Catarrh, a common condition experienced by many, can leave you feeling congested and uncomfortable. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for catarrh. Whether you’ve been dealing with a runny and stuffy nose, or persistent coughing, we’ve got you covered with all the information you need to understand and manage this bothersome condition. Get ready to breathe a little easier as we navigate the ins and outs of catarrh together.

Causes of Catarrh
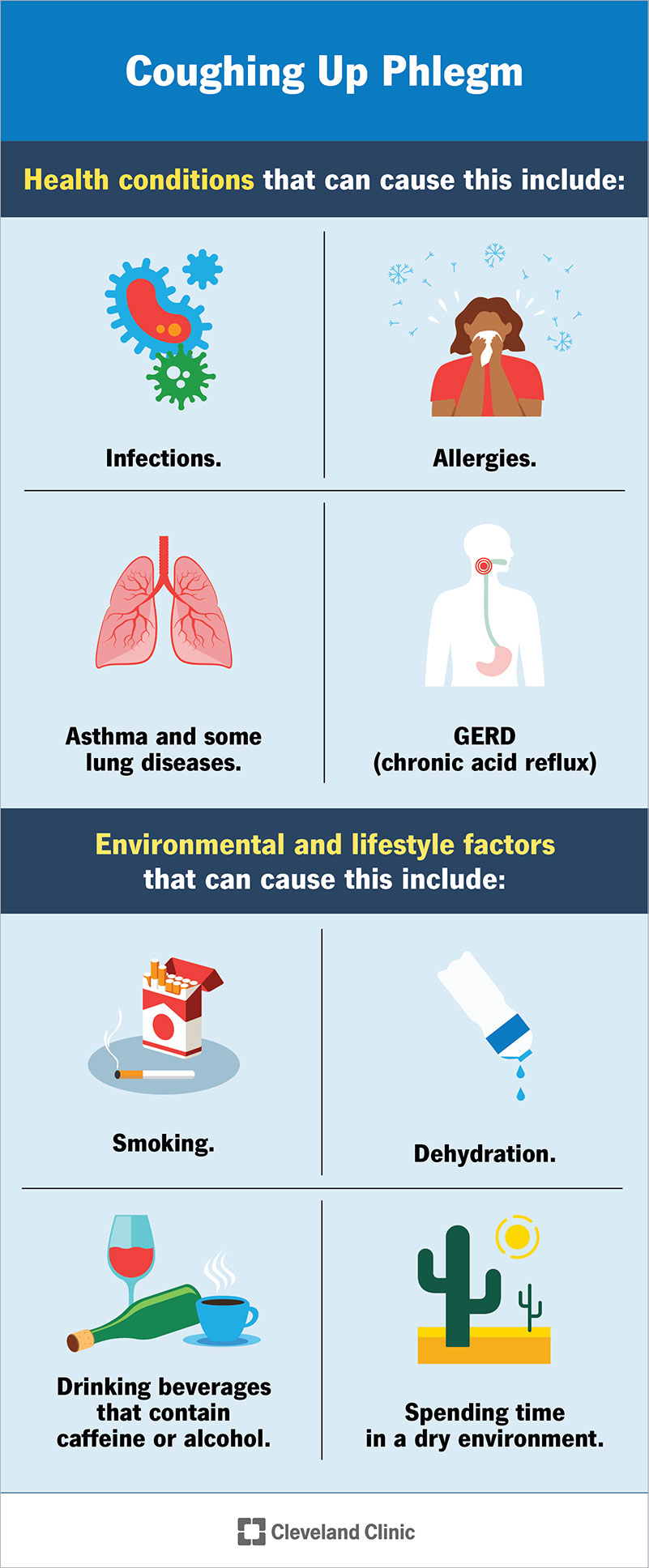
Catarrh is a common condition characterized by an excessive production of mucus in the respiratory system. It is often associated with other symptoms such as nasal congestion, postnasal drip, and coughing. Understanding the causes of catarrh is essential in managing and treating this condition effectively.
