In this informative article, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of Acute Renal Failure, a condition that can have a significant impact on your kidney function. We’ll explore the causes behind this condition, ranging from severe infections to medication side effects, and we’ll delve into the common symptoms you should be aware of, such as decreased urine output and swelling in the legs. Additionally, we’ll discuss the various treatment options available to manage this condition, including medications and dialysis. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive overview of Acute Renal Failure and be better equipped to recognize its signs and seek appropriate medical attention.
Understanding Acute Renal Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
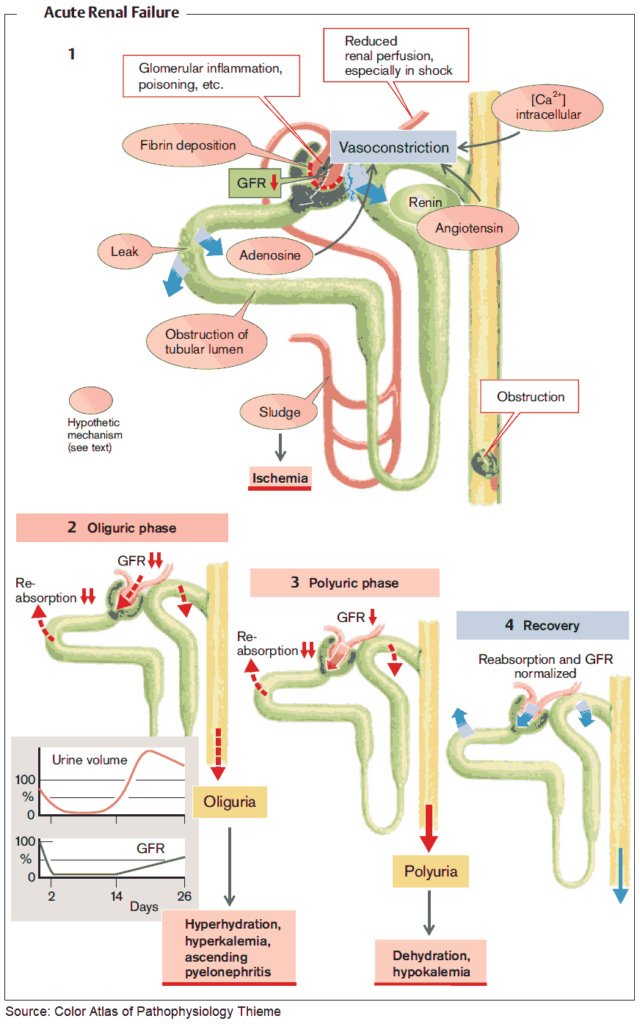
Acute renal failure, also known as acute kidney injury, is a sudden and severe decrease in kidney function. It can occur as a result of various causes, which can be categorized into three main types: prerenal causes, intrinsic renal causes, and postrenal causes. Each of these types of causes can have significant implications on kidney function and require different approaches to treatment.
Prerenal Causes
Prerenal causes of acute renal failure are conditions that occur before blood reaches the kidneys, leading to inadequate blood flow and subsequently affecting kidney function. Some common prerenal causes include hypovolemia (low blood volume), hypotension (low blood pressure), cardiogenic shock (a type of shock caused by heart failure), and renal vasoconstriction (narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the kidneys). These conditions can drastically reduce blood flow to the kidneys, depriving them of the oxygen and nutrients they need to function properly.
Intrinsic Renal Causes
Intrinsic renal causes of acute renal failure are conditions that directly affect the structure or function of the kidneys themselves. They can lead to damage or dysfunction of the kidney tissue, resulting in decreased kidney function. Some examples of intrinsic renal causes include acute tubular necrosis (damage to the kidney tubules), glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units), acute interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidney’s interstitial tissue), renal artery or vein thrombosis (blood clot formation in the kidney’s blood vessels), and renal ischemia (reduced blood flow to the kidneys). These conditions can impair the kidney’s ability to filter waste products and maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
Postrenal Causes
Postrenal causes of acute renal failure occur when there is a blockage or obstruction in the urinary tract, preventing urine from being excreted from the body. This obstruction can occur at different levels of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. Some common postrenal causes include urinary tract obstruction, kidney stones, prostate enlargement (in males), and bladder or ureteral cancer. These obstructions can increase pressure on the kidneys and prevent the normal flow of urine, leading to kidney dysfunction.
