In the article “Depression in Adolescents: Recognizing the Signs and Offering Support”, you will explore the important topic of depression among teenagers. As adolescents navigate the challenges of growing up, it is crucial to recognize the signs of depression and provide the necessary support. By understanding the symptoms and the potential impact on their lives, you can play a significant role in making a positive difference for those affected.
What is Depression?
Definition of depression
Depression is a common mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in daily activities. It affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, and can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems. Depression can occur at any age, but it is particularly prevalent in adolescents.
Prevalence in adolescents
Depression is a significant concern among adolescents, as it affects approximately one in five individuals during this stage of life. According to the World Health Organization, depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide in adolescents aged 10 to 19 years. The teenage years are a critical period of development, and experiencing depression during this time can have long-term consequences for an individual’s mental health and well-being.
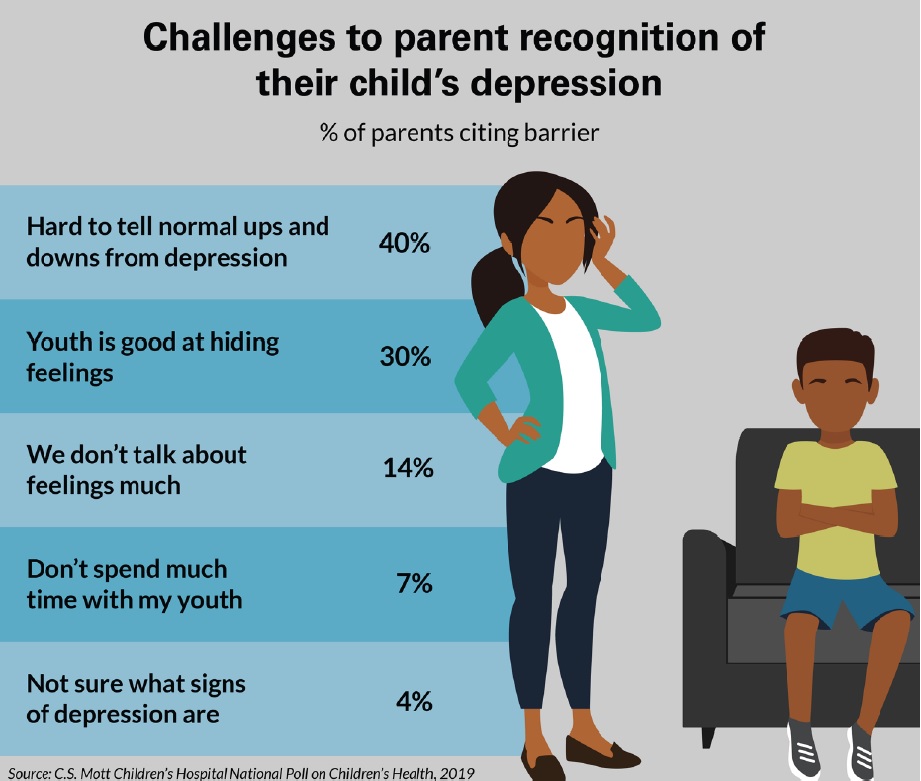
Importance of early recognition
Early recognition of depression in adolescents is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for timely intervention and treatment, which can significantly improve outcomes. Secondly, depression can often be misunderstood or mistaken for normal teenage behavior, leading to delays in seeking help. By recognizing the signs of depression early on, appropriate support can be provided, reducing the risk of long-term negative impact and promoting positive mental health outcomes.
Signs of Depression in Adolescents
Changes in mood and behavior
Adolescents with depression often experience persistent sadness, irritability, anger, or feelings of hopelessness. They may frequently cry, exhibit mood swings, or have difficulty controlling their emotions. Additionally, they might lose interest in activities they previously enjoyed and withdraw from social interactions.
Social withdrawal
Social withdrawal is a common sign of depression in adolescents. They may avoid social situations, isolate themselves from friends and family, and lose interest in engaging with others. It is essential to pay attention to any sudden changes in an adolescent’s social behavior, as it can indicate underlying depression.
