You’ve experienced it before – the uncontrollable meltdown, the loud cries, and the flailing limbs. Temper tantrums can be a challenge to handle, leaving both you and your child feeling frustrated. But fear not, there are effective ways to prevent these outbursts and maintain a peaceful environment for everyone involved. By understanding the triggers, setting clear boundaries, and employing calming techniques, you can help your child navigate their emotions and prevent temper tantrums from occurring. In this article, we’ll explore some practical strategies that can make a remarkable difference in reducing tantrums and fostering a harmonious household.

Understanding Temper Tantrums
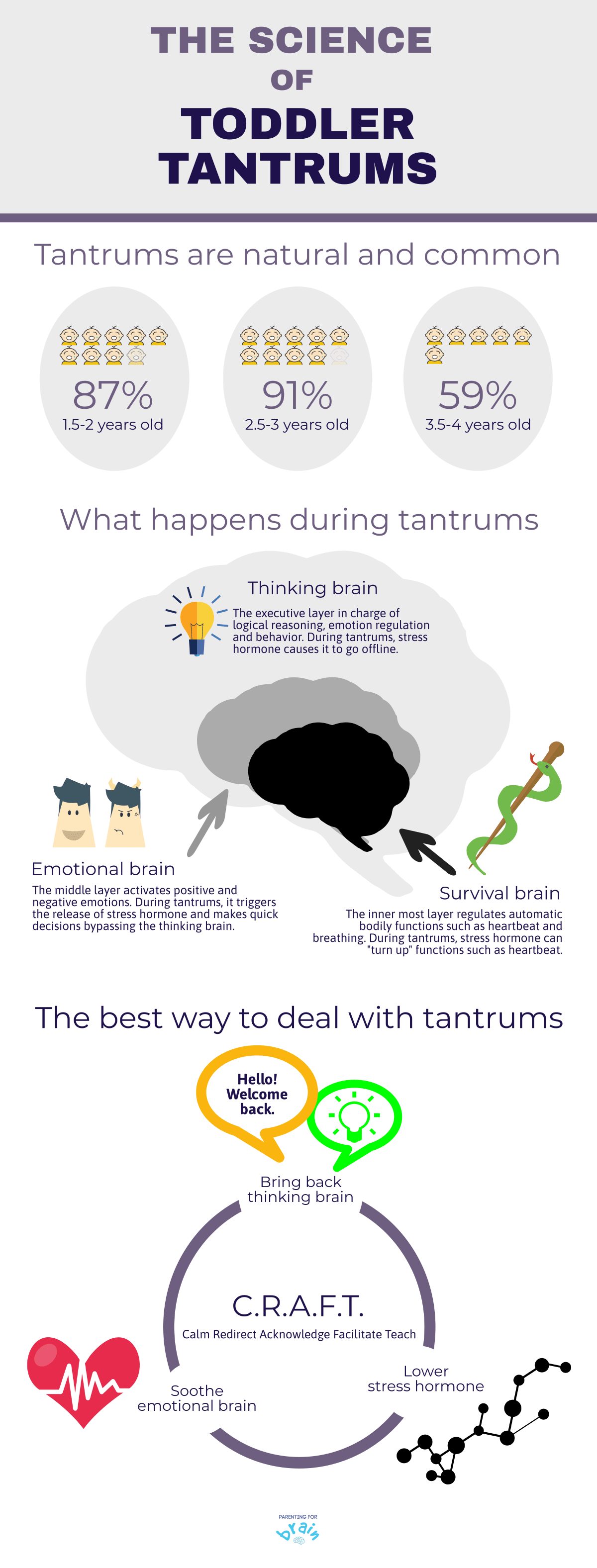
Temper tantrums are common behaviors displayed by young children when they are unable to regulate their emotions. These outbursts are often characterized by crying, screaming, kicking, and even physical aggression. While they can be frustrating for both children and caregivers, it’s important to understand that temper tantrums are a normal part of child development.
What are temper tantrums?
Temper tantrums are explosive displays of emotion that can occur in children between the ages of 1 and 4. These episodes are typically triggered by a child’s inability to communicate their needs and wants effectively. When children feel frustrated or overwhelmed, they may resort to tantrum behaviors as a means of expressing their emotions and seeking attention or control.

Why do children have temper tantrums?
There are several factors that contribute to the occurrence of temper tantrums in children. Firstly, young children are still developing their emotional regulation skills and may find it difficult to control their feelings effectively. Additionally, tantrums can arise from the child’s desire for independence and autonomy, as they struggle to navigate the boundaries set by their caregivers. Environmental factors such as changes in routine, hunger, fatigue, or overstimulation can also trigger temper tantrums.
How long do temper tantrums typically last?
While the duration of tantrums can vary from child to child, they typically last between 2 to 15 minutes. However, it is not uncommon for tantrums to persist for longer periods, especially if the child feels misunderstood or unable to satisfy their needs. As children grow and develop better emotional regulation skills, the frequency and intensity of tantrums tend to decrease.

