Have you ever felt that unpleasant churn in your stomach or a burning sensation in your chest that just won’t go away? If so, you might be dealing with nausea and acid reflux. These two conditions often intertwine, making it crucial to understand how they impact your life and overall well-being.
Understanding Nausea
Nausea is that uneasy feeling you get that often precedes the urge to vomit. It can be a bothersome and disruptive sensation, affecting your daily activities and overall mood. Various factors contribute to nausea, from simple causes like motion sickness to more complex conditions such as gastrointestinal issues or infections.
Common Causes of Nausea
Several conditions can lead to nausea. Understanding these can help you pinpoint potential triggers in your life:
-
Gastroenteritis: An inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often due to a viral infection. This can lead to stomach pain, diarrhea, and of course, nausea.
-
Food Poisoning: Eating contaminated food can lead to a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
-
Migraines: These intense headaches can be accompanied by a feeling of nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
-
Motion Sickness: If you’ve ever felt ill during a car ride or on a boat, you’re familiar with how motion sickness can lead to nausea.
-
Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can manifest physically, leading to feelings of nausea.
Recognizing Symptoms
Besides the primary sensation of nausea, you might also experience several accompanying signs. Here are a few to watch for:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Vomiting | The physical act of expelling stomach content. |
| Sweating | Increased perspiration, often accompanied by pallor. |
| Dizziness | A sensation of light-headedness or spinning. |
| Increased Heart Rate | Feeling your heart racing or pounding in your chest. |
| Loss of Appetite | A decreased desire to eat, often due to discomfort. |
Understanding these symptoms is essential, as they can help you inform your healthcare provider about your condition more accurately.
What is Acid Reflux?
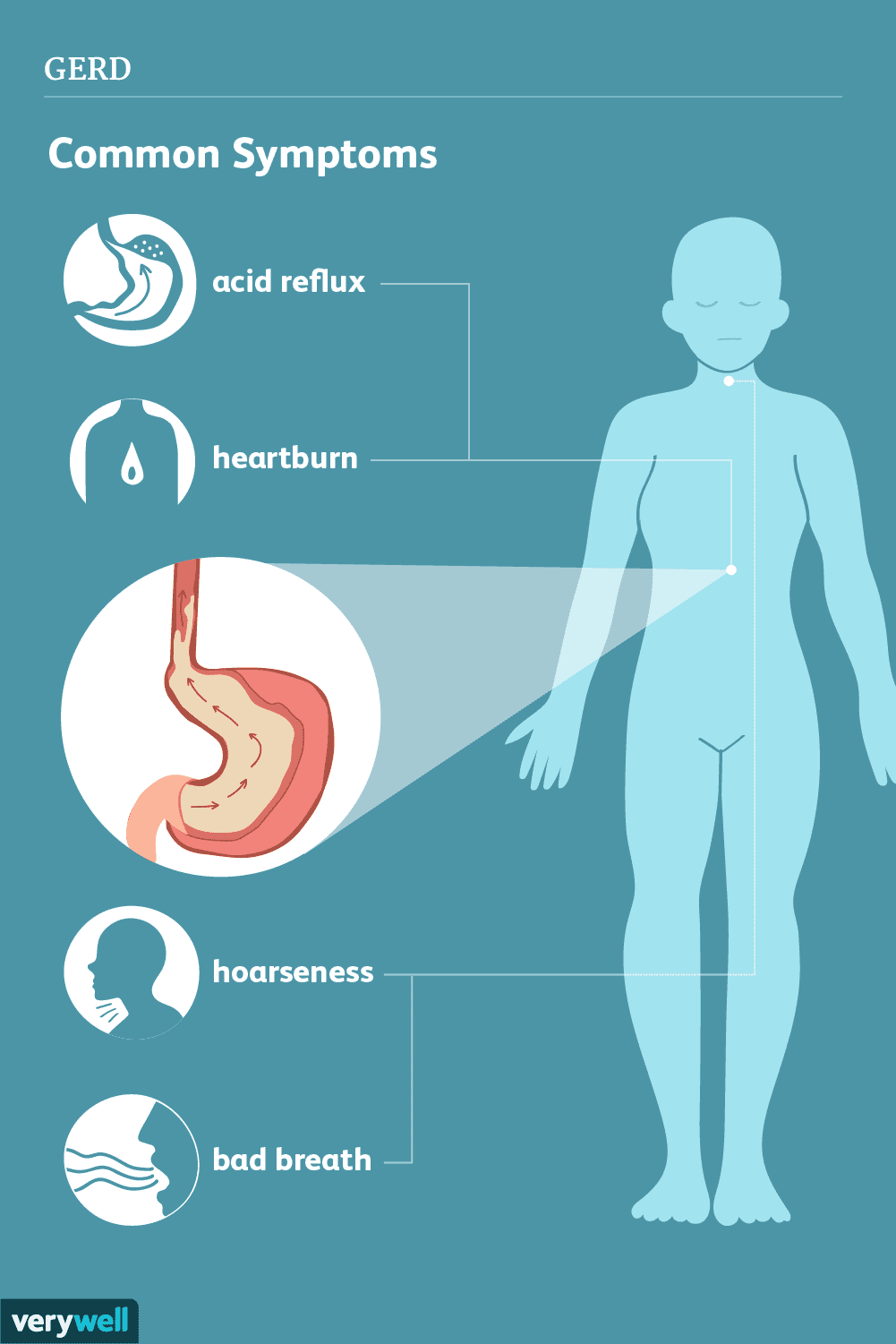
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This backward flow, or reflux, can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms, primarily heartburn.
