When it comes to internal bleeding, promoting recovery is crucial for restoring health and well-being. This article explores the importance of addressing internal bleeding and offers valuable insights on effective strategies to facilitate the healing process. By understanding the challenges associated with internal bleeding and implementing appropriate recovery methods, you can take control of your health and promote a speedy and successful recovery. Whether you’ve recently experienced internal bleeding or want to be prepared in case of an emergency, this article is your go-to guide for promoting healing and promoting a healthier future.
Understanding Internal Bleeding
Definition of internal bleeding
Internal bleeding refers to the leakage of blood from blood vessels within the body, leading to blood accumulating in areas where it should not be. Unlike external bleeding, where blood is visible on the outside, internal bleeding is not readily apparent and can pose significant health risks if left untreated. The blood may accumulate within organs, tissues, or even body cavities, causing damage and impairing their normal function.
Causes of internal bleeding
Internal bleeding can stem from various underlying causes. Trauma, such as a severe injury or accident, is a common cause of internal bleeding. It can result from broken bones, organ injuries, or damage to blood vessels. Medical conditions, such as ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, aneurysms, or blood clotting disorders like hemophilia, can also lead to internal bleeding. Additionally, certain medications, such as anticoagulants, can increase the risk of internal bleeding.
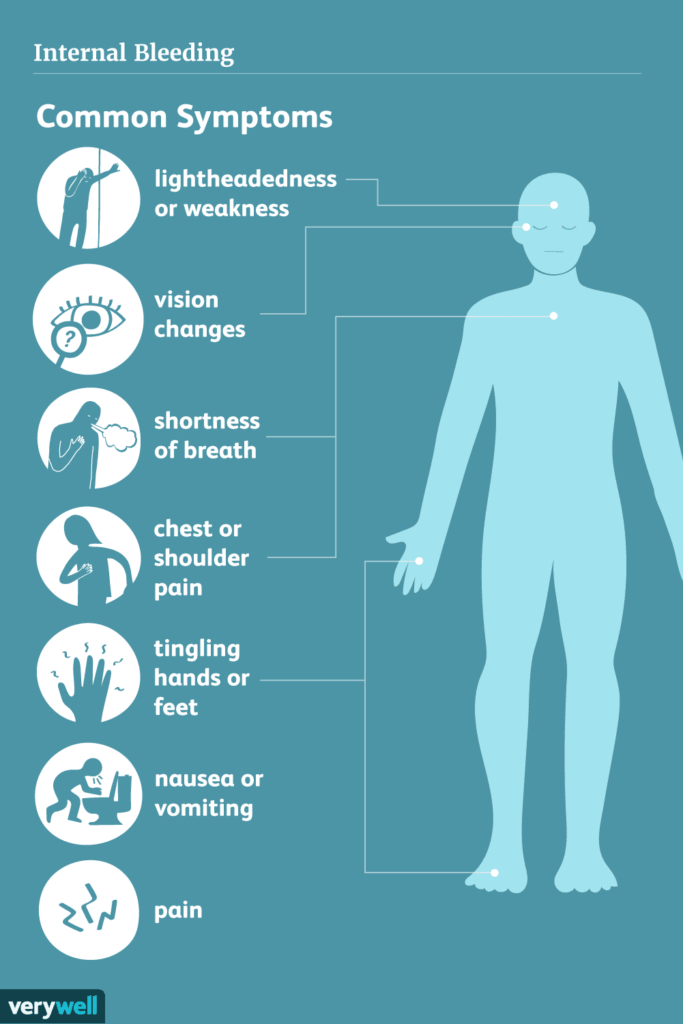
Symptoms of internal bleeding
Identifying the signs and symptoms of internal bleeding is crucial for early detection and prompt medical attention. While the specific symptoms may vary based on the location and severity of the bleeding, common signs include severe or persistent pain, swelling, tenderness, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath, excessive sweating, pale skin, or blood in urine or stools. It is important to note that some internal bleeding may not present with noticeable symptoms, underscoring the importance of regular check-ups and screenings.
Diagnosing internal bleeding
Diagnosing internal bleeding requires a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. Initially, a detailed medical history and physical examination will be conducted to assess symptoms and identify potential risk factors. Diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging scans like ultrasounds, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, and endoscopic procedures, may be employed to ascertain the presence and location of internal bleeding. These tests aid in examining damaged tissues, blood supply, and organ functions, assisting in the formulation of an appropriate treatment plan.
