In the world of medical conditions, there’s one that often goes unnoticed but can cause quite a bit of discomfort – Adenoiditis. This condition, which affects the adenoids, small glands located in the back of your nose and throat, can lead to symptoms ranging from nasal congestion to throat infections. But fear not, as understanding Adenoiditis is the first step towards finding relief and restoring your wellness. So, let’s take a closer look at this often misunderstood condition and discover ways to effectively manage it.
What is Adenoiditis
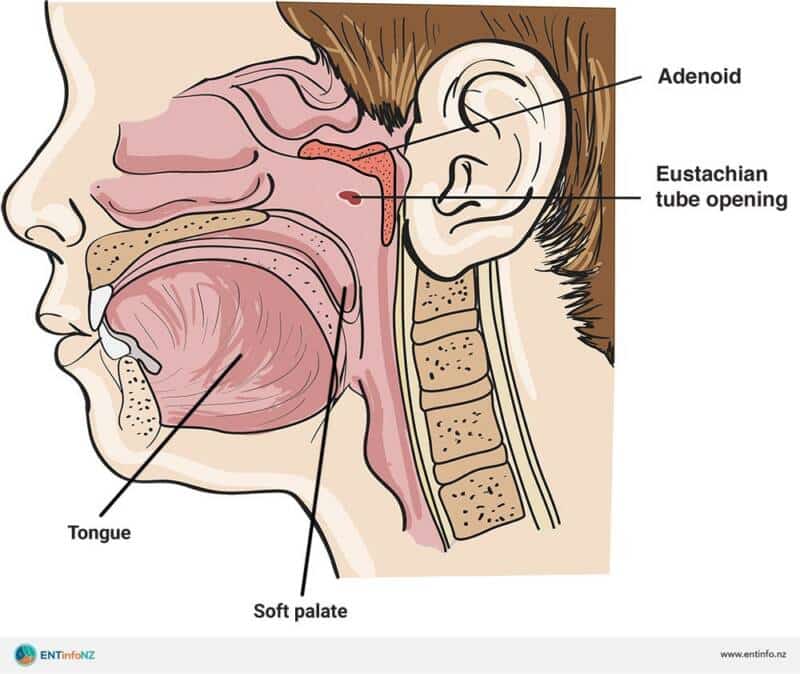
Adenoiditis is the inflammation and infection of the adenoids, which are a mass of tissue located at the back of the throat, above the tonsils. Adenoids are part of the immune system and play a vital role in filtering out bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the nose and mouth. Adenoiditis occurs when the adenoids become infected or swollen, causing various symptoms and discomfort. It is a common condition, particularly in children, and can often be managed with proper treatment.
Definition
Adenoiditis refers to the inflammation and infection of the adenoids. The adenoids are made up of lymphoid tissue and are located in the nasopharynx, behind the nose, and at the back of the throat. They are part of the immune system and help fight off infections by trapping bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose and mouth. Adenoiditis occurs when the adenoids become infected, leading to symptoms such as nasal congestion, sore throat, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
Causes
There are several causes of adenoiditis, including viral and bacterial infections, allergies, and enlarged adenoids. Infections caused by bacteria or viruses, such as the common cold or flu, can lead to the inflammation and infection of the adenoids. Allergies, particularly to substances like pollen or dust mites, can also trigger adenoiditis in individuals who are sensitive to these allergens. Additionally, the adenoids themselves may become enlarged, which can make them more prone to infection.
Symptoms
The symptoms of adenoiditis can vary from person to person, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Nasal congestion: Difficulty breathing through the nose due to a blocked or stuffy nose.
- Difficulty breathing through the nose: The adenoids may obstruct airflow through the nasal passages, leading to difficulty breathing.
- Snoring: Enlarged adenoids can cause airway obstruction, leading to snoring during sleep.
- Ear problems: Adenoiditis can result in ear infections or earache due to the close proximity of the adenoids to the Eustachian tubes.
- Sore throat and cough: Inflammation of the adenoids can cause a sore throat and persistent cough.
- Mouth breathing: The difficulty in breathing through the nose may cause individuals to breathe through their mouth.
- Bad breath: Adenoiditis can contribute to bad breath due to the accumulation of bacteria and mucus.
