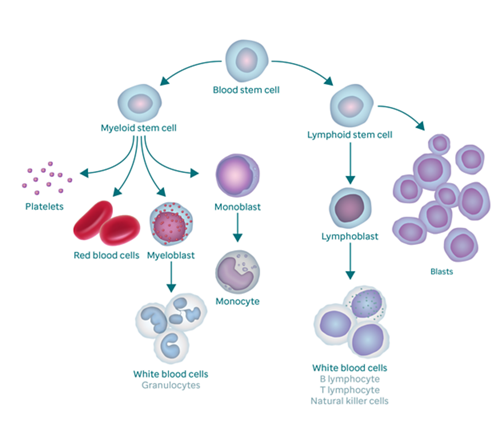
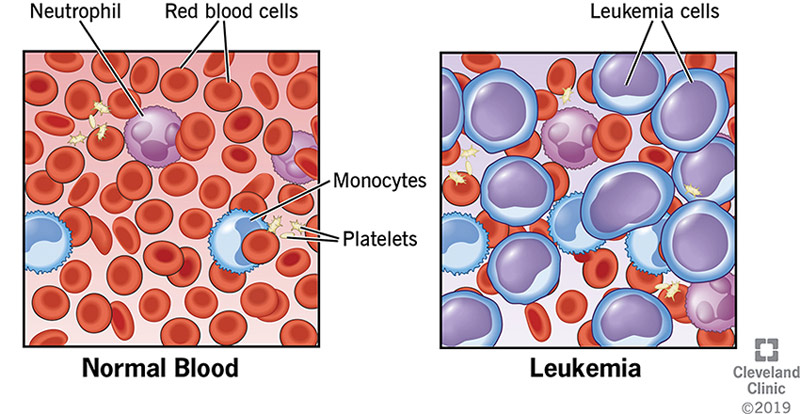
In this informative article, you will gain a deeper understanding of the symptoms and diagnosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) specifically in teenagers and young adults. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a rapidly progressing cancer of the blood and bone marrow that primarily affects these age groups. By exploring the common symptoms and various diagnostic methods, you will be equipped with valuable knowledge to recognize the signs and seek appropriate medical attention for yourself or a loved one. Let’s dive into this important topic together!

Symptoms of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer that affects the white blood cells. It primarily occurs in children, but it can also affect teenagers and young adults. Recognizing the symptoms of ALL is crucial for early diagnosis and timely treatment. While the symptoms may vary from person to person, there are some common signs that can indicate the presence of ALL.
Common Symptoms
The common symptoms of ALL include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. You may experience frequent infections or have a high fever that does not go away. Unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, and excessive sweating, especially during the night, can also be indicative of ALL. Some people may notice swelling or tenderness in the lymph nodes, while others may have easy bruising or bleeding, such as nosebleeds or excessive bleeding from cuts.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the common symptoms, there are some less common symptoms that can also occur in individuals with ALL. These include bone pain, especially in the joints, abdomen, or back. Some people may experience swollen testicles or have an enlarged liver or spleen. Skin rashes or tiny red spots on the skin, known as petechiae, can sometimes be observed. These less common symptoms can help provide a broader picture and aid in the diagnosis of ALL.
Potential Complications
If left untreated, ALL can lead to several potential complications. One of the most significant complications is the infiltration of leukemia cells into other organs, such as the brain and spinal cord. This can result in the development of leukemia in the central nervous system, known as central nervous system leukemia. Other complications can include anemia, due to a decrease in red blood cells, and thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by a low platelet count.
Diagnosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
The diagnosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia involves various medical procedures and tests to confirm the presence of leukemia cells. These investigations are crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan and assessing the disease progression.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the initial visit, the doctor will obtain a detailed medical history, including information about any symptoms you may be experiencing. A thorough physical examination will also be conducted to evaluate your overall health, check for any abnormalities, and assess the extent of the disease.
Blood tests
Blood tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis of ALL. A complete blood count (CBC) is performed to assess the number and types of blood cells. In individuals with ALL, the white blood cell count may be elevated, while the red blood cells and platelets may be reduced. Additionally, the presence of leukemia cells, known as blasts, can be detected in the blood sample.
Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
To definitively confirm the diagnosis of ALL, a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are usually performed. During the procedure, a small sample of bone marrow is taken from the hip bone using a thin needle. The sample is then examined under a microscope to check for the presence of leukemia cells. This test can help determine the subtype of ALL and provide valuable information about the extent of the disease.