Emergency Response and Immediate Care
Recognizing the signs of internal bleeding
Recognizing the signs of internal bleeding is crucial to initiate prompt emergency response and care. Pay attention to symptoms such as severe pain, fainting, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, or signs of shock, including pale skin, sweating, and confusion. An individual may also exhibit signs of internal bleeding, such as a swollen or rigid abdomen, bruising or discoloration over the affected area, or blood in vomit, urine, or stools. It is essential to trust your instincts and seek medical assistance immediately if you suspect internal bleeding.
Calling for emergency medical assistance
In the event of suspected internal bleeding, it is crucial to call for emergency medical assistance without delay. Dial the emergency services hotline or contact your local emergency medical services to notify them about the situation. Provide them with accurate information regarding the symptoms, any potential causes of the bleeding, and the patient’s current condition. Do not hesitate to reach out for help, as prompt intervention and transportation to a healthcare facility equipped to manage internal bleeding can be life-saving.
Managing the patient’s condition while waiting for help
While waiting for emergency medical assistance to arrive, there are measures you can take to manage the patient’s condition and minimize potential risks. If the bleeding is from an extremity, elevate the affected limb above heart level to reduce blood flow to the area. Applying direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage can help control bleeding. If conscious, keep the person calm and encourage them to lie down and avoid unnecessary movements that may exacerbate the bleeding. If unconscious, place them in a position that maintains an open airway while protecting their spine. It is essential to monitor vital signs and be prepared to administer cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if necessary.

Medical Interventions for Internal Bleeding
Intravenous fluid administration
Intravenous fluid administration is a common medical intervention for internal bleeding, especially in cases of hypovolemic shock or significant blood loss. It involves the introduction of fluids directly into a patient’s vein to help maintain blood pressure, restore fluid balance, and support vital organ functions. Intravenous fluids can also aid in replacing lost blood volume and preventing complications associated with blood loss.
Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is a critical medical intervention when internal bleeding results in significant blood loss or anemia. It involves the transfer of compatible blood or blood products from a donor to the patient through a vein. Blood transfusions help replenish lost red blood cells, restore oxygen-carrying capacity, and stabilize hemoglobin levels. They can be life-saving in cases of severe internal bleeding or ongoing blood loss.
Surgical interventions
Surgical interventions play a vital role in the management of internal bleeding, particularly when it originates from a specific organ or anatomical site. Surgeons may perform procedures like exploratory laparotomy, which involves making an incision in the abdomen to identify and address the source of bleeding. They may also employ minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy, to visualize and treat internal bleeding. Surgical interventions aim to stop the bleeding, repair damaged tissues, and prevent further complications.
Interventional radiology procedures
Interventional radiology procedures provide minimally invasive alternatives for controlling internal bleeding. Using imaging guidance, interventional radiologists can access and treat bleeding sites by deploying various techniques. These may include embolization, where small particles or coils are introduced into blood vessels to block the flow and stop the bleeding; or angiography, which involves injecting contrast dye into blood vessels to locate the site of bleeding and potentially cauterize it.
Medications for Internal Bleeding
Proton pump inhibitors
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications commonly prescribed for internal bleeding caused by gastrointestinal ulcers or conditions. PPIs work by reducing the production of stomach acid, which can help alleviate discomfort, promote healing, and prevent further bleeding. By inhibiting acid secretion, PPIs create an optimal environment for ulcer healing and contribute to the management of internal bleeding.
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs are commonly prescribed to manage conditions like deep vein thrombosis, stroke, or coronary artery disease. However, these medications can increase the risk of internal bleeding, especially in individuals on long-term therapy. While they play a crucial role in preventing blood clots, the potential for bleeding complications necessitates careful monitoring and adjustment of medications to balance their benefits and risks.
Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid is a medication that can help control bleeding by preventing blood clots from breaking down. It is commonly used in the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding, nosebleeds, and bleeding associated with certain surgical procedures. In cases of internal bleeding, tranexamic acid may be administered to decrease blood loss and facilitate clot formation, preventing further damage and potentially improving outcomes.
Factor VIIa
Factor VIIa is a medication approved for the treatment of certain bleeding disorders in which the clotting process is impaired. In internal bleeding cases, factor VIIa may be administered to stimulate the formation of blood clots and control bleeding. It works by assisting in the conversion of inactive clotting factors into their active forms, promoting clot formation and reducing blood loss.