- Swollen glands in the neck: In some cases, the lymph nodes in the neck may become swollen or tender due to the infection.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing adenoiditis typically involves a medical history review and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and inquire about any recent illnesses or exposure to allergens. During the physical examination, the doctor will examine your throat, nose, and neck for signs of inflammation or swelling. In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the condition.
Treatment
The treatment options for adenoiditis depend on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause. In mild cases, observation and homecare measures may be sufficient to manage the condition. This may include resting, staying hydrated, and using saline nasal sprays to alleviate nasal congestion. If the symptoms are more severe or persistent, medications such as antibiotics, nasal corticosteroids, nasal decongestants, or allergy medications may be prescribed to manage the infection and reduce inflammation. In some cases, if the adenoiditis is recurrent or chronic, surgery to remove the adenoids may be recommended.
Risk Factors for Adenoiditis
While adenoiditis can occur in individuals of all ages, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. It is important to be aware of these risk factors to take necessary precautions and seek medical attention if needed.
Age
Children are more susceptible to adenoiditis due to their developing immune systems and their increased exposure to infections. Adenoiditis commonly affects children between the ages of 3 and 7, but it can occur at any age. As children grow older, their adenoids tend to shrink and may become less prone to infection.
Exposure to Infections
Regular exposure to infections, such as colds or the flu, increases the risk of developing adenoiditis. Viruses and bacteria that cause respiratory infections can also affect the adenoids and lead to inflammation and infection. Individuals who are exposed to a greater number of infections, such as children in daycare or school settings, may be at an increased risk of adenoiditis.
Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene practices, such as not regularly washing hands or sharing contaminated items, can increase the risk of developing infections that can lead to adenoiditis. It is important to maintain good hygiene habits, especially during cold and flu seasons, to reduce the risk of infection and subsequent adenoiditis.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to underlying health conditions or certain medications, are more susceptible to infections, including adenoiditis. Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders, can make it harder for the body to fight off infections and increase the risk of developing adenoiditis.
Signs and Symptoms of Adenoiditis
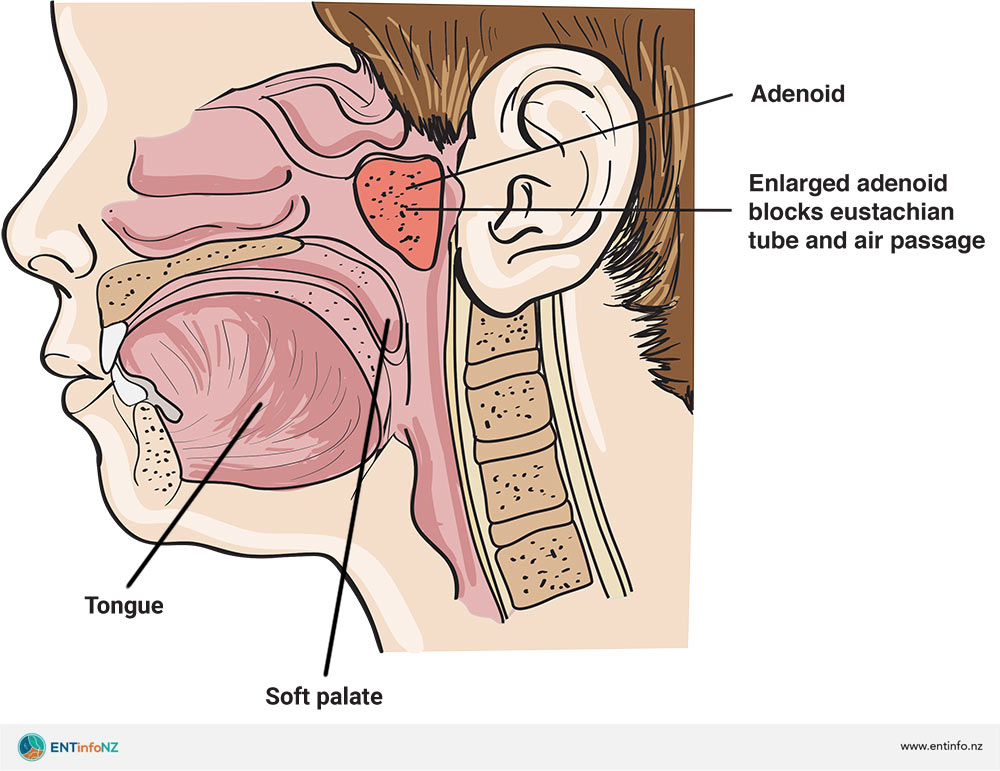
Adenoiditis can present with a variety of signs and symptoms, which may vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. It is important to recognize these symptoms to seek timely medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Nasal Congestion
One of the most common symptoms of adenoiditis is nasal congestion or a blocked or stuffy nose. The inflammation and swelling of the adenoids can obstruct the nasal passages, leading to difficulty breathing through the nose.
