, such as establishing emergency operations centers and coordinating with national and international partners.
Individual hygiene practices
Practicing good hygiene is an important individual preventive measure against Ebola. Regularly washing hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers can effectively kill the Ebola virus and other pathogens on the hands. Avoiding direct contact with the blood or body fluids of infected individuals, using personal protective equipment when in contact with potentially infected materials, and following safe burial practices are also crucial in preventing the transmission of Ebola.
Healthcare facility preparedness
Healthcare facilities need to be prepared to handle cases of Ebola effectively and safely. This includes establishing infection prevention and control measures, training healthcare workers on the use of personal protective equipment, and implementing proper waste management protocols. Healthcare facilities should also have systems in place to quickly identify suspected cases and isolate them from other patients to minimize the risk of transmission within the facility.
Surveillance and contact tracing
Prompt detection and surveillance of suspected cases are essential components of Ebola prevention. Health authorities track and investigate individuals who may have been in contact with Ebola patients to identify and monitor any possible transmission. Contact tracing helps to ensure that individuals who may have been exposed to the virus receive appropriate medical care and precautions to prevent further spread of the disease.

Promoting Awareness and Education
Community education programs
Promoting awareness and education about Ebola is crucial in empowering communities to prevent and control the disease. Community education programs focus on providing accurate information about Ebola, its transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures. These programs also address myths and misconceptions surrounding the disease, helping to reduce stigma and fear within the community.
Risk communication strategies
Effective risk communication strategies help to disseminate accurate and timely information about Ebola to the general public, healthcare workers, and other key stakeholders. Clear and consistent communication channels, including media campaigns, social media platforms, and community meetings, ensure that individuals have access to the latest information, understand the risks associated with Ebola, and know how to protect themselves and others.
Training of healthcare professionals
Training healthcare professionals is essential for effective Ebola prevention and control. Healthcare workers need to be equipped with the knowledge and skills to identify and manage suspected cases, implement infection prevention and control measures, and properly use personal protective equipment. Training programs also emphasize the importance of early detection and reporting to ensure a swift response to potential Ebola cases.
Dissemination of accurate information
The dissemination of accurate and reliable information about Ebola is crucial in combating misinformation and rumors that can fuel fear and panic within communities. Governments, international organizations, and public health authorities work together to ensure that accurate information about Ebola is widely available. Clear and concise messages, in local languages and culturally sensitive formats, ensure the information reaches a broad audience.
Engaging local communities
Engaging local communities is key to the success of Ebola prevention and control efforts. This involves working closely with community leaders, traditional healers, religious groups, and community-based organizations. By involving local communities in decision-making processes, addressing their concerns and cultural beliefs, and empowering them to take ownership of preventive measures, the effectiveness and sustainability of Ebola control programs can be greatly enhanced.
International Collaboration and Response
Global partnerships for surveillance and control
International collaboration is critical in responding to Ebola outbreaks. Global partnerships, such as those between governments, non-governmental organizations, research institutions, and international agencies, provide support in terms of expertise, resources, and coordination. These partnerships strengthen surveillance and control efforts, share best practices, and contribute to the development of effective strategies to prevent and respond to Ebola outbreaks.
Sharing data and research
Open sharing of data and research findings is invaluable in advancing the understanding of Ebola and developing effective preventive and treatment strategies. Collaboration among scientists, researchers, and public health professionals facilitates the exchange of knowledge, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to controlling Ebola. Transparent sharing of data also promotes accountability and fosters trust among the global health community.
Coordinating response efforts
Coordinating response efforts between national and international stakeholders is crucial in effectively managing Ebola outbreaks. Coordinated response efforts ensure a unified approach and maximize the impact of interventions. Effective coordination includes clear lines of communication, harmonized strategies and protocols, and collaborative decision-making processes. Coordinated response efforts also enable rapid mobilization of resources and technical assistance where they are most needed.
Supporting affected countries
Supporting affected countries is essential in their efforts to control and recover from Ebola outbreaks. This support can involve financial aid, provision of medical supplies and equipment, training and capacity building of healthcare workers, and assistance in strengthening healthcare systems. Effective and sustained support enables affected countries to respond promptly and effectively to Ebola outbreaks and build resilience for future health emergencies.