Lifestyle Changes to Promote Recovery
Avoiding activities that may worsen bleeding
After experiencing internal bleeding, it is important to avoid activities that may exacerbate or prolong bleeding. Engaging in high-impact sports, heavy lifting, or strenuous activities can increase blood flow and place additional stress on healing tissues or vulnerable organs. Following the advice of healthcare professionals and gradually reintroducing physical activities as guided by the recovery process can help prevent re-injury and promote healing.
Eating a balanced diet
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for promoting recovery from internal bleeding. A diet rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins, can support tissue healing, boost immune function, and aid in the production of healthy blood cells. Prioritizing foods like lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sources of healthy fats can provide the necessary building blocks for the body’s healing processes.
Staying hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and recovery from internal bleeding. Water plays a vital role in transporting nutrients, eliminating waste products, and maintaining optimal blood volume. Adequate hydration can help prevent complications associated with blood loss, such as low blood pressure or reduced organ perfusion. It is important to drink water regularly and ensure sufficient fluid intake, particularly during periods of increased physical activity or warmer weather.
Managing stress levels
Stress can have a significant impact on the body’s healing and recovery processes. When recovering from internal bleeding, it is important to manage stress levels and prioritize self-care. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging hobbies, can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being. Seeking support from friends, family, or even professional counseling services can also provide valuable emotional support during the recovery process.
Post-Recovery Management
Further diagnostic tests to determine underlying causes
Once an individual has recovered from an episode of internal bleeding, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to identify and address any underlying causes. These tests can help healthcare providers evaluate the health status of vital organs, assess blood clotting factors, and determine if there are any ongoing or chronic conditions that contributed to the bleeding. Understanding the root cause of the internal bleeding can guide further treatment and preventive measures.
Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial in ensuring proper post-recovery management and monitoring. These appointments allow healthcare professionals to assess the patient’s progress, address any lingering concerns or complications, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Additionally, follow-up appointments provide an opportunity for patients to discuss any new symptoms, receive further guidance on lifestyle modifications, and seek continued medical support.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy
Certain cases of internal bleeding may require rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, mobility, and function. These interventions are particularly relevant in instances where the bleeding has affected the musculoskeletal system or necessitated surgical interventions. Rehabilitation programs tailored to the individual’s needs may include exercises to restore range of motion, strengthen weakened muscles, or relearn specific skills. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in facilitating a full recovery and optimizing long-term outcomes.
Support groups and counseling
Recovering from internal bleeding, especially if it was a traumatic event, can have a significant psychological impact on individuals. Joining support groups or seeking counseling services can offer a valuable source of emotional support and understanding. Interacting with others who have undergone similar experiences can help normalize emotions, provide coping strategies, and offer insights into the recovery journey. Support groups and counseling can aid individuals in navigating the psychological aspects of recovery and promote overall well-being.
Preventing Future Occurrences
Identifying and addressing underlying medical conditions
To prevent future occurrences of internal bleeding, it is crucial to identify and address any underlying medical conditions that may pose a risk. Regular medical check-ups, including blood tests and imaging studies, can aid in the early detection and management of conditions like ulcers, aneurysms, or blood clotting disorders. By promptly addressing these underlying conditions, healthcare providers can implement preventive measures and minimize the risk of internal bleeding.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in preventing future occurrences of internal bleeding. This includes adopting habits such as regular exercise, consuming a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding behaviors that increase the risk of injury or bleeding. Making lifestyle choices that promote overall health and well-being can reduce the likelihood of experiencing internal bleeding and contribute to an improved quality of life.
Regular check-ups and screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings are crucial in preventing future occurrences of internal bleeding. These routine appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor an individual’s health, assess any potential underlying risk factors, and detect early signs of potential complications. By attending regular check-ups and following recommended screening guidelines, individuals can proactively manage their health and reduce the likelihood of encountering internal bleeding or related complications.
Risks and Complications
Internal organ damage
Internal bleeding can lead to internal organ damage if left untreated or if the bleeding is severe. Prolonged bleeding and compromised blood supply to vital organs can result in tissue necrosis, impaired organ function, or, in severe cases, organ failure. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention at the first signs of internal bleeding to minimize the risk of organ damage and optimize the chances of recovery.
Hemorrhagic shock
In some cases, internal bleeding can lead to hemorrhagic shock, a life-threatening condition characterized by significant blood loss and inadequate oxygen supply to body tissues. Hemorrhagic shock can occur rapidly and requires immediate medical intervention to stabilize vital signs, restore blood volume, and prevent further complications. It is essential to recognize the signs of hemorrhagic shock, such as rapid breathing, confusion, pale skin, weak pulse, or loss of consciousness, and seek emergency medical assistance without delay.