Difficulty Breathing Through the Nose
In addition to nasal congestion, adenoiditis can cause difficulty breathing through the nose. This can result in mouth breathing, particularly during sleep or physical activity.
Snoring
Enlarged adenoids can obstruct the airway and lead to snoring during sleep. Snoring can disrupt sleep patterns and may indicate the presence of adenoiditis.
Ear Problems
Adenoids are located close to the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. Inflammation and infection of the adenoids can cause ear problems, such as ear infections or earaches.
Sore Throat and Cough
Adenoiditis can cause a sore throat and persistent cough. The inflammation in the back of the throat can result in discomfort and irritation, leading to these symptoms.
Mouth Breathing
Difficulty breathing through the nose may cause individuals with adenoiditis to breathe through their mouth. This can lead to dry mouth, bad breath, and an increased risk of dental problems.
Bad Breath
The accumulation of bacteria and mucus in the back of the throat due to adenoiditis can contribute to bad breath. Brushing teeth and using mouthwash may not fully alleviate the bad breath, as the source of the odor is often the infected adenoids.
Swollen Glands in the Neck
In some cases, the lymph nodes in the neck may become swollen or tender due to the infection. Swollen glands can be a sign of adenoiditis and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or sore throat.
Causes of Adenoiditis
Adenoiditis can have various causes, including infections and underlying conditions that affect the immune system. Understanding these causes can help in managing the condition effectively.
Bacterial Infection
Bacterial infections, such as strep throat or sinusitis, can lead to adenoiditis. Bacteria can enter the adenoids and cause inflammation and infection, resulting in symptoms such as nasal congestion, sore throat, and ear problems.
Viral Infection
Viral infections, like the common cold or flu, can also cause inflammation and infection in the adenoids. Individuals with viral infections may experience symptoms such as nasal congestion, sore throat, cough, and ear problems.
Allergies
Allergies, particularly respiratory allergies, can trigger adenoiditis in individuals who are sensitive to specific allergens. Substances like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander can cause an allergic reaction in the body, leading to inflammation of the adenoids and subsequent infection.
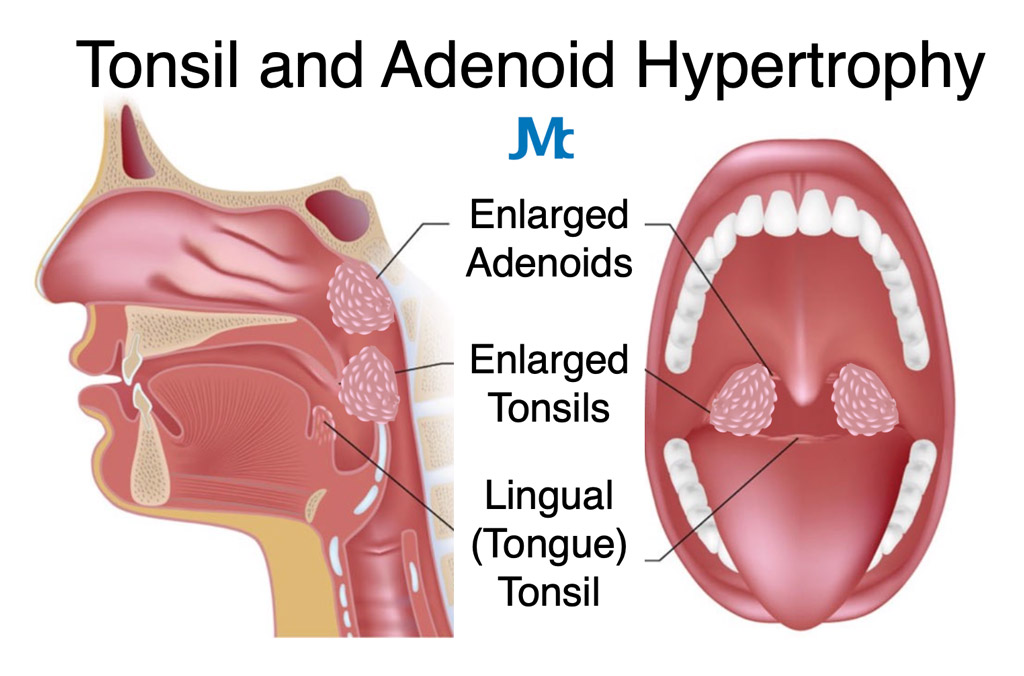
Enlarged Adenoids
Enlarged adenoids, also known as adenoid hypertrophy, can increase the risk of adenoiditis. Enlargement may be due to recurrent infections, allergies, or genetic factors. When the adenoids are larger than normal, they can obstruct the nasal passages and hinder proper airflow, leading to an increased risk of infection.

