In this article, you will explore the comprehensive diagnosis and treatment options available for Meningioma, a common form of brain tumor. Together, we will dive into the symptoms, risk factors, and various diagnostic techniques used to accurately identify this condition. With a friendly and informative tone, this article aims to empower readers with knowledge about the available treatment options and innovative approaches to manage and potentially cure Meningioma. Whether you are seeking information for yourself or a loved one, this article is here to support you on your journey towards understanding and addressing this health concern.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Meningioma
Overview of Meningioma
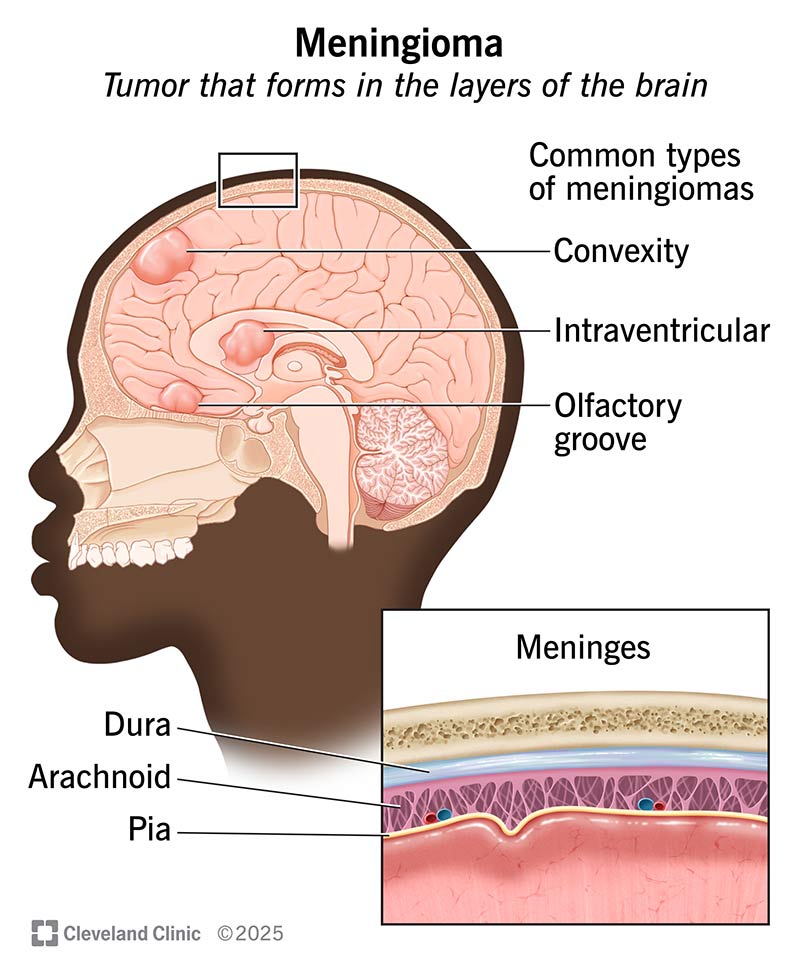
Meningioma is a type of brain tumor that develops in the meninges, which are the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This tumor arises from the cells of the meninges and can be either benign or malignant. Meningiomas are more common in women and usually occur in individuals aged 40-70. Although most meningiomas are slow-growing and noninvasive, they can cause symptoms if they exert pressure on nearby structures in the brain. Diagnosing and treating meningioma require a multi-disciplinary approach involving various diagnostic tools and treatment strategies.
Diagnostic Tools for Meningioma
The diagnosis of meningioma involves a combination of clinical evaluation, neuroimaging, and histopathological analysis. Your healthcare provider will begin by reviewing your medical history and conducting a thorough physical and neurological examination. They may ask you about your symptoms, any previous medical conditions, and any family history of brain tumors.