Emergency response planning
Preparing and planning for emergency responses is essential to minimize the impact of Ebola outbreaks. Countries and organizations need to develop and regularly update emergency response plans that outline strategies, roles, and responsibilities in the event of an outbreak. Regular simulations and drills help to test the effectiveness of these plans and identify areas for improvement. By being prepared, countries and organizations can mount swift and effective responses to mitigate the spread of Ebola.

Quarantine and Isolation Measures
Importance of isolation
Isolation is a crucial measure in preventing the spread of Ebola. Isolation involves the separation of individuals with confirmed or suspected Ebola from others to minimize the risk of transmission. By isolating infected individuals, healthcare facilities can provide appropriate care while protecting other patients, visitors, and healthcare workers from exposure to the virus.
Quarantine protocols
Quarantine is the restriction of movement and activities of individuals who have been exposed to Ebola but are not yet showing symptoms. Quarantine protocols ensure that individuals who may be incubating the virus are closely monitored and are not able to come into contact with others during the incubation period. Quarantine helps to prevent the spread of the disease and allows for early identification and isolation of infected individuals if they develop symptoms.
Isolation facilities
Properly equipped and staffed isolation facilities are essential in effectively managing Ebola cases. These facilities provide a safe and controlled environment for the care of infected individuals. Isolation facilities should have appropriate infection prevention and control measures in place to protect healthcare workers and prevent further transmission. Adequate supplies of personal protective equipment, medical equipment, and medication are also critical in providing quality care in isolation facilities.
Managing and monitoring quarantined individuals
Proper management and monitoring of quarantined individuals are necessary to ensure their well-being and compliance with quarantine protocols. Health authorities should establish systems to regularly check the health status of quarantined individuals, provide support and counseling services, and address any concerns or needs they may have during the quarantine period. Timely identification and isolation of individuals who develop symptoms are also crucial within quarantine settings.
Protective equipment and hygiene protocols
Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers is important in preventing the transmission of Ebola. PPE includes gloves, masks, goggles, gowns, and boots, which provide a physical barrier between healthcare workers and potentially infected individuals or materials. Strict adherence to hygiene protocols, such as handwashing and disinfection of surfaces, further reduces the risk of transmission. Regular training and monitoring of healthcare workers ensure the correct use of PPE and adherence to hygiene protocols.
Vaccination and Medical Interventions
Development of Ebola vaccines
Significant progress has been made in the development of Ebola vaccines. Multiple vaccine candidates have been tested in clinical trials and shown promising results in terms of safety and efficacy. The availability of effective vaccines can play a critical role in preventing and controlling Ebola outbreaks by providing immunity to individuals at risk of exposure.
Vaccine deployment strategies
Deploying Ebola vaccines in affected areas is a complex task that requires planning and coordination. Vaccination strategies may prioritize high-risk populations, such as healthcare workers and close contacts of Ebola cases. Vaccination campaigns should be conducted alongside other preventive measures, such as surveillance and infection control, to ensure a comprehensive approach to Ebola control. Effective monitoring and evaluation systems help to assess the impact and coverage of vaccination programs.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
Post-exposure prophylaxis involves providing preventive treatment to individuals who have been in contact with Ebola cases. This treatment can be in the form of antiviral drugs or monoclonal antibodies that neutralize the Ebola virus. Post-exposure prophylaxis aims to prevent infection in individuals who may have been exposed to the virus but have not yet developed symptoms. Timely administration of post-exposure prophylaxis can significantly reduce the risk of developing Ebola.
Experimental treatments
In addition to vaccines and post-exposure prophylaxis, various experimental treatments are being researched and evaluated for their effectiveness in treating Ebola. These experimental treatments may include antiviral drugs, antibody therapies, or plasma transfusions from Ebola survivors. Research and clinical trials help to determine the safety and efficacy of these treatments and contribute to the development of effective medical interventions.
