Imagine waking up to a throbbing pain in your mouth, making it difficult to eat, speak, or even smile. Dental abscesses are no laughing matter, causing immense discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. But fret not, as there are effective treatments available to relieve the pain and eradicate the infection. In this article, we will explore the various options at your disposal, from antibiotics to dental procedures, providing you with the guidance you need to combat dental abscesses and reclaim your oral health.
Overview of Dental Abscesses
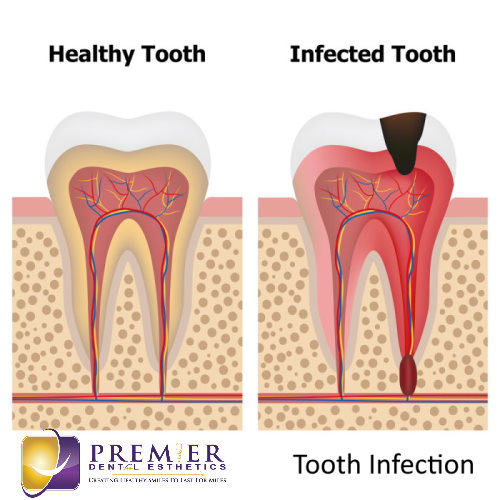
Dental abscesses are painful infections that occur in the mouth, specifically in the structures surrounding the teeth, such as the gums and jawbone. They are commonly caused by bacterial infections and can lead to severe discomfort, swelling, and even affect your overall health if left untreated. Understanding the definition, causes, signs, symptoms, and complications of dental abscesses is crucial in order to prevent and effectively manage this condition.
Definition of dental abscesses
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection within the teeth or gums. This infection can occur as a result of tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma. The pus-filled abscess is the body’s natural defense mechanism, attempting to isolate and prevent the spread of infection. While dental abscesses mainly occur near the root of the tooth, they can also develop in the gums or other structures surrounding the teeth.
Causes of dental abscesses
The primary cause of dental abscesses is a bacterial infection, usually stemming from poor oral hygiene practices. When oral bacteria accumulate and form plaque on the teeth, it can lead to tooth decay or gum disease. These conditions provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive and infiltrate the tooth or gums, resulting in an abscess. Additionally, dental trauma, such as a cracked tooth or an injury to the gums, can also introduce bacteria and cause an abscess to develop.
Signs and symptoms of dental abscesses
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a dental abscess is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common indicators include:
- Persistent toothache that worsens with biting or chewing
- Swelling and redness in the gums or face
- Severe and throbbing pain in the affected area
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw area
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek dental attention as soon as possible to prevent complications.
Complications of untreated dental abscesses
When left untreated, dental abscesses can lead to various complications. The infection can spread to surrounding tissues, causing cellulitis or even affecting distant areas of the body through the bloodstream. In severe cases, it can result in a condition called Ludwig’s angina, which is a potentially life-threatening infection that spreads rapidly and affects the floor of the mouth and neck. Dental abscesses can also cause the formation of gum boils, oral fistulas, damage to nearby bones, and even tooth loss. Timely intervention is essential to prevent these complications and ensure proper oral health.
Diagnosis of Dental Abscesses
Diagnosing a dental abscess involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a thorough clinical examination, and in some cases, the use of imaging techniques and laboratory tests.
Clinical examination
During a clinical examination, your dentist will carefully assess your teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. They will look for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, and areas of tenderness. Additionally, they may gently tap on the teeth to check for pain or sensitivity, and evaluate the nearby lymph nodes to gauge the extent of the infection. Based on the findings, your dentist can make an initial diagnosis of a dental abscess.
X-rays and imaging techniques
To get a closer look at the affected area, your dentist may request X-rays or other imaging techniques, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or a cone beam CT scan. These imaging tools can provide more detailed information about the abscess, including its size, location, and any bone involvement. X-rays are particularly useful in identifying dental abscesses that occur at the root of the tooth.
Laboratory tests for dental abscesses
In some cases, laboratory tests may be necessary to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most appropriate antibiotic treatment. Your dentist may take a sample of the pus from the abscess and send it to a laboratory for culture and sensitivity testing. This helps to identify the bacteria and determine which antibiotics are most effective in combating the infection.