Common cold viruses
One of the primary causes of catarrh is viral infections, particularly the common cold. When you catch a cold, your body’s immune system responds by producing excessive mucus as a defense mechanism against the invading virus. The increased mucus production can lead to nasal congestion and postnasal drip, contributing to the symptoms of catarrh.
Allergies
Allergies can also trigger catarrh in individuals who are sensitized to specific allergens. When you come into contact with allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites, your immune system releases histamines, causing inflammation and excess mucus production. This allergic response can result in catarrh symptoms.
Sinus infections
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, can cause catarrh. When the sinus cavities become inflamed and infected, excessive mucus production occurs, leading to catarrh symptoms. Sinus infections are commonly caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungal organisms.
Respiratory infections
In addition to the common cold, other respiratory infections like bronchitis or pneumonia can contribute to catarrh. These infections cause inflammation in the respiratory tract, triggering excessive mucus production as a protective response. The mucus buildup can result in coughing, postnasal drip, and other catarrh symptoms.
Environmental irritants
Exposure to environmental irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or strong chemicals can also cause catarrh. These irritants can irritate the respiratory system, leading to increased mucus production and catarrh symptoms. It is important to minimize exposure to these irritants to prevent or alleviate catarrh.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase your risk of experiencing catarrh. By understanding these risk factors, you can take proactive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
Age
Age plays a role in the susceptibility to catarrh. Young children and older adults are more prone to catarrh due to their developing or weakened immune systems, respectively. The immune system’s ability to control excessive mucus production may be compromised, increasing the likelihood of catarrh.
Exposure to cigarette smoke
Exposure to cigarette smoke, whether through firsthand or secondhand smoke, is a significant risk factor for catarrh. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can irritate the respiratory system, leading to inflammation and excessive mucus production. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to smoke can help prevent catarrh.
Weakened immune system
Individuals with a weakened immune system are more susceptible to catarrh. Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS, autoimmune diseases, or undergoing immune-suppressing treatments, can increase the risk of developing catarrh. Strengthening the immune system through a healthy lifestyle, adequate rest, and proper nutrition can help reduce the risk.
Family history
Family history of catarrh or respiratory conditions can also be a risk factor. Genetics may play a role in the susceptibility to developing catarrh. If your family members have a history of catarrh or other respiratory conditions, you may be at a higher risk.
Occupational exposure
Certain occupations may expose individuals to respiratory irritants or conditions that increase the risk of catarrh. For example, individuals working in industries where they are consistently exposed to dust, chemicals, or fumes may be more prone to developing catarrh. Taking precautions such as wearing protective masks and having good ventilation in the workplace can help reduce the risk.

Symptoms of Catarrh
Recognizing the symptoms of catarrh is crucial to understanding and managing this condition effectively. Common catarrh symptoms include:
Excessive mucus production
One of the hallmark symptoms of catarrh is the excessive production of mucus. You may notice increased mucus in the nose, throat, or chest. The mucus may appear thick, sticky, and may be difficult to expel.
Nasal congestion
Catarrh often presents with nasal congestion or a blocked nose. This congestion can make breathing through the nose difficult and may cause discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the sinuses.
Postnasal drip
Postnasal drip occurs when excessive mucus drips down the back of the throat. This can cause a constant need to clear your throat, coughing, or a sensation of mucus accumulating in the throat.
Coughing
Coughing is another common symptom of catarrh. The excess mucus in the respiratory system can trigger coughing as the body attempts to clear the airways.
Sore throat
Due to the postnasal drip and increased inflammation in the throat, catarrh can cause a sore throat. This soreness may be accompanied by hoarseness or a scratchy feeling.
Headache
Headaches can occur as a result of the increased pressure and inflammation in the sinuses. The headache may be localized around the forehead, temples, or behind the eyes.