Physical symptoms
Depression can also manifest in physical symptoms. Adolescents may complain of frequent headaches, stomachaches, or other unexplained aches and pains. They may experience changes in appetite and sleep patterns, such as increased or decreased sleep and loss of appetite or overeating.
Academic performance decline
Depression often impacts an adolescent’s ability to concentrate, resulting in a decline in academic performance. They may struggle to complete assignments, lose interest in school, and experience a significant drop in grades. Teachers and parents should be vigilant for such changes and offer support and understanding when needed.
Substance abuse
Adolescents with depression are at a higher risk of turning to substances like drugs and alcohol as a way to cope with their emotions. Substance abuse can worsen depression symptoms and increase the likelihood of self-destructive behavior. Any signs of substance abuse should be taken seriously and addressed promptly.
Suicidal thoughts
Perhaps the most critical and alarming sign of depression in adolescents is the presence of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Adolescents experiencing depression may express thoughts of self-harm, talk about suicide, or engage in self-destructive behaviors. It is essential to take any mention or indication of self-harm or suicide seriously and seek immediate professional help.

Causes and Risk Factors
Biological factors
Depression in adolescents can have biological underpinnings. It may be related to imbalances in brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and emotions. Hormonal changes during adolescence can also contribute to depression.
Social and environmental factors
Adolescents are particularly vulnerable to social and environmental factors that can contribute to depression. These factors can include social isolation, peer pressure, bullying, academic stress, familial conflict, and socioeconomic challenges. Additionally, exposure to violence or traumatic events can increase the risk of depression.
Family history
Having a family history of depression or other mental health disorders can increase an adolescent’s susceptibility to develop depression. Genetics and shared environmental factors within families play a role in shaping an individual’s risk for depression.
Trauma and life events
Experiencing traumatic events or significant life stressors, such as the loss of a loved one, divorce, or abuse, can trigger depression in adolescents. These events can disrupt an adolescent’s sense of stability and security, leading to the development of depressive symptoms.
Recognizing the Signs of Depression
Understanding the difference between normal teenage behavior and depression
It is essential to understand the difference between typical teenage behavior and signs of depression. Adolescents often experience mood swings, irritability, and changes in behavior as a part of their normal development. However, if these behaviors persist for an extended period or significantly interfere with an adolescent’s daily functioning, it may indicate depression.
Observing changes in behavior
Recognizing signs of depression involves observing changes in an adolescent’s behavior. Look for significant shifts in their mood, energy levels, social interactions, sleep patterns, and overall functioning. Pay attention to any patterns of withdrawal, loss of interest, or sudden deterioration in academic performance.
Listening and communicating effectively
Creating an open and non-judgmental space for adolescents to express their feelings is crucial. Active listening and effective communication can help adolescents feel understood and supported. Encourage them to share their thoughts and emotions, and validate their experiences. Let them know that help is available and that seeking support is a sign of strength.

Offering Support to Adolescents with Depression
Creating a supportive environment
Creating a supportive environment is essential for adolescents with depression. This includes offering unconditional love and acceptance, providing a safe and nurturing space for them to express their emotions, and reassuring them that they are not alone. Avoid judgment or blame, and emphasize that depression is a treatable illness.
Encouraging professional help
While providing emotional support is crucial, it is essential to encourage adolescents with depression to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists and therapists, can provide specialized treatment and support. Encourage adolescents to reach out to their school counselors or healthcare providers to access appropriate resources.
Promoting healthy coping mechanisms
Empower adolescents to develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage their depression. Encourage them to engage in activities they enjoy, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness, and prioritize self-care activities such as exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep. Teach them the importance of establishing a routine and engaging in pleasurable activities to enhance their overall well-being.
Educating friends and family about depression
Education is vital in understanding and supporting adolescents with depression. Encourage friends, family, and other loved ones to educate themselves about depression, its signs and symptoms, and the available treatment options. By fostering a supportive network, adolescents can receive the understanding and encouragement they need to overcome their challenges.
Preventing Depression in Adolescents
Promoting self-care and healthy lifestyle habits
Promoting self-care and healthy lifestyle habits is a crucial component of preventing depression in adolescents. Encourage adolescents to prioritize their physical and mental well-being by engaging in regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive screen time. Educate them on the importance of self-care activities, such as spending time with loved ones or pursuing hobbies and interests.
