Have you ever experienced that unsettling feeling of dizziness? It’s like the ground beneath you suddenly shifts, leaving you feeling off-balance and disoriented. Whether it’s a fleeting sensation or a persistent problem, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dizziness is crucial. In this article, we will shed light on this common ailment, exploring the various factors that can lead to dizziness and providing you with valuable insights to help you navigate through the dizzying world of lightheadedness. So, hold on tight and let’s unravel the mysteries of dizziness together!

Causes of Dizziness
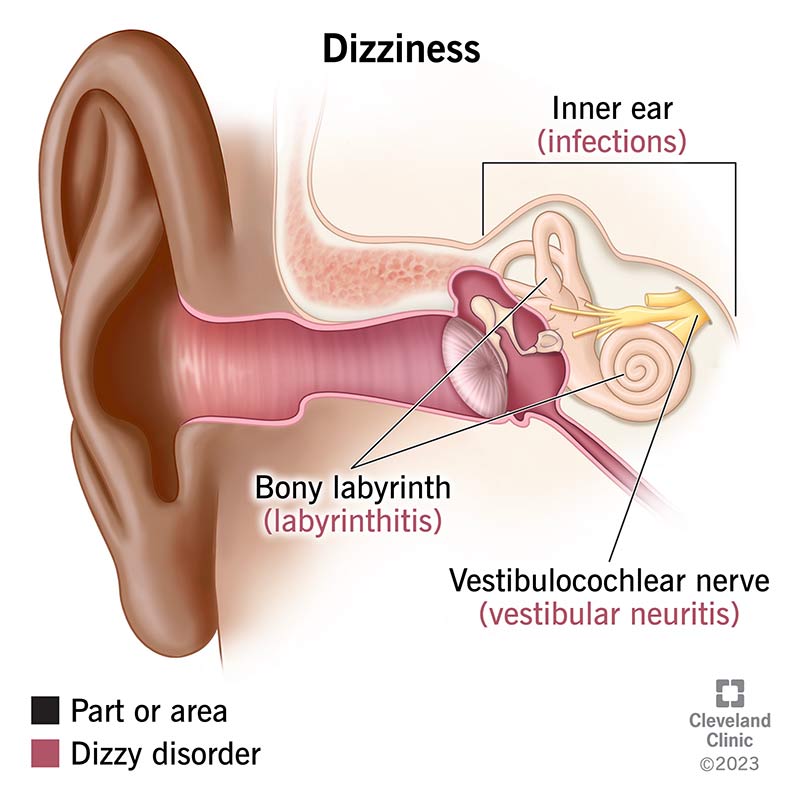
Inner Ear Problems
Dizziness can often be caused by problems in the inner ear, such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Meniere’s disease, or labyrinthitis. These conditions affect the balance and fluid levels in the inner ear, leading to symptoms of dizziness or vertigo.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, anxiety, or allergies, can have dizziness as a side effect. It’s important to speak with your doctor about any medications you are taking and the potential side effects they may cause.
Low Blood Pressure
When blood pressure drops suddenly, it can result in dizziness or lightheadedness. This can occur when standing up too quickly or due to certain medical conditions, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS).
Dehydration
Lack of proper hydration can cause dizziness, especially in hot weather or after intense physical activity. It’s important to drink enough fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration and its associated symptoms.
Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress can trigger feelings of dizziness. The body’s response to stress can include increased heart rate and changes in blood pressure, which can lead to dizziness or lightheadedness.
Migraine
Some migraines can cause dizziness or vertigo as a symptom. These types of migraines are often referred to as vestibular migraines, and they can be accompanied by other migraine symptoms like headache, sensitivity to light, and nausea.
Neurological Disorders
Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, can cause dizziness as a symptom. These conditions affect the central nervous system and can disrupt the body’s ability to maintain balance.
Cardiovascular Conditions
Heart conditions, such as arrhythmias or blocked arteries, can result in dizziness. These conditions can disrupt the flow of blood and oxygen to the brain, leading to feelings of lightheadedness or unsteadiness.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to feelings of dizziness. Fluctuations in hormones can affect blood flow and impact the body’s balance system.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
POTS is a condition characterized by an abnormal increase in heart rate upon standing up. This condition can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when transitioning from a sitting or lying position to standing.