Causes of Acid Reflux
Several factors can lead to the development of acid reflux. Identifying and addressing these can help you manage symptoms effectively:
-
Weak Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): The LES is a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus. If it’s too weak, it can allow stomach acid to escape.
-
Obesity: Extra weight can increase pressure on your abdomen, pushing stomach contents back up into your esophagus.
-
Hiatal Hernia: This occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm, often exacerbating reflux symptoms.
-
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure can lead to more frequent acid reflux episodes during pregnancy.
-
Certain Foods and Drinks: Spicy foods, caffeine, chocolate, and alcohol are common culprits that can trigger symptoms.
Recognizing Symptoms of Acid Reflux
The symptoms of acid reflux can vary, but they commonly include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Heartburn | A burning sensation in the chest or throat. |
| Regurgitation | The sensation of acid backing up into your throat or mouth. |
| Difficulty Swallowing | A feeling of food being stuck in the throat. |
| Chronic Cough | A persistent cough that may worsen after meals. |
| Sore Throat | Irritation resulting from stomach acid in the esophagus. |
Being aware of these symptoms enables you to take proactive steps in managing them.
The Connection Between Nausea and Acid Reflux
You might be wondering how nausea and acid reflux relate. While they are distinct conditions, they can often occur together. The discomfort caused by acid reflux, especially the sensation of burning in your chest, can lead to feelings of nausea. Conversely, nausea can trigger the urge to vomit, potentially bringing up stomach acid and exacerbating reflux symptoms.
Factors Leading to Both Conditions
A few overlapping factors can lead to the development of both nausea and acid reflux:
-
Diet: Consuming high-fat and spicy foods can stimulate acid production, leading to both symptoms.
-
Obesity: As mentioned earlier, obesity can contribute to acid reflux, further leading to sensations of nausea.
-
Medications: Certain medications can irritate the stomach lining or relax the LES, contributing to both conditions.
-
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking and heavy drinking can worsen the symptoms of acid reflux and lead to feelings of nausea.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Nausea and Acid Reflux
Managing these two conditions often requires lifestyle adjustments. You might find that small changes can lead to significant improvements in your symptoms.
Dietary Modifications
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing nausea and acid reflux:
-
Eat Smaller Meals: Large meals can increase abdominal pressure and contribute to reflux. Opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
-
Identify Trigger Foods: Keep a food journal to track what you eat and when you feel symptoms. Common triggers include spicy foods, citrus, tomatoes, and fried foods.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking clear fluids can help dilute stomach acid. Aim for water or herbal teas, and avoid carbonated beverages that can cause bloating.
Behavioral Adjustments
In addition to dietary changes, consider the following behaviors:
-
Avoid Lying Down After Eating: Wait at least 2-3 hours after meals before lying down to allow time for digestion.
-
Elevate Your Head While Sleeping: Use pillows or an adjustable bed to elevate your upper body, which can help reduce nighttime reflux.
-
Manage Stress: Since stress can exacerbate both conditions, incorporate stress reduction techniques. This could include mindfulness practices, exercises, or hobbies that relax you.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, discussing your symptoms with a healthcare provider is essential. They can recommend further testing or potential medications to help manage your conditions effectively.

Medical Treatments for Nausea and Acid Reflux
If symptoms persist, medical interventions are available. These can include both over-the-counter and prescription medications.
Over-the-Counter Options
-
Antacids: Medications like Tums or Rolaids neutralize stomach acid, providing rapid relief from heartburn and nausea.
-
H2 Blockers: These reduce acid production in the stomach. Common examples include ranitidine (Zantac) and famotidine (Pepcid).
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): For more severe cases, PPIs like omeprazole (Prilosec) can help by blocking acid production over a longer period.
Prescription Medications
If over-the-counter treatments don’t suffice, consult your doctor about prescription options. They may consider stronger H2 blockers or PPIs, depending on your symptoms’ severity and frequency.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While nausea and acid reflux are common conditions that many people experience from time to time, certain signs indicate that you should seek medical attention:
-
Persistent Symptoms: If your symptoms last more than a few days or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
-
Severe Pain: Intense pain in your chest or abdomen could signify a more serious condition and should be evaluated immediately.
-
Signs of Dehydration: If you’re unable to keep food or fluids down, symptoms such as dry mouth, dark urine, and lightheadedness may occur, necessitating immediate medical help.
-
Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss accompanying persistent nausea or acid reflux is a vital warning sign that needs assessment.

Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of nausea and acid reflux can empower you to take control of your health. By recognizing the symptoms, identifying triggers, making lifestyle changes, and seeking medical help when necessary, you can manage these conditions effectively. It’s essential to listen to your body and advocate for your well-being. Whether through dietary adjustments, stress management, or medical treatments, you’re equipped to navigate this path toward feeling better. So take a moment to reflect; you have the power to make positive changes in your life!