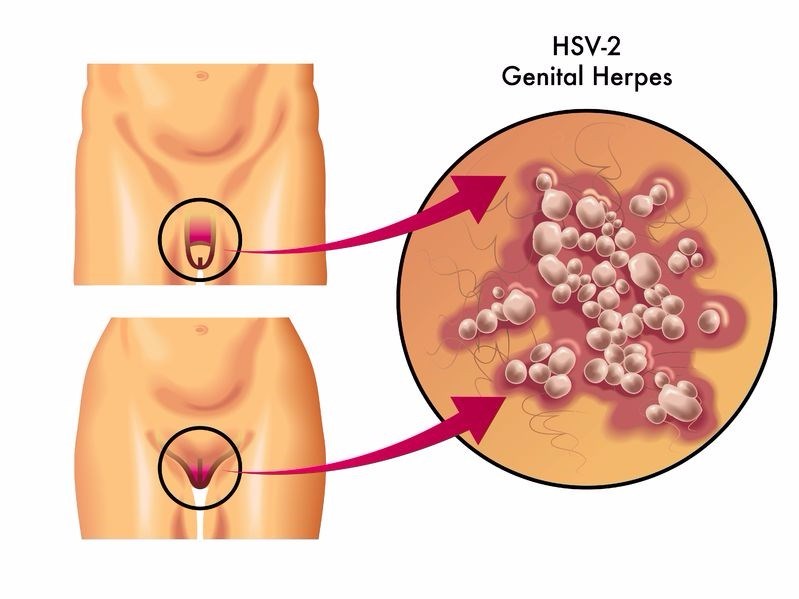
In today’s article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the causes and symptoms of genital herpes. Whether you’ve been personally affected by this condition or are simply interested in learning more, we’re here to provide you with valuable insights into this common and often misunderstood infection. By exploring the various factors that contribute to its development and the telltale signs to look out for, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions and support others who may be navigating this journey. So, let’s dive right in and shed some light on this important topic.

Causes of Genital Herpes
Transmission through Sexual Contact
Genital herpes is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The virus can be spread even when there are no visible symptoms or lesions. It is important to note that condoms, while reducing the risk of transmission, may not provide complete protection. Other forms of direct skin-to-skin contact in the genital area can also lead to the transmission of the virus.
Viral Infection: Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), specifically the HSV-1 or HSV-2 strains. HSV-2 is more commonly associated with genital herpes, while HSV-1 is often linked to oral herpes. However, both strains can infect the genitals, and each strain can also cause oral or genital infections, depending on the mode of transmission.
Types of HSV: HSV-1 and HSV-2
HSV-1 and HSV-2 are similar in many ways, but there are some important differences. HSV-1 is typically transmitted through oral contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils, while HSV-2 is mainly transmitted through sexual contact. However, due to changing sexual practices, there has been an increase in cases of HSV-1 genital infections in recent years.
Risk Factors for Genital Herpes
There are certain risk factors that can increase the likelihood of acquiring genital herpes. These include having multiple sexual partners, engaging in unprotected sex, having a weakened immune system, and having a previous history of sexually transmitted infections. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate precautions to reduce the risk of transmission.
Infection during Pregnancy
Genital herpes can pose specific risks during pregnancy. If a pregnant woman is infected with the herpes simplex virus, there is a possibility of vertical transmission to the fetus. This can lead to serious complications, including neonatal herpes, which is a life-threatening condition in newborns. It is crucial for pregnant women with genital herpes to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage and prevent transmission to their babies.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
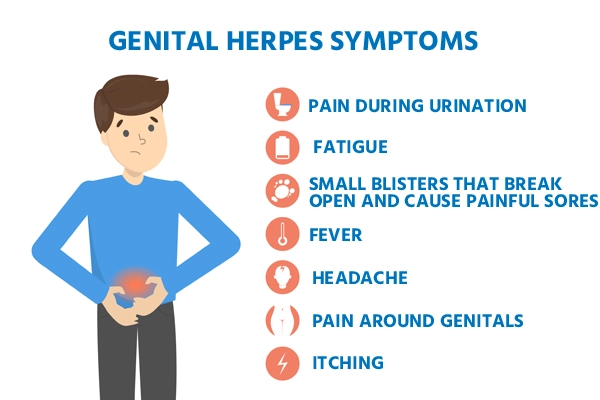
Initial Outbreak Symptoms
The initial outbreak of genital herpes is often the most severe. Common symptoms include small, painful blisters or sores on or around the genitals, buttocks, or thighs. These lesions may appear within two to 12 days after exposure to the virus and can last for several weeks. Other symptoms associated with the initial outbreak may include flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
Subsequent Outbreak Symptoms
After the initial outbreak, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate periodically, leading to subsequent outbreaks. These recurrent outbreaks are usually less severe and shorter in duration compared to the initial episode. Symptoms may include tingling or itching sensations, followed by the formation of small, painful sores. It is important to note that the frequency and severity of outbreaks can vary greatly among individuals.
Asymptomatic Shedding
One of the challenges of genital herpes is that the virus can be shed from the skin even when there are no visible symptoms or sores. This is known as asymptomatic shedding and can contribute to the spread of the virus. It is estimated that about 70% of new cases are caused by asymptomatic shedding. This highlights the importance of regular testing and practicing safe sexual behaviors, even in the absence of visible symptoms.
Potential Complications
While genital herpes is generally not life-threatening, it can lead to certain complications, especially if left untreated or if the immune system is compromised. These complications may include recurrent outbreaks, bacterial superinfections, urinary retention, meningitis, and in rare cases, spread of the virus to other parts of the body. It is crucial to seek medical attention and follow appropriate treatment plans to manage and prevent complications associated with genital herpes.
Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
Physical Examination
Diagnosing genital herpes typically involves a physical examination conducted by a healthcare provider. The examination may include inspecting the genital area for visible symptoms such as blisters or sores. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any symptoms or concerns you may have, as well as your sexual history to help guide the diagnosis.
Laboratory Blood Tests
In some cases, laboratory blood tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis of genital herpes. These tests detect the presence of antibodies to the herpes simplex virus, which can indicate a previous or ongoing infection. Blood tests can be particularly useful when there are no visible symptoms or if the symptoms are atypical. It is important to discuss with your healthcare provider which tests may be appropriate for you.
Treatment for Genital Herpes
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are commonly prescribed to manage and treat genital herpes. These medications can help alleviate symptoms, reduce the duration and severity of outbreaks, and decrease the frequency of recurrent episodes. They can also help reduce the risk of transmission to sexual partners. It is important to follow the prescribed treatment regimen and take the medications as directed by your healthcare provider.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to antiviral medications, there are certain home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help manage genital herpes outbreaks. These include keeping the affected area clean and dry, wearing loose-fitting clothing, avoiding triggers such as stress and excessive sun exposure, practicing safe sex, and maintaining a healthy immune system through regular exercise, balanced diet, and adequate sleep. It is important to discuss with your healthcare provider which strategies may be suitable for you.
Prevention of Genital Herpes
Safe Sexual Practices
Practicing safe sex is crucial in preventing the transmission of genital herpes. This includes using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity, including anal, vaginal, and oral sex. It is also important to be aware that condoms may not provide complete protection as they do not cover all potentially infected areas. Additionally, limiting the number of sexual partners and engaging in open and honest communication with your partner about sexual health can further reduce the risk of transmission.
Use of Condoms
Although condoms are not 100% effective at preventing the transmission of genital herpes, they are still an important tool in reducing the risk. Condoms create a barrier that can help prevent direct skin-to-skin contact, which is a common mode of transmission for the herpes simplex virus. It is important to use condoms consistently and correctly to maximize their effectiveness in preventing the spread of the virus.
Avoiding Sexual Contact during Outbreaks
To further reduce the risk of transmission, it is advisable to avoid sexual contact during outbreaks, including the presence of visible sores, itching, or tingling sensations. It is important to remember that the virus can still be shed from the skin even in the absence of symptoms. Open communication with sexual partners about any present or past infections is crucial in preventing the spread of genital herpes.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Genital Herpes
Stigma and Misconceptions
Genital herpes can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals, primarily due to the stigma and misconceptions surrounding the infection. Many people associate genital herpes with promiscuity or uncleanliness, which can lead to feelings of shame, guilt, and social isolation. It is important to recognize that genital herpes is a common infection and does not define a person’s worth or character.