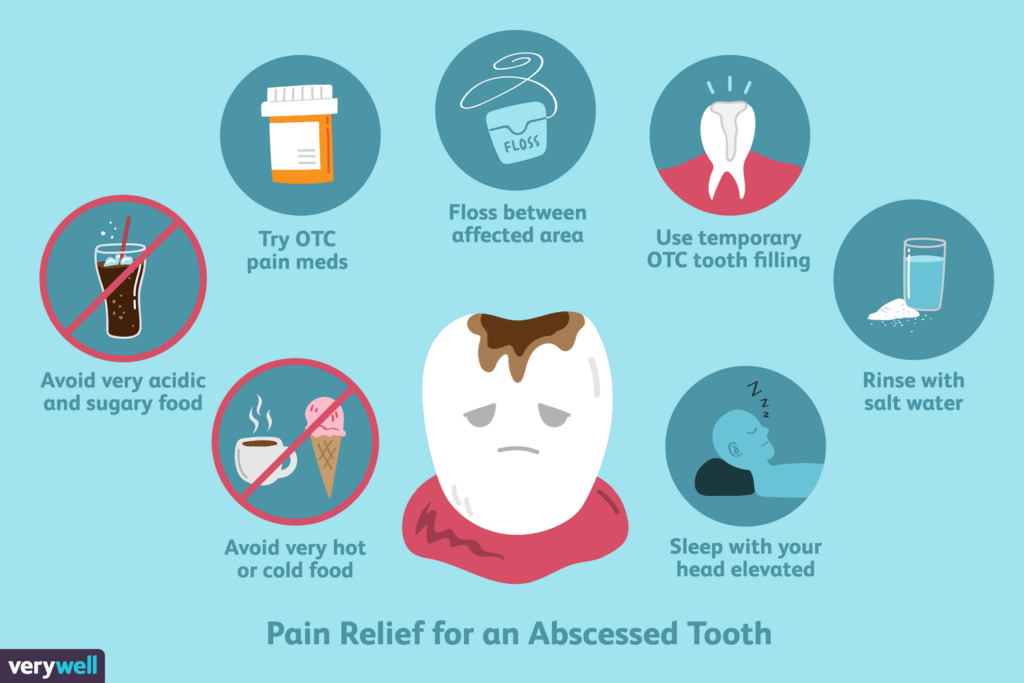
Non-Surgical Treatments for Dental Abscesses
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense for managing dental abscesses. These approaches aim to eliminate the infection, alleviate pain, and prevent further complications.
Prescription of antibiotics for dental abscesses
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to control the infection and prevent it from spreading. Depending on the severity of the abscess and the presence of any underlying conditions, your dentist may prescribe a broad-spectrum antibiotic or a more targeted one based on the results of the laboratory tests. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if the symptoms subside, to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
Pain management techniques for dental abscesses
To alleviate the pain associated with a dental abscess, your dentist may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribe stronger medication if necessary. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, applying a cold compress to the affected area can provide temporary relief.
Drainage of the dental abscess
In certain cases, the dental abscess may need to be drained to eliminate the pus and relieve pressure. Your dentist can perform an incision and drainage procedure, whereby a small cut is made in the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia to ensure your comfort during the process.
Preventive measures for dental abscesses recurrence
To prevent the recurrence of dental abscesses, your dentist will guide you on proper oral hygiene practices. This includes regular brushing and flossing, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and visiting your dentist for routine check-ups and cleanings. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods can also contribute to overall oral health. By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the chances of developing another dental abscess.
Surgical Treatments for Dental Abscesses
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat dental abscesses that do not respond to non-surgical treatments or cases where the abscess is severe and causing significant damage to the tooth or surrounding structures.
