Having trouble swallowing can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience, but fear not, because we’ve got some helpful tips for you. Whether it’s due to a medical condition or simply a temporary issue, managing difficulty swallowing can greatly improve your quality of life. This article will provide you with practical suggestions and strategies to make eating and drinking a more pleasant and safer experience. So sit back, relax, and get ready to discover some useful tips to overcome difficulty swallowing.

Medical Causes of Difficulty Swallowing
If you are experiencing difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, it is important to understand the potential medical causes behind it. Here are some common medical conditions that can lead to difficulty swallowing:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a condition where the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. This can lead to a narrowing of the esophagus, making it difficult for food to pass through. Symptoms of GERD may include heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain.
Esophageal Stricture
An esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus, often caused by scar tissue. This can result from long-term acid reflux, repeated exposure to certain medications, or damage to the esophagus. Strictures can make it challenging for food to pass through, causing difficulty swallowing.
Esophageal Spasm
Esophageal spasms are irregular contractions of the muscles in the esophagus. These spasms can cause chest pain and difficulty swallowing. While the exact cause of esophageal spasms is unknown, factors such as stress, anxiety, and certain medications may trigger these spasms.
Achalasia
Achalasia is a rare disorder that affects the muscle movement in the esophagus. This condition hinders the normal movement of food into the stomach, resulting in difficulty swallowing. The exact cause of achalasia is not fully understood, but it is thought to occur due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Tumors in the Throat or Esophagus
Tumors or growths in the throat or esophagus can obstruct the passage of food, leading to difficulty swallowing. These tumors may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). If you are experiencing difficulty swallowing along with symptoms such as persistent pain, hoarseness, or unintentional weight loss, it is crucial to seek medical attention.
Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke, can weaken the muscles involved in swallowing. This muscle weakness can result in difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia. If you have a neurological condition and are experiencing difficulty swallowing, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate management.
Muscular Disorders
Muscular disorders, such as muscular dystrophy or myasthenia gravis, can affect the muscles involved in swallowing. These conditions can cause weakness or paralysis in the muscles, making it challenging to swallow food. If you have a known muscular disorder and are experiencing difficulty swallowing, it is important to work closely with your healthcare team to manage your symptoms.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the connective tissues of the body. This condition can cause the esophagus to become stiff and narrow over time, leading to difficulty swallowing. If you have been diagnosed with scleroderma and are experiencing difficulty swallowing, it is essential to work with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, which can lead to a variety of physical and neurological symptoms. Depending on the location of the stroke, difficulty swallowing may occur due to muscle weakness or paralysis. If you or someone you know has had a stroke and is experiencing difficulty swallowing, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement and coordination. As the disease progresses, it can lead to muscle stiffness and difficulty swallowing. If you have Parkinson’s disease and are experiencing difficulty swallowing, it is important to discuss this symptom with your healthcare provider for appropriate management strategies.
Tips for Managing Difficulty Swallowing at Home
While medical treatment is crucial for managing underlying causes of difficulty swallowing, there are also some practical tips you can implement at home to make eating and swallowing easier. Here are some tips for managing difficulty swallowing:
Eat Slowly and Take Small Bites
When you have difficulty swallowing, it is important to take your time while eating. By eating slowly and taking small bites, you can reduce the risk of food getting stuck or causing discomfort.
Chew Thoroughly
Thoroughly chewing your food can help break it down into smaller, more manageable pieces, making it easier to swallow. Taking the time to chew your food properly can also aid in digestion.
Avoid Dry or Hard Foods
Dry or hard foods can be more challenging to swallow, especially if you have difficulty swallowing. Opt for softer or moist foods that are easier to chew and swallow.
Moisten Food with Sauce or Liquids
If you find that your food feels dry or is difficult to swallow, consider adding sauce or liquids to moisten it. This can make the food easier to swallow and prevent it from sticking in your throat.
Take Sips of Water or Other Fluids with Meals
Drinking small sips of water or other fluids throughout your meal can help lubricate your throat and make swallowing easier. However, be cautious not to drink excessively, as consuming too much liquid with meals can make you feel overly full and potentially worsen your swallowing difficulties.
Avoid Eating Too Close to Bedtime
Eating too close to bedtime can increase the likelihood of experiencing acid reflux or heartburn, which can exacerbate difficulty swallowing. Try to finish your meals at least a few hours before going to bed to allow proper digestion.
Maintain Good Posture While Eating
Sitting upright and maintaining good posture while eating can help facilitate easier swallowing. Slouching or lying down while eating can make it more challenging for food to pass through your esophagus.
