If you want to avoid experiencing a TIA, or Transient Ischemic Attack, then keep reading! This short article will provide you with some simple yet effective tips to prevent this temporary interruption in the blood flow to your brain. By following these strategies, you can greatly reduce your risk of experiencing a TIA and help ensure your overall brain health. So let’s jump right in and learn how to keep those TIAs at bay!
Understanding TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack
Definition of TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack
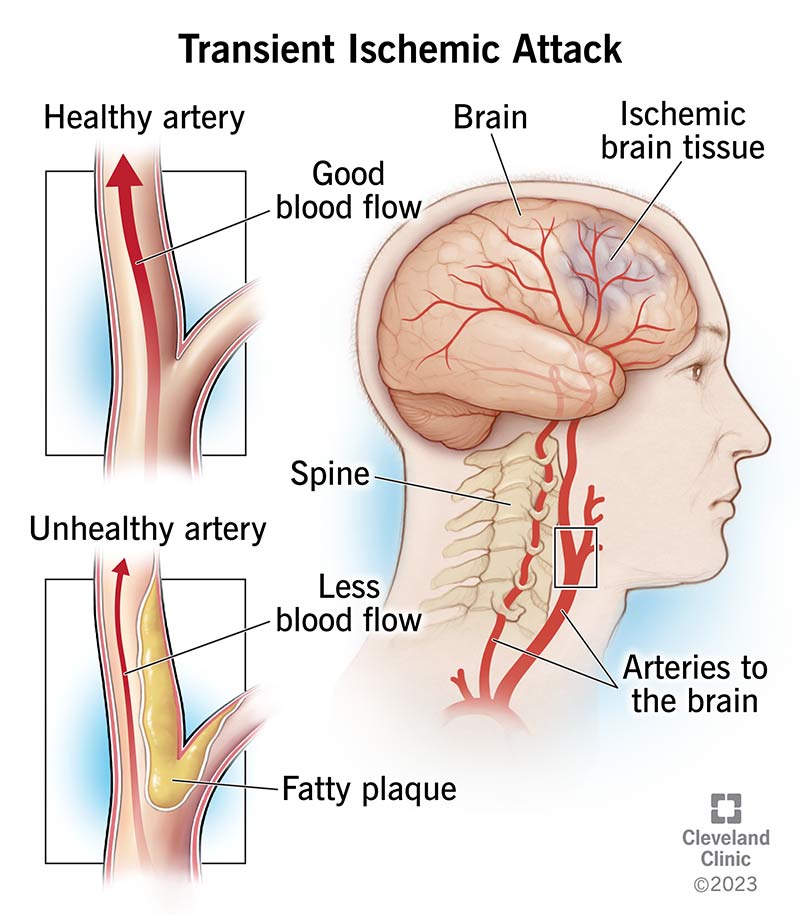
A TIA, or transient ischemic attack, is often referred to as a “mini-stroke.” It occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is temporarily blocked, leading to a temporary disruption in brain function. Unlike a stroke, which causes permanent damage, a TIA typically resolves within 24 hours. However, it is essential to recognize and take TIA episodes seriously, as they can be warning signs of an impending stroke.
Causes of TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack
The most common cause of a TIA is a blood clot or atherosclerosis, which narrows or blocks the blood vessels supplying the brain. Other underlying conditions, such as atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat), carotid artery disease, or diabetes, can also increase the risk of developing TIAs. Lifestyle factors, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and sedentary behavior, can contribute to the development of TIAs as well.
Symptoms of TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack
TIA symptoms may vary depending on which part of the brain is affected, but they generally come on suddenly and resolve within minutes to hours. Common symptoms include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech or difficulty understanding others, vision disturbances, dizziness, and severe headache. It is crucial to recognize and seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt treatment can prevent a more severe stroke.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack
Adopting a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet plays a significant role in reducing the risk of TIAs. Aim to include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Minimize the consumption of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Opt for heart-healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Additionally, limit your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages, as they can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of TIA.
Maintaining an Active Lifestyle
Regular physical activity is crucial for preventing TIAs. Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, each week. Additionally, incorporate strength training exercises to improve muscle tone and stamina. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts to avoid injuries. Being physically active not only reduces the risk of TIAs but also promotes overall cardiovascular health.
Quitting Smoking
Smoking significantly increases the risk of TIAs and strokes. The toxic chemicals in cigarettes damage blood vessels, decrease oxygen supply to the brain, and promote the formation of blood clots. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to prevent TIAs. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, or use nicotine replacement therapy if needed. Your lungs and your brain will thank you for it!
