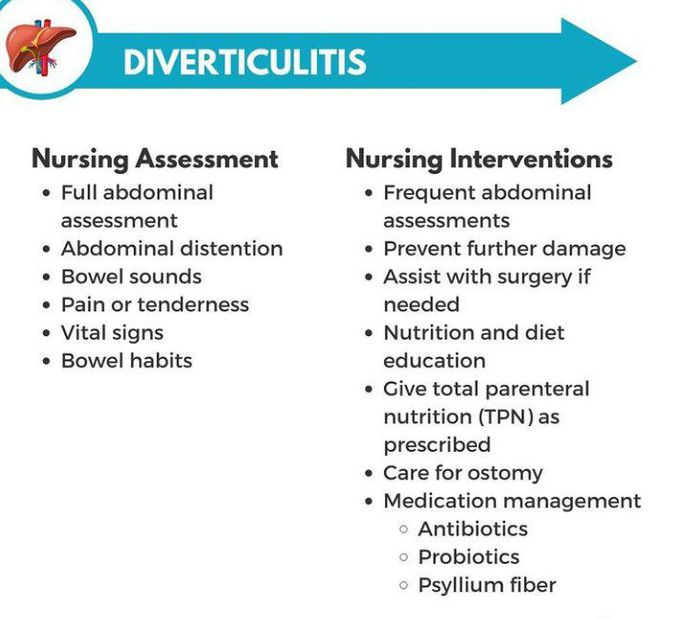
Are you a nurse looking for important information on managing diverticulitis? Look no further! This article provides vital nursing considerations and management strategies for dealing with diverticulitis. From understanding the disease process to implementing effective interventions, we’ve got you covered. So, grab a cup of coffee and get ready to enhance your knowledge on how to best care for patients with diverticulitis. Let’s dive right in!

Assessment and Diagnosis
Collecting patient history
In order to effectively manage and treat diverticulitis, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to collect a thorough patient history. This includes gathering information about the patient’s symptoms, such as abdominal pain, fever, and changes in bowel habits. Additionally, it is important to inquire about any past medical history, particularly related to gastrointestinal disorders or surgeries. By collecting a comprehensive patient history, healthcare providers can gain valuable insight into the individual’s condition and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Performing physical examination
A physical examination plays a crucial role in assessing and diagnosing diverticulitis. During the examination, healthcare professionals will carefully palpate the abdomen to evaluate for tenderness, distention, or the presence of an abdominal mass. They will also listen to the bowel sounds using a stethoscope. Additionally, a thorough examination of the rectal area may be conducted to check for tenderness or the presence of blood in the stool. By performing a comprehensive physical examination, healthcare providers can gather important information to support a diagnosis of diverticulitis.
Ordering diagnostic tests
In order to confirm a diagnosis of diverticulitis and rule out other possible conditions, healthcare providers may order various diagnostic tests. These tests can include blood work to assess for signs of infection or inflammation, such as an elevated white blood cell count. Imaging studies, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, may also be ordered to visualize the affected area of the colon and identify any complications, such as abscesses or perforations. These diagnostic tests play a crucial role in accurately diagnosing diverticulitis and guiding appropriate treatment plans.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Administering analgesics
One of the primary goals in managing diverticulitis is to alleviate pain and discomfort. Healthcare providers may prescribe analgesic medications to help manage the pain experienced by patients. Analgesics, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioid analgesics, can help reduce inflammation and provide relief. It is important for healthcare providers to assess the patient’s pain levels and administer analgesics as prescribed to ensure optimal pain management.
Monitoring pain levels
As part of pain management for diverticulitis, healthcare providers must monitor the patient’s pain levels regularly. This involves assessing the severity of pain, as well as evaluating the effectiveness of analgesic medications. By carefully monitoring pain levels, healthcare providers can make necessary adjustments to the medication regimen, ensuring that patients are experiencing adequate pain relief.
Promoting rest and comfort
Rest and comfort are important aspects of managing diverticulitis. Encouraging patients to rest and avoid strenuous physical activities can help promote healing and reduce the risk of complications. Additionally, providing comfort measures, such as ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment and offering position changes to relieve discomfort, can enhance the overall well-being of patients. By promoting rest and comfort, healthcare providers can contribute to the effective management of diverticulitis.
Implementing Dietary Modifications
Educating patients on a low-fiber diet
Dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing diverticulitis. Healthcare providers should educate patients about following a low-fiber diet during both acute episodes and recovery periods. This involves instructing patients to avoid foods that are high in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits with skin, and raw vegetables. Instead, patients should consume foods that are low in fiber, such as white bread, pasta, and canned fruits or vegetables. By providing education on a low-fiber diet, healthcare providers can help reduce the strain on the colon and alleviate symptoms of diverticulitis.
Promoting fluid intake
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for managing diverticulitis. Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration and soften stools. Encouraging patients to consume water, clear liquids, and low-fiber beverages can help promote adequate hydration. By promoting fluid intake, healthcare providers can support optimal bowel function and enhance overall management of diverticulitis.
