In this article, you will discover valuable tips and strategies for effectively managing juvenile diabetes. Living with diabetes as a young person can present unique challenges, but with the right knowledge and support, you can navigate this condition with confidence. From understanding blood sugar control to incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, this guide will provide practical advice to help you maintain your well-being and thrive in your daily life. Let’s explore the essential strategies for managing juvenile diabetes together.

Understanding Juvenile Diabetes
What is juvenile diabetes?
Juvenile diabetes, also known as type 1 diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little to no insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose from the bloodstream to enter the cells and provide them with energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Juvenile diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, adolescents, and young adults, but it can affect individuals of any age.
Causes of juvenile diabetes
The exact cause of juvenile diabetes is still unknown. However, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that individuals with certain genetic markers are more susceptible to developing the condition. Furthermore, exposure to certain viruses or other environmental triggers may trigger an autoimmune response, causing the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack and destroy the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
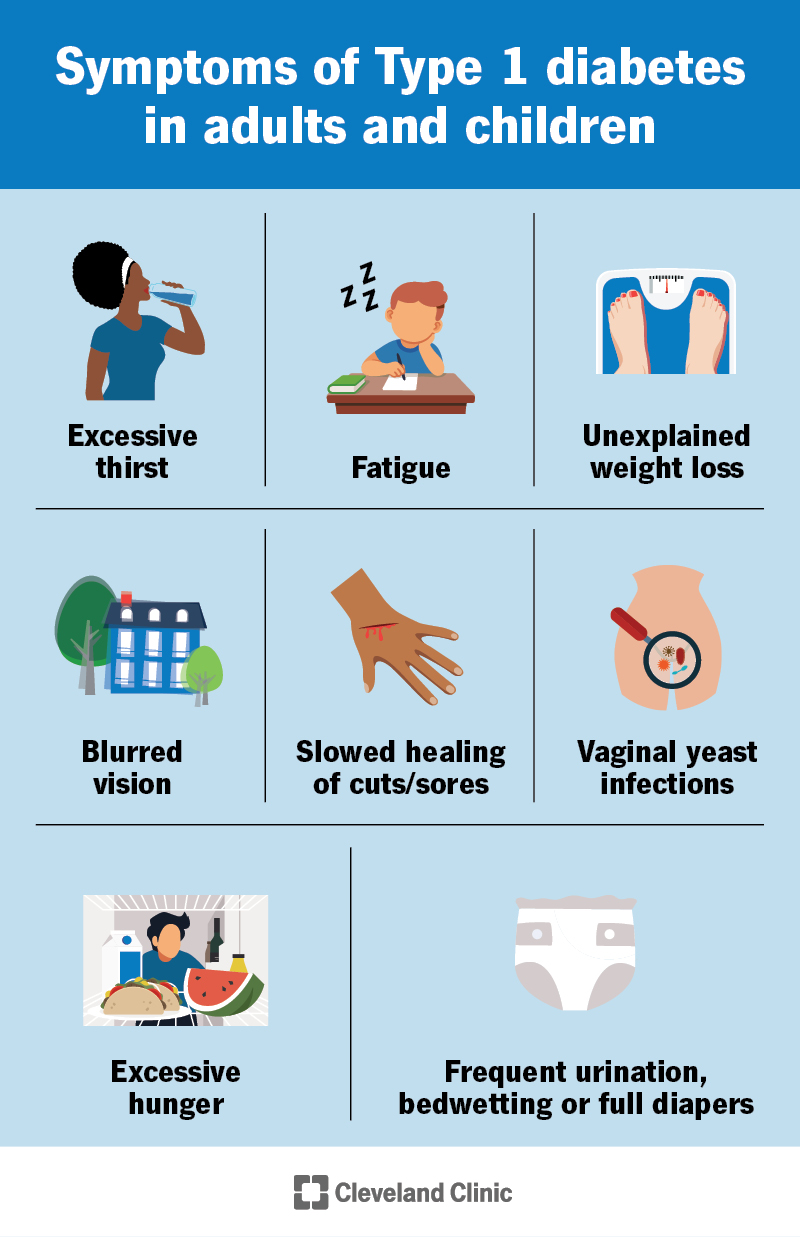
Symptoms of juvenile diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of juvenile diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, constant hunger, fatigue, irritability, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores or infections. Since these symptoms can be easily overlooked or attributed to other causes, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you or your child experience these signs.
Diagnosing juvenile diabetes
To diagnose juvenile diabetes, healthcare professionals typically perform a series of tests. The most common test is the blood glucose test, which measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in the bloodstream. A fasting plasma glucose test may be conducted after an overnight fast, and an oral glucose tolerance test may be performed to assess the body’s ability to process glucose. Additionally, a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) test provides an indication of the average blood sugar levels over the past few months. These diagnostic tests, along with a thorough medical history review, help in accurately diagnosing juvenile diabetes.
