Having a healthy set of ears is crucial for our overall well-being, but sometimes we might inadvertently expose ourselves to the risk of ear infections. These infections can be uncomfortable, painful, and disruptive to our daily lives. However, there are simple preventative measures you can take to keep your ears healthy and infection-free. By following a few easy steps, you can ensure that your ears stay in top condition and minimize the chances of experiencing the discomfort of an ear infection.

Understanding Ear Infections
What are ear infections?
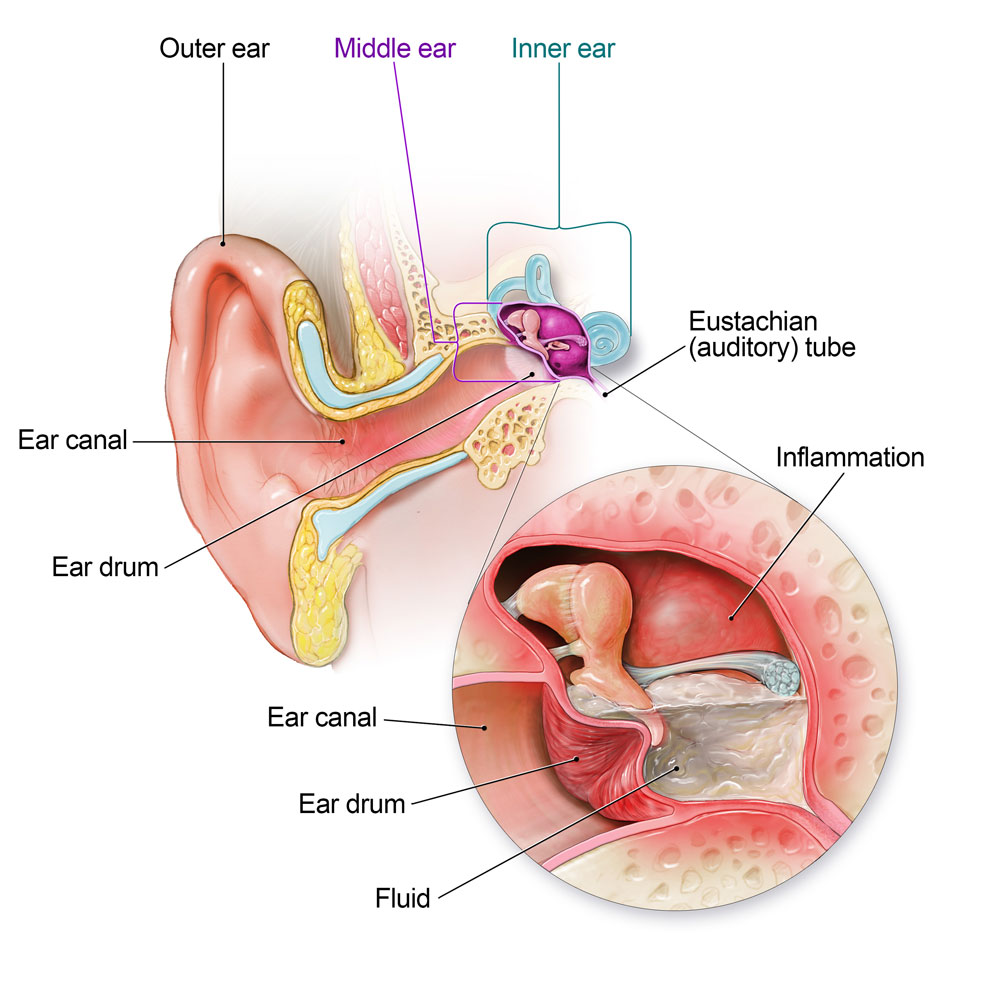
Ear infections, also known as otitis media, are a common condition that affects the middle ear. The middle ear is the space behind the eardrum, and it is responsible for transmitting sound to the inner ear. When the middle ear becomes infected, it can cause discomfort and hearing problems. Ear infections can occur in both children and adults, but they are more prevalent in children due to their shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes, which can make it easier for bacteria to enter the middle ear.
Causes of ear infections
Ear infections are often caused by bacteria or viruses that enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tubes. The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, and they help equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the outside air. When the Eustachian tubes become blocked or swollen, it can create an ideal environment for bacteria or viruses to thrive, leading to an infection. Common culprits of ear infections include respiratory infections, allergies, colds, sinus infections, and tonsillitis.
Types of ear infections
There are three main types of ear infections: acute otitis media (AOM), chronic otitis media with effusion (COME), and otitis externa, also known as swimmer’s ear. AOM is the most common type and is characterized by a sudden onset and short duration of symptoms. COME refers to the presence of fluid in the middle ear for an extended period, even after the infection has resolved. Swimmer’s ear is an infection of the ear canal, typically caused by water remaining in the ear after swimming.
