Are you familiar with the term “dental abscess”? These pesky little infections can cause a world of pain and discomfort in your mouth, but fear not, for we are here to help you understand them better. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of dental abscesses, what causes them, the symptoms to watch out for, and most importantly, how to effectively treat and prevent them. So sit back, relax, and let’s delve into the fascinating world of dental abscesses together!
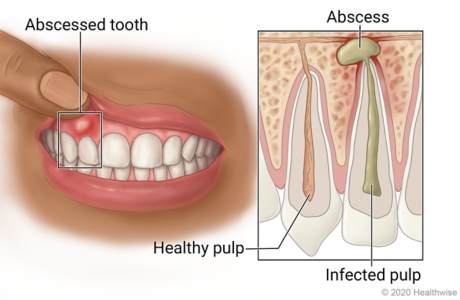
What is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess, also known as a tooth abscess, is a pocket of pus that forms within the teeth or gums. It occurs as a result of a bacterial infection, typically due to poor oral hygiene or untreated dental issues. A dental abscess can cause a range of painful symptoms and, if left untreated, can lead to complications. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for dental abscesses to maintain good oral health.
Definition of a Dental Abscess
A dental abscess is an oral health condition characterized by a collection of pus that forms when there is an infection in the mouth. Pus is a thick, yellowish fluid that consists of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. The abscess can develop either on the tooth itself or in the surrounding gum tissues. It is usually painful and can cause significant discomfort.

Types of Dental Abscesses
There are two main types of dental abscesses: periapical and periodontal abscesses.
A periapical abscess occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root. It often develops as a result of tooth decay or trauma that allows bacteria to enter the innermost part of the tooth, known as the dental pulp. This type of abscess can cause severe toothache and sensitivity.
On the other hand, a periodontal abscess forms in the gum tissues next to the tooth root. It typically arises from an infection that spreads from the gums to the deeper tissues, leading to the formation of an abscess. Periodontal abscesses may cause gum swelling, redness, and tenderness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of a dental abscess:
Dental Infection
The most common cause of a dental abscess is a bacterial infection. When bacteria penetrate the tooth or gums, they can lead to an abscess. Dental infections can arise from untreated cavities, cracked teeth, or previous dental procedures.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting proper oral hygiene practices allows bacteria to accumulate and thrive in the mouth. Failing to brush and floss regularly can increase the risk of developing a dental abscess.
Untreated Dental Issues
Neglecting to address dental problems promptly, such as cavities or gum disease, can exacerbate the risk of developing an abscess. These untreated conditions provide an environment in which bacteria can thrive and lead to infection.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with certain medical conditions or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to developing dental abscesses. Their decreased ability to fight off infections increases the likelihood of abscess formation.

Symptoms
Dental abscesses often present with various signs and symptoms, indicating the presence of an infection. It is crucial to be aware of these symptoms to seek prompt treatment. Common symptoms of a dental abscess include:
Toothache
A persistent, throbbing toothache is one of the most common symptoms of a dental abscess. The pain can be severe and worsen when biting or applying pressure to the affected tooth.
Swelling and Redness
Inflammation and swelling may occur in the affected area, such as the gums surrounding the tooth or the face. The swelling can be accompanied by redness and tenderness.
Pain and Sensitivity
Increased sensitivity to hot or cold substances can indicate the presence of a dental abscess. The affected tooth may become more sensitive to temperature changes and certain foods or drinks.
Fever and Malaise
In some cases, a dental abscess can cause systemic symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and a general feeling of malaise. These symptoms indicate that the infection may have spread beyond the oral cavity and require immediate attention.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To diagnose a dental abscess, a dentist will perform a thorough evaluation, which may involve the following steps:
Visual Examination
The dentist will visually inspect the affected area, looking for signs of swelling, redness, or a visible abscess. They may gently probe the tooth and surrounding gums to assess tenderness and sensitivity.
Dental X-rays
Dental X-rays are commonly used to determine the extent of the infection and identify potential underlying causes, such as tooth decay or bone loss. X-rays can provide valuable information to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Pus Culture
In some cases, the dentist may collect a sample of the pus for analysis. A pus culture can help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and guide the selection of targeted antibiotics.