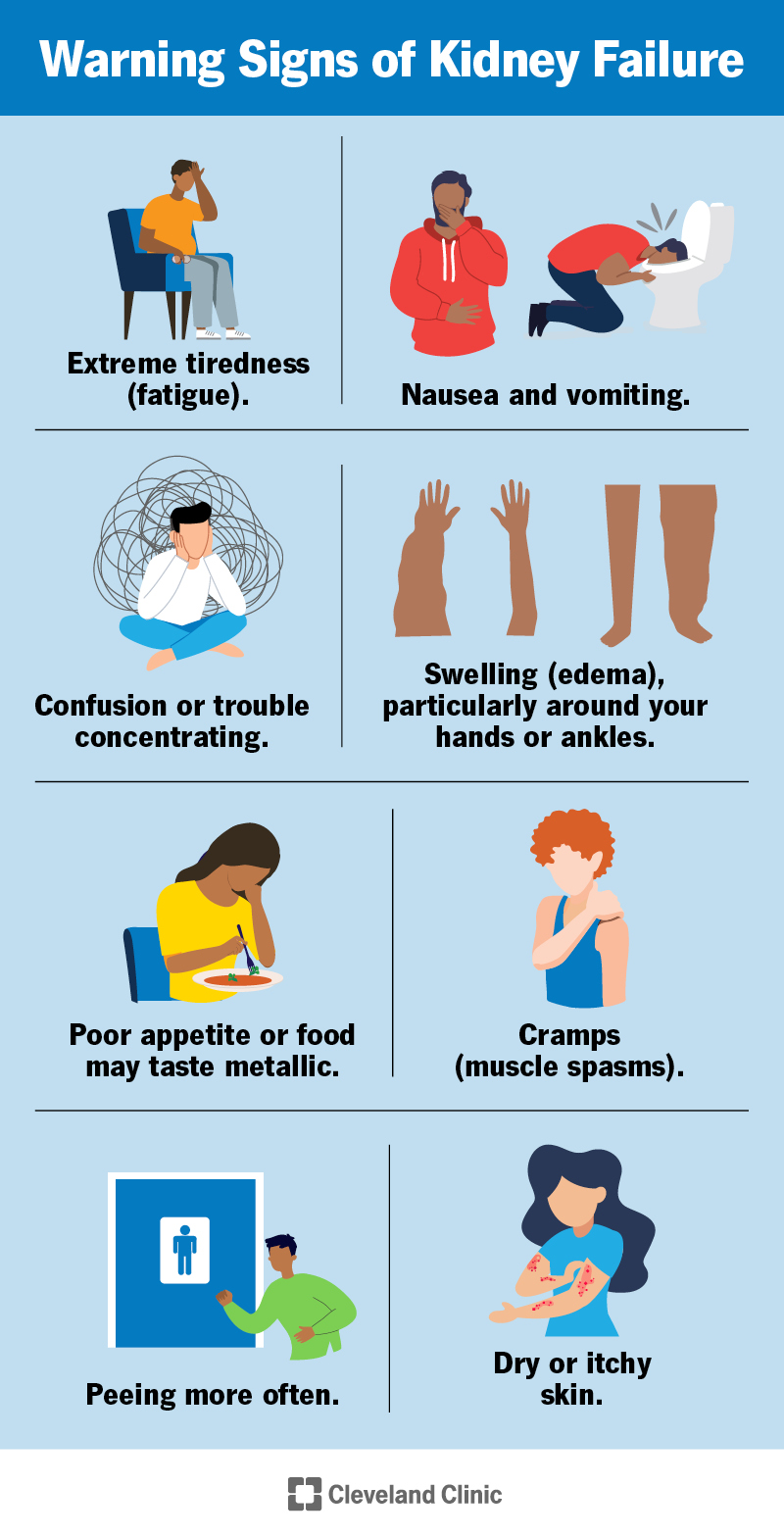
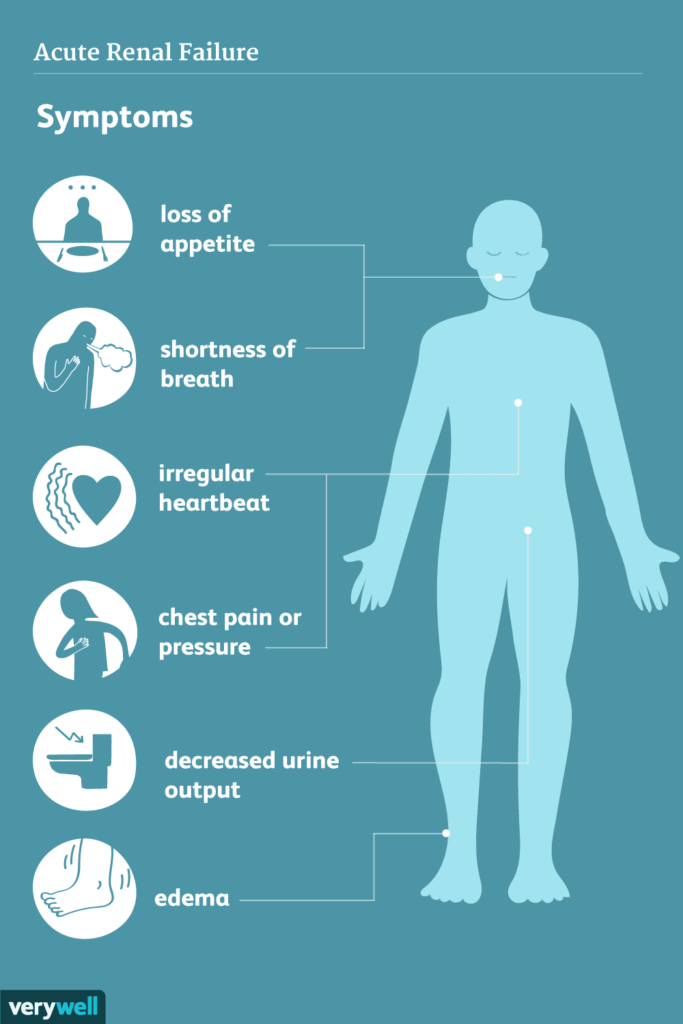
Symptoms of Acute Renal Failure
The symptoms of acute renal failure can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of kidney involvement. However, there are some common symptoms that may be experienced by individuals with acute renal failure. These symptoms include decreased urine output (oliguria), fluid retention, fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting, confusion and seizures, chest pain, and palpitations. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other medical conditions, so it is crucial to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of Acute Renal Failure
The treatment of acute renal failure focuses on addressing the underlying cause, managing fluid and electrolyte imbalances, and optimizing kidney function. The specific treatment approach may vary depending on the individual’s condition and the cause of acute renal failure.
Addressing the underlying cause is crucial in the treatment of acute renal failure. Treating infections, managing medications, correcting blood pressure abnormalities, and performing surgeries to remove obstructions are some of the potential interventions that may be necessary.
Fluid and electrolyte management plays a vital role in managing acute renal failure. Intravenous fluid therapy, diuretics to promote urine production, restricting fluid intake to prevent fluid overload, and balancing electrolyte levels are key components of this management strategy.
Medications may also be prescribed to improve kidney function. Diuretics can help increase urine output, calcium channel blockers can relax blood vessels and improve blood flow to the kidneys, ACE inhibitors can reduce blood pressure and protect the kidneys, and erythropoietin-stimulating agents can stimulate the production of red blood cells, improving oxygen delivery to the kidneys.
In some cases, when kidney function is severely impaired, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be necessary. Dialysis involves using a machine to filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood, while kidney transplantation replaces the non-functioning kidneys with a healthy kidney from a donor.
Acute renal failure is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment are essential for a positive outcome. By addressing the underlying cause, managing fluid and electrolyte imbalances, and using medications or procedures to improve kidney function, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care to individuals with acute renal failure. If you experience any symptoms associated with acute renal failure, it is important to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Understanding Acute Renal Failure
Acute Renal Failure And Causes, Acute Renal Failure And Dialysis, Acute Renal Failure And Diet, Acute Renal Failure And Fluid Replacement, Acute Renal Failure And Treatment, Acute Renal Failure Care Plan, Acute Renal Failure Case Study, Acute Renal Failure Case Study 30, Acute Renal Failure Case Study Pdf, Acute Renal Failure Cats