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some heart benefits, excessive alcohol intake can increase the risk of TIAs. Stick to the recommended guidelines, which advise no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. If you are struggling to control your alcohol consumption or suspect that you may have an alcohol problem, seek help from healthcare professionals or support groups. Reduce the intake of alcohol to protect your brain health.
Managing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can take a toll on both physical and mental health, increasing the risk of various medical conditions, including TIAs. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that help you relax. It is crucial to identify the sources of stress in your life and find healthy ways to cope with them. Remember, taking care of your mental well-being is just as important as taking steps to prevent TIAs.

Medical Interventions for TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack Prevention
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like apixaban or rivaroxaban, may be prescribed to individuals at high risk of developing blood clots. These medications work by thinning the blood and reducing its ability to clot, thus preventing the formation of clots that can lead to TIAs. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor the dosage and ensure the medication’s effectiveness and safety.
Antiplatelet Medications
Antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin, clopidogrel, or ticagrelor, are commonly prescribed to prevent TIAs. These medications help prevent blood cells from sticking together and forming clots. Aspirin is frequently recommended for individuals who have experienced TIAs or strokes, while other antiplatelet medications may be used in specific cases. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate medication based on your medical history and risk factors.
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing plaque build-up from the carotid arteries, the major blood vessels supplying the brain. Plaque build-up narrows the arteries and increases the risk of TIAs and strokes. This procedure aims to restore blood flow and reduce the risk of future TIAs and strokes. It is typically recommended for individuals with significant carotid artery disease and those who have experienced TIAs or strokes caused by carotid artery blockage.
Angioplasty and Stenting
Angioplasty and stenting are minimally invasive procedures used to treat narrowed or blocked blood vessels. A catheter with a balloon on its tip is inserted into the affected artery and inflated, opening up the narrowed area. A stent, a small wire mesh tube, is often placed to help keep the artery open. These procedures are commonly used to treat carotid artery disease and can help reduce the risk of TIAs and strokes by improving blood flow to the brain.
Surgery to Repair Aneurysms
If you have an aneurysm, a bulge in the blood vessel wall caused by a weakened spot, your healthcare provider may recommend surgery to repair it and prevent its rupture. The specific technique used depends on the size and location of the aneurysm. Surgery can involve placing a clip around the neck of the aneurysm to isolate it from the circulation or inserting tiny metal coils into the aneurysm to promote blood clot formation and subsequent healing. Treating aneurysms promptly is essential in preventing TIAs and potentially life-threatening strokes.
Controlling Underlying Medical Conditions
Management of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for TIAs and strokes. It is crucial to monitor and manage your blood pressure to prevent the occurrence of TIAs. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by adopting a low sodium, heart-healthy diet, reducing stress levels, and engaging in regular physical activity. Medications prescribed by your healthcare provider may also be necessary to control blood pressure effectively.
Control of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to various complications, including an increased risk of TIAs and strokes. It is essential to manage your blood sugar levels through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Monitor your blood sugar regularly and work closely with your healthcare team to maintain stable glucose levels and reduce your risk of TIAs.
Treatment of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol levels contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a major cause of TIAs. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. Adopt a heart-healthy diet, low in saturated and trans fats, and high in fiber-rich foods. Regular physical activity and medications, such as statins, may also be necessary to control cholesterol levels effectively.
Addressing Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is an irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots forming in the heart. If these clots travel to the brain, they can cause TIAs or strokes. It is essential to manage AFib through medication, such as anticoagulants, and lifestyle changes, including avoiding triggers like excessive caffeine or alcohol and managing stress levels. Regular monitoring and follow-up with your healthcare provider are crucial in preventing TIAs related to AFib.
Managing Obesity
Obesity increases the risk of developing various medical conditions, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol – all risk factors for TIAs. Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity are key to managing and maintaining a healthy weight. Consider working with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or a weight management specialist, to develop a personalized plan that suits your needs and goals.

Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Routine Medical Examinations
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for the early detection and management of underlying medical conditions. During these visits, your healthcare provider will assess your overall health, measure your blood pressure, and order necessary laboratory tests to monitor your cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Routine medical examinations allow for the identification of potential risk factors or warning signs of TIAs, giving you the chance to take proactive steps in preventing their occurrence.
Monitoring Blood Pressure
Monitoring your blood pressure regularly at home can provide valuable insight into your cardiovascular health. Invest in a reliable blood pressure monitor and learn how to accurately measure your blood pressure. Keep a record and share the results with your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments. By staying on top of your blood pressure, you can make informed decisions regarding lifestyle changes or adjustments to medications.
