In this article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of cataract: its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Cataract is a common eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing blurred vision and eventual loss of sight if left untreated. By learning about the underlying causes and recognizing the symptoms, you can take proactive steps towards managing and treating cataract effectively. From lifestyle changes to surgical interventions, this article will guide you through the various treatment options available, allowing you to make informed decisions about your eye health. So, let’s dive into the world of cataract and equip ourselves with the knowledge to overcome this visual impairment!
Definition of Cataract
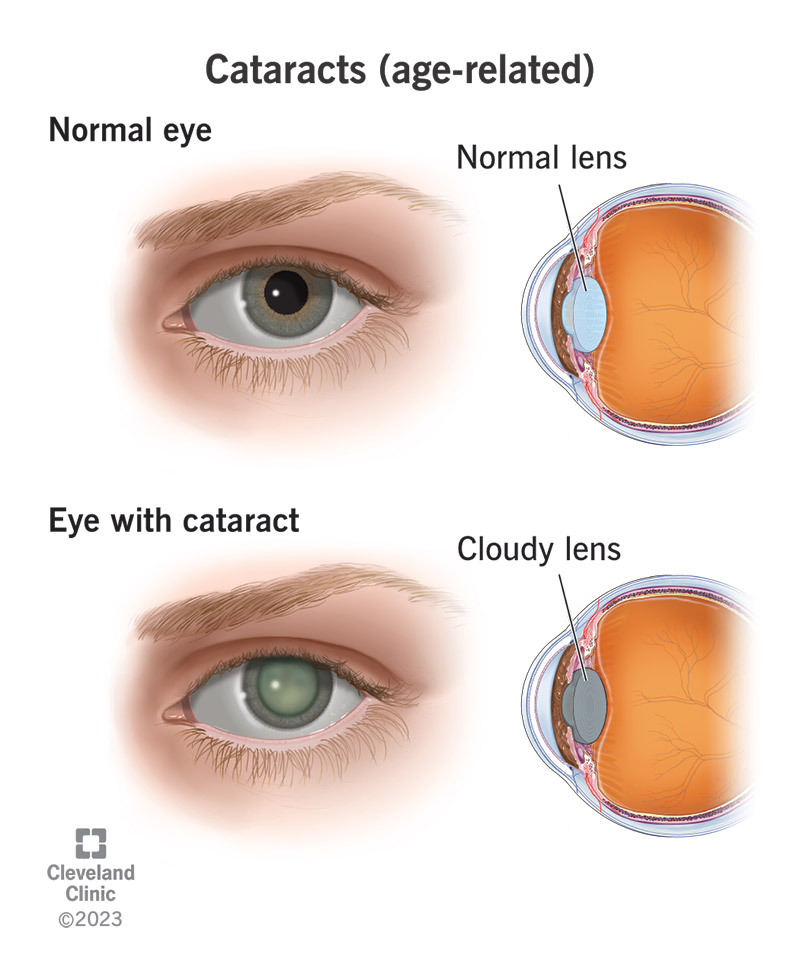
A cataract is a common eye condition that gradually clouds the lens of the eye, resulting in vision loss or blurred vision. The lens of the eye functions by focusing light onto the retina, which allows us to see clear images. When a cataract develops, the lens becomes opaque, obstructing the passage of light and causing vision problems.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Cataracts are one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness worldwide. This condition is most commonly associated with aging, and it is estimated that over half of all individuals aged 80 and above will have a cataract or have undergone cataract surgery. However, cataracts can also occur in younger individuals due to other factors such as trauma, certain medical conditions, or even as a result of medications.
Causes of Cataract
While the primary cause of cataracts is aging, there are several other risk factors that may contribute to their development. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, smoking, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and a family history of cataracts can increase your likelihood of developing this condition. Furthermore, certain medications like corticosteroids and long-term use of statins have been associated with cataract formation.
Types of Cataract
There are several types of cataracts, each categorized based on the location or cause of the opacity in the lens. The most common types include:
-
Nuclear Cataracts: These form in the center of the lens and are often associated with aging. Nuclear cataracts typically cause a gradual yellowing or browning of vision.
-
Cortical Cataracts: These develop in the outer edges of the lens and have a characteristic spoke-like appearance. They can make it difficult to see, especially under bright lights.
-
Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts: These occur at the back of the lens and tend to progress more rapidly than other types. They can cause difficulty with reading or glare sensitivity.
-
Congenital Cataracts: These are present at birth or develop during childhood. They can be caused by genetic factors, infections during pregnancy, or trauma.

