In this article, you will explore the important process of diagnosing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS). FAS is a condition that occurs when a developing fetus is exposed to alcohol in the womb, resulting in a range of physical, mental, and behavioral disabilities. By understanding the various diagnostic criteria and assessments used by healthcare professionals, you will gain valuable insight into identifying and understanding this complex syndrome. So, let’s get started on this journey of discovery and uncover the key factors in diagnosing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.
Overview
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a set of physical, neurological, and cognitive abnormalities that result from a baby’s exposure to alcohol while in the womb. It is a preventable condition, but unfortunately, it can cause lifelong challenges for individuals affected by it. FAS is a serious public health issue that requires awareness, education, and support to address effectively.
Causes of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
The primary cause of FAS is the consumption of alcohol during pregnancy. When a pregnant woman drinks alcohol, it passes through the placenta and enters the baby’s bloodstream. The developing fetus is not equipped to metabolize alcohol as efficiently as an adult, leading to harmful effects on the developing organs and tissues. The timing and quantity of alcohol consumption during pregnancy can have a significant impact on the severity of FAS.
Prevalence of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
While it is challenging to determine the exact number of FAS cases worldwide, it is estimated that FAS affects 1 in every 1,000 live births. The prevalence rates vary across different countries and populations. However, it is important to note that FAS is a global issue that can occur in any community where alcohol consumption during pregnancy is prevalent.
Symptoms and Signs
Physical Features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
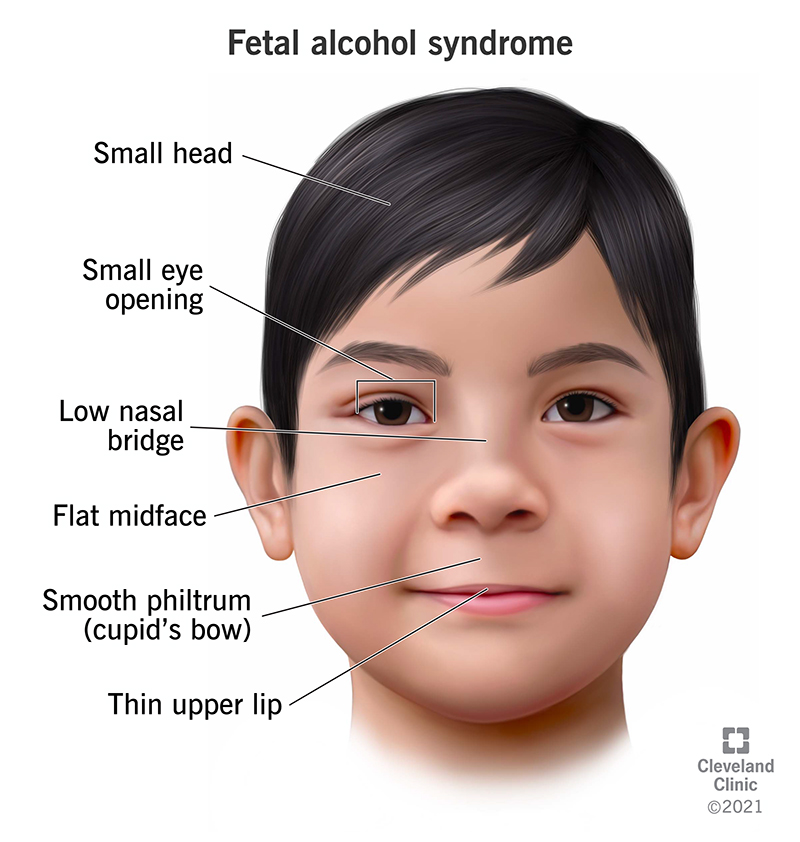
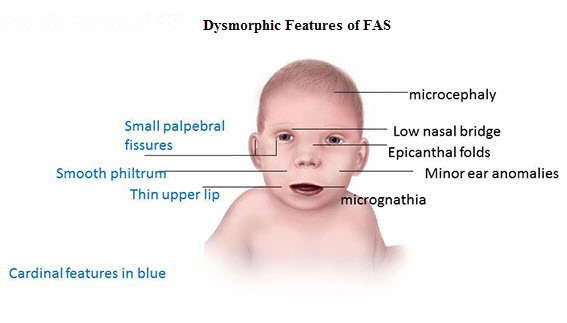
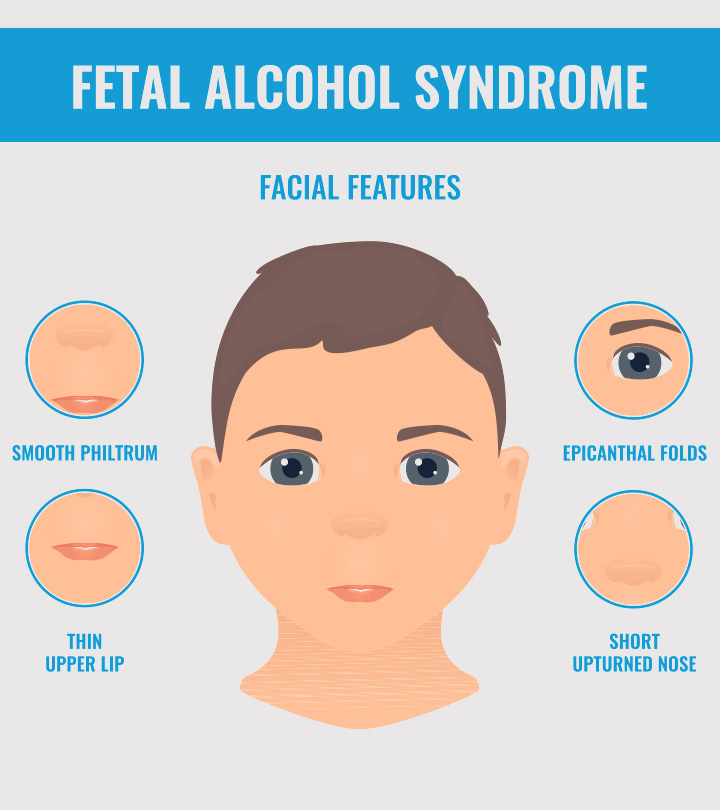
One of the hallmark physical features of FAS is the presence of distinct facial abnormalities. These may include a smooth philtrum (the area between the upper lip and nose), thin upper lip, and short eye openings. Additionally, individuals with FAS often have growth deficiencies, including low birth weight, smaller head circumference, and shorter stature compared to their peers.
Neurological and Behavioral Symptoms
Individuals with FAS may experience a range of neurological and behavioral symptoms. These can include difficulties with coordination, balance, and motor skills. They may also exhibit hyperactivity, attention deficit problems, and impulsivity. Some children with FAS may struggle with memory, learning difficulties, and academic challenges.
Psychological and Cognitive Impairments
Cognitive impairments are common in individuals with FAS and can range from mild to severe. They may have difficulty with abstract thinking, problem-solving, and understanding consequences. Individuals with FAS may also struggle with social skills, understanding social cues, and appropriate behavior in different situations.