Regular Blood Tests for Lipid Profile
A lipid profile is a blood test that measures various components of cholesterol and fats in your bloodstream. Regular monitoring of your lipid profile helps assess your cardiovascular risk and provides valuable information for managing cholesterol levels. Your healthcare provider may recommend periodic lipid profile testing to monitor the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medications prescribed to control cholesterol.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Holter Monitoring
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of your heart. It helps identify irregular heart rhythms, including AFib, which can contribute to the development of TIAs. Holter monitoring involves wearing a portable ECG device for a period of time, usually 24-48 hours, to record your heart’s activity during normal daily activities. These tests are essential in diagnosing and monitoring cardiac conditions that may increase the risk of TIAs.
Carotid Ultrasound or Doppler Study
Carotid ultrasound or Doppler study uses ultrasound waves to create images of the carotid arteries and assess blood flow. This non-invasive test can detect narrowing or blockages that could increase the risk of TIAs. Your healthcare provider may recommend this study if you have risk factors for carotid artery disease or have experienced TIAs. Regular monitoring can help detect changes in the carotid arteries and guide interventions to reduce the risk of future TIAs.
Staying Informed and Educated
Understanding the Risk Factors
Knowledge is power when it comes to preventing TIAs. Educate yourself about the risk factors associated with TIAs, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Understanding your personal risk factors enables you to take appropriate actions to minimize their impact and reduce the likelihood of TIAs occurring.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Familiarize yourself with the warning signs of TIAs, such as sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, vision changes, and severe headache. Prompt recognition of these symptoms allows for immediate medical attention, which can prevent a more severe stroke. Share this knowledge with your loved ones, as their awareness can also contribute to timely interventions.
Learning About Prevention Methods
Keep yourself up-to-date with the latest information on TIA prevention. Stay informed about healthy lifestyle habits, medical interventions, and management of underlying medical conditions. Reliable sources, such as reputable medical websites, healthcare professionals, and scientific journals, can provide valuable insights into the most effective prevention methods. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health and take proactive steps to prevent TIAs.
Staying Up-to-Date with Medical Research
Medical research continually advances our understanding of TIAs and their prevention. Regularly check trusted medical publications and websites to stay updated on the latest studies and findings in the field of TIA prevention. Understanding the current research landscape can help guide your discussions with healthcare providers and enable you to make informed decisions regarding prevention strategies.
Discussing with Healthcare Providers
Open communication with your healthcare providers is vital in preventing TIAs. Consult with them regularly, discussing any concerns, questions, or changes in symptoms you may experience. Share your family medical history, medication information, and lifestyle habits to allow healthcare professionals to provide personalized advice and interventions. Remember that your healthcare providers are your partners in maintaining optimum health and preventing TIAs.

Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Importance of Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preventing TIAs and improving overall cardiovascular health. Excess weight increases the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and other TIA risk factors. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, you can significantly reduce these risks and enhance your overall well-being.
Setting Realistic Weight Loss Goals
If you are overweight or obese, setting realistic weight loss goals is essential. Aim to lose weight gradually, aiming for a sustainable weight loss of about 1-2 pounds per week. Crash diets or extreme weight loss measures can be detrimental to your health and make it harder to maintain your weight in the long term. It is important to focus on making permanent lifestyle changes rather than pursuing short-term fixes.
Adopting Healthy Eating Habits
A healthy, balanced diet is essential for weight management. Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages high in added sugars. Practice portion control and mindful eating to avoid overeating. Remember, a healthy diet is not a temporary solution but a lifelong commitment to your well-being.
Incorporating Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is a key component of weight management. Engage in a variety of exercises to improve cardiovascular fitness, strength, and flexibility. Find activities that you enjoy, such as walking, biking, dancing, or swimming, and strive to engage in them at least 150 minutes per week. Consider incorporating strength training exercises to help build muscle and increase your metabolic rate, which aids in weight management.
Seeking Professional Advice and Support
Weight management can be challenging, and seeking professional advice and support can increase your chances of success. Consult with a registered dietitian or a weight management specialist who can help tailor a personalized plan to meet your specific needs and goals. They can provide guidance, monitor your progress, and offer support throughout your weight loss journey.
Reducing Alcohol Consumption
Understanding Alcohol and TIA Risk
Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly increase the risk of developing TIAs. Alcohol affects blood clotting, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, all of which can contribute to the formation of blood clots and the development of TIAs. By reducing alcohol consumption, you can lower your TIA risk and promote better overall brain and cardiovascular health.