Maintaining Good Ear Hygiene
Clean your ears regularly
Keeping your ears clean is an essential part of ear hygiene. However, it’s important to clean your ears properly to avoid causing damage or pushing wax further into the ear canal. Use a soft washcloth to gently clean the outer part of your ears during your regular bathing routine. Be careful not to insert anything into your ear canal, such as cotton swabs or bobby pins, as this can cause injury and increase the risk of infection.
Avoid excessive ear cleaning
While it’s important to keep your ears clean, excessive cleaning can do more harm than good. The ear is a self-cleaning organ, and excessive cleaning can disrupt the delicate balance of wax production and removal. Letting your ears naturally remove excess wax is usually sufficient for maintaining ear hygiene. If you frequently experience excess earwax or blockage, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Use proper cleaning techniques
If you feel the need to clean your ears beyond gentle wiping, it’s important to use proper techniques. Over-the-counter earwax removal drops can help soften earwax and make it easier to remove. Follow the instructions provided with the product, and avoid using them if you have an ear infection or a perforated eardrum. If you’re uncertain about the best cleaning method for your ears, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Avoiding Common Risk Factors
Prevent exposure to cigarette smoke
Exposure to cigarette smoke, both firsthand and secondhand, has been linked to an increased risk of ear infections. Smoking can irritate the respiratory tract, leading to inflammation in the Eustachian tubes and middle ear. If you smoke, consider quitting, and avoid exposing yourself and others, especially children, to secondhand smoke.
Avoid allergens and irritants
Allergens and irritants in the environment can contribute to ear inflammation and increase the risk of infections. Stay away from known allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, if you are sensitive to them. Additionally, be cautious around chemicals and substances that can irritate the ears, such as hair products, cleaning solutions, and certain fabrics.
Keep your ears dry
Excessive moisture in the ears can create a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria and fungi, leading to infections. After activities that involve water exposure, such as swimming or bathing, use a clean towel to gently dry your ears. Tilting your head to each side can help remove excess water from the ear canal. If you are prone to swimmer’s ear, consider using earplugs or a swim cap to protect your ears from prolonged exposure to water.
Promoting Immune System Health
Eat a balanced diet
A healthy and balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a strong immune system. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support immune function and help protect against infections, including ear infections.
Stay hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and immune function. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to keep your body properly hydrated. Staying hydrated can help maintain the moisture levels in your ears and prevent dryness, which can make you more susceptible to infections.
Get regular exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is not only beneficial for your overall well-being but also supports a healthy immune system. Exercise helps improve circulation, which enables immune cells to move more efficiently throughout the body. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, each week.
Adequate sleep and stress management
A good night’s sleep and effective stress management are crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. Lack of sleep and chronic stress can weaken your body’s defenses against infections, making you more susceptible to ear infections. Establish a consistent sleep routine, prioritize relaxation, and explore stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
Preventive Measures for Children
Breastfeed your baby
Breastfeeding provides important antibodies and nutrients that can strengthen your baby’s immune system, making them less prone to infections, including ear infections. If possible, aim to breastfeed exclusively for the first six months and continue breastfeeding while introducing solid foods until your baby is at least one year old.
Vaccinate your child
Vaccinations help protect children from various infections, including some bacterial and viral causes of ear infections. Follow the recommended vaccination schedule provided by healthcare professionals to ensure your child receives the necessary immunizations. Consult with your child’s pediatrician for more information on vaccinations and their role in preventing infections.
Maintain a smoke-free environment
Exposure to cigarette smoke is harmful to children and increases their risk of ear infections. Keep your home and surroundings smoke-free to create a healthy environment for your child. If you need support in quitting smoking, consult with healthcare professionals who can provide resources and assistance.
Avoid bottle-feeding while lying down
When bottle-feeding an infant, avoid letting them lie down flat. Feeding in a more upright position can help prevent milk from accumulating in the Eustachian tubes and reduce the risk of ear infections. Hold your baby in a semi-upright position and ensure the bottle’s nipple is tilted upward to promote proper fluid flow.
Encourage regular handwashing
Teaching your child proper handwashing techniques is an effective way to reduce the spread of infections, including those that can cause ear infections. Encourage your child to wash their hands frequently with soap and water, especially before meals, after using the bathroom, and after playing with others. Make handwashing a fun and regular part of their routine.
Limiting Exposure to Infections
Minimize contact with sick individuals
Avoid close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections, such as the common cold or influenza. Viruses and bacteria that cause respiratory illnesses can contribute to the development of ear infections. If someone in your household is sick, encourage them to practice good respiratory hygiene and take appropriate precautions to prevent spreading the infection.
Practice good respiratory hygiene
Covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections to others. Teach your children to use tissues or their elbow to cover their mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing. Additionally, dispose of used tissues properly and encourage regular handwashing.
Avoid crowded places during outbreaks
During periods of increased illness activity, such as seasonal flu outbreaks, it may be wise to avoid crowded places where respiratory infections can easily spread. Consider limiting your exposure to crowded areas or practicing extra precautions, such as wearing a face mask, to reduce the risk of contracting infections.
