Hey there! Have you ever wondered how to recognize the symptoms of internal bleeding? Well, look no further! In this article, we will guide you through the signs and symptoms that may indicate internal bleeding, allowing you to take prompt action and seek medical attention. Internal bleeding can be serious and potentially life-threatening, so it’s essential to be aware of the warning signs. So, let’s dive right into it and learn how to spot the red flags of internal bleeding!

Understanding Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding refers to bleeding that occurs within the body, rather than on the surface. It can be a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention and treatment. Understanding the causes, types, complications, and risk factors of internal bleeding is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Definition
Internal bleeding is the escape of blood from blood vessels that occurs inside the body. This blood may accumulate in specific organs or body cavities, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. It can be caused by trauma, underlying medical conditions, or certain medications.
Causes
There are several potential causes of internal bleeding. Trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, is one of the most common causes, as it can result in damage to internal organs or blood vessels. Medical conditions, such as ulcers, aneurysms, or certain cancers, can also lead to internal bleeding. Additionally, certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the risk of internal bleeding.
Types
Internal bleeding can occur in different parts of the body, leading to various types of manifestations. Some of the common types of internal bleeding include intracranial hemorrhage (bleeding inside the skull), retroperitoneal hemorrhage (bleeding behind the abdominal cavity), and intra-abdominal hemorrhage (bleeding within the abdominal cavity).
Complications
If left untreated, internal bleeding can lead to serious complications. Excessive blood loss can result in anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Internal bleeding in specific organs, such as the brain or lungs, can lead to organ damage and potentially life-threatening conditions. It is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing internal bleeding. Individuals who participate in contact sports or high-risk activities are more prone to experiencing trauma-related internal bleeding. Those with underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease, or blood disorders, may also have an increased risk. Additionally, individuals taking medications that affect blood clotting are at a higher risk of internal bleeding.
Common Symptoms of Internal Bleeding
Recognizing the symptoms of internal bleeding is crucial for early detection and prompt medical intervention. While the specific symptoms may vary depending on the location and severity of the bleeding, there are several general symptoms that may indicate internal bleeding. It is important to note that not all individuals will experience the same symptoms, and some may not have any symptoms at all.
General Symptoms
General symptoms of internal bleeding can include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Rapid heart rate
- Shortness of breath
These symptoms occur due to the loss of blood or decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract can cause various symptoms, including:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Black, tarry stools (melena)
- Vomiting blood (hematemesis)
- Blood in the stool (hematochezia)
These symptoms may indicate bleeding from the stomach, intestines, or rectum.
Urinary Symptoms
Internal bleeding in the urinary system can present with the following symptoms:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen
These symptoms may suggest bleeding from the kidneys or urinary tract.
Respiratory Symptoms
When internal bleeding occurs in the respiratory system, it may cause symptoms such as:
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
These symptoms can indicate bleeding in the lungs or airways.
Cardiovascular Symptoms
Internal bleeding in the cardiovascular system can lead to symptoms including:
- Sudden and severe chest pain
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
These symptoms may suggest bleeding around the heart or within the blood vessels.
Cerebral Symptoms
Bleeding within the brain can present with the following symptoms:
- Severe headache
- Changes in vision
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
These symptoms may indicate intracranial hemorrhage, which requires immediate medical attention.
Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Internal bleeding in the musculoskeletal system can cause symptoms such as:
- Swelling, bruising, or deformity around the injured area
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Limited range of motion
These symptoms may suggest internal bleeding within a joint or muscle.
Skin Symptoms
Internal bleeding can sometimes present with skin symptoms, including:
- Red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae)
- Rash or discoloration
- Cool and clammy skin
These symptoms may occur if bleeding is close to the skin’s surface.
Reproductive Symptoms
In women, internal bleeding in the reproductive system can lead to symptoms such as:
- Vaginal bleeding outside of menstruation
- Severe pelvic pain or cramping
- Dizziness or fainting
These symptoms may suggest a potential gynecological condition associated with internal bleeding.