Coping Strategies and Support
Coping with the emotional and psychological impact of genital herpes can be challenging. It is important to seek support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family members who can provide understanding and empathy. There are also support groups and online communities available where individuals can connect with others who have similar experiences. Learning about the infection, practicing self-care strategies, and maintaining a positive mindset can also contribute to a healthier emotional well-being.
Genital Herpes and its Association with Other Health Issues
Increased Risk of HIV Infection
It is important to be aware that genital herpes can increase the risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Genital herpes can cause microscopic breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, which can serve as entry points for HIV. Additionally, the presence of genital herpes can increase the viral load of HIV, thereby increasing the risk of transmission. It is crucial to adopt preventive measures, such as practicing safe sex and getting tested regularly for both genital herpes and HIV.
Connection with Cervical Cancer
Genital herpes, particularly the HSV-2 strain, has been associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer. The presence of the herpes simplex virus can lead to inflammation and changes in the cervical cells, making them more susceptible to the development of cancerous changes. Regular cervical cancer screening, such as Pap tests and HPV tests, is essential for early detection and timely intervention.
Genital Herpes in Pregnant Women and Infants
Vertical Transmission to Newborns
Genital herpes can pose serious risks to newborns if contracted during pregnancy or delivery. There is a possibility of vertical transmission, where the virus is passed from the mother to the baby during childbirth. This can lead to neonatal herpes, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition. It is important for pregnant women with genital herpes to inform their healthcare providers and follow appropriate management and prevention strategies.
Management and Prevention in Pregnancy
Managing genital herpes during pregnancy involves working closely with healthcare providers to minimize the risk of transmission to the baby. This may include antiviral medications to suppress outbreaks, regular monitoring through physical examinations and blood tests, and discussing the options for mode of delivery. In some cases, a cesarean section may be recommended to reduce the risk of vertical transmission. It is crucial for pregnant women to receive timely and appropriate care to protect the health of both themselves and their babies.

Genital Herpes in Adolescents and Young Adults
Education and Awareness
Adolescents and young adults are particularly vulnerable to acquiring genital herpes due to changes in sexual behaviors and a lack of awareness about sexually transmitted infections. Promoting comprehensive sexual education that includes information about genital herpes, its transmission, and prevention strategies is essential in empowering young individuals to make informed decisions. It is important to provide accurate and non-judgmental information to promote responsible sexual behavior among adolescents and young adults.
Promoting Safe Sexual Practices
Encouraging safe sexual practices among adolescents and young adults is crucial in preventing the spread of genital herpes. This includes promoting the use of condoms, regular testing for sexually transmitted infections, and open communication with sexual partners about sexual health. It is important to create a supportive and non-stigmatizing environment where young individuals feel comfortable seeking information and accessing appropriate healthcare services.
Living with Genital Herpes: Tips and Advice
Disclosure to Sexual Partners
Disclosure is an important aspect of living with genital herpes. While it may feel challenging or uncomfortable, it is crucial to inform sexual partners about the infection to allow them to make informed decisions about their own health. It is recommended to have the conversation before engaging in any sexual activity and to provide accurate information about transmission risks, safe sex practices, and treatment options. Open communication can foster trust and build stronger relationships.
Supportive Relationships
Living with genital herpes can be easier when surrounded by supportive relationships. Friends, family members, or support groups can provide understanding, empathy, and encouragement. It is important to have a support system to lean on during difficult times, as well as to celebrate successes in managing the infection. Building strong relationships based on trust and open communication can contribute to overall well-being.
Self-Care Strategies
Engaging in self-care strategies can help individuals living with genital herpes better manage the infection and maintain their overall health and well-being. This may include getting adequate sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress through relaxation techniques or counseling. It is important to prioritize self-care and create a positive and nurturing environment for oneself.
In conclusion, genital herpes is a common and manageable infection that can be transmitted through sexual contact. It is crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, and methods of diagnosis to seek appropriate treatment and take preventive measures. While living with genital herpes may present emotional and psychological challenges, there are coping strategies, support systems, and self-care practices that can help individuals lead fulfilling lives. Education, awareness, and promoting safe sexual practices are essential in preventing the spread of genital herpes and protecting the overall sexual health of individuals.