Infection
Internal bleeding can create an environment that is susceptible to infection. Blood that accumulates outside blood vessels can serve as a medium for bacterial growth, increasing the risk of infection. Additionally, surgeries or procedures performed to address internal bleeding carry the inherent risk of introducing infectious agents. Preventive measures, such as maintaining good hygiene, administering appropriate antibiotics, or employing sterile techniques during procedures, are crucial to minimize the risk of infection and facilitate recovery.
Formation of blood clots
While internal bleeding poses risks, the medications and treatments used to manage it can also increase the risk of blood clot formation. This occurs due to the delicate balance between managing bleeding and preventing clotting disorders. Healthcare professionals carefully monitor individuals receiving medication interventions to balance the benefits of preventing further bleeding with the potential risks of promoting blood clots. Appropriate management and timely adjustments of medications can help minimize the risk of excessive clot formation.

Promising Research and Advances
Development of pro-coagulant agents
Researchers are continually exploring the development of pro-coagulant agents that can promote the formation of blood clots, aiding in the management of internal bleeding. These agents aim to enhance blood clotting processes without compromising normal blood flow or increasing the risk of undesired clot formation. By further refining these pro-coagulant agents, researchers hope to minimize the consequences of internal bleeding and improve patient outcomes.
Potential use of stem cells
Stem cell research shows promise in the realm of internal bleeding management. The unique regenerative properties of stem cells offer potential avenues for repairing damaged blood vessels and enhancing the body’s natural clotting abilities. While still in early stages, research suggests that stem cells can contribute to tissue regeneration and improved healing outcomes in cases of internal bleeding.
Improved imaging techniques
Advancements in imaging techniques have enhanced the ability to diagnose and manage internal bleeding. Innovations such as contrast-enhanced imaging, three-dimensional imaging, or real-time imaging guidance during interventions allow for improved visualization of bleeding sites, precise localization, and more targeted treatment approaches. Improved imaging techniques have revolutionized the field of interventional radiology and fostered better outcomes for individuals with internal bleeding.
Advancements in non-surgical treatments
Non-surgical treatments for internal bleeding continue to evolve, reducing the need for invasive surgeries and associated risks. Innovative approaches, such as the use of sealants, targeted medications, or embolization techniques, offer minimally invasive alternatives for controlling bleeding and promoting recovery. Advancements in non-surgical treatments strive to decrease the overall trauma to the body, shorten recovery times, and improve patient comfort and outcomes.
Supporting the Recovery Process
Providing emotional support to the patient
Emotional support plays a vital role in the recovery process from internal bleeding. Friends, family, and healthcare providers can provide a supportive environment that encourages individuals to express their emotions, cope with anxiety or stress, and navigate the challenges associated with recovery. Active listening, providing reassurance, and offering empathy can positively impact an individual’s mental well-being and contribute to their overall recovery.
Understanding the psychological impact
Recovering from internal bleeding can have a significant psychological impact on individuals. It is crucial to recognize the potential emotional and psychological challenges that patients may face during their recovery journey. Anxiety, fear, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can arise due to the traumatic event, the physical and emotional toll of treatment, or the fear of recurrence. Developing a comprehensive recovery plan that addresses these psychological aspects can enhance overall healing and well-being.
Assisting with daily activities and lifestyle adjustments
During the recovery period, individuals may require assistance with daily activities and adjustments to their lifestyle. This can include help with household chores, transportation to medical appointments, or support in accomplishing tasks that may be physically challenging. Friends, family members, or caregivers can play a crucial role in providing practical assistance, allowing individuals to focus on their recovery and minimizing any unnecessary strain.
Educating caregivers
Educating caregivers is key in providing optimal support to individuals recovering from internal bleeding. Caregivers should receive information on the specific condition, treatment procedures, and any potential complications. This knowledge equips them to address the needs of the recovering individual, recognize signs of complications, ensure adherence to the treatment plan, and provide a safe and supportive environment. Regular communication and collaboration with healthcare providers are essential for caregivers to stay informed and provide the best possible care.
In conclusion, internal bleeding poses significant risks and should not be taken lightly. Recognizing the signs, seeking immediate medical attention, and following appropriate treatment plans are essential for a successful recovery. While medical interventions, medications, and lifestyle modifications play crucial roles in managing internal bleeding, offering support and understanding throughout the recovery journey is equally important. By promoting awareness, advancing medical research, and supporting individuals throughout the recovery process, we can work towards better outcomes in the management of internal bleeding.