If your child has been diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), you may be wondering how to effectively manage their symptoms and provide the support they need. ADHD can present unique challenges for children, but with the right strategies and interventions, it is possible to create a nurturing environment that promotes their growth and development. From implementing structure and routine to utilizing behavioral interventions, this article explores various approaches to managing ADHD in children, empowering you to guide your child towards a successful future.

Understanding Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent symptoms of inattentiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily life, including their academic, social, and emotional well-being.
Definition of ADHD
ADHD is a complex disorder that involves difficulties with executive functions, which are responsible for organizing, planning, and focusing attention. In individuals with ADHD, these functions may not work as efficiently as in those without the disorder. This can result in challenges with paying attention, staying on task, and controlling impulses.
Causes of ADHD
The exact cause of ADHD is still not fully understood. However, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors may contribute to its development. In many cases, there is a genetic predisposition to ADHD, with a higher likelihood of the disorder occurring if a close relative also has it. Other factors, such as prenatal exposure to tobacco smoke, alcohol, or certain medications, may also increase the risk.
Types of ADHD
ADHD can be categorized into three subtypes based on the predominant symptoms:
-
Predominantly Inattentive Presentation: Individuals with this subtype primarily struggle with inattentiveness. They may have difficulty sustaining attention, following instructions, organizing tasks, and frequently lose things.
-
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation: This subtype is characterized by hyperactivity and impulsivity. Individuals may struggle with excessive fidgeting, talking excessively, interrupting others, and difficulty waiting or taking turns.
-
Combined Presentation: This is the most common subtype, where individuals exhibit symptoms of both inattentiveness and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Recognizing the Symptoms of ADHD
Recognizing the symptoms of ADHD is crucial for early identification and appropriate intervention. While it is normal for children to display some level of inattentiveness, hyperactivity, or impulsivity, individuals with ADHD consistently exhibit these behaviors to a greater extent, often leading to impairments in various areas of life.
Common symptoms in children
Children with ADHD may display a range of symptoms, including:
- Inattention: Difficulty maintaining focus, becoming easily distracted, and making careless mistakes.
- Hyperactivity: Constant restlessness, excessive talking, and difficulty staying seated.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, interrupting conversations or games, and lack of patience.
Distinguishing ADHD from typical childhood behavior
It is important to differentiate between typical childhood behavior and symptoms of ADHD, as many children can exhibit similar behaviors at times. What sets ADHD apart is the persistence and intensity of these behaviors, which significantly impact a child’s ability to function in various settings. A diagnosis of ADHD requires that these symptoms be present over an extended period and across different environments.
Potential symptoms in adults
ADHD is not limited to children and can persist into adulthood. In fact, many individuals go undiagnosed until later in life. Adults with ADHD may exhibit symptoms such as forgetfulness, poor time management, impulsivity, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can affect their relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.

Diagnosing ADHD in Children
Early diagnosis is crucial for effectively managing ADHD and promoting optimal development. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a pediatrician or psychiatrist. The diagnostic process includes several steps to ensure accurate identification.
Importance of early diagnosis
Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and support, which can significantly improve a child’s long-term outcomes. By identifying ADHD early on, parents, caregivers, and educators can better understand the child’s needs and provide appropriate strategies and accommodations tailored to their specific challenges.
Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria for ADHD are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), a widely used manual for diagnosing mental health conditions. To be diagnosed with the disorder, a child must meet specific criteria, including the presence of persistent and impairing symptoms that are not better explained by other factors.
Steps in the diagnostic process
The diagnostic process typically involves gathering information from various sources, including parents, teachers, and direct observations of the child. The healthcare professional will assess the child’s behavior, emotional functioning, and academic performance to determine if the symptoms meet the criteria for ADHD. It is essential to rule out other potential causes for the symptoms before making a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment Options for ADHD
ADHD is a manageable condition, and there are various treatment options available to help individuals with the disorder thrive. Treatment plans are often tailored to the specific needs and preferences of each individual, taking into account the severity of symptoms and their impact on daily life.
Behavioral interventions
Behavioral interventions are a fundamental component of ADHD treatment. These strategies aim to modify behaviors, develop self-control, and improve executive functioning skills. Techniques such as behavioral therapy, parent training, and social skills training can be highly effective in reducing symptoms and improving functioning in various settings.
Pharmacological treatment
In some cases, medication may be recommended to help manage the symptoms of ADHD. Stimulant medications, such as Ritalin or Adderall, are commonly prescribed and are known to improve attention and impulse control. Non-stimulant medications, like Strattera, may also be used. The decision to use medication should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional, considering the potential benefits and side effects.