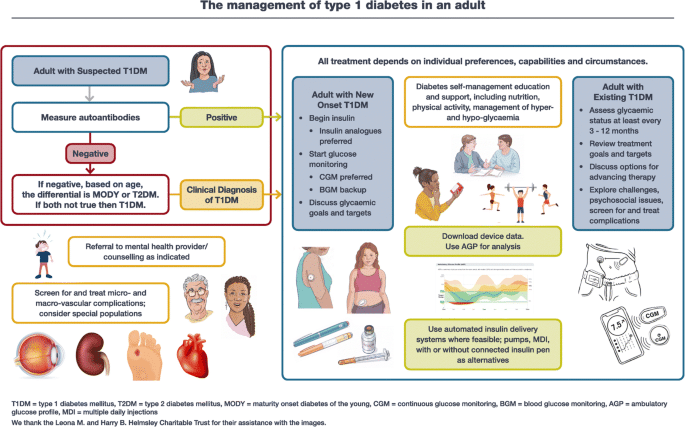
Medical Management of Juvenile Diabetes
Role of insulin in managing juvenile diabetes
Insulin plays a crucial role in managing juvenile diabetes. Since the body does not produce enough insulin, individuals with type 1 diabetes require external insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. Insulin can be administered through multiple daily injections or by using an insulin pump. It is important to work closely with a healthcare team to determine the appropriate insulin dosage and delivery method for effective blood sugar control.
Monitoring blood glucose levels
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for managing juvenile diabetes. This involves using a blood glucose meter to measure the amount of sugar in the blood. The frequency at which blood glucose levels should be checked may vary depending on individual needs and treatment plans. Tracking blood glucose levels helps individuals make necessary adjustments to their insulin dosages, diet, and lifestyle to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Managing hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar levels, which can occur if too much insulin is administered, meals are delayed or skipped, or excessive physical activity is undertaken. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, confusion, dizziness, sweating, and fatigue. Treating hypoglycemia involves consuming a source of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juice, or candy.
Conversely, hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels. This occurs when too little insulin is administered, meals are not properly balanced with insulin dosage, or during periods of illness or stress. Symptoms of hyperglycemia include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. The correction of hyperglycemia involves adjusting insulin doses, consuming adequate fluids, and adhering to a healthy eating plan.
Long-term complications and management strategies
Managing juvenile diabetes also involves addressing long-term complications that may arise from chronic high blood sugar levels. These complications can affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular system. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are crucial to monitor and manage any potential complications. Furthermore, individuals with juvenile diabetes need to prioritize their overall health by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and receiving appropriate preventive care.

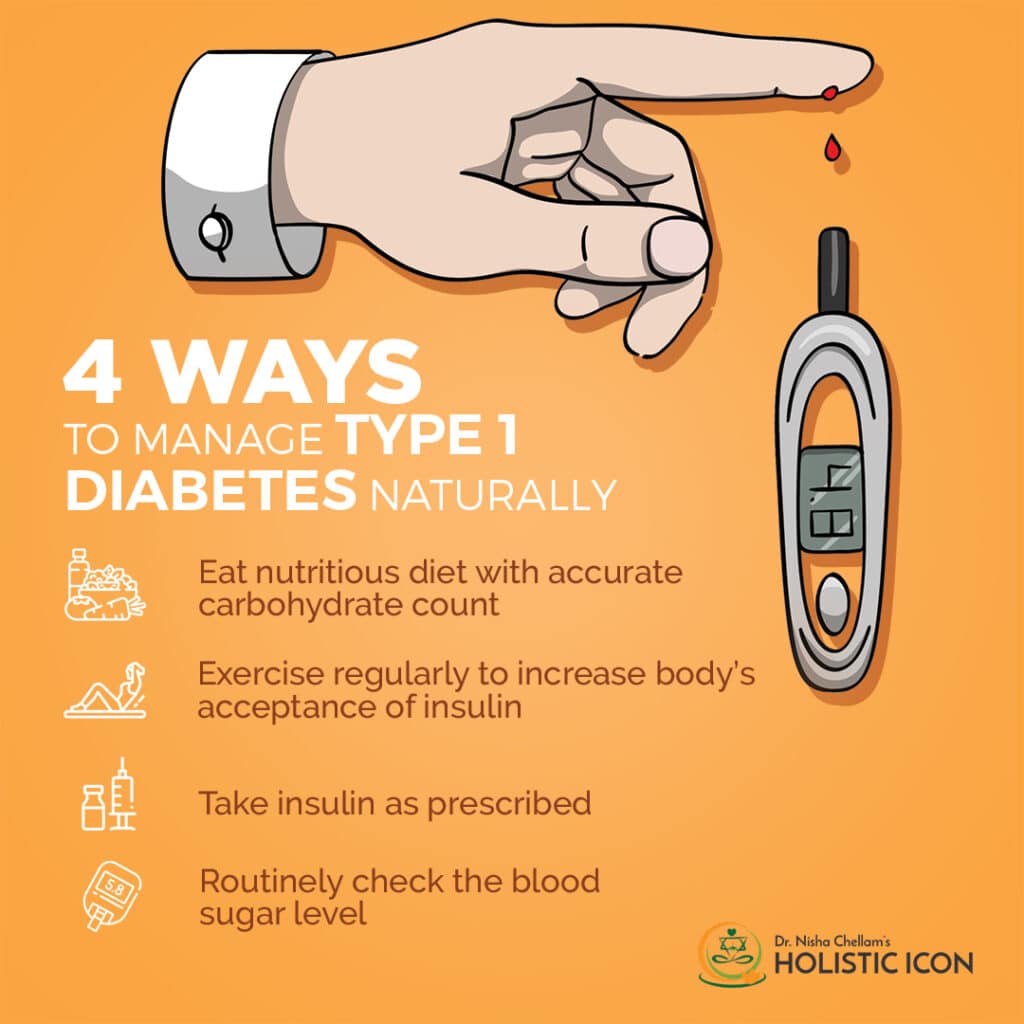
Nutritional Management of Juvenile Diabetes
Importance of balanced diet for juvenile diabetics
Maintaining a balanced diet is vital for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with juvenile diabetes. A balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar by providing a steady supply of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates, in particular, have the most significant impact on blood sugar, so managing carbohydrate intake is a key aspect of nutritional management.
Carbohydrate counting and meal planning
Carbohydrate counting is a widely used method in nutritional management for juvenile diabetes. It involves estimating the amount of carbohydrates in a specific food or meal and adjusting insulin dosage accordingly. Individuals with juvenile diabetes can work with a registered dietitian to learn effective carbohydrate counting techniques and create a personalized meal plan that aligns with their insulin regimen and activity levels.
