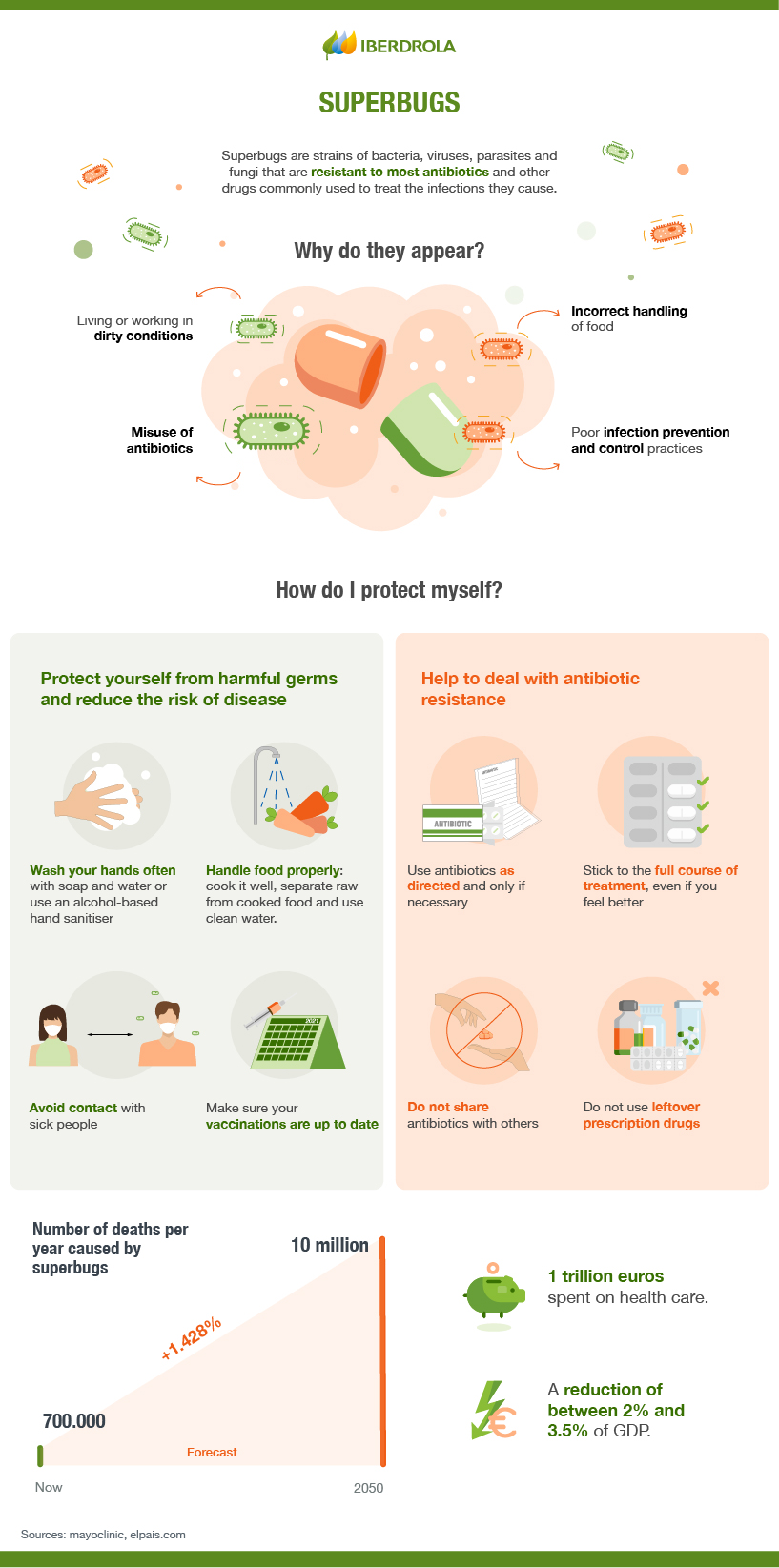
You may not realize it, but superbugs pose a significant threat to our health and well-being. These antibiotic-resistant bacteria have become increasingly common and can cause severe infections that are difficult to treat. In order to safeguard ourselves and the community from superbugs, it is crucial to adopt preventive measures. This article will provide you with practical tips and advice on how to effectively prevent the spread and development of these dangerous pathogens. By following these simple steps, you can help ensure a healthier future for everyone.