Swimmer’s Ear Prevention
Keep your ears dry and clean after swimming
After swimming or participating in water activities, it’s important to dry your ears thoroughly to prevent moisture from remaining in the ear canal. Use a clean towel to gently dry your ears, and consider tilting your head from side to side to facilitate drainage. Tilting your body to each side or pulling on your earlobe can also help remove any excess water.
Use earplugs or a swim cap
If you swim frequently or in bodies of water with questionable cleanliness, consider using earplugs or wearing a swim cap to protect your ears. Both options help prevent water from entering the ear canal and lower the risk of developing swimmer’s ear.
Avoid swimming in polluted water
Swimming in polluted water can increase the risk of developing swimmer’s ear and other infections. Avoid swimming in areas with stagnant water, high bacterial contamination, or known pollution. Opt for swimming pools, maintained bodies of water, or natural water sources that have been deemed safe for swimming.
Avoid inserting foreign objects into the ear
Inserting foreign objects, such as cotton swabs or hairpins, into the ear canal can cause damage to the delicate structures inside and increase the risk of infections. It’s essential to resist the urge to clean your ears by inserting objects into the canal. Instead, let your ears naturally clean themselves or use proper cleaning techniques as previously mentioned.
Preventing Ear Infections in Winter
Keep your ears warm and covered
Cold weather can cause discomfort and increase the risk of ear infections. Protect your ears from the cold by wearing hats, ear muffs, or ear warmers when outdoors. Keeping the ears warm helps maintain proper blood flow and temperature regulation, reducing the likelihood of ear infections.
Avoid prolonged exposure to cold and wind
Prolonged exposure to cold and windy environments can increase the risk of developing ear infections. When spending time outdoors during winter, take breaks in sheltered areas or indoors to allow your body, including your ears, to warm up. Dress in layers and cover your ears to protect them from the elements.
Maintain good ventilation and humidity levels indoors
Dry and poorly ventilated indoor environments can contribute to dryness and irritation of the ears, making them more susceptible to infections. Ensure proper ventilation by opening windows or using fans to circulate fresh air. Additionally, use a humidifier to maintain adequate humidity levels, especially during colder months when indoor heating systems can cause dryness.
Strengthen your immune system
During winter, when cold and flu viruses are more prevalent, it’s crucial to support your immune system to prevent infections, including ear infections. Follow the tips mentioned earlier for promoting immune system health, such as eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and prioritizing adequate sleep and stress management.

Seeking Prompt Medical Care
Recognize the symptoms of ear infections
Being able to recognize the symptoms of an ear infection is important for seeking prompt medical care. Common symptoms include ear pain, fullness or pressure in the ear, hearing loss, fever, drainage from the ear, and irritability in young children. If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect an ear infection, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Consult a healthcare professional
If you suspect an ear infection, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They can examine your ears, evaluate your symptoms, and determine the most appropriate course of treatment. Additionally, they can help identify any underlying causes or risk factors that may contribute to recurring ear infections.
Follow the prescribed treatment
If a healthcare professional diagnoses you with an ear infection, they may prescribe antibiotics, pain relievers, or other medications to help alleviate symptoms and resolve the infection. It’s essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan, take the medication as directed, and complete the full course of antibiotics if prescribed. Failure to complete the treatment can result in incomplete resolution of the infection and potential recurrence.
Complete the full course of antibiotics if prescribed
If antibiotics are prescribed for an ear infection, it’s crucial to complete the full course of medication as directed by the healthcare professional. Even if symptoms improve before completing the treatment, it’s important to continue taking the antibiotics as prescribed. This helps ensure the complete eradication of the infection and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
When to Consider Ear Tubes
Understanding ear tubes
Ear tubes, also known as tympanostomy tubes or ventilation tubes, are tiny cylindrical devices inserted into the eardrum to assist with the drainage of fluids and equalization of pressure in the middle ear. They are typically made of silicone or metal and are most commonly used in cases of recurrent or chronic ear infections, as well as persistent middle ear fluid.
Indications for ear tube placement
The decision to consider ear tube placement is typically based on the frequency and severity of ear infections or the persistence of middle ear fluid. If a child experiences recurrent ear infections (more than three within six months) or has chronic, persistent fluid in the middle ear for three months or longer, ear tubes may be recommended by an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
Consultation with an ear, nose, and throat specialist
If you or your child meet the criteria for ear tubes, it’s important to schedule a consultation with an ear, nose, and throat specialist, also known as an otolaryngologist. The specialist will evaluate the individual’s specific condition, assess the potential benefits and risks of ear tube placement, and discuss the procedure in detail. They will also address any concerns or questions regarding the necessity and potential outcomes of the procedure.
In conclusion, understanding ear infections and taking proactive measures to reduce the risk of developing them is crucial for maintaining good ear health. By following proper ear hygiene practices, avoiding common risk factors, promoting immune system health, and seeking prompt medical care when necessary, you can significantly decrease the likelihood of ear infections and promote overall wellbeing. Remember, prevention is key, and taking care of your ears can go a long way in preserving your hearing and quality of life.