Common triggers for temper tantrums
Temper tantrums can be triggered by a variety of factors. Some common triggers include hunger, fatigue, illness, transitions or changes in routine, limitations on autonomy, and unmet desires or expectations. Identifying these triggers can help caregivers better understand their child’s needs and proactively prevent or manage tantrum behavior.
Creating a Positive Environment
Establishing regular routines can provide children with a sense of stability and predictability, reducing their likelihood of feeling overwhelmed. When children know what to expect, they feel more secure and are less likely to engage in tantrum behaviors.
Setting clear and consistent expectations is crucial in creating a positive environment. By establishing age-appropriate rules and boundaries, children understand the limits and can navigate their behavior accordingly. Being consistent in enforcing these expectations helps children develop self-discipline and reduces the likelihood of tantrums occurring.
Encouraging open communication is essential for creating a nurturing atmosphere. Providing a safe space for children to express their thoughts and emotions allows them to feel heard and understood. When children feel valued and listened to, they are less likely to resort to tantrums as a means of seeking attention.
Providing a calm and nurturing atmosphere is also important in preventing temper tantrums. Caregivers should strive to create a peaceful and supportive environment where children feel safe and loved. By modeling calm and controlled behavior themselves, caregivers can help children learn to regulate their own emotions.

Teaching Emotional Regulation
Helping children identify and express emotions is a vital skill in preventing temper tantrums. Children need to understand their feelings and have the vocabulary to express them in appropriate ways. Caregivers can engage in conversations about emotions and provide examples of situations where different emotions may arise.
Teaching coping strategies empowers children with the tools they need to manage their emotions effectively. Deep breathing exercises, counting to ten, or engaging in a calming activity can help children self-soothe when they feel overwhelmed. By practicing these techniques together, caregivers can reinforce their effectiveness and encourage their use during moments of distress.
Encouraging positive outlets for emotions is another effective way to promote emotional regulation. Engaging in activities such as drawing, dancing, or playing sports allows children to express their emotions in a healthy and constructive manner. Caregivers can support and encourage these outlets by providing the necessary materials or participating in the activities alongside the child.
Modeling calm and controlled behavior is crucial in teaching children how to regulate their emotions. Children learn by observing those around them, so caregivers should strive to exhibit patience, self-control, and empathy. By showcasing healthy emotional regulation, caregivers set a positive example for their children to follow.
Effective Discipline Techniques
Using positive reinforcement is a highly effective discipline technique to prevent temper tantrums. By acknowledging and praising desired behavior, children feel valued and encouraged to continue behaving in appropriate ways. Offering rewards or small incentives can further reinforce positive behavior and motivate children to make good choices.
Setting appropriate limits and boundaries is necessary for guiding children’s behavior. Clearly communicating the expectations and consequences helps children understand what is acceptable and what is not. By consistently enforcing these limits, caregivers provide children with a sense of structure that reduces the likelihood of tantrums occurring.
Employing time-outs effectively can be an effective strategy to address intense emotions during a temper tantrum. Time-outs give children an opportunity to calm down and reflect on their behavior. It is important, however, to ensure that time-outs are used as a tool for teaching and not as a punishment. After the time-out, caregivers should have a conversation with the child to help them understand what triggered the tantrum and how they can better handle their emotions in the future.
Redirecting attention to alternative activities can divert a child’s focus from the trigger of their tantrum. Offering a distraction such as a favorite toy or engaging in a preferred activity can help shift their attention and redirect their emotions in a more positive direction.
Promoting Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Ensuring adequate sleep is crucial for a child’s emotional well-being. Fatigue can increase irritability and make children more susceptible to tantrums. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment can help regulate a child’s sleep pattern and reduce the likelihood of tantrums associated with tiredness.
Encouraging regular physical exercise is another important aspect of promoting emotional health in children. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers. Engaging in activities such as running, swimming, or dancing not only helps children burn off excess energy but also provides them with an outlet for their emotions.
Balancing a nutritious diet is essential for maintaining stable energy levels and supporting emotional regulation. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can positively impact a child’s mood and reduce the likelihood of tantrums caused by hunger or fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Reducing exposure to screen time is important in promoting healthy lifestyle habits and minimizing overstimulation. Excessive screen time can lead to overexcitement and interfere with a child’s ability to regulate their emotions. Setting boundaries and encouraging alternative activities, such as reading books or engaging in imaginative play, can help children develop healthier screen habits.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Identifying signs of frustration or anger is crucial for preventing tantrums. Caregivers should be attentive to changes in a child’s behavior, such as increased irritability, restlessness, or difficulty concentrating. By recognizing these warning signs, caregivers can intervene early and help the child navigate their emotions before a full-blown tantrum occurs.
Noticing triggers or patterns in a child’s tantrum behavior can provide valuable insights into their emotional needs. Caregivers should pay attention to specific situations or circumstances that consistently precede tantrums. By identifying these triggers, caregivers can take proactive steps to prevent or minimize tantrum behavior.
Understanding an individual child’s temperament is essential in managing tantrum behavior effectively. Each child is unique and may have different triggers or responses to emotional stimulation. Caregivers should be sensitive to their child’s temperament and adjust their approach accordingly, taking into account factors such as sensitivity, adaptability, and intensity of emotions.