Cytogenetic and Molecular Testing
Cytogenetic and molecular testing are essential to gain a deeper understanding of the genetic characteristics of leukemia cells. These tests analyze the chromosomes and genes within the leukemia cells, providing information about any specific genetic abnormalities that may impact treatment decisions.
Lumbar Puncture
A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, may be performed to check for the presence of leukemia cells in the cerebrospinal fluid. This procedure involves the insertion of a thin needle into the lower back, and a small amount of fluid is extracted for analysis. If leukemia cells are detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, additional treatment, such as intrathecal chemotherapy, may be necessary to prevent the spread of leukemia to the central nervous system.
Referral and Consultation
Knowing when to seek medical advice and consulting the right specialists are crucial steps in managing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Timely referral and consultation can ensure that you receive the appropriate care and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience any persistent symptoms associated with ALL, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Symptoms such as unexplained fatigue, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, and persistent fever should not be ignored. It is better to be cautious and consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying health conditions.
Specialists to Consult
Once you seek medical advice, your primary care physician may refer you to a hematologist-oncologist, a specialist who focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of blood-related cancers. In some cases, depending on the individual’s age and specific circumstances, pediatric oncologists or medical oncologists may also be involved in the management of ALL. These specialists have the expertise and knowledge to provide comprehensive care and guide you through the treatment process.
Key Risk Factors
While the exact cause of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is unknown, certain risk factors have been identified that may contribute to the development of the disease. Understanding these risk factors can help in assessing the likelihood of developing ALL and taking necessary precautions.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors play a role in the development of ALL. Certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, increase the risk of developing leukemia. Additionally, genetic abnormalities within the leukemia cells themselves can influence the prognosis and treatment outcomes.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors may also increase the risk of developing ALL. Prenatal exposure to high levels of radiation or certain chemicals, such as benzene, has been associated with an increased likelihood of developing leukemia. Additionally, children who undergo intensive radiation therapy or chemotherapy for other conditions may have a higher risk of developing ALL later in life.
Understanding the Disease Progression
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia follows a specific progression pattern, and understanding its stages, prognosis, and potential for relapse is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan.
Stages of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
ALL is classified into different stages based on the extent of the disease and the involvement of different organs. The stages range from low-risk disease with a favorable prognosis to high-risk disease with a more challenging treatment outcome. The staging helps healthcare professionals determine the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis of ALL depends on various factors, including age, overall health, genetic characteristics of the leukemia cells, and the response to treatment. With advances in treatment options, the survival rates for ALL have significantly improved over the years. Successful treatment can lead to long-term remission and cure in many cases.
Relapse and Recurrence
Despite successful treatment, there is a possibility of relapse or recurrence of ALL. Relapse occurs when leukemia cells reappear after a period of remission. The risk of relapse varies based on the individual’s specific circumstances. Close monitoring and regular follow-up visits with healthcare professionals are essential to detect any signs of relapse early on and initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
Treatment Options
The treatment for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia typically involves a combination of different therapeutic approaches. The specific treatment plan may vary depending on the individual’s age, overall health, genetic characteristics of the leukemia cells, and the stage of the disease.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for ALL. It involves the use of powerful medications to destroy cancer cells and prevent their growth. Depending on the stage and characteristics of the leukemia cells, different chemotherapy regimens may be used. Chemotherapy can be administered orally, intravenously, or directly into the cerebrospinal fluid during a lumbar puncture.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be recommended in certain cases to target specific areas affected by leukemia cells. It utilizes high-energy radiation beams to kill cancer cells and reduce the risk of relapse. Radiation therapy is often used in conjunction with chemotherapy to increase the chances of successful treatment.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation, also known as a bone marrow transplant, may be considered for individuals with high-risk ALL or those who experience a relapse. The procedure involves replacing the damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a compatible donor or the individual’s own cells. Stem cell transplantation can provide a chance for long-term remission and potential cure.
Targeted Therapies
Advances in research and understanding of the genetic characteristics of ALL have led to the development of targeted therapies. These therapies specifically target certain genetic mutations or abnormalities within the leukemia cells, aiming to disrupt their growth and survival. Targeted therapies are still evolving, and their use may be limited to specific cases or clinical trials.