Choosing the right foods
When it comes to food choices, it is essential for individuals with juvenile diabetes to focus on nutrient-dense options. This includes incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into their meals and snacks. Avoiding sugary beverages, highly processed foods, and excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats is important for maintaining optimal blood sugar control and overall health.
Benefits of regular exercise
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with juvenile diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, promotes weight management, reduces cardiovascular risk factors, and enhances overall well-being. It is important to engage in both aerobic exercise and strength training, but it is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia.
Psychological aspects of Juvenile Diabetes management
Impact of juvenile diabetes on mental health
Managing juvenile diabetes involves addressing the psychological aspects associated with the condition. The daily demands of monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medication, and adhering to a strict diet can have a significant emotional and psychological impact, especially on young individuals. Stress, anxiety, depression, and a negative body image are common among those with juvenile diabetes. It is important to acknowledge and address these emotional challenges to promote overall well-being.
Educating and involving the child in self-care
Providing comprehensive education about diabetes management is crucial for empowering children with juvenile diabetes to take an active role in their self-care. Educating children about the importance of blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, and healthy lifestyle choices helps them understand the impact of their actions on their health. Involving children in decision-making processes and setting achievable goals can boost their confidence and sense of control over their condition.
Supporting the emotional well-being of the child
Supporting the emotional well-being of a child with juvenile diabetes involves creating an open and supportive environment where they feel safe discussing their feelings and concerns. Encouraging open communication, actively listening to their experiences, and providing emotional support can help alleviate stress and anxiety. Additionally, connecting with support groups, counseling services, or mental health professionals can offer valuable resources and guidance for both the child and their family.
Coping with diabetes-related stress
Living with juvenile diabetes can sometimes be challenging and stressful, but there are various coping strategies that can help manage stress and maintain a positive outlook. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can provide a sense of relaxation and relief. Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can also provide a valuable source of encouragement and understanding during difficult times.
Managing Juvenile Diabetes at School
Creating an individualized diabetes management plan
Managing juvenile diabetes at school requires collaboration between parents, healthcare professionals, and school staff. Creating an individualized diabetes management plan is essential to ensure that the child’s specific needs and accommodations are met. This plan should outline the child’s insulin regimen, blood glucose monitoring requirements, meal/snack schedule, emergency action plan, and any other necessary information related to their diabetes management.