Alternative therapies
In addition to traditional treatments, alternative therapies can complement the management of ADHD symptoms. These may include mindfulness techniques, dietary modifications, and neurofeedback training. While there is limited scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness, some individuals may find these approaches helpful in combination with other interventions.
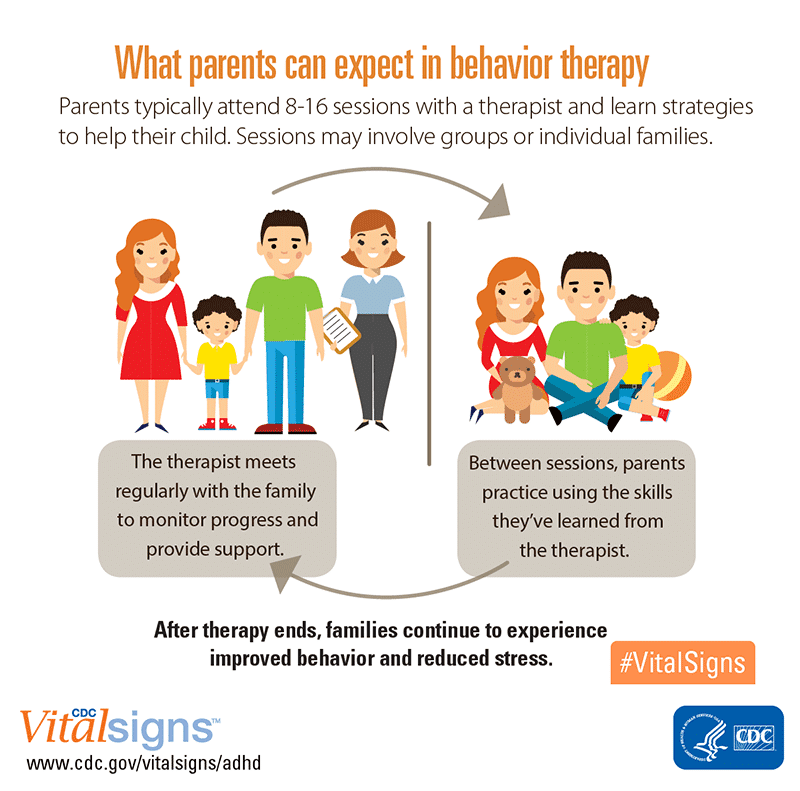
Creating a Supportive Environment
Providing a supportive environment is vital for individuals with ADHD to thrive and reach their full potential. By implementing strategies that promote structure, understanding, and effective communication, caregivers can help individuals with ADHD manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Structured routines and schedules
Individuals with ADHD often benefit from structured routines and schedules. Establishing consistent daily routines helps reduce anxiety and provides a predictable framework for managing tasks and responsibilities. Visual schedules, calendars, and reminders can be useful tools in maintaining structure and promoting organization.
Effective communication strategies
Clear and effective communication is essential when working with individuals with ADHD. Using simple and concise language, providing clear instructions, and allowing time for processing information can enhance understanding and promote successful task completion. Active listening and offering positive reinforcement can also facilitate effective communication and foster a positive relationship.
Establishing clear rules and expectations
Setting up clear rules and expectations is important for individuals with ADHD. Clearly defined rules help establish boundaries and provide a framework for appropriate behavior. Communicate these rules consistently and reinforce them with positive rewards for compliance. Reinforcement systems, such as token economies, can motivate individuals with ADHD to meet expectations and achieve desired outcomes.
Educating and Collaborating with Teachers
Collaboration with teachers is critical for facilitating a supportive learning environment for children with ADHD. By sharing information about the child’s condition and working together to develop effective strategies, teachers can help maximize the child’s academic success and overall well-being.
Informing the school about the child’s condition
Informing the school about a child’s ADHD diagnosis is an essential step in ensuring they receive the necessary support and accommodations. Sharing information about the child’s strengths, challenges, and specific strategies that have been effective can help teachers tailor their approach to meet the child’s needs.
Developing an individualized education plan
In collaboration with the school, parents and teachers can develop an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) for children with ADHD. An IEP outlines the specific accommodations, modifications, and support services that the child requires to access education successfully. This plan ensures that the child receives appropriate academic, behavioral, and emotional support.
Collaborating with teachers for effective classroom strategies
Ongoing communication and collaboration between parents and teachers are crucial for implementing effective classroom strategies for children with ADHD. Teachers can employ strategies such as visual aids, frequent breaks, and flexible seating arrangements to support attention and reduce impulsivity. Regular check-ins and progress monitoring can also help track the child’s development and adjust interventions as needed.