Diagnosing Adenoiditis
Diagnosing adenoiditis involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. The doctor may also recommend additional tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the condition.
Medical History and Physical Examination
To diagnose adenoiditis, the doctor will review your medical history and inquire about your symptoms. They may ask about recent illnesses, exposure to allergens, and the duration and severity of your symptoms. During the physical examination, the doctor will examine your throat, nose, and neck for signs of inflammation or swelling. They may use a tongue depressor or a small lighted instrument to get a better view of the back of the throat and evaluate the size and condition of the adenoids.
Endoscopy
In some cases, an endoscopy may be performed to provide a more detailed examination of the adenoids. A thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end, called an endoscope, is inserted through the nose or mouth to visualize the adenoids. This procedure allows the doctor to assess the size, shape, and condition of the adenoids more accurately.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be recommended to further evaluate the adenoids and surrounding structures. These tests can help identify any structural abnormalities or complications associated with adenoiditis, such as fluid accumulation in the ears or sinus infections.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, the doctor may request laboratory tests, such as a throat swab or a blood test, to determine the cause of the infection. These tests can help identify whether the infection is bacterial or viral in nature, which can guide the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Adenoiditis
The treatment options for adenoiditis depend on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause. In mild cases, observation and homecare measures may be sufficient to manage the condition. However, more severe or persistent cases may require medications or surgical intervention.
Observation and Homecare
For mild cases of adenoiditis, the doctor may recommend observation and homecare measures. This may include rest, staying hydrated, and using saline nasal sprays to alleviate nasal congestion. Avoiding triggers, such as allergens or cigarette smoke, can also help manage symptoms. Regular follow-up appointments may be advised to monitor the condition and ensure proper healing.
Medications
Medications can be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and treat the underlying infection or inflammation associated with adenoiditis. Antibiotics may be prescribed if the infection is bacterial in nature. Nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone or budesonide, can help reduce inflammation in the nose and throat. Nasal decongestants may be recommended for short-term relief of nasal congestion, but their long-term use should be avoided. In cases where allergies play a role, allergy medications such as antihistamines or leukotriene inhibitors may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
Surgery
When adenoiditis is recurrent or chronic, or if complications arise, surgery may be recommended. Adenoidectomy, the surgical removal of the adenoids, is a common procedure performed to alleviate symptoms and prevent future infections. It is typically considered when other treatment options have failed or when the adenoids are chronically enlarged. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and involves removing the adenoids through the mouth, without any external incisions.
Prevention of Adenoiditis
While it may not be possible to completely prevent adenoiditis, certain measures can help reduce the risk of developing this condition. Taking preventive steps can minimize exposure to infections and allergens, which are common triggers for adenoiditis.
Practice Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene habits can help prevent the spread of infections that can lead to adenoiditis. This includes washing hands frequently with soap and water, using hand sanitizers when soap is not available, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick. Encouraging children to cover their mouths and noses when sneezing or coughing can also help prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
Avoid Exposure to Infections
Minimizing exposure to infections can reduce the risk of developing adenoiditis. This can be achieved by avoiding crowded places during flu seasons, maintaining proper ventilation in enclosed spaces, and encouraging regular handwashing. It may also be helpful to teach children about proper hygiene practices and the importance of avoiding sharing food, drinks, or personal items with others.