Imaging Techniques for Meningioma
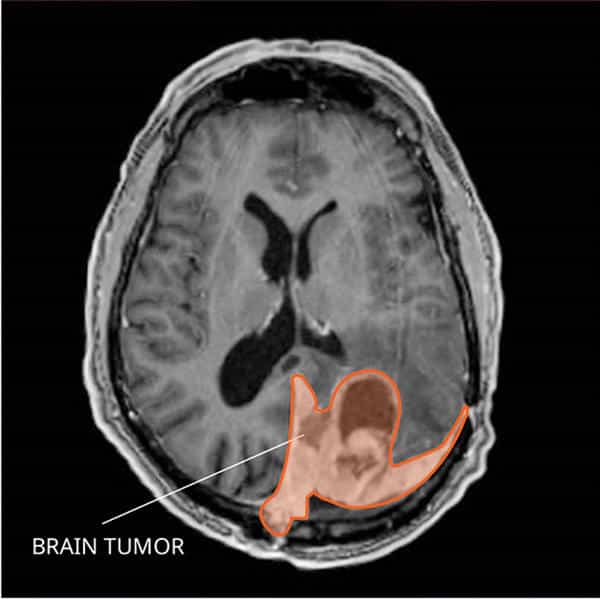
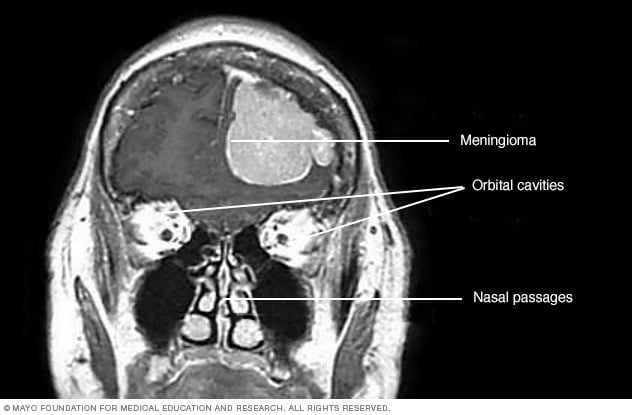
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the detection and localization of meningiomas. The most common imaging tool used for meningioma diagnosis is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI provides detailed images of the brain and helps in assessing the size, location, and characteristics of the tumor. Additionally, computed tomography (CT) scans may be performed to evaluate the bony structures and provide further information about the tumor’s extent.
Biopsy and Pathology of Meningioma
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of meningioma and determine its subtype. During a biopsy, a small sample of the tumor tissue is removed and examined under a microscope. The pathologist will analyze the biopsy specimen and classify the meningioma based on its histological features. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established a grading system for meningiomas, ranging from Grade I (benign) to Grade III (malignant).
Classification and Grading of Meningioma
The classification and grading of meningiomas are essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan. The WHO classification system categorizes meningiomas based on their histopathological characteristics. Grade I meningiomas are the most common and typically have a favorable prognosis. Grade II meningiomas are atypical, and Grade III meningiomas are malignant and associated with a poorer prognosis.
Treatment Options for Meningioma
The treatment options for meningioma depend on several factors, including the tumor size, location, grade, and the patient’s overall health. The main treatment modalities for meningioma include surgery, radiation therapy, and medical management. The choice of treatment is individualized and should be discussed with a team of specialists, including neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, and neuro-oncologists.
Surgical Approaches for Meningioma
Surgery is the primary treatment for meningioma and aims to remove the tumor while preserving neurological function. The surgical approach depends on the tumor location and involves techniques such as craniotomy or endoscopic surgery. During the procedure, the neurosurgeon will carefully remove as much of the tumor as possible, taking into consideration the surrounding brain structures.
Radiation Therapy for Meningioma
Radiation therapy may be recommended as the primary treatment or as an adjuvant therapy following surgery. It involves the use of high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy is the most common form of radiation therapy for meningioma. Stereotactic radiosurgery, a non-invasive technique that delivers a high dose of radiation to a specific area, may also be used for smaller tumors or in cases where surgery is not feasible.
Medical Management of Meningioma
Medical management plays a supportive role in the treatment of meningioma. This may involve the use of corticosteroids to reduce brain swelling and alleviate symptoms. Anticonvulsant medications may also be prescribed to control seizures, which can occur in some cases. Additionally, regular follow-up visits and monitoring are crucial to assess the response to treatment and detect any potential recurrence or complications.
Emerging Treatment Strategies for Meningioma
Research and clinical trials are continuously exploring new treatment strategies for meningioma. Targeted therapies, such as medications that specifically inhibit the growth of meningioma cells, are being investigated. Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, shows promise in the treatment of advanced or recurrent meningioma. Furthermore, advances in genomics and molecular profiling may help identify new therapeutic targets and personalize treatment approaches.
In conclusion, the diagnosis and treatment of meningioma require careful evaluation and a multidisciplinary approach. From diagnostic tools such as imaging techniques and biopsies to treatment options like surgery, radiation therapy, and medical management, there are several strategies available to manage meningioma. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as tumor characteristics, grade, and the patient’s overall health. Research into emerging treatment strategies offers hope for continued improvement in outcomes for individuals with meningioma.