Monitoring nutritional status
In order to ensure proper nutrition and support the healing process, healthcare providers should monitor the nutritional status of patients with diverticulitis. This includes assessing for signs of malnutrition or deficiencies. Regular assessment of weight, body mass index (BMI), and albumin levels can help identify any nutritional deficits and guide appropriate interventions, such as dietary supplements or referrals to dietitians. By monitoring nutritional status, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall well-being and recovery of patients with diverticulitis.
Preventing Complications
Monitoring for signs of perforation or abscess
Diverticulitis can sometimes lead to serious complications, such as perforation or abscess formation. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring patients for signs of these complications. This involves regularly assessing the patient’s vital signs, as well as conducting thorough physical examinations to check for signs of infection or peritonitis. Any changes in the patient’s condition, such as worsening abdominal pain, fever, or increased tenderness, should be promptly evaluated and appropriate interventions implemented.
Administering antibiotics as prescribed
In cases of diverticulitis associated with infection, healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. It is crucial for healthcare providers to administer antibiotics as prescribed and closely monitor the patient’s response to the medication. Regular assessment of symptoms and laboratory markers for infection, such as white blood cell count, can help determine the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. By administering antibiotics in a timely manner, healthcare providers can help prevent the progression of infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Ensuring proper wound care for potential surgical interventions
In some cases of severe or complicated diverticulitis, surgical interventions may be necessary. Healthcare providers must ensure proper wound care for patients who undergo surgery. This involves monitoring the surgical incision site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage. Proper wound care techniques, such as dressing changes and sterile techniques, should be implemented to promote healing and prevent complications. By ensuring proper wound care, healthcare providers can contribute to the successful recovery of patients who require surgical interventions.

Administering Medications
Educating patients on prescribed medications
Medication management is an important aspect of diverticulitis management. Healthcare providers should educate patients about the prescribed medications, including their purpose, dosage, and potential side effects. It is crucial for patients to have a clear understanding of their medications to ensure compliance with the prescribed regimen. By providing education on prescribed medications, healthcare providers can help patients feel informed and empowered in their treatment journey.
Monitoring for medication side effects
As patients take prescribed medications for diverticulitis, it is important for healthcare providers to monitor for any potential side effects. Common side effects of medications used to manage diverticulitis include gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Regular assessment and communication with patients can help identify any side effects and allow for timely interventions or adjustments to the medication regimen. By monitoring for medication side effects, healthcare providers can ensure the safe and effective use of medications in diverticulitis management.
Administering prescribed antibiotics
In cases where diverticulitis is associated with an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed by healthcare providers. It is crucial for healthcare providers to administer the prescribed antibiotics according to the prescribed schedule and dosage. This includes providing clear instructions to patients on the proper administration of antibiotics, such as timing and any food restrictions. By administering prescribed antibiotics correctly, healthcare providers can contribute to the successful treatment of diverticulitis.
Assisting with Surgical Interventions
Providing preoperative care
When surgical interventions are deemed necessary for diverticulitis management, healthcare providers play a vital role in providing preoperative care. This can include conducting preoperative assessments, ensuring patients have undergone the necessary preoperative preparations, and addressing any concerns or questions patients may have. Additionally, healthcare providers may collaborate with the surgical team to coordinate the patient’s care plan and optimize their readiness for surgery. By providing thorough preoperative care, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall success of surgical interventions.
Assisting during laparoscopic or open surgery
During surgical interventions for diverticulitis, healthcare providers may be directly involved in assisting the surgical team. This can include providing support in the operating room, ensuring the necessary instruments and equipment are available, and actively participating in the procedure as required. Healthcare providers must be prepared to assist with both laparoscopic and open surgeries, depending on the specific needs of the patient. By actively assisting during surgery, healthcare providers can ensure a smooth and efficient procedure.
Ensuring postoperative care and monitoring
Following surgical interventions for diverticulitis, healthcare providers must ensure comprehensive postoperative care and monitoring. This includes closely monitoring the patient’s vital signs and assessing for any complications, such as postoperative pain, infection, or bowel obstruction. Healthcare providers must also carefully manage the patient’s pain and provide appropriate wound care. Regular follow-up appointments and consultations are crucial to track the patient’s progress and address any concerns or complications that may arise. By ensuring proper postoperative care and monitoring, healthcare providers can support the patient’s recovery and prevent potential complications.

Promoting Bowel Regularity
Educating patients on bowel habits
Promoting bowel regularity is an important aspect of diverticulitis management. Healthcare providers should educate patients on healthy bowel habits, including the importance of regular bowel movements and avoiding constipation. This may involve discussing dietary modifications, such as increasing fiber intake, as well as promoting physical activity and regular exercise. By educating patients on bowel habits, healthcare providers can empower them to actively participate in their own care and maintain optimal bowel regularity.
Encouraging physical activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for promoting bowel regularity in patients with diverticulitis. Healthcare providers should encourage patients to engage in appropriate physical activities, such as walking or gentle exercises. Physical activity helps stimulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. Additionally, it contributes to overall well-being and improves overall gastrointestinal health. By encouraging physical activity, healthcare providers can support optimal bowel regularity in patients with diverticulitis.