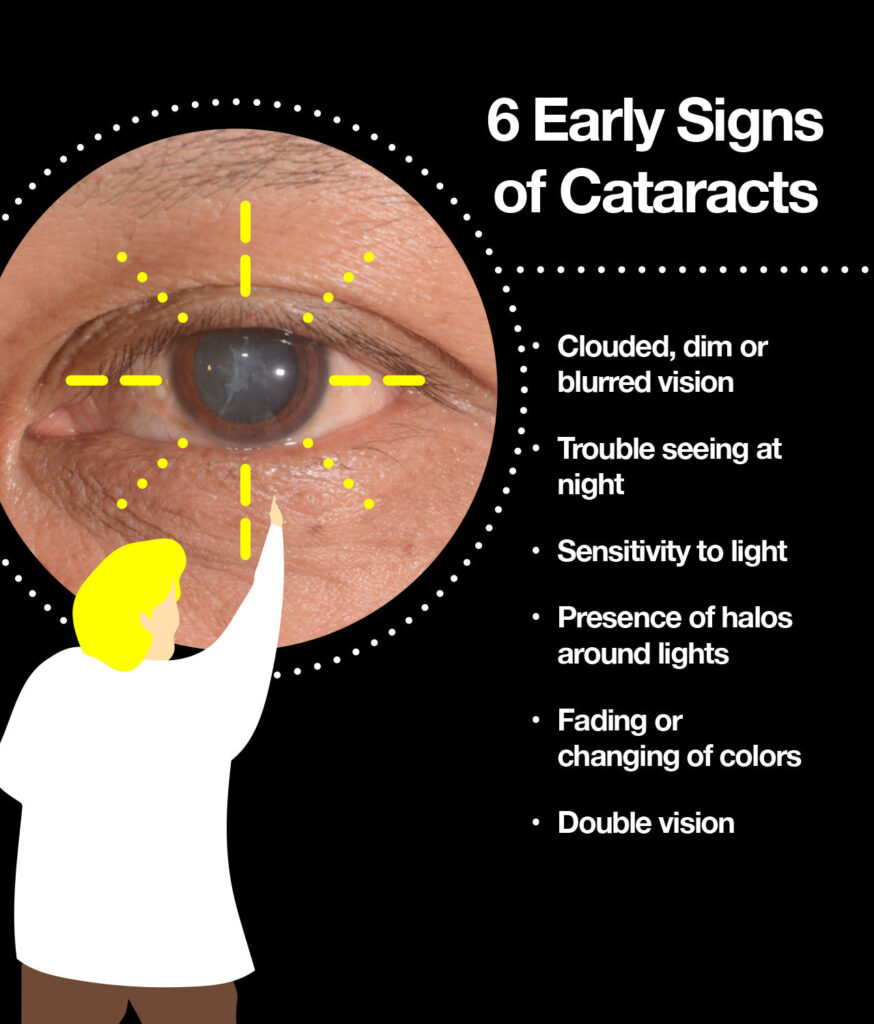
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of cataracts can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Blurred, cloudy, or dim vision
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Needing brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing halos around lights
- Faded or yellowed colors
- Double vision in one eye
Diagnosis of Cataract
If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, it is important to consult an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye examination. The examination may involve checking your visual acuity, performing a slit-lamp examination to assess the lens, and dilating your pupils to obtain a clearer view of the lens and retina. Based on the findings, your eye care professional will diagnose the presence and severity of cataracts.

Prevention of Cataract
While age-related cataracts cannot be entirely prevented, certain lifestyle choices and precautions can help delay their onset or reduce their progression. Here are some tips to minimize your risk of developing cataracts:
- Wear sunglasses that offer 100% UV protection when outdoors.
- Quit smoking or avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Follow a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Manage any underlying medical conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
- Control your weight and exercise regularly.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
In the early stages of cataract development, non-surgical treatment options may help improve your vision or delay the need for surgery. These options include:
-
Updating your eyeglass prescription: Wearing the correct prescription lenses can optimize your vision despite the presence of cataracts.
-
Using brighter lighting: Increasing the amount of light in your environment can improve your ability to see.
-
Using magnifying lenses: These can be useful for reading small print or performing detailed tasks.
-
Medications: Certain eye drops may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms such as dry eyes or temporary blurriness.
Surgical Treatment Options
When cataracts significantly affect your daily activities and quality of life, surgical intervention may be necessary. Cataract surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This outpatient procedure is typically safe, effective, and has a high success rate. Some common surgical techniques for cataract removal include phacoemulsification and extracapsular cataract extraction.
Post-Surgery Care
After cataract surgery, it is important to follow your surgeon’s instructions for post-operative care. This may include:
-
Using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and aid in the healing process.
-
Avoiding strenuous activities or heavy lifting for a few weeks.
-
Wearing a protective eye shield or glasses to protect the eye from injury.
-
Attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing and ensure optimal visual outcomes.
-
Taking any prescribed medications as directed.
Remember to contact your eye care professional if you experience any unusual symptoms, such as severe pain, prolonged redness, or sudden vision changes, after surgery.
In conclusion, understanding cataracts, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you make informed decisions about your eye health. By following preventive measures, seeking timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, you can maintain clear vision and enjoy a better quality of life even with the presence of cataracts. Remember to consult with an eye care professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific needs.