Communicating with school staff and teachers
Effective communication with school staff and teachers is vital for ensuring a safe and supportive learning environment for children with juvenile diabetes. Parents or guardians should educate school personnel about their child’s condition, symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and emergency procedures. Sharing a copy of the child’s diabetes management plan and discussing any modifications or adjustments in treatment with the school staff helps them actively participate in the child’s care.
Ensuring proper diabetes care during school hours
To ensure proper diabetes care during school hours, it is essential for the child to have easy access to necessary supplies such as blood glucose meters, insulin, glucose tablets, and snacks. School staff should be trained on how to administer insulin or assist with blood sugar monitoring if needed. Regular communication between parents and school personnel is crucial to stay updated on the child’s health status and make any necessary adjustments to their diabetes management plan.
Addressing social and emotional challenges
Managing juvenile diabetes at school can present social and emotional challenges for children. The fear of being different, exclusion from activities, or facing teasing or bullying can affect a child’s emotional well-being. Encouraging open dialogue, fostering an inclusive school environment, and promoting diabetes education and awareness among peers can help address these challenges. Additionally, implementing anti-bullying policies and providing support through school counselors or support groups can offer valuable resources for children and their families.
Family Support and Juvenile Diabetes
Educating family members about diabetes management
Family support plays a critical role in the successful management of juvenile diabetes. Educating family members about diabetes, its management, and the importance of lifestyle modifications can help create a supportive environment for the child. Explaining the impact of diabetes on daily life and involving family members in the child’s healthcare routine can strengthen their understanding and active participation in diabetes management.
Building a strong support system
Building a strong support system is essential for families navigating the challenges of managing juvenile diabetes. This can involve connecting with other families affected by the condition through support groups, online communities, or local events. Sharing experiences, exchanging information, and seeking advice from individuals who have firsthand knowledge of living with juvenile diabetes can provide invaluable emotional support and practical guidance.
Involving siblings in the care process
Involving siblings in the care process can help them gain a better understanding of their sibling’s condition and foster empathy and support. Educating siblings about diabetes management, encouraging them to participate in blood glucose checks, and involving them in meal planning and healthy lifestyle choices can create a sense of inclusion and teamwork within the family. Siblings can also play a crucial role in providing emotional support and being a source of encouragement for the child with juvenile diabetes.
Managing diabetes-related financial costs
Managing juvenile diabetes may incur various financial costs, including medical expenses, medication, blood glucose monitoring supplies, and healthy food choices. Understanding available insurance coverage, seeking financial assistance programs, and exploring community resources can help alleviate some of the financial burdens. Utilizing cost-saving strategies such as purchasing medications in bulk, choosing generic brands, and meal planning can also contribute to managing diabetes-related expenses.
Advocacy and Resources for Juvenile Diabetes
Connecting with diabetes support organizations
Connecting with diabetes support organizations can provide a wealth of resources, information, and support for families managing juvenile diabetes. Organizations such as JDRF (formerly known as Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation), American Diabetes Association (ADA), Beyond Type 1, and diabetes-specific online communities offer access to educational materials, advocacy opportunities, support hotlines, and local events. Collaborating with these organizations can empower families to become strong advocates for their child’s healthcare needs.
Accessing community resources and programs
Communities often provide various resources and programs for individuals with juvenile diabetes and their families. Local hospitals, clinics, and public health organizations may offer diabetes education classes, support groups, or counseling services. Additionally, community centers or recreational facilities may provide opportunities for children to engage in physical activities and participate in diabetes-friendly programs. Exploring these resources helps families connect with others, gain knowledge, and access valuable support within their own community.
Advocating for diabetes-friendly policies
Advocating for diabetes-friendly policies is another crucial aspect of managing juvenile diabetes. This can involve supporting initiatives that improve access to affordable insulin, promote diabetes education in schools, or raise awareness about the rights and needs of individuals with diabetes. Writing letters to policymakers, participating in advocacy campaigns, or joining local or national organizations dedicated to diabetes awareness can contribute to positive policy changes that benefit the diabetes community.
Staying updated on research and medical advancements
Staying updated on research and medical advancements is important for families managing juvenile diabetes. Research studies and clinical trials constantly explore new treatment options, technologies, and potential cures for diabetes. Subscribing to reputable diabetes journals, attending medical conferences, and consulting with healthcare professionals can help families stay informed about the latest developments in diabetes management, allowing them to make well-informed decisions about their child’s care.
Transitioning to Adulthood with Juvenile Diabetes
Preparing for the transition process
Transitioning from pediatric to adult care can be a significant milestone for individuals with juvenile diabetes. It is important to begin preparing for this transition process well in advance to ensure a smooth and successful transfer of care. This involves discussing the transition with the healthcare team, understanding the differences between pediatric and adult diabetes care, and addressing any concerns or questions about the transition.