Implementing bowel training programs
In cases where patients may experience difficulties with bowel movements or have a history of chronic constipation, healthcare providers may implement bowel training programs. These programs involve developing a structured routine for bowel movements, including specific times for toileting and techniques to promote bowel evacuation. Healthcare providers should collaborate with patients to create personalized bowel training programs that suit their individual needs and preferences. By implementing bowel training programs, healthcare providers can help establish regular bowel habits and improve overall bowel regularity in patients with diverticulitis.
Educating Patients on Self-care
Teaching about disease management techniques
Educating patients about disease management techniques is crucial for supporting self-care in diverticulitis management. Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive education on various self-care strategies, such as following a low-fiber diet, maintaining adequate hydration, and engaging in physical activity. Additionally, patients should be educated on recognizing and managing symptoms, such as abdominal pain or changes in bowel habits. By teaching patients about disease management techniques, healthcare providers can empower them to actively participate in their own care and effectively manage their condition.
Providing information on lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in diverticulitis management. Healthcare providers should provide patients with information on adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, and managing stress. These lifestyle modifications can help prevent diverticulitis flare-ups and promote overall gastrointestinal health. By providing information on lifestyle modifications, healthcare providers can support patients in making positive changes that contribute to their overall well-being.
Promoting adherence to follow-up appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are essential in monitoring the progress and managing long-term care for patients with diverticulitis. Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of adhering to scheduled appointments and consultations. These follow-up visits allow healthcare providers to assess the patient’s condition, evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan, and address any new concerns or symptoms. By promoting adherence to follow-up appointments, healthcare providers can ensure ongoing support and optimize diverticulitis management.

Providing Emotional Support
Addressing patient concerns and fears
Patients with diverticulitis may experience concerns and fears related to their condition and its management. Healthcare providers should create a supportive and empathetic environment to address these emotional needs. By actively listening to patients’ concerns and fears, healthcare providers can provide reassurance and help alleviate anxiety. Open communication and a non-judgmental approach are crucial in fostering a therapeutic relationship and offering emotional support to patients with diverticulitis.
Offering psychological support
Diverticulitis can have a significant impact on a patient’s psychological well-being. Healthcare providers should offer psychological support by providing information, resources, and referrals to individuals or groups specializing in mental health. This can help patients cope with the emotional challenges associated with their condition. Additionally, healthcare providers should encourage patients to seek professional help if needed and promote self-care strategies for managing stress and anxiety. By offering psychological support, healthcare providers can contribute to the holistic care of patients with diverticulitis.
Referring patients to support groups or counseling
Patients with diverticulitis may benefit from joining support groups or seeking counseling services. These resources can provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, gain support from peers, and access expert guidance. Healthcare providers should be knowledgeable about local support groups or counseling services that specialize in gastrointestinal conditions. By referring patients to support groups or counseling, healthcare providers can help patients navigate their emotional journey and find additional sources of support.
Collaborating with the Interdisciplinary Team
Communicating with physicians and surgeons
Collaboration between healthcare providers is crucial for effective diverticulitis management. Healthcare providers, including nurses, should maintain regular and open communication with physicians and surgeons involved in the patient’s care. This ensures that all healthcare professionals are informed about the patient’s condition, treatment plan, and any changes in their status. Through effective communication, healthcare providers can facilitate coordinated care and optimize outcomes for patients with diverticulitis.
Coordinating care with dietitians and pharmacists
The involvement of dietitians and pharmacists is essential in diverticulitis management. Dietitians can provide expert guidance on dietary modifications, ensuring patients receive appropriate nutrition while managing their condition. Pharmacists play a crucial role in medication management, providing information on drug interactions, possible side effects, and proper administration. Healthcare providers should collaborate and coordinate care with dietitians and pharmacists to ensure comprehensive and integrated care for patients with diverticulitis.
Engaging in multidisciplinary conferences for comprehensive care planning
Multidisciplinary conferences are valuable for comprehensive care planning in diverticulitis management. These conferences bring together healthcare professionals from various disciplines, including physicians, surgeons, nurses, dietitians, and pharmacists. Through active participation in these conferences, healthcare providers can share their expertise, discuss complex cases, and collaboratively develop effective care plans. By engaging in multidisciplinary conferences, healthcare providers can ensure that all aspects of diverticulitis management are thoroughly addressed and optimize patient outcomes.
In conclusion, diverticulitis management requires a comprehensive and multidimensional approach. From assessment and diagnosis to administration of medications and surgical interventions, healthcare providers play a vital role in supporting patients with diverticulitis. By addressing pain and discomfort, implementing dietary modifications, preventing complications, and providing emotional support, healthcare providers can enhance the overall well-being and quality of life for patients with diverticulitis. Through collaboration with the interdisciplinary team and promoting self-care, healthcare providers can empower patients to actively participate in their own care and effectively manage their condition. With their expertise and compassionate care, healthcare providers contribute to the successful management and treatment of diverticulitis.