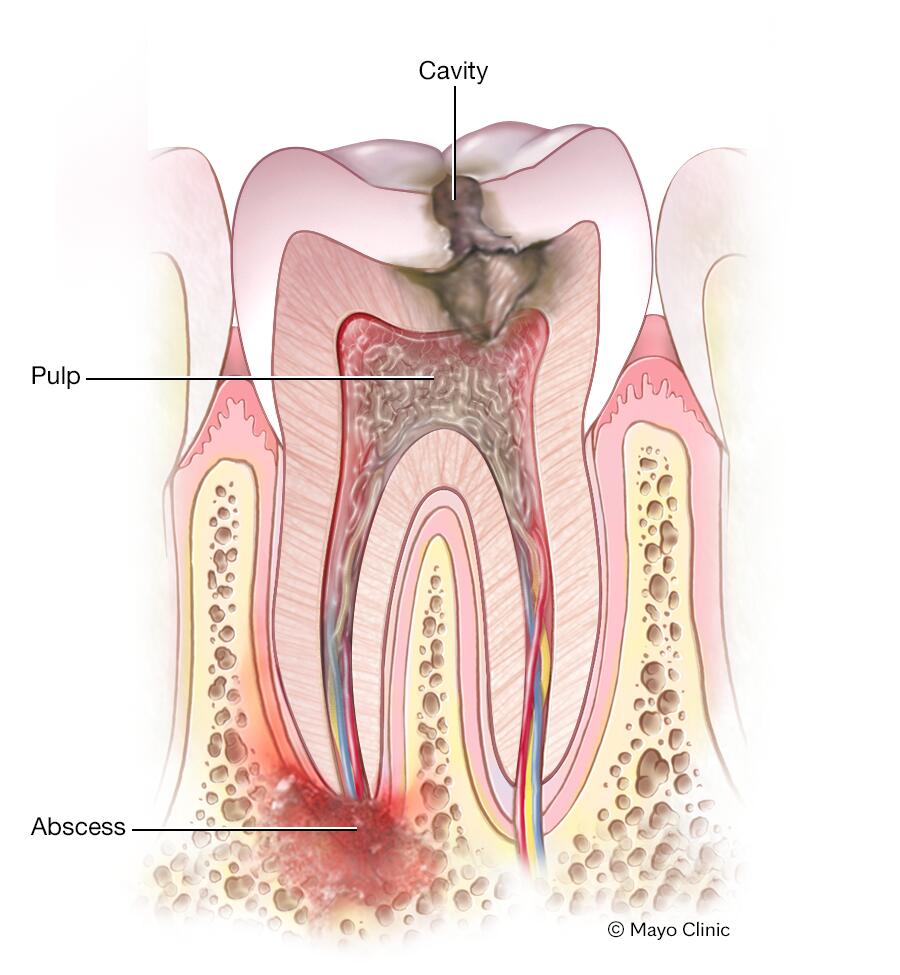
Complications
If left untreated, a dental abscess can lead to several complications:
Spread of Infection
The infection can spread to nearby tissues, such as the jawbone, face, or neck. This can result in severe pain, swelling, and difficulty in opening the mouth. In severe cases, the infection can even spread to other organs, leading to serious health consequences.
Jawbone Osteomyelitis
A dental abscess that spreads to the jawbone can cause a condition known as jawbone osteomyelitis. This is a serious infection of the bone that can lead to chronic pain, jaw stiffness, and even bone loss.
Ludwig’s Angina
Ludwig’s angina is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when a tooth infection spreads to the spaces below the tongue and floor of the mouth. It can cause rapidly escalating swelling and difficulty in breathing, requiring immediate medical attention.
Sepsis
In rare cases, a dental abscess can progress to sepsis, which is a severe systemic infection that can be life-threatening. Sepsis requires immediate medical intervention and can lead to organ failure if not treated promptly.
Treatment Options
The treatment of a dental abscess depends on the severity of the infection and the extent of the symptoms. Common treatment options include:
Drainage
To relieve pain and promote healing, the dentist may need to drain the abscess. This involves making a small incision to allow the pus to drain out. After drainage, the dentist will thoroughly clean the affected area to remove any remaining infection.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent its spread. They may be necessary when the abscess is large, the infection is severe, or there are signs of spreading beyond the oral cavity. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
Root Canal Treatment
In cases where the dental abscess has affected the dental pulp, root canal treatment may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning and disinfecting the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection. A dental crown may be placed on the treated tooth to restore its strength and appearance.
Extraction
If the affected tooth is severely damaged, cannot be saved, or poses a risk of further infection, extraction may be the best treatment option. This is usually done when other treatment options have failed or when the tooth cannot be restored.
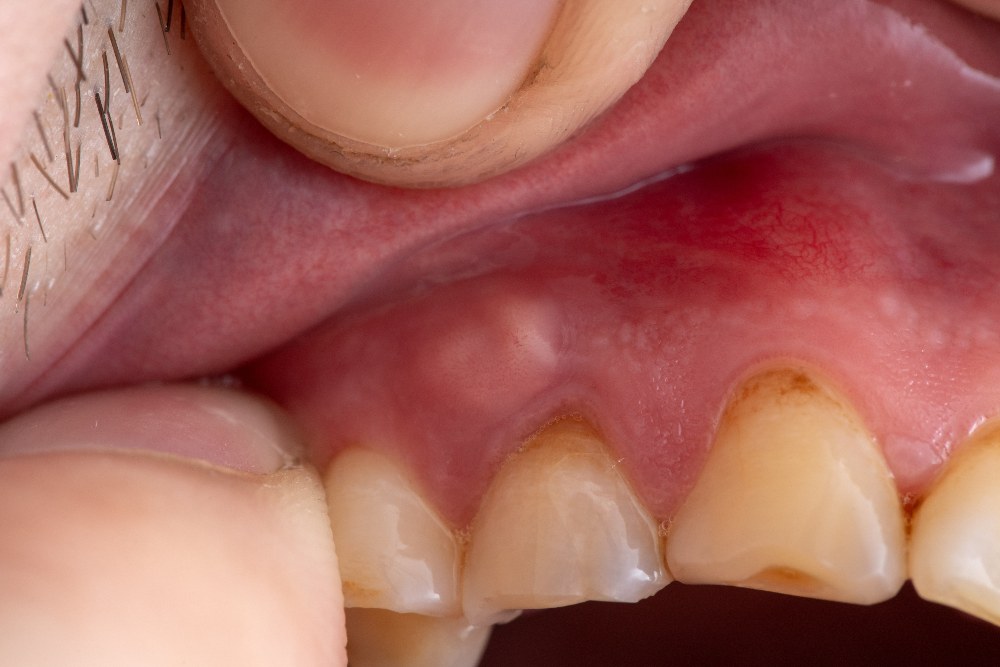
Home Remedies and Pain Management
While professional dental treatment is necessary to address a dental abscess, there are some home remedies and pain management techniques that can provide temporary relief:
Warm Saltwater Rinse
Rinsing the mouth with warm saltwater can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and swish it around the mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Over-the-counter options such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dentist before taking any medication.
Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help numb the area, reduce swelling, and relieve pain. Place an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a clean cloth against the cheek adjacent to the affected tooth for around 15 minutes at a time.
Prevention
Preventing dental abscesses involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices and addressing dental issues promptly. Some preventive measures include:
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the risk of infection. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help kill bacteria.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular visits to the dentist for check-ups and professional cleanings can help identify and address potential dental issues early on, preventing abscess formation. Dentists can detect cavities, gum disease, and other problems before they progress.
Addressing Dental Issues Promptly
If you experience any dental problems, such as tooth decay or gum inflammation, it is important to seek dental care promptly. Treating these issues early can prevent them from progressing into more serious conditions, such as abscesses.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall oral health. Avoiding excess sugar, eating a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption can help maintain strong teeth and gums.
When to Seek Professional Help
While home remedies and pain management techniques can provide temporary relief, it is essential to seek professional dental help when certain symptoms or conditions arise:
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If the symptoms of a dental abscess persist or worsen despite home remedies, it is important to consult a dentist. Increasing pain, swelling, or fever may indicate an escalating infection that requires medical intervention.
High Fever
A high fever that accompanies a dental abscess can be a sign of a severe infection. It is crucial to seek immediate dental or medical attention to prevent the infection from spreading further.
Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing
If a dental abscess leads to difficulty swallowing or breathing, it may indicate a potentially life-threatening condition such as Ludwig’s angina. Emergency medical care should be sought immediately.
Conclusion
A dental abscess is a potentially serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. It is essential to be aware of the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with dental abscesses in order to maintain good oral health. By practicing good oral hygiene, seeking regular dental check-ups, and addressing dental issues promptly, you can reduce the likelihood of developing a dental abscess. If you experience any signs of a dental abscess, it is important to consult a dental professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, prevention and early intervention are key to ensuring a healthy smile.