Availability of medical resources
Ensuring the availability of medical resources, including vaccines, drugs, and medical equipment, is crucial in effectively responding to Ebola outbreaks. Strategic stockpiling of essential medical supplies and establishing systems for rapid deployment of resources to affected areas are important in ensuring a timely and effective response. Partnerships between governments, international organizations, and manufacturers play a key role in securing the availability and accessibility of these resources.
Safe Burial Practices
Risks associated with unsafe burials
Unsafe burial practices can contribute to the spread of Ebola. Direct contact with the bodies of deceased individuals who have died from Ebola can result in infection. Traditional burial practices, such as washing or touching the body, can also increase the risk of transmission. It is important to understand and address these risks to prevent further spread of the virus.
Guidelines for safe burials
Safe burial practices follow specific guidelines to minimize the risk of transmission of Ebola. These guidelines include ensuring the bodies of Ebola victims are handled by trained personnel, using appropriate personal protective equipment, and conducting burials in designated areas or cemeteries. Safe burial practices aim to respect cultural beliefs and traditions while prioritizing public health and preventing the spread of the disease.
Training of burial teams
Proper training of burial teams is essential in carrying out safe burials for Ebola victims. Burial teams should be trained on infection prevention and control measures, the correct use of personal protective equipment, and safe handling and disposal of deceased individuals. Training programs also emphasize the importance of effective communication and sensitivity towards the cultural and emotional needs of the affected communities.
Use of personal protective equipment
Burial teams should use personal protective equipment, such as gloves, masks, gowns, and boots, to protect themselves during the burial process. Proper donning and doffing techniques, as well as regular training and monitoring, ensure the correct use of personal protective equipment and minimize the risk of transmission. Availability of adequate and appropriate personal protective equipment is critical in facilitating safe burials.
Cultural considerations
Respecting cultural beliefs and practices is essential when implementing safe burial practices. Communities should be engaged in discussions and decisions regarding safe burial protocols, ensuring that these practices are culturally sensitive and acceptable. Cultural considerations include providing opportunities for family members to participate in the burial process within the limits of safety measures and addressing any concerns or fears related to safe burials.
Border Control and Travel Restrictions
Importance of border control
Border control measures play a crucial role in preventing the importation of Ebola cases from affected areas into other regions. Strict monitoring and control at border checkpoints help to identify individuals who may have been exposed to the virus and implement appropriate measures to prevent further transmission. By effectively managing travel and monitoring high-risk areas, border control measures contribute to the overall containment of Ebola outbreaks.
Screening and surveillance at border checkpoints
Screening and surveillance procedures at border checkpoints involve assessing individuals for symptoms of Ebola, such as fever, and determining their travel history to identify potential exposure. These measures can include temperature checks, questionnaires, and visual assessments. Individuals who meet the criteria for possible exposure may undergo further evaluation and testing, and appropriate actions, such as isolation or quarantine, will be taken.
Travel restrictions and advisories
Implementing travel restrictions and advisories may be necessary during Ebola outbreaks to limit the movement of individuals from affected areas. Travel restrictions can include the suspension of flights or other modes of transportation to and from high-risk regions. Travel advisories provide updated information on the situation in affected areas and recommend appropriate precautions for travelers, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with sick individuals.
Cooperation with international transportation networks
Cooperation with international transportation networks, such as airlines, seaports, and ground transportation providers, is critical in implementing effective border control measures. Close coordination between national authorities and transportation networks ensures the proper screening and monitoring of passengers, as well as the implementation of necessary preventive measures. Effective cooperation minimizes the risk of international spread and contributes to the overall containment of Ebola outbreaks.
Strict monitoring of high-risk areas
High-risk areas, such as regions experiencing ongoing Ebola outbreaks, require strict monitoring and control measures to prevent the spread of the disease. Enhanced surveillance, active case finding, and increased healthcare capacity in these areas help to detect and respond to new cases promptly. By focusing resources and interventions in high-risk areas, the overall impact of Ebola outbreaks can be reduced.

Community Engagement and Mobilization
Engaging local leaders and community organizations
Engaging local leaders and community organizations is essential in mobilizing communities to prevent and control Ebola. These key stakeholders play a crucial role in disseminating accurate information, addressing stigma and misconceptions, and promoting community participation in preventive measures. By involving local leaders and organizations, individuals are more likely to trust and adhere to recommended actions, leading to better community-wide prevention efforts.