Managing Medication for ADHD
Medication can be an effective tool in managing ADHD symptoms, but it requires careful monitoring and management to ensure optimal outcomes.
Understanding the role of medication
ADHD medications work by balancing brain chemicals involved in attention and impulse control. They can help improve focus, decrease hyperactivity, and enhance self-control. It is essential to understand that medication is just one component of a comprehensive treatment plan and should be used in conjunction with behavioral interventions and supportive strategies.
Types of ADHD medications
The type of medication prescribed for ADHD depends on various factors, including the individual’s age, symptoms, and personal preferences. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, are commonly used and have been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms. Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine and guanfacine, may be prescribed as alternative options or in conjunction with stimulants.
Monitoring and adjusting medication
Finding the right medication and dosage often requires careful monitoring and adjustment. Healthcare professionals typically start with a low dose and gradually increase it to achieve optimal symptom management while minimizing side effects. Regular follow-up appointments allow for necessary adjustments based on the individual’s response to the medication.
Implementing Behavioral Techniques
Behavioral techniques play a crucial role in managing ADHD symptoms and improving overall functioning. These strategies focus on teaching individuals new skills, promoting positive behaviors, and providing support and guidance.
Positive reinforcement and rewards
Positive reinforcement is a highly effective technique for encouraging desired behaviors in individuals with ADHD. Parents, caregivers, and teachers can use rewards, praise, and privileges to reinforce positive behaviors and motivate individuals to meet specific goals. This approach helps build confidence, self-esteem, and a sense of accomplishment.
Teaching organizational and time management skills
Difficulties with organization and time management are common challenges for individuals with ADHD. Teaching strategies such as using planners, breaking tasks into smaller steps, and setting goals can help improve these skills. Visual aids, checklists, and timers are valuable tools in assisting with organization and time management.
Implementing cognitive-behavioral therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on identifying and modifying negative thoughts and behaviors. CBT can help individuals with ADHD develop coping strategies, improve problem-solving skills, and build resilience. It also addresses co-existing conditions, such as anxiety or depression, which are often present in individuals with ADHD.

Supporting Social and Emotional Development
Supporting the social and emotional development of individuals with ADHD is essential for nurturing healthy relationships and overall well-being. By addressing self-esteem, social skills, and emotional challenges, caregivers can help individuals with ADHD navigate interpersonal interactions with confidence.
Building self-esteem and confidence
Individuals with ADHD may struggle with low self-esteem due to the challenges they face. It is crucial to recognize and celebrate their strengths and accomplishments, reinforcing a positive self-image. Encouraging involvement in activities that capitalize on their interests and abilities can further boost self-esteem and confidence.
Developing social skills
Social skills training can be valuable for individuals with ADHD, as they may face difficulties in social interactions. Teaching skills such as active listening, turn-taking, and recognizing social cues can enhance their ability to build and maintain relationships. Role-playing, group activities, and social coaching can provide opportunities for practicing and refining these skills.
Addressing emotional challenges
ADHD can often be accompanied by emotional challenges, such as difficulties regulating emotions, mood swings, or heightened sensitivity. Providing emotional support, teaching coping strategies, and fostering emotional intelligence can help individuals better manage these challenges. Encouraging healthy outlets for emotions, such as journaling, exercise, or artistic expression, can also be beneficial.
Coping Strategies for Parents and Caregivers
Caring for a child with ADHD can be challenging and overwhelming at times. It is essential for parents and caregivers to prioritize their own well-being to effectively support their child.
Seeking support and resources
Finding support is crucial for parents and caregivers of children with ADHD. Connect with local support groups, online communities, or seek professional counseling. Learning more about ADHD through reputable resources, such as books and websites, can also empower parents with knowledge and practical strategies.
Maintaining self-care
Self-care is vital for parents and caregivers to manage stress and maintain their well-being. It is important to prioritize time for relaxation, engage in hobbies or activities that bring joy, and practice self-compassion. Taking care of one’s physical and emotional health allows parents to be more present and effective in supporting their child with ADHD.
Effective stress management techniques
Parents and caregivers of children with ADHD may experience increased stress levels. Implementing stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness practices, can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being. It is also helpful to establish a support network of family and friends who can provide emotional support and practical assistance when needed.
In conclusion, understanding ADHD is crucial for parents, caregivers, educators, and healthcare professionals to provide the necessary support and interventions for individuals with the disorder. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatment approaches are essential steps in helping individuals with ADHD thrive and reach their full potential. With the right strategies, a supportive environment, and ongoing support, individuals with ADHD can successfully navigate their challenges and lead fulfilling lives.