Fatigue
Catarrh can leave you feeling fatigued or generally run down. The constant effort of coughing, clearing your throat, or dealing with nasal congestion may contribute to this feeling of tiredness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing catarrh usually involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and specific tests performed by healthcare professionals. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing persistent or severe catarrh symptoms.
Medical history and physical examination
Your healthcare provider will first review your medical history and inquire about your symptoms. They may ask about the duration and frequency of your symptoms, as well as any underlying medical conditions. A physical examination may include examining your nasal passages, throat, and listening to your breathing.
Nasal endoscopy
In some cases, a nasal endoscopy may be performed to examine the nasal passages and sinuses in more detail. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it is inserted into the nose to visualize the structures within.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be ordered to provide a more detailed view of the sinuses and respiratory system. These tests can help identify any underlying issues, such as sinus infections or nasal polyps, that may be contributing to catarrh symptoms.
Allergy tests
If your healthcare provider suspects that allergens are causing your catarrh, allergy tests may be conducted. These tests can help identify specific allergens that may trigger catarrh symptoms. Common allergy tests include skin prick tests, blood tests, or patch tests.
Complications
If left untreated or poorly managed, catarrh can lead to various complications. Understanding these potential complications can help you take appropriate measures to prevent or address them.
Sinusitis
One common complication of catarrh is sinusitis, which occurs when the sinuses become infected and inflamed. Sinusitis can lead to more severe symptoms such as facial pain or pressure, persistent headaches, and thick, discolored nasal discharge.
Ear infections
The excessive mucus production and congestion associated with catarrh can also contribute to ear infections. The Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, may become blocked, leading to ear pain, hearing difficulties, or fluid buildup in the middle ear.
Chronic cough
Catarrh-related coughing can become persistent and chronic if not properly managed. A chronic cough can affect your quality of life, disrupt sleep, and even lead to further complications such as muscle strain or rib fractures.
Asthma exacerbation
For individuals with asthma, catarrh can exacerbate their respiratory symptoms. The excessive mucus and inflammation can trigger asthma attacks, causing wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
Prevention
Preventing catarrh involves taking proactive measures to minimize exposure to potential triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are some prevention strategies you can adopt:
Frequent handwashing
Regular handwashing is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of viruses and bacteria that can cause catarrh. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially before touching your face or eating.
Avoiding close contact with sick individuals
If someone around you is sick with a cold or respiratory infection, try to minimize close contact with them. Viruses and bacteria can spread through respiratory droplets, so maintaining a safe distance can reduce your risk of catching catarrh.
Taking allergy medication
If you have catarrh symptoms related to allergies, taking appropriate allergy medication can help alleviate symptoms and prevent catarrh episodes. Consult with your healthcare provider or allergist to determine the most suitable medication for your specific allergies.
Using air purifiers
Investing in an air purifier can help filter out potential irritants, allergens, or pollutants from the air, reducing your exposure to these triggers. Place air purifiers in key areas of your home or office to maintain cleaner air quality.
Quitting smoking
If you are a smoker, quitting smoking is crucial in preventing and managing catarrh. Smoking irritates the respiratory system, damages cilia (hair-like structures that help move mucus), and weakens the immune response, making you more susceptible to catarrh.

Home Remedies
In addition to preventive measures, several home remedies can provide relief and alleviate catarrh symptoms. While these remedies may not cure catarrh, they can help manage the symptoms and enhance overall comfort.
Steam inhalation
Steam inhalation can help loosen mucus, reduce nasal congestion, and soothe irritated respiratory passages. Boil water and carefully inhale the steam, covering your head with a towel to create a steam-filled tent. Be cautious of the temperature to avoid burning yourself.
Nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation, using a saline solution, can help flush out excess mucus and clear nasal passages. You can use a neti pot or a nasal irrigation device to gently rinse your nasal passages with the saline solution.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated can help thin the mucus and prevent it from becoming excessive and sticky. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water and warm herbal teas, to keep your body hydrated and promote healthy mucus production.