Use Gravity to Help Swallow
When eating, try to sit in an upright position and tilt your head slightly forward. This can help utilize gravity to assist with swallowing and prevent food from getting stuck in your throat.
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Instead of consuming large meals all at once, consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This can help prevent overloading your esophagus and making swallowing more difficult.
Avoid Alcohol and Smoking
Alcohol and smoking can irritate the throat and exacerbate difficulty swallowing. Avoiding these substances can help minimize throat irritation and improve your overall swallowing experience.

Dietary Considerations for Difficulty Swallowing
Modifying your diet can also play a significant role in managing difficulty swallowing. Here are some dietary considerations to keep in mind:
Modify Food Texture
If you have difficulty swallowing, it may be helpful to modify the texture of your food. For example, pureeing or finely chopping solid foods can make them easier to swallow.
Assistive Devices for Eating
Assistive devices, such as specialized utensils or cups with built-in straws, can be helpful for individuals with difficulty swallowing. These devices are designed to make eating and drinking easier and more comfortable.
Experiment with Temperature
Some individuals find that extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can make swallowing more challenging. Experiment with different food and beverage temperatures to determine what works best for you.
Avoid Foods That Irritate the Throat
Certain foods, such as spicy or acidic foods, can irritate the throat and make swallowing more difficult. If you notice that certain foods trigger discomfort or worsen your swallowing difficulties, it may be best to avoid them.
Ensure Adequate Nutrition
Difficulty swallowing can sometimes make it more challenging to meet your nutritional needs. Consult with a registered dietitian to ensure you are consuming a well-balanced diet that provides adequate nutrients.
Consult with a Registered Dietitian
A registered dietitian can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs and difficulties with swallowing. They can help create a modified diet plan that ensures you meet your nutritional requirements while addressing your swallowing issues.
Consider Liquid Nutritional Supplements
For individuals who have significant difficulty swallowing or are unable to consume solid foods, liquid nutritional supplements can be a helpful option. These supplements provide essential nutrients in an easily drinkable form.
Use Thickening Agents to Modify Liquids
If you have difficulty swallowing thin liquids, such as water or juice, using thickening agents can help. These agents can transform thin liquids into a consistency that is easier to swallow, reducing the risk of choking or aspiration.
Use a Straw or Spoon to Control Food Flow
Using a straw or a spoon to control the flow of food can facilitate easier swallowing. This technique allows you to take smaller, more manageable sips or bites, preventing overwhelming your swallow reflex.
Try Cold or Frozen Foods
For some individuals, cold or frozen foods may be easier to swallow compared to hot or room temperature foods. Experiment with different temperatures to determine which works best for you.
Home Remedies and Techniques for Easing Swallowing Difficulties
In addition to medical treatments and dietary modifications, there are several home remedies and techniques that can help ease swallowing difficulties. Here are some suggestions:
Gargle with Warm Salt Water
Gargling with warm salt water can help soothe the throat and relieve any irritation that may be contributing to your difficulty swallowing. Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and gargle for 30 seconds, then spit out.
Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate difficulty swallowing. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and promote a calmer state during mealtimes.
Use Throat Lozenges or Hard Candy
Throat lozenges or hard candy can help stimulate saliva production and provide temporary relief for dryness or discomfort in the throat. Choose sugar-free options if you have underlying dental concerns.
Suck on Ice Chips
Sucking on ice chips can help numb any discomfort you may be experiencing while swallowing. It can also provide a soothing effect on the throat.
Stay Hydrated
Keeping your body properly hydrated is essential for optimal swallowing function. Make sure to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can contribute to dryness and difficulty swallowing.
Use a Humidifier
Dry air can irritate the throat and worsen swallowing difficulties. Using a humidifier in your home can help add moisture to the air, reducing dryness in your throat.
Avoid Talking While Eating
Talking while eating can increase the risk of choking or aspirating food. Focus on eating your meal without distractions to ensure a safe and smooth swallowing experience.
Massage the Throat
Gently massaging the muscles in your throat can help alleviate tension and improve swallowing function. Use circular motions with light pressure to massage the sides of your throat.
Practice Swallowing Exercises
Certain exercises can help strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing. These exercises may include tongue presses, throat stretches, or swallowing saliva. Consult with a speech therapist or healthcare provider for specific exercises tailored to your needs.