Maintain good hygiene practices
Wash hands frequently
One of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent the spread of superbugs is by washing your hands frequently. Washing your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds can help remove any bacteria or viruses that may be lingering on your hands. It is especially important to wash your hands before eating, after using the restroom, and after touching surfaces that may be contaminated. Remember to scrub all parts of your hands, including between your fingers and under your nails, to ensure a thorough clean.
Use hand sanitizers
In situations where soap and water are not readily available, using hand sanitizers can be a convenient and effective alternative. Make sure to choose a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol. Apply a generous amount of sanitizer to the palm of your hand and rub it all over your hands until they are dry. Hand sanitizers can be especially useful when you are out in public, such as when using public transportation or visiting crowded places. However, it’s important to note that hand sanitizers are not as effective as handwashing when it comes to removing certain types of bacteria and viruses, so it’s still important to prioritize handwashing whenever possible.
Cover mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
Superbugs can easily spread through respiratory droplets when someone coughs or sneezes. That’s why it’s crucial to cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when you cough or sneeze. This simple act can help prevent the release of potentially infectious droplets into the air and reduce the risk of transmitting superbugs to others. Always keep a supply of tissues with you and dispose of them properly immediately after use. Remember to wash your hands thoroughly afterwards to further reduce the risk of contamination.
Dispose of tissues properly
Proper disposal of used tissues is vital in preventing the spread of superbugs. When you cough, sneeze, or blow your nose, make sure to use tissues and dispose of them in a waste bin immediately. Avoid leaving used tissues on surfaces or letting them accumulate in pockets or bags. By disposing of tissues properly, you reduce the chances of spreading infectious superbugs to others and minimize the risk of contaminating your environment. Remember to always wash your hands thoroughly after handling used tissues.
Practice safe food handling
Cook food thoroughly
Cooking food thoroughly is essential for killing any harmful bacteria or viruses that may be present. Make sure to cook all meats, including poultry, beef, pork, and seafood, to their recommended internal temperatures. Use a food thermometer to ensure that the food has reached a safe temperature. Additionally, be cautious when reheating leftovers, making sure they are heated thoroughly to avoid any potential bacterial growth.
Store food properly
Proper food storage can help prevent the growth and spread of bacteria that can lead to serious illnesses. Keep your refrigerator temperature below 40°F (4°C) and ensure that any perishable foods, such as raw meats, are stored in sealed containers or wrapped securely to prevent cross-contamination. Moreover, store raw foods separately from cooked foods to avoid any potential contamination.
Separate raw and cooked food
Cross-contamination is a common way for superbugs to spread in the kitchen. To prevent this, always use separate cutting boards, utensils, and plates for raw and cooked foods. This helps minimize the risk of transferring harmful bacteria from raw foods, such as chicken or fish, to ready-to-eat foods. Remember to wash all utensils, cutting boards, and surfaces thoroughly with hot, soapy water after handling raw meats.
Avoid cross-contamination
When handling food, it’s crucial to be aware of cross-contamination and take the necessary precautions to prevent it. Avoid using the same utensils or cutting boards for different types of foods, as this can lead to the transfer of bacteria or other pathogens. Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling different food items. By being mindful of cross-contamination, you can significantly reduce the risk of superbug infections caused by contaminated food.

Immunization and vaccination
Stay up-to-date with vaccinations
Vaccinations are a powerful tool in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, including those caused by superbugs. Make sure you and your family are up-to-date with all recommended vaccines. By staying immunized, you not only protect yourself but also contribute to the overall community immunity, making it harder for superbugs to spread and cause outbreaks.
Get annual flu shots
Influenza, or the flu, is a common illness that can be caused by different strains of viruses. Getting an annual flu shot is an important step in protecting yourself and others from superbug-related complications. The flu shot helps reduce the risk of contracting and spreading the influenza virus, which can weaken the immune system and make it more susceptible to other infections, including those caused by superbugs.
Consider additional vaccines for at-risk individuals
Certain individuals, such as the elderly, young children, pregnant women, and those with underlying health conditions, may be at higher risk of developing severe infections, including those caused by superbugs. It’s important for these at-risk individuals to consult with their healthcare professionals and consider additional vaccines that can provide extra protection. Vaccination can greatly reduce the likelihood of contracting superbug infections and minimize the potential for complications.
Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use
Only take antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional
Antibiotics are powerful medications that can effectively treat bacterial infections. However, they should only be taken when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, and their misuse can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant superbugs. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the appropriate use of antibiotics, including dosage and duration of treatment.
Do not demand antibiotics for viral infections
Superbugs thrive on the misuse and overuse of antibiotics. It is important to understand that antibiotics are not appropriate for treating viral infections, as they are designed to target bacteria only. When you have a viral infection, such as a cold or the flu, demanding antibiotics will not only be ineffective but also contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Trust your healthcare professional’s judgment in determining the most appropriate course of treatment for your specific condition.
Complete the full course of antibiotic treatment
When prescribed antibiotics for a bacterial infection, it is crucial to complete the full course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished. Prematurely stopping antibiotics can lead to the survival of more resistant bacteria, which can contribute to the development of superbugs. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and take the antibiotics for the prescribed duration to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated and prevent the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.

Prevent infections in healthcare settings
Follow hand hygiene protocols
Hand hygiene is of utmost importance in healthcare settings to prevent the spread of superbugs. Healthcare professionals should strictly follow hand hygiene protocols, including washing hands with soap and water or using hand sanitizers regularly. Proper hand hygiene helps minimize the transmission of superbugs between patients and healthcare workers, reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
Implement proper infection control measures
Healthcare facilities should have comprehensive infection control measures in place to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, including superbugs. This includes regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, equipment, and patient care areas. Proper waste management and disposal procedures should be followed to decrease the risk of contamination. Healthcare workers should be trained to use personal protective equipment correctly, such as gloves and masks, to protect themselves and patients.
Use sterile techniques during medical procedures
Invasive medical procedures, such as surgeries or inserting catheters, present an increased risk of infection if proper sterile techniques are not followed. Healthcare professionals must adhere to strict sterile protocols during any invasive procedure to minimize the introduction of superbugs into the body. This includes using sterile gloves, masks, and gowns, as well as ensuring that all instruments and equipment used are properly sterilized.
Ensure proper cleaning and disinfection of medical equipment
Medical equipment, devices, and tools must be cleaned and disinfected regularly to prevent the spread of superbugs. Healthcare facilities should have robust protocols in place for the cleaning and disinfection of equipment, following manufacturer guidelines and best practices. Ensuring that medical equipment is free from contamination helps reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections and protects both patients and healthcare workers.
Promote antibiotic stewardship
Educate healthcare professionals and patients about appropriate antibiotic use
A key aspect of preventing the emergence and spread of superbugs is promoting antibiotic stewardship. This involves educating healthcare professionals and patients about the appropriate use of antibiotics. Healthcare professionals should be knowledgeable about current antibiotic prescribing guidelines and practices, while patients should be educated on the importance of following prescribed antibiotic regimens and the risks associated with unnecessary antibiotic use.
Implement guidelines for antibiotic prescribing
Healthcare facilities should establish clear guidelines for antibiotic prescribing to ensure that antibiotics are used judiciously and appropriately. These guidelines should take into account factors such as the type of infection, the susceptibility of the bacteria, and the patient’s individual characteristics. By implementing evidence-based guidelines for antibiotic prescribing, healthcare professionals can help minimize the risk of superbug development and spread.
Monitor antibiotic resistance patterns
Regular monitoring of antibiotic resistance patterns is crucial in understanding the prevalence and trends of superbugs. Healthcare facilities should have robust surveillance systems in place to track antibiotic-resistant bacteria and identify potential outbreaks. This data can help guide antibiotic prescribing practices, identify areas of improvement in infection control measures, and facilitate the development of strategies to combat superbugs effectively.

Encourage proper waste management
Implement proper disposal methods for infectious waste
Proper waste management is essential in preventing the spread of superbugs, particularly in healthcare settings. Healthcare facilities should have designated methods for the disposal of infectious waste, such as contaminated dressings, needles, and other materials. These waste materials should be placed in secure containers and disposed of according to local regulations and guidelines to minimize the risk of contamination and prevent the transmission of superbugs to the general population.
Train healthcare workers on waste management
Healthcare workers should receive comprehensive training on proper waste management practices to ensure the safe handling and disposal of infectious waste. This includes understanding the different categories of waste, using appropriate personal protective equipment when handling waste, and following proper procedures for segregation and disposal. By equipping healthcare workers with the knowledge and skills necessary for effective waste management, the risk of superbug transmission can be significantly reduced.
