Have you ever experienced difficulty swallowing? If the answer is yes, it could be an indication of a swallowing disorder. Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, can range from mild discomfort to severe complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for swallowing disorders, providing you with a better understanding of this common yet often overlooked condition. So, let’s dive right in and uncover the complexities behind swallowing problems!
Understanding Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, refer to difficulties or abnormalities in swallowing food, liquids, or saliva. While swallowing may seem like a simple and automatic process, it actually involves a coordinated effort of many muscles and nerves in the mouth, throat, and esophagus. When any of these structures or processes are affected, it can lead to various swallowing problems. It is important to understand swallowing disorders, their types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, associated medical conditions, treatment options, prevention, and support available for individuals dealing with these disorders.
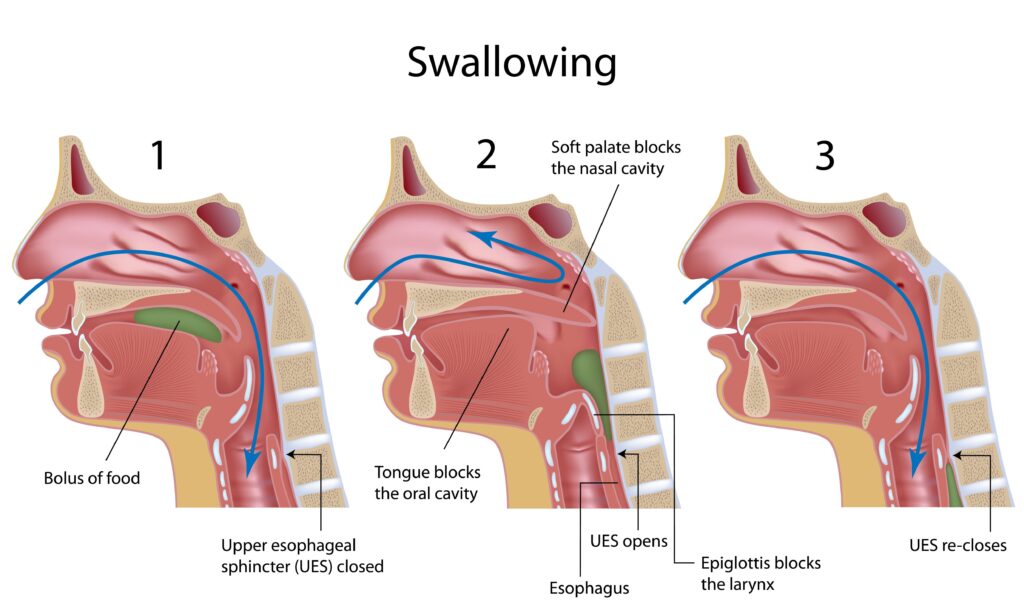
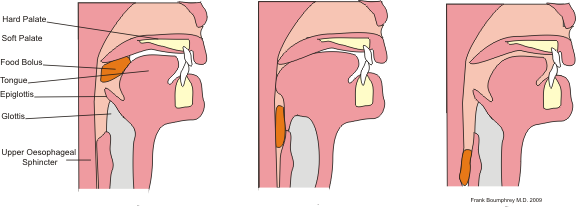
Overview of Swallowing Problems
Swallowing problems can occur at any age and can range from mild to severe. They can affect the oral, pharyngeal, or esophageal phases of swallowing, or a combination of these phases. The oral phase involves chewing and forming a bolus (a small mass) of food or liquid, the pharyngeal phase involves moving the bolus from the mouth to the throat, and the esophageal phase involves transporting the bolus from the throat to the stomach. Any disruption in these phases can lead to swallowing difficulties.
Types of Swallowing Disorders
There are various types of swallowing disorders, which can be categorized based on their underlying cause or the specific phase of swallowing affected. Some common types include:
-
Oral dysphagia: This refers to difficulties in the oral phase of swallowing, such as problems with chewing, forming a bolus, or keeping food in the mouth.
-
Pharyngeal dysphagia: This type involves difficulties in the pharyngeal phase, where the bolus does not move smoothly from the throat to the esophagus. It can lead to issues like choking, coughing, or frequent throat clearing during or after swallowing.
-
Esophageal dysphagia: This type is characterized by difficulties in the esophageal phase of swallowing, where the bolus encounters problems in its passage through the esophagus. It can cause sensations of food being stuck in the chest or throat.
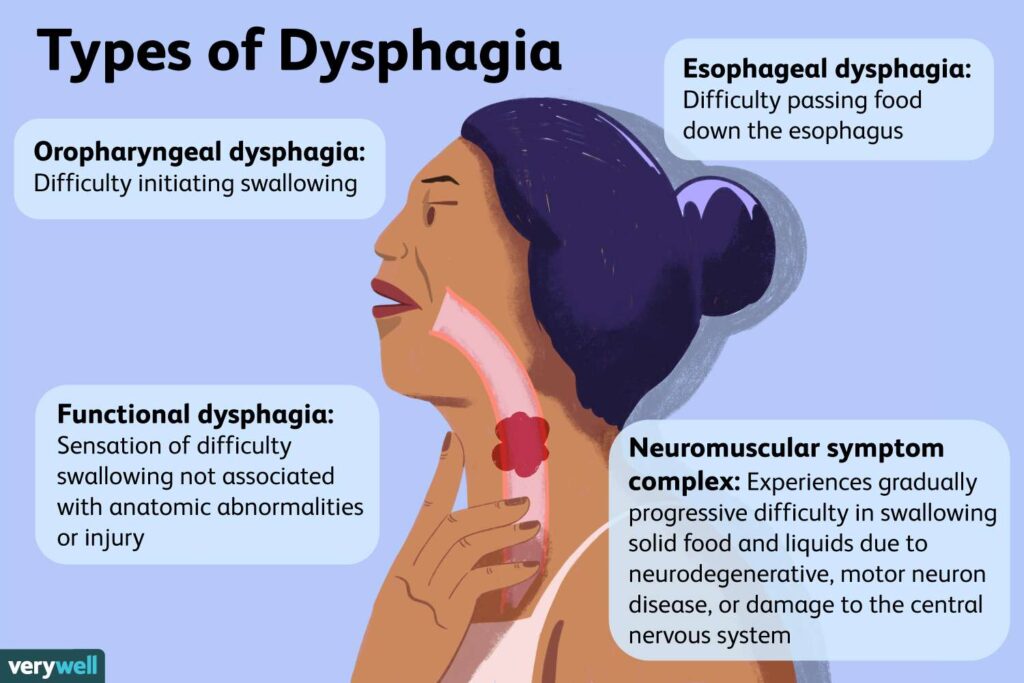
Etiology of Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders can have various underlying causes. Some common etiologies include:
-
Structural abnormalities: Certain structural issues, such as a narrowed esophagus, tumors, or strictures (narrowings) in the throat or esophagus, can interfere with the smooth passage of the bolus.