Symptoms in Children
Children may exhibit specific symptoms when experiencing internal bleeding. These symptoms can vary depending on the age of the child and the location of the bleeding. Some common symptoms in children may include:
- Restlessness or irritability
- Vomiting or spitting up blood
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Pale skin or fatigue
- Refusal to eat or drink
If any of these symptoms are present in a child, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
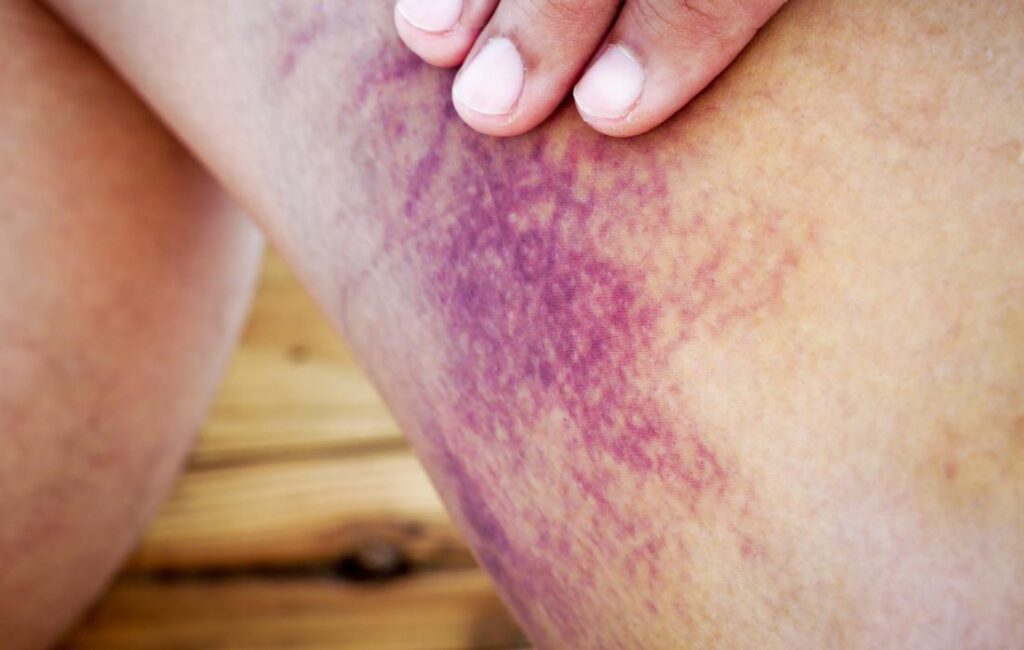
Unusual Manifestations of Internal Bleeding
While internal bleeding can occur in various body systems, there are some unusual manifestations that may occur. These manifestations may present unique challenges in identifying and diagnosing internal bleeding.
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage refers to bleeding inside the skull and brain. This can occur due to trauma or certain medical conditions. Symptoms may include severe headache, changes in vision, weakness or numbness in the face or extremities, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs behind the abdominal cavity. This type of bleeding can result from trauma or spontaneous rupture of blood vessels. Symptoms may include severe abdominal or back pain, low blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Intra-abdominal Hemorrhage
Intra-abdominal hemorrhage refers to bleeding within the abdominal cavity. Causes can include trauma, organ rupture, or bleeding from underlying medical conditions. Symptoms may include abdominal pain or distention, tenderness upon palpation, low blood pressure, and signs of shock.
Hemothorax
Hemothorax is the accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity, which surrounds the lungs. It can occur as a result of trauma, lung or chest wall injuries, or certain medical conditions. Symptoms may include chest pain, difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, and decreased breath sounds on one side of the chest.
Hemopericardium
Hemopericardium is the accumulation of blood in the pericardial sac surrounding the heart. It can occur due to trauma, ruptured blood vessels, or certain medical conditions. Symptoms may include severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, and signs of cardiac tamponade, such as low blood pressure.
Intramuscular Hematoma
Intramuscular hematoma refers to bleeding within a muscle. It can occur as a result of trauma or muscle tears. Symptoms may include localized pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the affected muscle.
Intracompartmental Hemorrhage
Intracompartmental hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs within a muscle compartment surrounded by a tough membrane called fascia. It can occur due to trauma, fractures, or crush injuries. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling, numbness or tingling, and decreased pulse or sensation in the affected limb.
Hematuria
Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It can be caused by various factors, including trauma, urinary tract infections, or underlying medical conditions. The presence of blood in the urine should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding outside of normal menstruation may be a sign of internal bleeding in the reproductive system. It can be caused by various factors, including trauma, gynecological conditions, or pregnancy complications. It is important to seek medical attention if experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Rectal Bleeding
Rectal bleeding can occur due to internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. It can result from conditions such as ulcers, hemorrhoids, or colorectal cancer. If experiencing rectal bleeding, it is important to seek medical evaluation to determine the cause.
Identifying Internal Bleeding in Different Body Systems
Internal bleeding can occur in various body systems, and identifying the symptoms associated with each system is crucial for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
Digestive System
In the digestive system, internal bleeding can occur in the stomach, intestines, or rectum. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, black or tarry stools, vomiting blood, or blood in the stool. Swallowing difficulties or discomfort in the upper abdomen may also occur.
Urinary System
Internal bleeding in the urinary system can lead to symptoms such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen. In some cases, blood clots may be present in the urine. Individuals may also experience urinary urgency or inability to empty the bladder fully.
Respiratory System
When internal bleeding occurs in the respiratory system, symptoms may include coughing up blood, difficulty breathing, and chest pain or discomfort. Individuals may also exhibit rapid breathing or cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin).
Cardiovascular System
Internal bleeding in the cardiovascular system may present with symptoms such as sudden and severe chest pain, rapid heart rate, or fainting. Low blood pressure may also be observed. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if experiencing chest pain or other symptoms associated with cardiovascular system involvement.
Endocrine System
Internal bleeding in the endocrine system may be less common but can occur in organs such as the adrenal glands or pancreas. Symptoms may vary depending on the specific organ affected. Seek medical attention if experiencing unexplained abdominal pain or hormonal imbalances.
Nervous System
In the nervous system, internal bleeding can occur within the brain or spinal cord. Symptoms may include severe headache, changes in vision, weakness or numbness in the face or extremities, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, or loss of coordination. Altered mental status or changes in consciousness may also occur.
Musculoskeletal System
Internal bleeding in the musculoskeletal system can cause symptoms such as localized pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the affected muscle or joint. Bruising or discoloration may also be observed around the injured area. Seek medical attention if experiencing severe pain or inability to move a limb.
Integumentary System
Internal bleeding close to the skin’s surface may cause skin symptoms, including red or purple spots (petechiae), rash, or cool and clammy skin. Seek medical evaluation if observing unexplained skin discoloration or unusual symptoms.
Reproductive System
In women, internal bleeding in the reproductive system may lead to symptoms such as abnormal vaginal bleeding outside of menstruation, severe pelvic pain or cramping, dizziness, or fainting. Seek medical attention if experiencing unexplained vaginal bleeding or concerning reproductive symptoms.
Hematologic System
Internal bleeding within the hematologic system may present as anemia symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath. Individuals may also have easy bruising or prolonged bleeding after an injury. Seek medical evaluation if experiencing unexplained anemia or abnormal bleeding tendencies.

Emergency Signs and Symptoms
Certain signs and symptoms of internal bleeding require immediate medical attention. If any of these emergency signs and symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance.
Significant Drop in Blood Pressure
A sudden and significant drop in blood pressure may indicate severe internal bleeding. This can lead to shock, which is a life-threatening condition. Symptoms may include dizziness, lightheadedness, rapid and weak pulse, and cold and clammy skin.
Rapid Heart Rate
An abnormally fast heart rate, known as tachycardia, can be a sign of internal bleeding. The body compensates for the loss of blood by pumping the heart faster to maintain blood flow to vital organs. Seek medical attention if experiencing a rapid heart rate that is unexplained or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Rapid Breathing
Rapid and shallow breathing, also known as tachypnea, can be an indication of internal bleeding. It may occur as the body tries to compensate for the decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Seek immediate medical attention if experiencing rapid breathing or difficulty breathing.
Weakness or Fatigue
Internal bleeding can lead to a decreased oxygen supply to the body, resulting in weakness and fatigue. If experiencing unexplained and severe weakness or fatigue, it is important to seek medical evaluation promptly.
Confusion or Disorientation
Internal bleeding, especially within the brain, can cause confusion or disorientation. Changes in mental status should be taken seriously and warrant immediate medical attention. Seek medical help if experiencing sudden confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, or altered level of consciousness.
Pale or Cold Skin
Internal bleeding can lead to decreased blood flow to the skin, resulting in paleness or coolness. If observing sudden paleness or coldness of the skin, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Vomiting Blood
Vomiting blood, also known as hematemesis, is a severe symptom of internal bleeding. It may indicate bleeding within the gastrointestinal tract. If vomiting blood, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention.
Passing Black or Tarry Stools
Passing black or tarry stools, also known as melena, can be a sign of internal bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. This appearance is due to the digestion of blood in the stomach and small intestine. If experiencing black or tarry stools, it is important to seek medical evaluation.
Difficulty Breathing
Difficulty breathing, also known as dyspnea, can be a sign of internal bleeding in the respiratory system or chest cavity. If experiencing sudden and unexplained difficulty breathing, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Non-specific Symptoms that may Indicate Internal Bleeding
Some symptoms may be nonspecific and can be attributed to various other conditions. However, they should not be ignored and may warrant medical evaluation to rule out internal bleeding.
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain can be a symptom of various conditions, including internal bleeding. If experiencing persistent or severe abdominal pain, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause.
Chest Pain
Chest pain may be associated with internal bleeding in the cardiovascular or respiratory system. While chest pain can have many causes, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation if experiencing sudden and severe chest pain.
Back Pain
Back pain can occur with internal bleeding, particularly in cases of retroperitoneal hemorrhage or bleeding within the musculoskeletal system. Seek medical attention if experiencing severe or unexplained back pain.
Dizziness
Dizziness can result from various factors, including internal bleeding. If experiencing persistent or severe dizziness, it is important to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting can be symptoms of internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal system. If experiencing persistent or severe nausea and vomiting, it is important to seek medical attention.
Headache
While headaches can have many causes, severe or sudden headaches may be associated with internal bleeding in the brain. Seek medical evaluation if experiencing severe or unexplained headaches.
Joint Pain
Joint pain can occur with internal bleeding within the musculoskeletal system. If experiencing severe or persistent joint pain, it is important to seek medical attention.
Swelling or Bruising
Swelling or bruising can occur with internal bleeding in the musculoskeletal system. If observing unexplained or severe swelling or bruising, it is important to seek medical evaluation.
Fainting or Loss of Consciousness
Fainting or loss of consciousness can be a symptom of internal bleeding, particularly if accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as chest pain or dizziness. Seek immediate medical attention if experiencing fainting or loss of consciousness.
Seizures
Seizures can occur with intracranial hemorrhage. If experiencing a seizure or witnessing someone having a seizure, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention.

Symptoms Difficult to Recognize or Attributed to Other Conditions
Some symptoms of internal bleeding may be subtle, particularly in certain populations or associated with specific medical conditions. These symptoms may be challenging to recognize or attributed to other conditions.
Subtle Changes in Mental Status
Subtle changes in mental status, such as confusion, restlessness, or irritability, can occur with internal bleeding, particularly in older adults or individuals with underlying medical conditions. Seek medical attention if observing unexplained changes in mental status.
Internal Bleeding in Elderly
Internal bleeding in elderly individuals can present with nonspecific symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, or confusion. Changes in appetite, unexplained weight loss, or altered urine output may also be observed. It is important to seek medical evaluation if observing concerning symptoms in the elderly.
Internal Bleeding in Infants
Infants may exhibit nonspecific symptoms when experiencing internal bleeding, such as irritability, difficulty feeding, or persistent crying. Changes in skin color or decreased activity level may also occur. If observing concerning symptoms in infants, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Internal Bleeding in Pregnant Women
Pregnant women may display symptoms of internal bleeding that can be attributed to other pregnancy-related conditions, such as abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding. If experiencing abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Internal Bleeding in Athletes
Internal bleeding in athletes can be challenging to recognize, as symptoms may be attributed to exercise or sports-related injuries. Persistent or severe pain, swelling, or difficulty moving a limb should not be ignored and warrant medical evaluation.
Internal Bleeding in Cancer Patients
Cancer patients may have a higher risk of internal bleeding due to the effects of the disease or cancer treatments on blood clotting. Symptoms can vary depending on the location and extent of bleeding. If experiencing new or worsening symptoms, it is important for cancer patients to seek prompt medical evaluation.
Internal Bleeding in Patients with Blood Disorders
Patients with underlying blood disorders, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease, may have an increased risk of internal bleeding. Symptoms may vary depending on the specific disorder and location of bleeding. If experiencing unexplained or prolonged bleeding, it is important for patients with blood disorders to seek medical attention.
Internal Bleeding in Patients on Anticoagulants
Patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin or heparin, may be at higher risk of internal bleeding. Symptoms may be similar to those of internal bleeding in other individuals. If experiencing unexplained or severe symptoms, it is important for patients on anticoagulants to seek immediate medical attention.
Internal Bleeding in Patients with Liver Disease
Patients with liver disease may have an increased risk of internal bleeding, particularly if they have liver cirrhosis. Symptoms may include unexplained abdominal pain, easy bruising, or signs of bleeding, such as bloody stools or vomiting blood. It is crucial for patients with liver disease to seek medical evaluation if experiencing concerning symptoms.
Internal Bleeding in Patients with Kidney Disease
Patients with kidney disease may be at higher risk of internal bleeding due to abnormalities in blood clotting. Symptoms may vary depending on the location and extent of bleeding. If experiencing unexplained or prolonged bleeding, it is important for patients with kidney disease to seek medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Determining when to seek medical attention for internal bleeding depends on the severity and specific symptoms. In some cases, immediate medical attention is necessary, while in others, urgent or non-urgent medical evaluation may be appropriate.