Building resilience
Building resilience is an effective strategy to prevent depression in adolescents. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and cope with adversity. Encourage adolescents to develop problem-solving skills, learn effective stress management techniques, and foster positive relationships. Building resilience helps adolescents navigate challenges and bounce back from setbacks, reducing their vulnerability to depression.
Addressing school-related stress
Academic stress can significantly impact an adolescent’s mental health. It is essential to address school-related stressors and create a supportive academic environment. Encourage effective time management, promote study strategies, and provide resources for stress reduction, such as counseling services or stress management workshops. By reducing academic pressure, adolescents can experience better overall mental well-being.
Educating adolescents about mental health
Education plays a vital role in preventing depression in adolescents. Promote mental health literacy by educating adolescents about mental health, its importance, and the available resources for support. Encourage open discussions about emotions and mental health, fostering an environment where seeking help is seen as a proactive step towards overall well-being.

Treatment Options for Adolescent Depression
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is an essential component of treating adolescent depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is commonly utilized and focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and developing healthy coping strategies. Other forms of therapy, such as interpersonal therapy (IPT) and family therapy, can also be beneficial in addressing underlying issues and improving overall mental health.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of depression in adolescents. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be effective in conjunction with therapy. However, it is essential that medication be closely monitored by a mental health professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Alternative and complementary approaches
Complementary approaches, such as yoga, meditation, and art therapy, can be valuable additions to traditional treatment for adolescent depression. These approaches can help promote relaxation, improve emotional regulation, and provide alternative outlets for expression. It is important to work with a qualified professional who specializes in these modalities to ensure their safety and appropriateness.
Involvement of family in treatment
Involving the family in an adolescent’s treatment can be crucial for their recovery. Family therapy sessions can help improve communication, address familial conflicts or dynamics that may contribute to depression, and provide support and education for family members. A united and supportive family environment can significantly impact an adolescent’s journey to recovery.
Importance of Early Intervention
Reducing long-term negative impact
Early intervention is instrumental in reducing the long-term negative impact of depression on an adolescent’s life. Untreated depression can lead to increased risk of recurrent depressive episodes, difficulties in personal relationships, poor academic performance, and even substance abuse or self-harm. By recognizing and addressing depression early on, these risks can be mitigated, and positive outcomes can be achieved.
Improving quality of life
Timely intervention can significantly improve an adolescent’s quality of life. Effective treatment, support, and resources can help them regain control over their emotions, rebuild relationships, and focus on personal growth. By addressing depression early, adolescents have the opportunity to experience joy, develop healthy coping mechanisms, and lead fulfilling lives.
Promoting positive mental health outcomes
Early intervention in depression promotes positive mental health outcomes for adolescents. By actively addressing depression and providing appropriate support, adolescents can acquire the skills and strategies necessary to manage their mental health effectively. This sets a strong foundation for their future well-being, empowering them to navigate challenges and seek help when needed.

Supporting Adolescents during COVID-19 Pandemic
Impact of the pandemic on adolescent mental health
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on adolescent mental health. Isolation, disruption of routines, increased stress, and uncertainty have contributed to heightened levels of depression and anxiety among adolescents. The lack of social interactions, closure of schools, and limited access to mental health resources have further intensified these challenges.
Offering remote support and access to resources
During these challenging times, it is crucial to offer remote support and ensure access to mental health resources for adolescents. Virtual therapy sessions, online support groups, and helplines are vital tools that can provide assistance and guidance. It is essential to communicate and share information about these resources with adolescents and their families to ensure they receive the necessary support.
Conclusion
Encouraging open dialogue about mental health is paramount in addressing and supporting adolescents with depression. By recognizing the signs of depression, offering support, promoting preventative measures, and providing appropriate treatment options, we can make a significant difference in the lives of adolescents. Continued research and understanding of depression in adolescents are essential for improved support and mental health outcomes. Together, we can create a future where every adolescent feels seen, heard, and supported when it comes to their mental well-being.