Diagnosis
Screening for Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Early identification and diagnosis of FAS are crucial for timely interventions and support. However, due to the broad range of symptoms and the variability of presentations, FAS can be challenging to diagnose. Healthcare providers use various screening tools and questionnaires to gather information about maternal alcohol consumption, physical features, and developmental concerns.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is an essential component of diagnosing FAS. The distinct facial features associated with FAS, growth deficiencies, and any other physical anomalies are carefully assessed. This examination helps healthcare providers determine if the observed physical features are consistent with FAS.
Neurobehavioral Assessments
Neurobehavioral assessments aim to evaluate the neurological, cognitive, and behavioral functioning of individuals suspected of having FAS. These assessments may include tests of intelligence, attention, memory, executive functioning, and social-emotional skills. Gathering comprehensive information about an individual’s strengths and weaknesses helps in formulating an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Criteria
To establish a formal diagnosis of FAS, healthcare providers refer to specific diagnostic criteria established by medical and psychiatric organizations. These criteria typically include the presence of facial abnormalities, growth deficiencies, and confirmed prenatal alcohol exposure. Additionally, cognitive and behavioral impairments consistent with FAS are considered in making a diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Distinguishing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome from Other Disorders
Differential diagnosis is essential to rule out other developmental conditions with overlapping symptoms. FAS may share similarities with conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and genetic syndromes. Careful evaluation, examination, and assessment of an individual’s history, genetic testing, and developmental patterns help differentiate FAS from other disorders.

Complications
Physical Health Problems
Individuals with FAS may experience various physical health problems throughout their lives. These can include heart defects, kidney and liver abnormalities, hearing and vision impairments, and compromised immune function. Regular medical follow-ups and monitoring are necessary to manage and address these potential complications.
Developmental Delays
Developmental delays are common in individuals with FAS. They may experience delays in reaching developmental milestones such as sitting, walking, and talking. Early intervention services, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, can help support these individuals in reaching their full potential and acquiring essential skills.
Learning Difficulties
FAS can significantly impact an individual’s learning abilities. Difficulties may be observed in areas such as reading, writing, math, and understanding abstract concepts. Specialized educational support, individualized instruction, and accommodations can help individuals with FAS succeed academically.