Incision and drainage procedure
If the dental abscess persists despite non-surgical measures, an incision and drainage procedure may be performed. This involves making a larger incision than in a non-surgical drainage procedure to thoroughly drain the abscess. After draining, the dentist will clean the area and may prescribe antibiotics to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
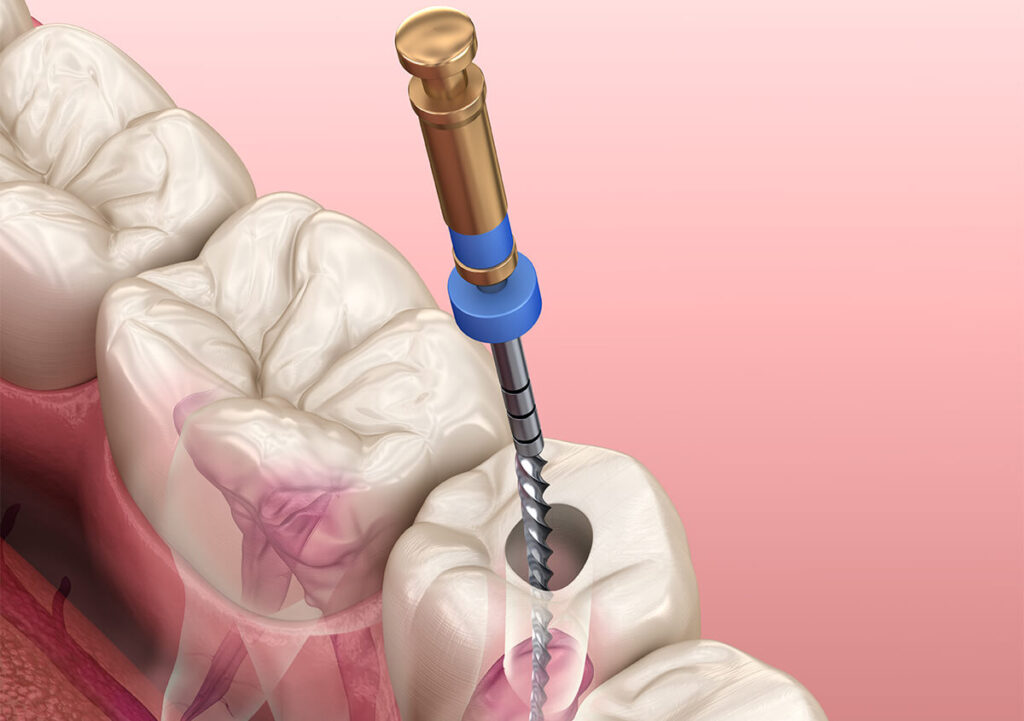
Root canal treatment for dental abscesses
In cases where the abscess originates from an infected tooth, a root canal treatment may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the root canal, and then sealing it to prevent reinfection. By saving the tooth through root canal treatment, the dentist can eliminate the abscess and restore its function.
Tooth extraction as a treatment option
If the tooth is severely infected and cannot be saved through root canal treatment, tooth extraction may be recommended. This is typically the last resort when all other options have been exhausted. The infected tooth is carefully removed, eliminating the source of the abscess. After extraction, your dentist may discuss possible tooth replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges, to maintain proper oral function and aesthetics.
Apicoectomy to treat persistent dental abscesses
An apicoectomy may be considered in cases where a persistent dental abscess continues to affect the tooth even after root canal treatment. This surgical procedure involves removing the tip of the tooth’s root (apex) and cleaning the surrounding infected tissue. By eliminating the source of the infection and sealing the root, an apicoectomy can help alleviate the abscess and promote healing.
Home Remedies for Dental Abscesses
While home remedies cannot replace professional dental treatment, they can provide temporary relief and aid in the management of dental abscesses. It is essential to note that these remedies should complement professional care and not serve as a substitute for dental intervention.
Rinsing with warm saltwater
Rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation associated with dental abscesses. Saltwater has natural disinfectant properties, which can help to temporarily control the infection. Simply dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and gently swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
Using a cold compress for pain relief
Applying a cold compress to the affected side of the face can help numb the area, reduce swelling, and provide temporary pain relief. Simply wrap a bag of ice or a cold pack in a thin towel and apply it to the external area where the abscess is present. Be sure not to apply the ice directly to the skin to prevent potential skin damage.
Applying over-the-counter oral gels or creams
Over-the-counter oral gels or creams that contain benzocaine or other numbing agents can provide temporary relief by desensitizing the affected area. Apply a small amount of the gel or cream directly to the abscess, following the instructions on the packaging.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices
Practicing good oral hygiene is crucial in managing dental abscesses and preventing their recurrence. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Additionally, floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and along the gumline. Use an antibacterial mouthwash as recommended by your dentist to further reduce oral bacteria.
Prevention of Dental Abscesses
Preventing dental abscesses starts with maintaining good oral health and seeking timely dental care. By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing a dental abscess.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings play a vital role in preventing dental abscesses. Your dentist can identify early signs of tooth decay or gum disease, enabling timely intervention before they progress to abscess formation. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup, reducing the risk of bacterial infections.
Practicing proper oral hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is essential in preventing dental abscesses. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Remember to clean your tongue as well, as bacteria can accumulate on its surface. Additionally, floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
Early treatment of dental issues
Addressing dental issues promptly is crucial in preventing the development of dental abscesses. Seek dental attention if you experience tooth pain, sensitivity, or notice any changes in your oral health. Timely intervention can prevent infections from progressing and reduce the likelihood of developing an abscess.