Avoid Acidic or Spicy Foods
Acidic or spicy foods can irritate the throat and make swallowing more uncomfortable. Limit your consumption of these foods to minimize discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
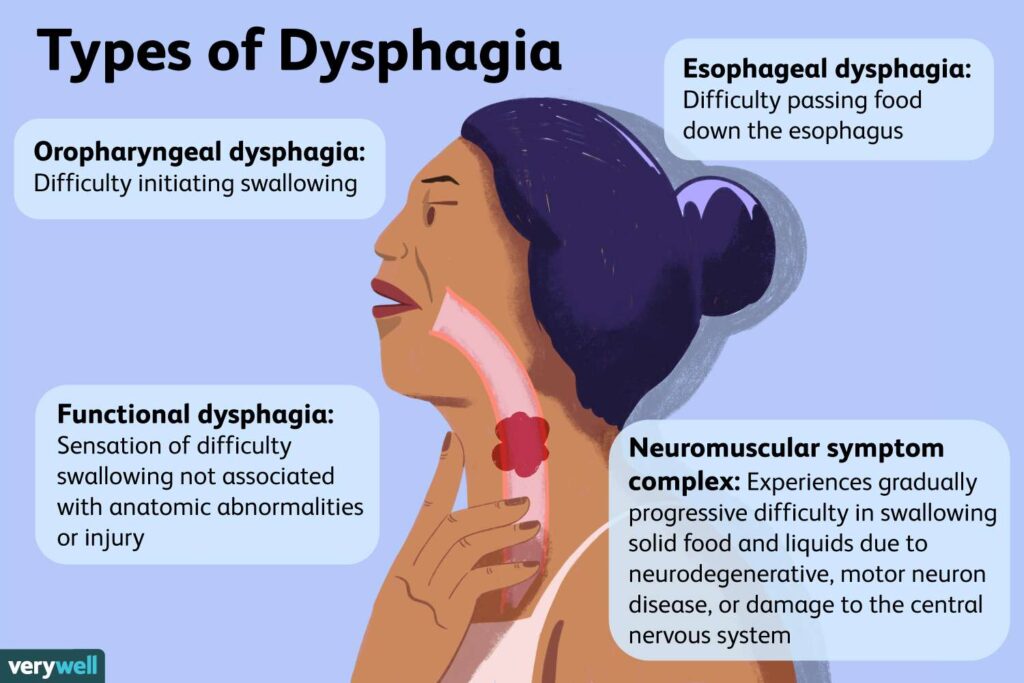
When to Seek Medical Help
While a comprehensive home management plan can be effective for some individuals with difficulty swallowing, certain symptoms warrant medical attention. It is important to seek medical help if you experience any of the following:
Persistent or Worsening Difficulty Swallowing
If your difficulty swallowing persists or becomes progressively worse, it may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires further evaluation and treatment.
Unintentional Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss can be a concerning sign and may be indicative of a more serious underlying cause. If you are experiencing difficulty swallowing and have unintentionally lost a significant amount of weight, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Coughing or Choking while Eating
Frequent coughing or choking episodes while eating can be a sign that food is not properly passing through your esophagus. These symptoms should not be ignored and should prompt medical evaluation.
Pain or Discomfort in the Chest or Throat
Persistent pain or discomfort in the chest or throat, especially while swallowing, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. This may indicate a more serious condition that requires medical attention.
Frequent Heartburn or Acid Reflux
If you experience frequent heartburn or acid reflux along with difficulty swallowing, it may be a sign of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition should be assessed and managed by a healthcare professional.
Regurgitation of Food or Liquids
If you frequently regurgitate food or liquids after swallowing, it is important to seek medical attention. This symptom may indicate a problem with the functioning of your esophagus.
Neck or Throat Mass
The presence of a neck or throat mass could be a sign of a tumor or growth obstructing the passage of food. Any new or suspicious masses should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Inability to Swallow Liquids
If you are unable to swallow liquids or feel that they are getting stuck or going down the wrong way, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. This can be a serious concern and require urgent medical intervention.
Difficulty Breathing after Swallowing
If you experience difficulty breathing or a shortness of breath after swallowing, it is essential to seek emergency medical care. This can be a sign of a severe swallowing problem that requires immediate attention.
Drooling or Excessive Saliva Production
Excessive drooling or saliva production can be a sign of a swallowing problem, especially in conjunction with difficulty swallowing. This symptom should prompt a medical evaluation.
