If you’ve ever experienced lower back pain, you know just how debilitating it can be. But have you ever considered that your posture may be playing a significant role in this discomfort? In this informative article, we will explore the connection between posture and lower back pain. From understanding the impact of sitting or standing incorrectly to learning practical tips for improving posture, you’ll gain valuable insights into how to alleviate and prevent lower back pain. Get ready to discover the power of good posture and its potential to transform your well-being.
The Role of Posture in Lower Back Pain
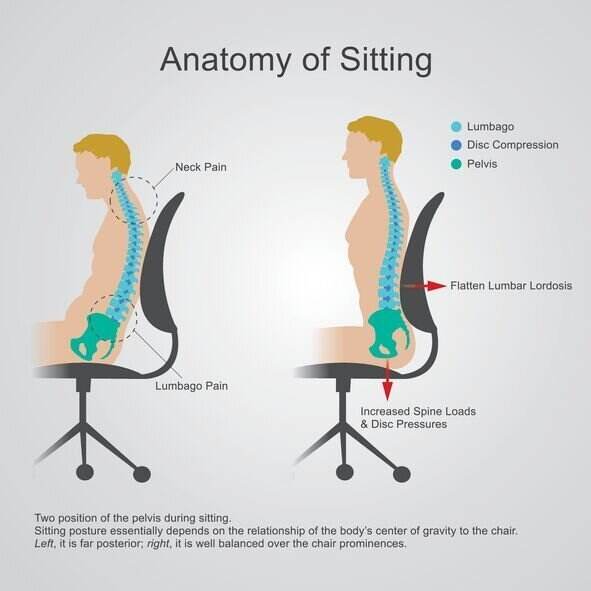
Understanding the Anatomy of the Lower Back
To fully grasp the role of posture in lower back pain, it’s crucial to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the lower back. The lower back, also known as the lumbar region, is composed of five vertebrae (L1-L5) that support the weight of the upper body. These vertebrae provide stability and flexibility, allowing us to bend, twist, and move freely.
In addition to the vertebrae, there are also intervertebral discs located between each vertebra. These discs act as shock absorbers, cushioning the spine and preventing excessive wear and tear. The muscles, ligaments, and tendons surrounding the lower back provide support and help maintain proper alignment of the spine. Therefore, any imbalance or misalignment of the lower back can significantly impact its function and lead to pain and discomfort.
Defining Posture and its Importance
Posture refers to the alignment and positioning of the body, particularly the spine, in relation to the force of gravity. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the spine and supporting its optimal function. Good posture ensures that the weight of the body is evenly distributed, relieving pressure on the spine and its surrounding structures.
Poor posture, on the other hand, involves the misalignment of the spine due to habitual positions or activities that place excessive strain on certain structures. This can lead to muscle imbalances, spinal misalignments, and increased stress on the intervertebral discs and nerves, ultimately resulting in lower back pain.
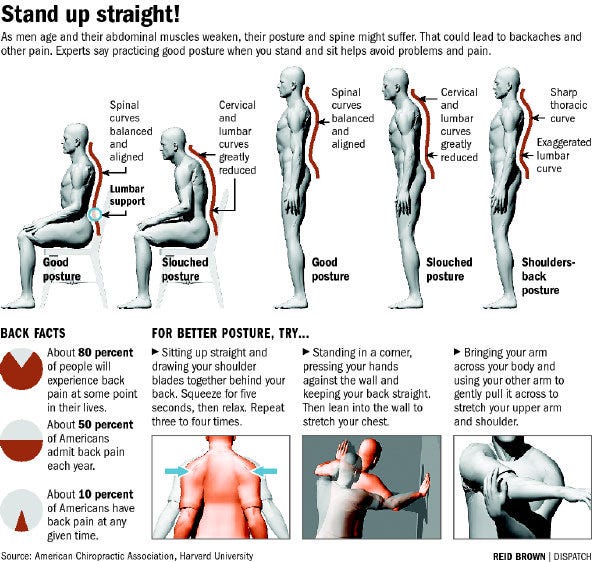
Causes and Risk Factors for Lower Back Pain
There are various causes of lower back pain, and many of them are directly related to posture. The most common cause is mechanical or non-specific lower back pain, which is often associated with poor posture and muscle imbalances. Other common causes include herniated discs, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, and sciatica.
Several risk factors may contribute to the development of lower back pain. These include sedentary lifestyles, repetitive activities, poor ergonomics, obesity, weak core muscles, and previous injuries or trauma to the lower back. It’s essential to understand these risk factors and take preventive measures to minimize the chances of developing lower back pain.
Effects of Poor Posture on the Lower Back
Poor posture can have significant negative effects on the lower back. When the spine is not properly aligned, it can lead to muscular imbalances, causing some muscles to become tight and overactive while others become weak and underactive. This imbalance can put excessive strain on the muscles, ligaments, and tendons of the lower back, leading to pain and discomfort.
Furthermore, poor posture can increase the pressure on the intervertebral discs and nerves within the spine. This pressure can cause the discs to compress, bulge, or herniate, resulting in nerve impingements and radiating pain. The long-term effects of poor posture can also contribute to degenerative changes in the spine, such as osteoarthritis and spinal stenosis.