Finding appropriate medical care as an adult
Finding appropriate medical care as an adult with juvenile diabetes is crucial for continuity of care. Adult endocrinologists specializing in diabetes management are best suited to oversee the healthcare needs of individuals transitioning from pediatric care. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, seeking referrals, and researching specialized diabetes clinics can help ensure a seamless transition to adult care.
Managing diabetes while pursuing higher education or career
Managing diabetes while pursuing higher education or a career requires careful planning and preparation. This involves coordinating with the school or workplace to ensure necessary accommodations are in place, such as access to blood glucose monitoring supplies, the ability to monitor blood sugar levels discreetly, and flexibility for meals and snacks. Preparing a diabetes management plan, communicating with professors or supervisors, and being proactive in addressing any challenges that may arise helps individuals maintain optimal diabetes control while pursuing their goals.
Maintaining independence and self-care skills
Transitioning to adulthood also involves developing and maintaining independence and self-care skills. This includes taking responsibility for blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, meal planning, and making informed decisions about their healthcare. Building confidence and competence in managing diabetes empowers individuals to take charge of their health and navigate the challenges of daily life as they transition into adulthood.
Emergency Preparedness for Juvenile Diabetes
Creating an emergency action plan
Creating an emergency action plan is essential for individuals with juvenile diabetes and their families. This plan outlines the steps to be taken in case of diabetes-related emergencies. It should include a list of emergency contact numbers, symptoms to watch out for (such as severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis), and appropriate actions to take. Sharing this plan with family members, friends, school staff, and other relevant individuals ensures everyone is prepared to respond effectively in case of an emergency.
Recognizing and treating diabetes emergencies
Recognizing and promptly treating diabetes emergencies is crucial for individuals with juvenile diabetes. Severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) are potential emergencies that require immediate attention. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures, or inability to consume oral carbohydrates. DKA is characterized by high blood sugar, excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting. Knowing how to recognize these emergencies and providing appropriate treatment, such as administering glucagon for severe hypoglycemia or seeking immediate medical care for DKA, can be life-saving.
Ensuring access to medication and supplies
Ensuring access to necessary medication and supplies is crucial to managing diabetes during emergencies. It is important to have an adequate supply of insulin, blood glucose monitoring supplies, and fast-acting sources of glucose readily available. Creating an emergency kit that includes these supplies, along with a list of medications, prescriptions, and important medical information, helps ensure that everything needed is easily accessible during times of crisis.
Communicating with emergency responders
Communicating effectively with emergency responders is essential for individuals with juvenile diabetes. It is important to inform the responders about the individual’s condition, any relevant medical history, and ongoing diabetes management needs. Carrying a medical ID bracelet or card that clearly indicates the person has diabetes can help emergency personnel quickly identify the condition and provide appropriate care. Informing family members and close contacts about the steps to take in case of an emergency also helps ensure the individual’s safety and well-being.
Future Outlook for Juvenile Diabetes Management
Advancements in diabetes technology
The future of juvenile diabetes management holds exciting possibilities with advancements in diabetes technology. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, insulin pumps with automated insulin delivery features, and closed-loop systems are rapidly evolving to provide more accurate and convenient ways to manage blood sugar levels. These advancements aim to minimize the burden of day-to-day diabetes management and improve overall quality of life for individuals with juvenile diabetes.
Promising research on cure and prevention
Ongoing research efforts are focusing on finding a cure for juvenile diabetes or developing preventative strategies. Researchers are exploring ways to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, develop immunotherapies to prevent autoimmunity, and genetically modify cells to produce insulin. While a cure has not yet been found, the progress being made in these areas provides hope for the future of diabetes management.
Impacting policy changes for better management
Efforts to impact policy changes are essential for improving the management of juvenile diabetes. Advocacy organizations and individuals affected by diabetes continue to work towards increasing access to affordable insulin, improving insurance coverage for diabetes supplies and medications, and promoting diabetes education in schools. By influencing policy changes at local, national, and international levels, the diabetes community strives to create a more supportive and equitable environment for individuals with juvenile diabetes.
Improving quality of life for juvenile diabetics
Overall, advancements in diabetes management, increased awareness, and improved support systems are enhancing the quality of life for individuals with juvenile diabetes. By focusing on early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, comprehensive support services, and empowering individuals to actively participate in their own care, the aim is to enable individuals with juvenile diabetes to live life to the fullest, pursue their dreams, and thrive despite the challenges posed by their condition.