Addressing underlying issues is important in preventing tantrum behavior. Sometimes, tantrums can be a manifestation of unmet needs or unresolved emotional distress. Caregivers should be supportive and attentive to their child’s feelings, providing comfort and reassurance when needed. By addressing underlying issues, caregivers can help reduce the likelihood of tantrums occurring.
Preventing Overstimulation
Creating a calm and predictable environment is important in preventing overstimulation. By establishing a consistent routine and minimizing sudden changes or disruptions, children feel more secure and less overwhelmed. Consistency and predictability provide a sense of stability that can help reduce tantrum behavior.
Limiting sensory overload is essential in preventing tantrums triggered by overwhelming stimuli. Caregivers can create a soothing environment by reducing clutter, dimming lights, and minimizing loud noises. Providing a designated quiet space where children can retreat when they feel overstimulated can also be helpful.
Providing opportunities for downtime is crucial in preventing overstimulation. Children need breaks from stimulating activities to recharge and relax. Quiet activities such as reading, coloring, or listening to calming music can help children decompress and avoid becoming overwhelmed.
Limiting exposure to loud noises or crowded places can help prevent tantrum behavior. Noisy environments or crowded situations can often overstimulate a child, leading to heightened emotions. Caregivers should be mindful of the child’s comfort level and adjust their surroundings or activities accordingly.
Promoting Effective Communication
Encouraging active listening is a fundamental aspect of effective communication. Caregivers should give their full attention when children express their thoughts and feelings. This demonstrates respect and validates their emotions, fostering a positive and supportive environment.
Teaching children effective communication skills helps them express themselves in non-confrontational ways. Caregivers can model and encourage the use of “I” statements, which promote ownership and responsibility for one’s feelings. Additionally, teaching children to use appropriate words to describe their emotions can help them communicate their needs more effectively.
Providing opportunities for expression is important in promoting effective communication. Children should feel encouraged to share their thoughts, ideas, and concerns without fear of judgment or criticism. By creating a safe space for open expression, caregivers foster trust and nurture healthy communication.
Modeling respectful dialogue is crucial in promoting effective communication. Caregivers should be mindful of their tone and language choices when engaging in conversations with children. By modeling respectful and constructive communication, caregivers inspire children to follow suit and resolve conflicts in a positive manner.
Managing Expectations
Understanding age-appropriate behavior is essential for managing expectations. It is important to recognize that young children are still learning and developing the skills necessary to regulate their emotions effectively. Setting unrealistic expectations can lead to frustration and increase the likelihood of tantrums.
Avoiding overreaction or punishment is important in managing expectations. It is natural for children to make mistakes and exhibit challenging behaviors as they learn and grow. Instead of reacting with anger or punishment, caregivers should approach these situations with patience and understanding. Offering guidance and support helps children learn from their mistakes and encourages growth.
Setting realistic goals is crucial in managing expectations and preventing tantrums. Caregivers should consider a child’s age, abilities, and developmental stage when setting expectations. By setting achievable goals, children experience success and gain confidence, reducing the likelihood of tantrum behavior.
Encouraging growth and progress is an important aspect of managing expectations. Instead of focusing solely on the end result, caregivers should celebrate and acknowledge the effort and improvement made by the child. Positive reinforcement and encouragement motivate children to continue working towards their goals.
Seeking Support and Professional Help
Consulting with pediatricians or therapists can provide valuable insights and guidance in managing temper tantrums. These professionals can help determine whether a child’s tantrum behavior is within the normal range or if there may be underlying developmental or emotional issues. They can also offer strategies and interventions tailored to the specific needs of the child.
Connecting with parenting support groups can be a valuable source of comfort and advice for caregivers. These groups provide an opportunity to share experiences and learn from others who may have faced similar challenges. The support and understanding received from peers can help caregivers navigate the complex emotions associated with tantrum behavior.
Seeking professional guidance if needed is crucial in ensuring the well-being of both the child and the caregiver. If tantrum behavior becomes frequent, intense, or significantly impacts the child’s daily life, it may be necessary to seek professional help. Mental health professionals specializing in child behavior can provide comprehensive assessments and recommend appropriate interventions.
Identifying resources for assistance is important for caregivers who may need additional support. Local community centers, schools, and educational institutions often offer workshops or programs aimed at supporting parents in managing challenging behaviors. Caregivers should explore available resources and take advantage of the support networks available to them.
In conclusion, understanding temper tantrums and implementing strategies to prevent and manage them can greatly improve the well-being of both children and caregivers. By creating a positive environment, teaching emotional regulation, employing effective discipline techniques, promoting healthy lifestyle habits, recognizing warning signs, preventing overstimulation, promoting effective communication, managing expectations, and seeking support when necessary, caregivers can help children navigate their emotions in a healthy and constructive manner. With patience, understanding, and consistent effort, tantrums can become less frequent and less intense, allowing both children and caregivers to enjoy happier and more peaceful experiences.