Symptoms of Dizziness
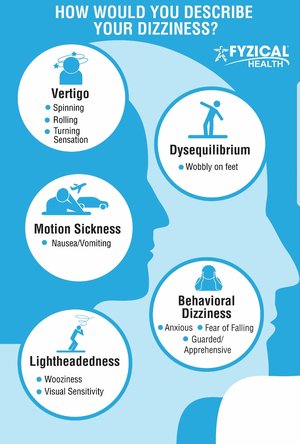
Vertigo
Vertigo is a spinning or rocking sensation that makes you feel like you or your surroundings are moving even though they are not. It is a common symptom of inner ear problems or vestibular migraines.
Lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a feeling of faintness or being on the verge of passing out. It can be caused by low blood pressure, dehydration, anxiety, or medication side effects.
Loss of Balance
Dizziness can also manifest as a loss of balance or unsteadiness when walking or standing. This can be particularly concerning, as it increases the risk of falls and injuries.
Feeling Faint
Feeling faint is similar to lightheadedness but may be accompanied by a temporary loss of consciousness or near-loss of consciousness. It can be a result of a drop in blood pressure or inadequate blood flow to the brain.
Nausea and Vomiting
Dizziness can often be accompanied by feelings of nausea and even vomiting. This can be a particularly distressing symptom and can be caused by conditions such as Meniere’s disease or vestibular migraines.
Blurred Vision
Blurred vision is a common symptom of dizziness. It can occur due to the disruption of blood flow to the eyes or as a result of the brain’s difficulty in processing visual information during an episode of dizziness.
Confusion
Dizziness can sometimes lead to confusion or difficulty concentrating. This can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks and may increase the risk of accidents or injuries.
Sweating
Excessive sweating can occur during episodes of dizziness. This can be a result of the body’s physiological response to stress or as a symptom of certain medical conditions.
Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat
Heart palpitations or a rapid/irregular heartbeat can accompany dizziness. This can be due to changes in blood pressure or heart rhythm abnormalities.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus refers to the perception of sound in the ears or head that is not caused by an external source. It can often occur alongside episodes of dizziness and may be a sign of an underlying condition affecting the inner ear.

Diagnosing Dizziness
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your doctor will start by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination. They will ask you questions about your symptoms, medical conditions, medications, and any recent incidents or changes that may be contributing to your dizziness.
Balance and Hearing Tests
Balance tests, such as the Romberg test or the Dix-Hallpike maneuver, can help determine if there is an issue with your vestibular system. Hearing tests, such as audiometry, can rule out hearing loss as a cause of dizziness.
Blood Pressure Monitoring
Monitoring your blood pressure is crucial in diagnosing dizziness. Your doctor may check your blood pressure in various positions, such as lying down, sitting, and standing, to detect any significant fluctuations or drops.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) can assess the electrical activity of your heart and detect any abnormalities or arrhythmias that may be contributing to your dizziness.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
In some cases, your doctor may order an MRI scan to evaluate the structures of your brain and inner ear. An MRI can help detect any structural abnormalities or lesions that may explain your dizziness symptoms.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can provide valuable information about your overall health and rule out underlying medical conditions, such as anemia or thyroid disorders, that could be causing your dizziness.
Tilt Table Test
A tilt table test involves being securely strapped to a table that is gradually tilted to different angles. This test helps evaluate blood pressure and heart rate responses to changes in position and can diagnose conditions like POTS.
Electronystagmography (ENG)
ENG is a test that measures involuntary eye movements (nystagmus) to assess the health of the inner ear and evaluate vestibular function. It can help identify inner ear problems or other vestibular disorders.
Treatment Options for Dizziness
Treating the Underlying Cause
The most effective treatment for dizziness is targeting and treating the underlying cause. Depending on the specific cause, this may involve medication adjustments, physical therapy, surgery, or lifestyle changes.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to alleviate dizziness or manage the symptoms of underlying conditions. These medications can include anti-vertigo drugs, anti-anxiety medications, or medications to regulate blood pressure or heart rhythm.
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is a type of physical therapy that focuses on strengthening the vestibular system and improving balance. VRT exercises can help reduce symptoms of dizziness and improve overall balance and stability.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help reduce episodes of dizziness. This may include avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or alcohol, maintaining healthy hydration levels, and managing stress.
Home Remedies
Simple home remedies can provide relief from mild dizziness symptoms. These may include lying down in a quiet and dark room, practicing deep breathing exercises, or applying a cool compress to the forehead.
Surgery
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat underlying conditions that are causing dizziness. This may involve procedures to restore proper inner ear function or to address structural abnormalities affecting the balance system.
Alternative Therapies
Certain alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or herbal supplements, may be used to alleviate symptoms of dizziness. However, it’s important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional before trying them.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can be beneficial for individuals experiencing dizziness related to anxiety or phobias. CBT techniques can help identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to dizziness.
Stress Management Techniques
Managing stress levels through techniques like mindfulness, relaxation exercises, or counseling can help reduce dizziness symptoms. Stress reduction techniques can also assist in preventing dizziness triggers.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific acupuncture points to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. Some individuals find acupuncture helpful in relieving dizziness symptoms.
Preventing Dizziness
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water and staying hydrated is crucial in preventing dizziness, especially in hot weather or during physical activity. Be sure to drink fluids throughout the day, and consider an electrolyte drink if you are engaging in intense exercise.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients can contribute to overall health and help prevent dizziness. Be mindful of including foods rich in vitamins and minerals, as deficiencies can contribute to dizziness.
Avoid Triggers
Identify and avoid potential triggers that may induce dizziness. These can include certain foods or beverages, exposure to bright lights or loud noises, or specific activities that worsen symptoms.
Get Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise can improve cardiovascular health, reduce stress, and improve overall balance and coordination. Be sure to choose exercises that are appropriate for your fitness level and consider low-impact activities like swimming or walking.
Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate dizziness symptoms, so it’s important to develop effective stress management techniques. This can include relaxation exercises, meditation, or engaging in activities that bring joy and help you unwind.
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine
Alcohol and caffeine can contribute to dehydration and disrupt the body’s balance system, increasing the risk of dizziness. Limiting or avoiding these substances can help prevent dizziness episodes.
Avoid Rapid Position Changes
To prevent dizziness caused by changes in blood pressure, avoid sudden or rapid changes in position, particularly when transitioning from lying down to standing up.
Use Assistive Devices
When experiencing dizziness, using assistive devices like canes or walkers can provide stability and reduce the risk of falls. Talk to your healthcare provider about appropriate assistive devices for your specific situation.
Monitor Medication Side Effects
If you experience dizziness as a side effect of medication, speak with your doctor about potential alternatives or adjustments to your current medication regimen. Never stop or adjust your medication without medical guidance.
Fall Prevention Strategies
Implementing fall prevention strategies can help reduce the risk of injury during episodes of dizziness. This can involve removing tripping hazards in your home, installing handrails, or using non-slip mats in the bathroom.
When to Seek Medical Help
It’s important to recognize when your dizziness may require medical attention. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
Frequent or Severe Dizziness
If you have recurring or severe episodes of dizziness that significantly impact your daily life, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can help identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Dizziness Accompanied by Neurological Symptoms
If your dizziness is accompanied by neurological symptoms such as severe headache, numbness or weakness in your limbs, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, or changes in vision, seek immediate medical attention.
Dizziness after a Head Injury
If you experience dizziness after a head injury, it’s essential to seek medical help. Dizziness following a head injury can be a sign of a more severe condition, such as a concussion or internal bleeding.
Presence of Other Serious Health Conditions
If you have preexisting health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or a history of stroke, consult your healthcare provider if you experience dizziness. This is particularly important if the dizziness is new or worsening.
Signs of Dehydration
If you experience dizziness along with symptoms of dehydration, such as dark urine, dry mouth, or excessive thirst, seek medical attention. Severe dehydration can have serious health consequences and requires prompt treatment.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If your dizziness persists or worsens despite home remedies or lifestyle changes, it’s important to seek medical guidance. Persistent or progressive symptoms may require further evaluation and a more targeted treatment approach.
Impact on Daily Activities
If your dizziness significantly affects your ability to perform everyday tasks, such as driving, working, or caring for yourself or others, consult a healthcare professional. They can help you manage your symptoms and restore your quality of life.
Concerns about Medication Side Effects
If you suspect that your dizziness is a side effect of your medication, discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your medication regimen and make appropriate adjustments, if necessary.
Sudden Onset of Dizziness
If you experience a sudden, severe onset of dizziness with no apparent cause, seek immediate medical attention. This can be a sign of a medical emergency, such as a stroke or heart attack.
Difficulty Breathing
If your dizziness is accompanied by difficulty breathing or a feeling of chest tightness, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a cardiac or respiratory emergency.
Conclusion
Dizziness can be a distressing symptom that can significantly impact your daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dizziness is crucial in managing and preventing these episodes. By seeking medical help when needed, making necessary lifestyle changes, and following appropriate treatment plans, you can effectively manage your dizziness and improve your overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and personalized guidance based on your specific situation.