Promote recycling and responsible disposal of medications
Apart from infectious waste, proper management of other types of waste, such as recyclables and medications, is also important in preventing the spread of superbugs. Healthcare facilities should promote recycling programs and provide designated recycling bins for non-infectious waste. Additionally, responsible disposal of medications, such as returning unused or expired drugs to pharmacies, helps prevent the inappropriate use or accidental exposure to antibiotics, reducing the risk of superbug development and spread.
Educate the public
Increase awareness about superbugs and their risks
Raising public awareness about superbugs and the risks associated with them is vital in promoting preventive measures. Educational campaigns through various channels, such as public health campaigns, schools, community centers, and media platforms, can help raise awareness about the emergence of superbugs, the importance of proper hygiene practices, and the appropriate use of antibiotics. By increasing knowledge and understanding among the public, individuals can make informed decisions to protect themselves and their communities.
Promote good hygiene practices at home and in public spaces
Good hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing the spread of superbugs both at home and in public spaces. Educational initiatives should emphasize the importance of handwashing, proper cough and sneeze etiquette, and regular cleaning and disinfection of commonly touched surfaces. By promoting these practices, individuals can reduce the risk of acquiring and transmitting superbugs, contributing to a healthier and safer environment.
Provide information on the appropriate use of antibiotics
Educating the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics is essential for combating the development of superbugs. Initiatives should focus on explaining the difference between bacterial and viral infections, the limited efficacy of antibiotics against viral illnesses, and the importance of finishing prescribed antibiotic courses. By empowering individuals with accurate information, they can make responsible decisions when seeking medical treatment and avoid contributing to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant superbugs.
Support research and development
Invest in developing new antibiotics
Continued research and development are crucial in the fight against superbugs. Investing resources into the development of new antibiotics can help combat the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance. Scientists and pharmaceutical companies need support to explore new compounds, discover innovative mechanisms of action, and develop effective antibiotics that can target multidrug-resistant bacteria. By investing in research, we can stay ahead of the evolving superbug landscape.
Explore alternative treatments for infections
In addition to developing new antibiotics, exploring alternative treatments for infections can offer valuable options in the prevention and management of superbugs. This includes researching and developing novel therapies, such as phage therapy, which utilizes bacteriophages to target and kill specific bacteria. By diversifying treatment options, healthcare professionals can have a broader range of tools to combat superbugs effectively.
Investigate new prevention strategies
Prevention is always better than cure, and in the case of superbugs, it becomes even more crucial. Investing in research to investigate new prevention strategies can provide valuable insights into how to reduce the transmission of superbugs. This includes exploring the effectiveness of vaccines, new disinfection methods, and innovative approaches to infection control. By continuously exploring new prevention strategies, we can stay one step ahead of superbugs and minimize their impact on public health.
Collaborate internationally
Share surveillance data on antibiotic resistance
Superbugs do not recognize borders, which is why international collaboration is essential in combating their spread. Sharing surveillance data on antibiotic resistance patterns and outbreaks can help identify global trends, monitor the emergence of new superbugs, and guide appropriate public health responses. By working together, countries can collectively respond and develop strategies to address superbugs on a global scale.
Coordinate efforts to combat superbugs globally
Coordinated efforts among countries and international organizations are crucial in effectively combating superbugs. This involves sharing best practices, coordinating research initiatives, and harmonizing policies and guidelines. By pooling resources and knowledge, countries can develop comprehensive strategies and interventions to prevent the emergence and spread of superbugs, safeguarding global public health.
Exchange knowledge and expertise in infection prevention
International collaboration allows for the exchange of knowledge and expertise in infection prevention and control. Sharing best practices and learning from different healthcare systems can improve infection prevention measures and raise the overall standard of care. By embracing a collaborative approach, healthcare professionals from around the world can enhance their understanding of superbugs, develop innovative solutions, and ultimately protect populations from the devastating effects of these resistant bacteria.
In conclusion, preventing the emergence and spread of superbugs requires a comprehensive and collaborative effort involving individuals, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and researchers. By maintaining good hygiene practices, practicing safe food handling, staying up-to-date with vaccinations, avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, implementing proper infection control measures, promoting antibiotic stewardship, encouraging proper waste management, educating the public, supporting research and development, and collaborating internationally, we can effectively tackle the threat of superbugs and safeguard global health for generations to come. Let’s all play our part in preventing superbugs and ensuring a healthier future.