Behavioral Challenges
Behavioral challenges are often present in individuals with FAS. These may include impulsivity, difficulty with self-regulation, emotional lability, and challenges with social interactions. Behavior management strategies, therapeutic interventions, and support services can help individuals with FAS develop coping skills and navigate their behavioral challenges more effectively.
Treatment and Management
Early Intervention & Education
Early intervention is key in addressing the unique needs of individuals with FAS. Starting interventions as early as possible can help minimize the impact of the condition on the child’s development. Early intervention programs may involve speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, and specialized educational strategies tailored to the individual’s needs.
Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral interventions focus on teaching individuals with FAS appropriate and adaptive behaviors while addressing challenging behaviors. These interventions may incorporate behavior management techniques, social skills training, and positive reinforcement strategies. Consistency, structure, and clear expectations are essential components of successful behavioral interventions.
Medication
Medication may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms and comorbid conditions associated with FAS. For example, stimulant medication may be used to address attention deficit and hyperactivity symptoms. However, medication should always be carefully considered and monitored by healthcare professionals, taking into account the individual’s unique needs and potential side effects.
Supportive Services
Individuals with FAS benefit from a comprehensive support system that addresses their physical, educational, behavioral, and emotional needs. This can include access to counseling services, support groups, case management, and advocacy. Additionally, families and caregivers also require support to navigate the challenges associated with FAS and provide ongoing care for their loved one.
Prevention
Educational Campaigns
Raising awareness and providing education about the risks of alcohol consumption during pregnancy is crucial for preventing FAS. Educational campaigns targeting healthcare providers, pregnant women, families, and the general public can help promote healthier choices and underscore the importance of abstaining from alcohol during pregnancy.
Reducing Alcohol Consumption during Pregnancy
Preventing FAS starts with ensuring pregnant women abstain from alcohol throughout their pregnancy. Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of not consuming alcohol during this critical period and provide necessary guidance and support. Pregnant women should be encouraged to seek alternative coping mechanisms and social support instead of turning to alcohol.
Importance of Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care plays a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Comprehensive prenatal care allows healthcare providers to monitor the progress of the pregnancy, provide necessary guidance, and address any concerns promptly. Encouraging pregnant women to prioritize prenatal care can help prevent FAS and other potential pregnancy complications.
Support and Resources
Support Groups
Support groups provide a valuable resource for individuals with FAS, their families, and caregivers. These groups offer a safe space for sharing experiences, gathering information, and receiving emotional support from others who understand the challenges associated with FAS. Connecting with support groups can help individuals and families feel less isolated and more empowered.
Therapeutic Services
Therapeutic services, such as counseling and therapy, can play a vital role in supporting individuals with FAS. These services help address emotional and behavioral challenges, develop coping strategies, and improve overall well-being. Individual, family, and group therapy sessions can provide the support and guidance needed to navigate the complexities of living with FAS.
Community Programs
Community programs that cater specifically to individuals with FAS can provide enriching experiences and opportunities for social interaction. These programs may include recreational activities, skill-building workshops, and peer support groups. Engaging with community programs fosters a sense of belonging and helps individuals with FAS develop important life skills.
Online Resources
The internet provides a wealth of resources for individuals with FAS and their families. Online platforms host informative websites, interactive forums, research publications, and supportive communities. These resources can assist individuals in gaining knowledge, accessing the latest research, and connecting with others who share similar experiences.

Current Research
Advances in Early Detection
Current research focuses on improving early detection and diagnosis of FAS. Researchers are continually striving to refine screening methods, develop more accurate diagnostic tools, and explore the impact of various maternal alcohol consumption patterns on fetal development. These advances can contribute to earlier interventions and better outcomes for individuals with FAS.
Exploring New Treatment Approaches
Researchers are also exploring innovative treatment approaches for individuals with FAS. This includes investigating the efficacy of different therapies, medications, and interventions in improving cognitive functioning, reducing behavioral challenges, and enhancing quality of life. Ongoing research provides hope for more effective treatments and management strategies.
Long-term Outcomes
Understanding the long-term outcomes and trajectories of individuals with FAS is a critical area of research. Investigating factors that influence outcomes, such as early intervention, supportive services, and environment, can aid in developing targeted interventions and support systems. Longitudinal studies provide valuable insights into the developmental progression and life experiences of individuals with FAS.
Conclusion
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is a complex condition that demands attention, understanding, and support. By increasing awareness about the risks of alcohol consumption during pregnancy, enhancing early detection and diagnosis methods, and providing comprehensive interventions and support, we can mitigate the challenges faced by individuals with FAS. Through a collective effort, we can promote a healthier future for all and prevent the lifelong impact of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome.