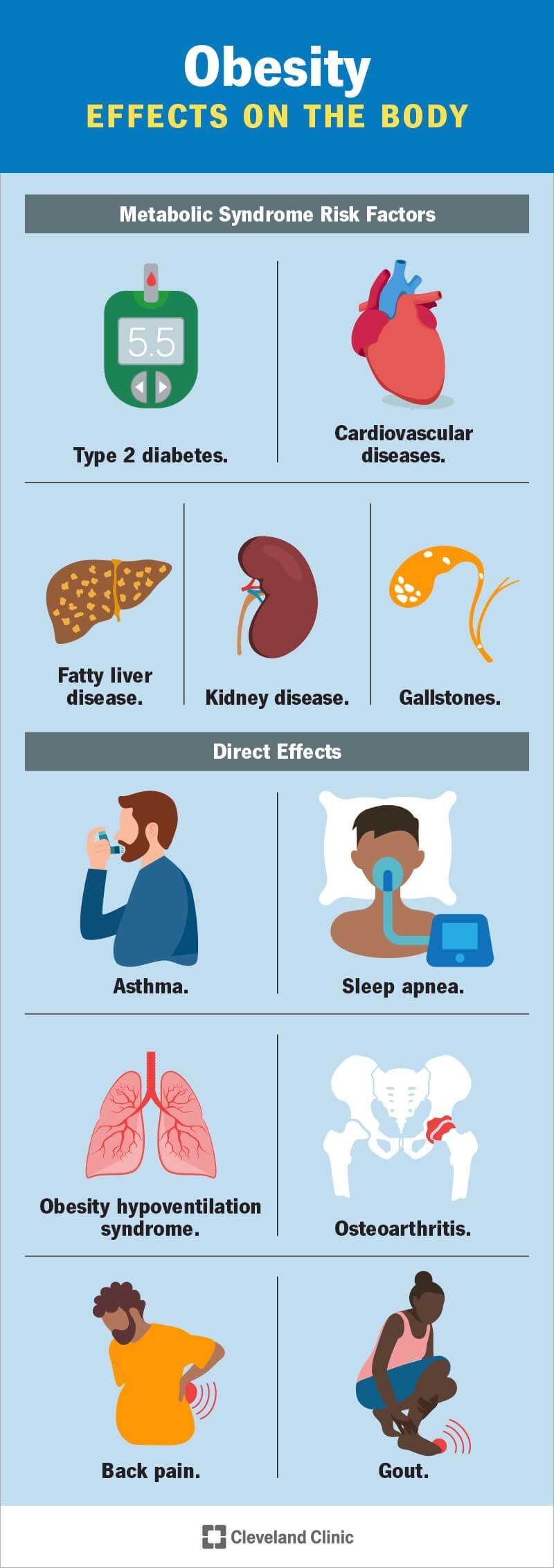
Obesity, the rising concern that affects millions worldwide, is a complex issue influenced by various risk factors. In this article, explore the underlying causes of obesity and discover effective precautions to combat this health condition. You will gain valuable insights into the importance of a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and the significance of mental well-being in maintaining a healthy weight. Let us delve into this crucial topic, empowering you with knowledge to lead a fulfilling and healthy lifestyle.
Risk Factors for Obesity
Obesity is a complex condition that is influenced by a variety of factors including genetics, lifestyle, dietary habits, physical activity levels, psychological factors, medical conditions, medications, pregnancy, age, and socioeconomic status. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent or manage obesity in their lives.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to obesity. Family history is a crucial factor, as studies have shown that if one or both of your parents are obese, you are more likely to develop obesity yourself. Genetic variations can also contribute to obesity, as certain genes may affect how your body processes and stores fat. Additionally, epigenetics, which involves changes in gene expression without altering the underlying genetic code, can be influenced by various environmental factors and contribute to obesity development.

Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors can have a profound impact on the development of obesity. Unhealthy diet choices, characterized by high consumption of processed and fast foods, excessive calorie intake, and excessive sugar consumption, can lead to weight gain and obesity. Sedentary lifestyles, driven by the prevalence of desk jobs and the use of technology, contribute to physical inactivity, resulting in the body burning fewer calories. Lack of sleep, high stress levels, and smoking and alcohol consumption can also increase the risk of obesity.
Dietary Habits
Dietary habits play a crucial role in the development of obesity. High-calorie intake, whether from consuming large portions or eating energy-dense foods, can lead to weight gain. Excessive sugar consumption, often found in sugary beverages and processed foods, can also contribute to obesity. Consuming a diet filled with processed and fast foods, which are typically high in unhealthy fats and added sugars, can lead to weight gain and poor health outcomes. Another dietary habit that can contribute to obesity is skipping meals, as this can disrupt the body’s metabolism and promote overeating later in the day. Emotional eating, which involves using food to cope with emotions rather than for nutritional purposes, is also a risk factor for obesity.

Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle is a significant risk factor for obesity. Lack of exercise or regular physical activity can lead to weight gain and obesity. In today’s modern society, many jobs require long hours of sitting, reducing opportunities for movement throughout the day. Insufficient physical activity, such as not meeting the recommended guidelines of at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of obesity.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors can have a profound impact on an individual’s risk of obesity. Conditions such as depression and anxiety can lead to emotional eating and a loss of motivation for physical activity, increasing the likelihood of weight gain and obesity. Stress eating, where individuals turn to food as a coping mechanism during stressful times, can also contribute to weight gain. Additionally, binge eating disorder, characterized by recurring episodes of excessive food consumption, can lead to obesity if not properly managed.

Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, can lead to weight gain. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder common in women, is associated with weight gain and increased risk of obesity. Cushing’s syndrome, a condition characterized by high levels of cortisol in the body, can also result in obesity. Prader-Willi syndrome, a genetic disorder, causes individuals to have an insatiable appetite, leading to excessive weight gain. Additionally, insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, can contribute to obesity.
Medications
Certain medications have been associated with weight gain and an increased risk of obesity. Antidepressants, commonly prescribed for the management of depression and anxiety disorders, can affect the body’s metabolism and lead to weight gain. Similarly, antihypertensive drugs used to treat high blood pressure and antipsychotic medications used to manage various mental health conditions can also contribute to weight gain. Corticosteroids, often prescribed for the treatment of inflammatory conditions, can cause weight gain and the accumulation of fat in the abdomen.

Pregnancy
Pregnancy can be a risk factor for obesity, as excessive weight gain during pregnancy can lead to long-term weight retention. Gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy, can also increase the risk of obesity post-pregnancy. Hormonal changes and lifestyle factors during pregnancy can contribute to weight gain and obesity, making it essential for pregnant individuals to maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce their risk.
Age
Age is a risk factor for obesity, as metabolism tends to slow down with age. Additionally, muscle mass decreases while fat mass increases as we grow older, making weight management more challenging. It is important for individuals as they age to maintain a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, and make lifestyle choices that support a healthy weight.
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status can significantly impact an individual’s risk of obesity. Limited access to nutritious foods due to financial constraints and living in neighborhoods with limited opportunities for physical activity can lead to weight gain and obesity. Additionally, stress related to economic hardships and other challenges associated with lower socioeconomic status can contribute to emotional eating and poor dietary choices.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are concerned about your risk of obesity or are already struggling with obesity, there are professionals who can help. Consulting a nutritionist or dietitian can provide personalized guidance on healthy eating patterns and weight management. A fitness trainer can help design an exercise program tailored to your needs and abilities. Psychologists or psychiatrists can provide support and strategies for managing stress, emotional eating, and other psychological factors associated with obesity. Support groups can also be valuable in providing a sense of community and encouragement throughout your journey towards a healthier weight.
In conclusion, obesity is influenced by a wide range of risk factors, including genetics, lifestyle factors, dietary habits, physical inactivity, psychological factors, medical conditions, medications, pregnancy, age, and socioeconomic status. By understanding these risk factors and taking proactive measures to address them, you can minimize your risk of obesity and promote a healthier lifestyle. Seek professional help when needed and remember that small, sustainable changes in your everyday choices can make a significant difference in managing or preventing obesity.