Stigma reduction and social support
Stigma is a significant challenge during Ebola outbreaks and can hinder effective prevention and control efforts. Reducing stigma involves addressing fear, misconceptions, and discrimination surrounding Ebola. Advocacy campaigns, community dialogues, and social support networks help to create an inclusive and supportive environment for individuals affected by Ebola and their families. Stigma reduction is crucial in encouraging early reporting of cases and promoting open communication within communities.
Involving traditional healers and religious groups
Traditional healers and religious groups are influential figures within many communities, and involving them in Ebola prevention and control efforts can have a profound impact. Collaboration with traditional healers can help integrate traditional practices with validated prevention measures, ensuring a more comprehensive approach. Religious groups can disseminate accurate information and promote preventive measures through their existing communication channels. By working together, traditional healers, religious groups, and public health authorities can establish trust and credibility with communities.
Community-based surveillance
Community-based surveillance involves training and empowering community members to identify and report potential cases of Ebola. By creating a network of trained individuals who can recognize early symptoms, community-based surveillance ensures rapid detection and response to suspected cases. This early warning system enables public health authorities to initiate appropriate interventions promptly, limiting the spread of the disease.
Employment and economic support
Ebola outbreaks can have far-reaching socio-economic impacts on affected communities. Loss of income, disruptions to local markets, and limited access to essential services can further exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals affected by the disease. Providing employment opportunities and economic support, such as cash transfers or vouchers, helps to alleviate the financial burden on affected communities and promotes community resilience in the face of Ebola outbreaks.
Preparedness and Resilience Building
Creating national and regional preparedness plans
Creating national and regional preparedness plans is essential in ensuring countries are ready to respond to Ebola outbreaks. These plans outline strategies, roles, responsibilities, and resource allocation in the event of an outbreak. Preparedness plans consider aspects such as disease surveillance, laboratory capacity, response coordination, communication strategies, and training of healthcare workers. Regular updating and testing of these plans help ensure the effectiveness and readiness of response systems.
Training healthcare workers
Training healthcare workers is vital in building preparedness and response capacity. Healthcare workers need to be familiar with the signs and symptoms of Ebola, know how to properly use personal protective equipment, and be trained in infection prevention and control measures. Training programs should also include simulation exercises and drills to enable healthcare workers to practice and reinforce their skills in a realistic setting.
Stockpiling essential medical supplies
Stockpiling essential medical supplies, including personal protective equipment, diagnostics, pharmaceuticals, and medical equipment, is crucial for a swift and effective response to Ebola outbreaks. Adequate and secure storage of these supplies, along with regular inventory management and rotation, ensures their availability and functionality when needed. Partnerships with manufacturers and distributors help to ensure a reliable supply chain for these critical resources.
Establishing emergency response systems
Establishing emergency response systems involves creating structures and processes to facilitate a coordinated response to Ebola outbreaks. This includes establishing emergency operations centers, activating incident management teams, and implementing surveillance and reporting systems. Clear lines of communication, standard operating procedures, and regular information sharing ensure a seamless and efficient response in times of crisis.
Simulations and drills for outbreak scenarios
Simulations and drills are essential in preparing healthcare workers and response teams for outbreak scenarios. These exercises create opportunities to practice and evaluate response plans, test coordination and communication systems, and identify areas for improvement. Simulations and drills help to build resilience and confidence among healthcare workers and response teams, ensuring a rapid and effective response to Ebola outbreaks.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively addressing the various aspects of the Ebola Virus Disease is crucial in preventing its spread and mitigating its impact. From understanding the transmission and symptoms of Ebola to implementing preventive measures, engaging communities, and building preparedness and response capacity, a comprehensive approach is necessary to control outbreaks. By promoting awareness, fostering international collaboration, implementing quarantine and isolation measures, developing medical interventions, advocating safe burial practices, ensuring border control, engaging communities, and building resilience, we can work together to prevent and control the Ebola virus disease.