Management of Side Effects
During the treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, various side effects may occur due to chemotherapy or other treatment modalities. Managing these side effects is an essential part of the overall care plan and can significantly improve the individual’s quality of life.
Nausea and Vomiting
Chemotherapy medications can often cause nausea and vomiting. Anti-nausea medications, dietary changes, and relaxation techniques can help manage these side effects. It is essential to communicate with healthcare professionals about any discomfort to ensure appropriate supportive care.
Hair Loss
Hair loss is a potential side effect of chemotherapy. Although it is temporary, it can still impact an individual’s self-esteem and body image. Supportive measures, such as scalp cooling devices or wigs, can mitigate the emotional impact of hair loss and help individuals regain confidence.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common side effect experienced during and after treatment for ALL. It is important to balance rest and physical activity while listening to the body’s needs. Engaging in gentle exercise, such as walking or yoga, and maintaining a balanced diet can help combat fatigue.
Infection Control
Due to the suppression of the immune system during treatment, individuals with ALL are more susceptible to infections. Proper hand hygiene, avoiding crowds or sick individuals, and staying up to date with vaccinations can reduce the risk of infections. It is essential for family members and friends to also practice good hygiene to minimize the chances of transmission.
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a crucial role in managing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia effectively. It encompasses various aspects of care aimed at improving the overall well-being and quality of life for individuals with ALL.
Psychological Support
A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, and managing the emotional and psychological impact is essential. Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help individuals cope with the challenges of ALL.
Nutrition and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise are important aspects of supportive care. A well-balanced diet ensures that the body receives the necessary nutrients for healing and recovery. Physical activity, even in moderation, can improve strength, endurance, and overall well-being.
Pain Management
Some individuals with ALL may experience pain due to the disease itself or as a side effect of treatment. Managing pain effectively is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals specialized in pain management can help individuals find relief and improve their comfort.

Importance of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a vital role in advancing the understanding and treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Participation in clinical trials not only provides individuals with access to innovative treatments but also contributes to the overall knowledge of the disease.
Advancements in Treatment
Clinical trials are designed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new treatment options. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with ALL can be at the forefront of medical advancements, potentially receiving treatments that are not yet widely available. This can significantly impact the individual’s outcome and offer hope for better treatment options in the future.
Participating in Clinical Trials
Participation in clinical trials is a personal decision and should be discussed with healthcare professionals. It is essential to understand the purpose and potential risks and benefits of the trial before making an informed decision. Clinical trials often have strict eligibility criteria, and not all individuals may be eligible to participate. However, for those who meet the criteria, participation can be a valuable opportunity.
The Role of Family and Friends
Having a strong support system is crucial for individuals with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Family and friends can play an active role in providing emotional support and practical assistance throughout the treatment journey.
Providing Emotional Support
Emotional support from family and friends can significantly impact the well-being and outlook of individuals with ALL. Simply being present, lending a listening ear, and offering words of encouragement can make a world of difference. Understanding the challenges and emotions associated with ALL and providing empathy and compassion can help individuals feel supported and loved.
Practical Assistance
Practical assistance can be invaluable for individuals undergoing treatment for ALL. This can include helping with household chores, cooking meals, providing transportation to medical appointments, or helping with childcare responsibilities. By alleviating some of the practical burdens, family and friends allow individuals to focus on their treatment and recovery.
Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is crucial for teenagers and young adults. Recognizing the common and less common symptoms can aid in early detection and prompt treatment. A comprehensive diagnosis involves various medical procedures, including blood tests, bone marrow aspiration, and biopsy. Referral to specialists and consulting with appropriate healthcare professionals ensure comprehensive care and treatment. Recognizing the key risk factors, understanding disease progression, and exploring treatment options provide a holistic approach to managing ALL. Managing side effects, receiving supportive care, and considering participation in clinical trials contribute to better outcomes. The role of family and friends in providing emotional support and practical assistance cannot be overstated. With comprehensive knowledge and support, individuals with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia can navigate their treatment journey with confidence and hope.
Watch This Video Below
Related Terms About Understanding the Symptoms and Diagnosis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Teenagers and Young Adults
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Symptoms, How Is Acute Leukemia Diagnosed, How Is Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Diagnosed, Symptoms Of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cancer, Symptoms Of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Cancer