Recommended Guidelines for Alcohol Intake
To reduce the risk of TIAs and other health problems, it is important to follow recommended guidelines for alcohol intake. These guidelines recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. It is important to note that these guidelines refer to standard drink sizes and vary depending on the type of beverage.
Identifying Problematic Drinking Patterns
If you suspect that your alcohol consumption is problematic or impacting your health, it is important to identify and address the issue. Signs of problematic drinking include an inability to control or limit alcohol intake, neglecting responsibilities due to alcohol use, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking, or a preoccupation with alcohol. Recognizing these signs and seeking help from healthcare professionals or support groups is crucial in reducing TIA risk and promoting overall well-being.
Seeking Help for Alcohol Abuse
If you are struggling with alcohol abuse, it is important to seek professional help. Healthcare providers, addiction specialists, and support groups can provide guidance and support in overcoming alcohol dependence. They can help you develop strategies to manage cravings, cope with triggers, and establish a healthier relationship with alcohol. Addressing alcohol abuse is essential in reducing the risk of TIAs and improving your overall quality of life.
Alternative Strategies for Socializing
Reducing alcohol consumption does not mean giving up socializing. There are various alternative strategies for enjoying social activities without relying on alcohol. Consider engaging in group fitness classes, joining hobby clubs, volunteering in your community, or participating in outdoor activities with friends and family. These alternative approaches not only provide opportunities for social interaction but also promote a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle.

Controlling High Blood Pressure
Effects of High Blood Pressure on TIA Risk
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for TIAs. It damages blood vessels, increases the risk of blood clots, and puts strain on the heart, making it more susceptible to strokes. Controlling high blood pressure is crucial in reducing the risk of TIAs and maintaining overall cardiovascular health.
Monitoring Blood Pressure Regularly
Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is essential in managing hypertension effectively. Invest in a home blood pressure monitor and learn how to use it correctly. Measure your blood pressure regularly, keeping a record of the results. Share these records with your healthcare provider for evaluation and to guide medication adjustments or lifestyle modifications.
Adopting a Low Sodium Diet
Excessive sodium intake contributes to high blood pressure. Adopting a low sodium diet can help manage hypertension and reduce the risk of TIAs. Minimize your consumption of processed and packaged foods, as they are often high in sodium. Instead, choose fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Flavor your dishes with herbs, spices, and other sodium-free seasonings.
Reducing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can raise blood pressure levels, increasing the risk of TIAs. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy. Prioritize self-care and find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. By managing stress effectively, you can promote better blood pressure control and reduce the risk of TIAs.
Taking Medications as Prescribed
If you have been prescribed medication to control high blood pressure, it is important to take it as directed by your healthcare provider. Adhering to your prescribed medication regimen helps maintain stable blood pressure levels and reduces the risk of TIAs. If you have concerns about your medication or are experiencing side effects, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss potential adjustments or alternative options.
Conclusion
Summary of TIA-Transient Ischemic Attack Prevention Methods
Preventing TIAs requires a comprehensive approach that involves making lifestyle changes, managing underlying medical conditions, and seeking medical interventions when necessary. By adopting a healthy diet, maintaining an active lifestyle, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress levels, and monitoring underlying medical conditions, you can significantly reduce the risk of TIAs and their potentially severe consequences.
Importance of Early Recognition and Action
Early recognition of TIA symptoms is crucial in preventing further brain damage and more severe strokes. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden weakness, numbness, vision changes, or difficulty speaking. Recognizing the warning signs and taking quick action can save lives and improve outcomes.
Empowerment Through Knowledge and Lifestyle Changes
Educating yourself about TIA risk factors, prevention methods, and available medical interventions empowers you to make informed decisions and take control of your health. By implementing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, being physically active, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can significantly reduce your risk of TIAs and promote better overall well-being.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and monitoring are vital in preventing TIAs. Routine examinations, blood pressure measurements, blood tests for lipid profile, electrocardiograms, carotid ultrasounds, and discussions with healthcare providers help detect potential risk factors or warning signs early on. Regular monitoring enables healthcare professionals to provide personalized advice, interventions, and follow-up care, contributing to the prevention of TIAs.
In conclusion, preventing TIAs involves a proactive approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, management of underlying medical conditions, and regular monitoring. By adopting healthy habits, staying informed, seeking medical interventions when necessary, and maintaining a positive relationship with healthcare providers, you can significantly reduce the risk of TIAs and improve your overall health and well-being. Empower yourself through knowledge and take the necessary steps to prevent TIAs. Your brain and your future self will thank you!