Avoiding sugary and acidic foods
A diet high in sugar and acidity increases the risk of tooth decay, which can ultimately lead to dental abscesses. Limit your consumption of sugary and acidic foods and beverages, such as soda, candy, and citrus fruits. Opt for healthier alternatives and remember to rinse your mouth with water after consuming acidic or sugary substances.
Possible Complications of Dental Abscesses
Understanding the potential complications of dental abscesses emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, dental abscesses can lead to various issues affecting both oral and overall health.
Spread of infection to surrounding tissues or other parts of the body
When a dental abscess is not treated, the infection can spread to nearby tissues, such as the jawbone or facial structures. In some cases, the infection can enter the bloodstream and potentially affect other parts of the body, leading to serious systemic complications.
Development of a chronic abscess
A dental abscess can become chronic if the infection persists or keeps recurring. Chronic abscesses are more challenging to treat and may require more aggressive interventions to eradicate the infection effectively.
Formation of a facial or oral fistula
If a dental abscess remains untreated for an extended period, it may cause the formation of a fistula. A fistula is an abnormal channel that connects the abscess to the skin surface or a hollow area, such as the mouth. This can result in the drainage of pus or fluid through an opening near the abscess, leading to chronic discharge and discomfort.
Damage to bones or nearby teeth
Prolonged presence of a dental abscess can cause damage to the surrounding bone tissue. The infection can erode the jawbone, leading to compromised support for the teeth and potentially resulting in tooth loss. Additionally, nearby teeth may also be affected as the infection can spread to neighboring tooth roots, leading to further complications.
Risks and Side Effects of Dental Abscess Treatments
While dental abscess treatments are generally safe and effective, there are some potential risks and side effects associated with certain procedures and medications used in their management.
Allergic reactions to antibiotics
Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain antibiotics prescribed for dental abscesses. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include rash, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. If you develop any of these symptoms after taking antibiotics, seek immediate medical attention.
Pain or discomfort during and after procedures
During procedures such as incision and drainage, root canal treatment, or tooth extraction, it is common to experience some level of pain or discomfort. Your dentist will take measures to minimize discomfort, such as administering local anesthesia or prescribing pain medication for post-procedure pain management.
Swelling, bruising, or bleeding at the treatment site
Following surgical treatments for dental abscesses, such as incision and drainage or apicoectomy, swelling, bruising, or bleeding at the treatment site may occur. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with cold compresses and over-the-counter pain relievers.
Damage to surrounding structures
In rare cases, dental abscess treatments may result in damage to surrounding structures, such as nerves or blood vessels. Your dentist will take precautions to minimize these risks, but it is important to be aware of such potential complications.
FAQs about Dental Abscesses
Can dental abscesses heal on their own?
While it is possible for small dental abscesses to drain on their own, it is not recommended to rely on self-healing. It is essential to seek professional dental care to effectively treat the abscess, prevent complications, and ensure optimal oral health.
How long does it take for dental abscesses to heal?
The time it takes for a dental abscess to heal depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection, the treatment approach taken, and individual healing capabilities. With proper and timely treatment, most dental abscesses show improvement within a few days, but complete healing may take a couple of weeks or longer.
Can dental abscesses lead to other health problems?
Yes, dental abscesses can potentially lead to other health problems if left untreated. The infection can spread to other parts of the body, causing systemic complications. Additionally, chronic dental abscesses can affect overall well-being and quality of life.
What should I do if I suspect I have a dental abscess?
If you suspect you have a dental abscess, it is important to seek prompt dental care. Contact your dentist to explain your symptoms and schedule an appointment. In the meantime, practice good oral hygiene, rinse your mouth with warm saltwater, and use over-the-counter pain relief as needed.
Conclusion
Dental abscesses are painful infections that require prompt attention to prevent complications and ensure overall oral health. Understanding the causes, signs, and symptoms of dental abscesses is essential for early diagnosis. Non-surgical and surgical treatments, as well as home remedies, provide effective management options. By practicing good oral hygiene, seeking regular dental check-ups, and adhering to preventive measures, the risk of dental abscesses can be greatly reduced. If you suspect you have a dental abscess, it is important to seek professional dental care to receive appropriate treatment and prevent further complications. Remember, timely intervention is key in resolving dental abscesses and maintaining a healthy smile.