-
Neuromuscular disorders: Conditions that affect the muscles or nerves involved in swallowing, such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or muscular dystrophy, can lead to swallowing difficulties.
-
Aging and age-related changes: As we age, the muscles involved in swallowing may weaken, and the coordination between the various structures involved in swallowing may decline. This can contribute to swallowing problems in older adults.
-
Traumatic injuries or surgeries: Injuries to the head, neck, or chest, or surgeries that affect the structures involved in swallowing, can result in temporary or permanent swallowing difficulties.
Common Symptoms of Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders can manifest in various ways, and the specific symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the phase of swallowing affected. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort while swallowing
- Choking or coughing during or after swallowing
- Feeling of food or liquid getting stuck in the chest or throat
- Regurgitation of food or liquid
- Weight loss or malnutrition due to difficulty in eating enough
- Frequent respiratory infections or pneumonia, possibly due to aspiration of food or liquids into the lungs
- Avoidance of certain foods or liquids
- Refusing to eat or drink altogether
- Changes in voice or speech

Diagnosis of Swallowing Disorders
A thorough evaluation is necessary to diagnose swallowing disorders and determine their underlying cause. The diagnostic process may involve:
-
Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any underlying conditions or surgeries that may contribute to swallowing difficulties.
-
Physical examination: A physical examination of the mouth, throat, and neck may be conducted to check for any visible abnormalities or signs of muscle weakness.
-
Swallowing assessment: Various tests, such as a modified barium swallow study or a fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing, may be conducted to evaluate the movement of the bolus during swallowing and identify any abnormalities.
-
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to visualize the structures involved in swallowing and detect any structural abnormalities or obstructions.
Medical Conditions Associated with Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders can be associated with various medical conditions, which may contribute to or worsen the swallowing difficulties. Some common conditions include:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): This condition, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to swallowing problems.
-
Neurological disorders: Conditions like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) can affect the nerves and muscles involved in swallowing.
-
Head and neck cancers: Tumors or cancers in the mouth, throat, or esophagus can obstruct the passage of the bolus and impair swallowing.
-
Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like scleroderma or lupus can cause inflammation and scarring of the esophagus, leading to swallowing difficulties.

Treatment Options for Swallowing Disorders
The treatment approach for swallowing disorders depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual needs. Some common treatment options include:
-
Dietary modifications: Adjusting the consistency of foods and liquids to make swallowing easier, such as consuming pureed foods or thickened liquids.
-
Swallowing exercises: Working with a speech-language pathologist to perform specific exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing and improve coordination.
-
Medications: In certain cases, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms like acid reflux or to address underlying conditions contributing to swallowing difficulties.
-
Surgical interventions: For structural abnormalities or obstructions, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove the blockages or repair the damaged structures.
Prevention and Management of Swallowing Disorders
While some causes of swallowing disorders cannot be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk or manage the condition effectively. These include:
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene: Regular dental care and oral hygiene practices can help prevent oral infections or dental problems that may interfere with swallowing.
-
Eating slowly and chewing thoroughly: Taking time to eat and ensuring thorough chewing can help prevent choking or difficulties in forming a bolus.
-
Sitting upright during meals: Eating in an upright position can aid in the smooth passage of the bolus and reduce the risk of choking or aspiration.
-
Avoiding known triggers: If certain foods or drinks worsen swallowing difficulties, avoiding or modifying them can help manage the condition.
Swallowing Disorders in Children
Swallowing disorders can also occur in children, and early identification and intervention are crucial for their overall growth and development. Common causes of swallowing problems in children include developmental delays, neurological conditions, structural abnormalities, or feeding difficulties. Pediatricians and speech-language pathologists play a key role in assessing and managing swallowing disorders in children, and treatment options can include feeding therapy, positioning techniques, or dietary modifications based on individual needs.
Life Impact and Support for Individuals with Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals who have to cope with these challenges. Difficulties in eating and drinking can lead to malnutrition, weight loss, or social isolation. However, various support systems and strategies are available to help manage and adapt to these conditions. Speech-language pathologists, dietitians, support groups, and online resources can provide valuable guidance, education, and emotional support to individuals and their families.
In conclusion, swallowing disorders are complex conditions that can have significant implications on a person’s ability to eat, drink, and communicate effectively. Understanding the different types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, prevention, and support available for individuals with swallowing disorders is crucial for enhancing their quality of life. Seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences persistent swallowing difficulties to ensure early intervention and appropriate management. Remember, you are not alone in your journey, and there are resources and professionals ready to support you every step of the way.