Immediate Medical Attention
Immediate medical attention is warranted in the following situations:
- Severe or uncontrolled bleeding that cannot be stopped
- Signs of shock, such as a significant drop in blood pressure, rapid heart rate, or pale and cold skin
- Loss of consciousness, fainting, or seizures
- Sudden and severe chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Changes in vision, weakness or numbness in the face or extremities, or difficulty speaking
- Head trauma with loss of consciousness, severe headache, or altered mental status
Urgent Medical Attention
Urgent medical attention should be sought for the following symptoms:
- Vomiting blood or passing black or tarry stools
- Significant abdominal pain or swelling
- Severe back pain or difficulty moving
- Persistent or severe joint pain, swelling, or limited range of motion
- Unexplained and severe weakness, fatigue, or dizziness
- Sudden onset of confusion, restlessness, or irritability
- Unexplained or persistent nausea, vomiting, or changes in appetite
- New or worsening symptoms in cancer patients or individuals with blood disorders
Non-Urgent Medical Attention
Non-urgent medical attention may be appropriate for symptoms that are concerning but not immediately life-threatening. Examples include:
- Mild to moderate abdominal pain or discomfort
- Minor bruising or swelling without other concerning symptoms
- Mild joint pain or limited range of motion
- Nonspecific symptoms that could potentially be attributed to internal bleeding
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and appropriate management.
Pregnant Women and Internal Bleeding
Pregnant women should seek immediate medical attention if experiencing symptoms such as vaginal bleeding or severe abdominal pain. These symptoms may indicate a potential threat to the pregnancy and require prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional.

Diagnosing Internal Bleeding
Diagnosing internal bleeding requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The diagnostic process may involve:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will assess the individual’s medical history, including any underlying medical conditions, medication use, and previous injuries or surgeries. A thorough physical examination will be performed to check for signs of bleeding, such as bruising, swelling, or abnormal vital signs.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to evaluate the individual’s blood count, clotting factors, and organ function. Elevated levels of certain enzymes or markers may indicate internal bleeding or organ damage.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, may be performed to visualize the location and extent of internal bleeding. These imaging modalities can provide detailed images of the organs and tissues affected by the bleeding.
Endoscopic Procedures
Endoscopic procedures, such as gastroscopy or colonoscopy, may be used to directly visualize the gastrointestinal tract and identify any sources of bleeding. In some cases, biopsies may be taken during these procedures for further evaluation.
Laparoscopy and Exploratory Surgery
Laparoscopy or exploratory surgery may be necessary in certain cases to directly visualize and address internal bleeding. These procedures involve making small incisions and using a camera or surgical instruments to explore the abdominal cavity.
Other Diagnostic Techniques
Other diagnostic techniques, such as angiography or ultrasound, may be employed depending on the specific circumstances and suspected location of internal bleeding. These techniques can provide additional information about blood flow and abnormalities in the affected areas.
Treatment and Management of Internal Bleeding
The treatment and management of internal bleeding depend on the location, severity, and underlying cause of the bleeding. Prompt intervention is crucial to prevent further complications and restore stability.
Stabilization and Supportive Care
In cases of significant internal bleeding, the immediate focus is on stabilizing the individual and providing supportive care. This may include administering intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, or medications to maintain blood pressure and vital organ function.
Medications and Treatments
Medications or treatments may be used to address the underlying cause of the internal bleeding. For example, blood transfusions or clotting factor replacements may be necessary in cases of severe anemia or coagulation disorders. Medications to control bleeding, such as clotting agents or vasoconstrictors, may also be administered.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical intervention is required to stop bleeding or repair damaged organs or blood vessels. Surgical procedures may include laparotomy, angiography with embolization, or open surgery to repair or replace affected structures.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures, such as endoscopy or interventional radiology techniques, can be used to diagnose and treat internal bleeding. These procedures involve accessing the affected area through small incisions or through natural body openings, minimizing the need for extensive surgery.
Transfusion of Blood Products
Transfusion of blood products, such as packed red blood cells, platelets, or fresh frozen plasma, may be necessary to replace lost blood or restore clotting factors. These transfusions help maintain an adequate oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and prevent further bleeding.
Post-Treatment and Recovery
After treatment for internal bleeding, individuals may require close monitoring and follow-up care. This may involve regular blood tests to assess clotting function and organ function. Physical therapy or rehabilitation may also be necessary to regain strength and function following surgery or severe bleeding episodes.
Internal bleeding is a serious medical condition that requires prompt recognition, diagnosis, and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and possible complications of internal bleeding can help individuals seek timely medical attention and prevent further harm. If experiencing any concerning symptoms or suspecting internal bleeding, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and management.