Medical Treatments for Difficulty Swallowing
Depending on the underlying cause of your difficulty swallowing, various medical treatments may be recommended by your healthcare provider. Here are some medical treatment options:
Medications to Reduce Acid Reflux
If gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is causing your difficulty swallowing, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to reduce stomach acid production or neutralize acid. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and improve swallowing function.
Dilation Procedures
If you have an esophageal stricture, your healthcare provider may perform a dilation procedure to widen the narrowed area. This procedure involves using an endoscope to stretch or widen the esophagus, allowing food to pass through more easily.
Botox Injection
For certain conditions, such as achalasia or esophageal spasm, your healthcare provider may recommend injecting Botox into the muscles of the esophagus. Botox can help relax the muscles, making swallowing easier.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat underlying causes of difficulty swallowing. This may involve removing tumors, repairing strictures, or correcting anatomical abnormalities.
Speech Therapy
Speech therapy can be beneficial for individuals with difficulty swallowing. A speech-language pathologist can provide techniques and exercises to improve swallowing function and ensure safe eating and drinking.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing. A physical therapist can provide specific exercises and techniques to improve muscle coordination and swallowing function.
Swallowing Exercises
Certain swallowing exercises, known as dysphagia therapy exercises, can help improve muscle strength and coordination for swallowing. These exercises are typically performed under the guidance of a speech-language pathologist.
Strengthening Exercises for Muscles
If your difficulty swallowing is due to muscular weakness or impaired coordination, your healthcare provider may recommend specific strengthening exercises for the muscles involved in swallowing. These exercises can help improve muscle function and swallowing ability.
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate the muscles involved in swallowing. This can help improve muscle strength and coordination for swallowing.
Laparoscopic Surgery
In some cases, laparoscopic surgery may be recommended for treating underlying causes of difficulty swallowing, such as achalasia or certain esophageal disorders. This minimally invasive surgical technique involves using small incisions and a camera to perform the procedure.

Supportive Care for Difficulty Swallowing
In addition to medical treatments, supportive care is crucial for individuals with difficulty swallowing. Here are some aspects of supportive care that can help manage the challenges associated with difficulty swallowing:
Psychological Support
Difficulty swallowing can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life and emotional well-being. It is important to seek psychological support, such as counseling or therapy, to address any emotional or mental health concerns that may arise.
Speech and Language Therapy
Speech and language therapy plays a vital role in managing difficulty swallowing. A speech-language pathologist can help individuals develop strategies to improve swallowing function, enhance communication skills, and address any speech-related difficulties.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on assisting individuals in carrying out daily activities and tasks. An occupational therapist can provide techniques and recommendations to make mealtimes more manageable, such as adaptive eating utensils or positioning aids.
Dietary Modifications
Working with a registered dietitian can ensure that your nutritional needs are met despite any dietary restrictions or difficulties with swallowing. A registered dietitian can help create a customized meal plan that takes into consideration your specific swallowing issues.
Swallowing Optimizations
Simple modifications, such as adjusting your head position or taking smaller bites, can significantly improve swallowing function. Working with a healthcare professional, such as a speech-language pathologist, can help identify specific strategies tailored to your needs.
Counseling and Education
Counseling and education play a crucial role in supporting individuals with difficulty swallowing. Learning about your condition, understanding available treatment options, and addressing any concerns or fears can help you make informed decisions and feel more empowered.
Support Groups
Joining a support group for individuals with difficulty swallowing can provide a sense of community, understanding, and emotional support. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can be beneficial for both practical advice and emotional well-being.
Access to Specialist Healthcare Professionals
Collaboration with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals is essential for proper management of difficulty swallowing. Access to specialists, such as gastroenterologists, otolaryngologists, or neurologists, can ensure comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of your condition.
Palliative Care Options
For individuals with advanced or progressive conditions causing difficulty swallowing, palliative care can play an essential role. Palliative care focuses on improving quality of life and providing comfort measures, helping individuals and their families navigate the challenges associated with the condition.
Assistive Devices for Daily Living
Various assistive devices, such as modified eating utensils, jar openers, or adaptive cups, can make daily activities easier for individuals with difficulty swallowing. Occupational therapists can provide recommendations and assistance in selecting and using these devices effectively.
In conclusion, difficulty swallowing can be caused by various medical conditions, ranging from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) to neurological disorders. While medical treatment is important, implementing practical strategies at home and making dietary modifications can significantly improve swallowing function. It is crucial to seek medical help if symptoms persist or worsen, as certain underlying causes may require specific interventions or management plans. With the right medical treatment, home remedies, and support, individuals with difficulty swallowing can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall quality of life.