Immunizations
Staying up to date with recommended immunizations can help prevent certain infections that can lead to adenoiditis. Vaccines for diseases such as the flu, pneumonia, and whooping cough can provide protection against these infections and reduce the risk of adenoiditis.
Avoiding Allergens
If allergies play a role in your adenoiditis, avoiding exposure to specific allergens can help prevent flare-ups. This may involve minimizing contact with pollen, using dust mite covers on pillows and mattresses, or keeping pets out of certain areas of the house. Identifying and managing your specific allergies with the help of an allergist can be beneficial in preventing allergic reactions and subsequent adenoiditis episodes.
Complications of Adenoiditis
While adenoiditis is generally a manageable condition, complications can arise if left untreated or not properly managed. It is important to be aware of these potential complications and seek appropriate medical attention to prevent further health problems.
Middle Ear Infections
Untreated adenoiditis can lead to complications such as middle ear infections or otitis media. The close proximity of the adenoids to the Eustachian tubes can allow bacteria and viruses to travel from the adenoids to the middle ear, resulting in infection. Middle ear infections can cause symptoms such as ear pain, fluid accumulation, and temporary hearing loss.
Sinus Infections
Chronic adenoiditis or recurrent infections can also contribute to the development of sinus infections or sinusitis. The adenoids and sinuses are interconnected, and infection or inflammation in the adenoids can spread to the sinuses, leading to pain, facial pressure, and nasal congestion.
Sleep Apnea
Enlarged adenoids can obstruct the airway during sleep, contributing to a condition known as sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in disrupted sleep patterns, daytime fatigue, and other health problems. Prompt treatment of adenoiditis can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of developing sleep apnea.
Chronic Respiratory Problems
Untreated or recurrent adenoiditis can lead to chronic respiratory problems, particularly in children. Persistent inflammation and infection in the adenoids can affect the overall respiratory function, making individuals more prone to respiratory infections and breathing difficulties.
When to See a Doctor
While mild cases of adenoiditis can often be managed with homecare measures, it is important to seek medical attention if certain symptoms or complications arise. Certain signs indicate that it is time to see a doctor for further evaluation and treatment.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If your symptoms persist for more than a few days or worsen despite homecare measures, it is important to see a doctor. Persistent nasal congestion, sore throat, cough, or ear problems may require medical intervention.
Severe Throat Pain
If you experience severe throat pain that persists or is accompanied by difficulty swallowing or speaking, it is important to seek medical attention. Severe throat pain can indicate a more severe infection or other complications.
High Fever
A persistently high fever, particularly in children, may indicate a more serious infection or complication. Fever combined with other symptoms, such as severe throat pain or difficulty breathing, should not be ignored, and medical attention should be sought as soon as possible.
Difficulty Breathing
If you experience difficulty breathing, particularly if it becomes severe or is accompanied by wheezing or stridor (a high-pitched sound when breathing in), it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Difficulty breathing can be a sign of airway obstruction and requires prompt evaluation and treatment.
Severe Headache
If you experience severe headaches that are persistent or accompanied by other neurological symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor. Severe headaches can be a sign of complications associated with adenoiditis or may indicate other underlying health conditions that require medical attention.
Adenoiditis is a common condition characterized by the inflammation and infection of the adenoids. It can cause various symptoms, including nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, snoring, ear problems, sore throat, and bad breath. Adenoiditis is often caused by viral or bacterial infections, allergies, or enlarged adenoids. Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Treatment options range from observation and homecare measures to medications and, in some cases, surgical removal of the adenoids. Preventive measures include practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to infections, staying up to date with immunizations, and managing allergies. Complications can arise if adenoiditis is left untreated or not properly managed, including middle ear infections, sinus infections, sleep apnea, and chronic respiratory problems. It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist, severe throat pain or fever develop, or if there is difficulty breathing or severe headaches. By understanding adenoiditis and taking appropriate steps, individuals can effectively manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Understanding Adenoiditis
Adenoiditis Causes, Adenoiditis Child, Adenoiditis Chronic, Adenoiditis Complications, Adenoiditis Cronica, Adenoiditis Ct, Adenoiditis Cure, Adenoiditis Definition, Adenoiditis Icd 10, Adenoiditis Image