Signs and Symptoms of Poor Posture
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of poor posture is essential for identifying and addressing potential issues before they develop into chronic lower back pain. Some physical signs of poor posture include rounded shoulders, forward head posture, an excessive curve in the lower back (lordosis), and a protruding abdomen.
Individuals with poor posture may also experience pain and discomfort in the lower back itself. The pain is often described as a dull ache, stiffness, or a deep, gnawing sensation. In some cases, poor posture can cause pain that radiates from the lower back to the hips, buttocks, and even down into the legs.
Diagnosing Lower Back Pain Related to Posture
If you suspect that your lower back pain is related to poor posture, it’s important to seek an evaluation from a healthcare professional. They will perform a physical examination and evaluate your posture to determine the underlying causes of your pain. Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may also be used to identify any structural abnormalities or degenerative changes in the spine.
A proper diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan that targets the root cause of the pain. By addressing the underlying postural issues, you can effectively alleviate your lower back pain and prevent its recurrence in the future.

Preventing Lower Back Pain through Good Posture
The best way to prevent lower back pain is by maintaining good posture throughout the day. Whether sitting, standing, or performing daily activities, practicing proper posture can help minimize the strain on the lower back and reduce the risk of developing pain.
When sitting, it’s important to sit up straight with your back against the chair and your feet flat on the floor. Avoid crossing your legs or slouching, as this can put unnecessary pressure on the lower back. When standing, make sure to distribute your weight evenly on both feet and engage the core muscles to support the spine. It is also advisable to take frequent breaks from prolonged sitting or standing to stretch and move around.
In addition to proper posture, ergonomics plays a vital role in preventing lower back pain. Ergonomics refers to the design of workstations and equipment to optimize efficiency and reduce the risk of injury. Using ergonomic chairs, desks, and accessories that promote good posture can significantly alleviate strain on the lower back. Correct lifting techniques are also essential to protect the lower back from injury and pain.
Ergonomics and its Influence on Posture
Ergonomics is a science-based approach that focuses on designing and arranging work environments to fit the capabilities and limitations of the individuals using them. When applied to posture, ergonomics aims to create a supportive environment that promotes good spinal alignment and prevents strain on the lower back.
By ensuring that workstations, chairs, and equipment are ergonomically designed, individuals can maintain proper posture and reduce the risk of developing lower back pain. Ergonomic factors that influence posture include the height and adjustability of chairs and desks, the placement of computer monitors, the use of specialized keyboards and mice, and the availability of lumbar support.

Exercises and Stretches to Improve Posture
Regular exercise and stretching play a crucial role in improving posture and reducing lower back pain. Strengthening the core muscles, including the abdominal and back muscles, helps support the spine and maintain proper alignment. Exercises such as planks, bridges, and bird dogs can target these muscle groups and improve postural stability.
Stretching exercises are also beneficial to counteract the effects of prolonged sitting or poor posture. Stretching the chest, hips, and hamstrings can help restore flexibility and release tension in the muscles that may contribute to postural imbalances. Incorporating exercises and stretches into your daily routine, such as yoga or Pilates classes, can be an effective way to improve posture and prevent lower back pain.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Correcting Posture
Physical therapy is an essential component of treating lower back pain related to posture. A physical therapist specializes in evaluating and treating musculoskeletal conditions, including postural imbalances. They can assess your posture, identify any muscular imbalances or weaknesses, and develop a personalized treatment plan to correct your posture and alleviate your lower back pain.
Physical therapy may include a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and postural correction exercises. These interventions aim to strengthen weak muscles, stretch tight muscles, and educate individuals on proper body mechanics and ergonomics. Working with a physical therapist can provide guidance, support, and accountability to ensure that you make sustainable changes to your posture and ultimately reduce your lower back pain.
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain Associated with Posture
When it comes to treating lower back pain associated with poor posture, there are several non-surgical interventions available. These include physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage therapy. These treatment options focus on addressing the underlying postural imbalances and musculoskeletal issues that contribute to lower back pain.
In some cases, medication and pain management techniques may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and topical pain relievers may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, complementary therapies such as heat or cold therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and relaxation techniques can provide temporary relief.
For severe cases of lower back pain that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options may be considered. These procedures, such as spinal fusion or laminectomy, aim to stabilize the spine, decompress nerves, and alleviate pain. However, surgery is typically only recommended when all non-surgical treatments have been exhausted and the individual’s quality of life is significantly compromised.
In conclusion, posture plays a crucial role in lower back pain. Understanding the anatomy of the lower back, defining proper posture, recognizing the causes and risk factors, and addressing the effects of poor posture are essential steps in preventing and managing lower back pain. By practicing good posture, incorporating ergonomic principles, engaging in exercises and stretches, and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can maintain a healthy spine and minimize the impact of poor posture on their lower back.