Warm compresses
Applying warm compresses to your face can help alleviate sinus pain and pressure associated with catarrh. Use a clean towel soaked in warm water and gently place it on your face, focusing on the sinus areas.
Eucalyptus oil
Inhalation of eucalyptus oil can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion and soothe inflamed respiratory passages. Add a few drops of eucalyptus oil to a bowl of hot water and inhale the steam or use a diffuser.
Medications
Several medications are available to help manage catarrh symptoms. These medications can provide temporary relief and help alleviate discomfort caused by excessive mucus and inflammation.
Decongestants
Decongestants can help reduce nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels, thereby reducing swelling in the nasal passages. These medications are available in both oral and nasal spray forms but should be used for short-term relief to avoid potential rebound congestion.
Nasal sprays
Nasal sprays, such as saline sprays or steroid sprays, can help moisturize nasal passages and reduce inflammation. Saline sprays can also help flush out excess mucus from the nasal cavities.
Antihistamines
If allergies are causing or contributing to your catarrh symptoms, antihistamines can help control the allergic response. These medications block histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction, reducing inflammation and mucus production.
Expectorants
Expectorants are cough-relieving medications that help thin and loosen mucus, making it easier to cough up and expel. These medications can be beneficial if your catarrh symptoms include a persistent cough with difficulty clearing mucus.
Pain relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate headaches, sore throat, and other discomfort associated with catarrh. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to conventional medications and remedies, some individuals may explore alternative treatments to manage catarrh symptoms. It is important to note that these alternative treatments may have limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness, so it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before pursuing them.
Herbal remedies
Certain herbs, such as ginger, elderberry, or peppermint, may have properties that can help reduce inflammation or soothe catarrh symptoms. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional or experienced herbalist to ensure the safety and efficacy of herbal remedies.
Acupuncture
Some individuals find acupuncture beneficial in managing catarrh symptoms. Acupuncture involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points in the body to stimulate the flow of energy and promote healing. Consult with a licensed acupuncturist to discuss its potential benefits for your specific condition.
Chiropractic care
Chiropractic care focuses on the alignment of the spine and musculoskeletal system. Some individuals believe that spinal adjustments can improve immune function and alleviate symptoms associated with catarrh. Consult with a qualified chiropractor to explore this option further.
Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a holistic approach that uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s self-healing response. Homeopathic remedies for catarrh are individually prescribed based on specific symptoms and constitutional factors. Consult with a trained homeopath for personalized guidance.
Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy involves the use of essential oils to promote physical and emotional well-being. Certain essential oils, such as eucalyptus, peppermint, or tea tree oil, may help ease congestion, reduce inflammation, or promote relaxation. Use essential oils with caution and follow proper dilution and application guidelines.
Surgical Options
In severe cases of catarrh that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options may be considered. These surgical interventions aim to address underlying structural or anatomical issues that contribute to catarrh symptoms.
Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoids, the small tissues located at the back of the throat. Adenoids can become enlarged and contribute to nasal congestion, excessive mucus production, and catarrh symptoms. Adenoidectomy may be recommended if other treatment options have been exhausted.
Sinus surgery
Sinus surgery, also known as sinusotomy or sinus washout, involves clearing and reopening the blocked sinus passages. This procedure can help improve drainage, reduce inflammation, and alleviate catarrh symptoms due to chronic sinusitis.
Turbinectomy
Turbinectomy involves the removal or reduction of the size of the turbinates, structures inside the nasal passages responsible for humidifying and filtering the air we breathe. Enlarged or swollen turbinates can contribute to nasal congestion and excessive mucus production and may be surgically addressed in severe cases of catarrh.
Septoplasty
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to correct a deviated nasal septum, which can obstruct the nasal passages and lead to catarrh symptoms. The septum is straightened or reshaped to improve airflow and reduce excessive mucus production.
It is important to note that surgical options are typically considered when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief, and the severity of symptoms warrants further intervention. Consult with an experienced ear, nose, and throat specialist to discuss the potential benefits and risks associated with surgical options.