If you’ve ever experienced the excruciating pain and inflammation caused by gout, you know just how important it is to understand the risk factors and take necessary precautions to prevent its onset. In this article, we’ll explore the various risk factors associated with gout and provide some simple yet effective precautions to help you manage and minimize the risk of developing this debilitating condition. So, grab a cup of tea, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of gout and how you can protect yourself from its wrath.
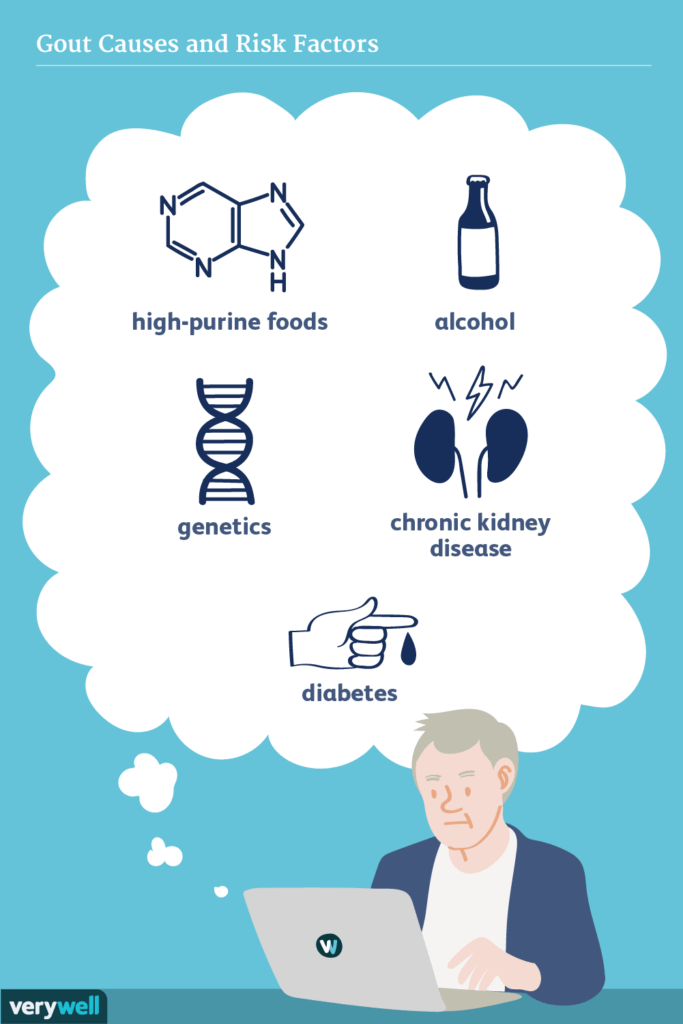
Risk Factors for Gout
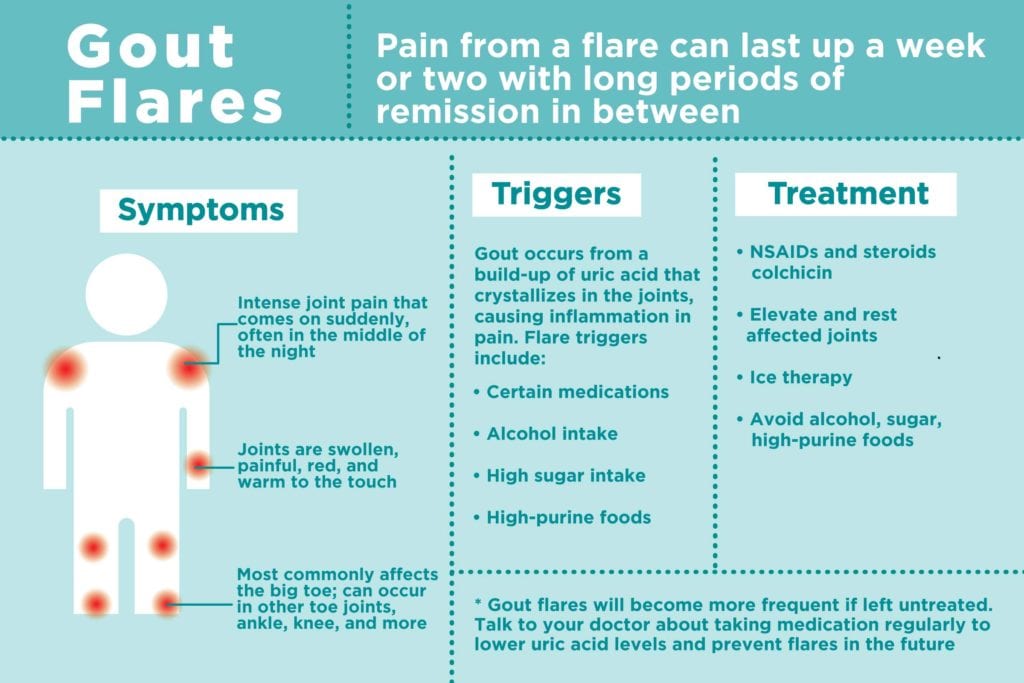
Gout is a type of arthritis that is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in the joints. While anyone can develop gout, there are certain risk factors that can increase your chances of developing this painful condition. By understanding these risk factors, you can take necessary precautions to prevent or manage gout effectively.
Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in determining your risk of developing gout. If you have a family history of gout, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself. This is known as familial gout. Additionally, certain ethnicities, such as African American, Pacific Islander, or Maori descent, have an increased genetic predisposition to gout.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese is another major risk factor for gout. Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can contribute to higher levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines, which are found in certain foods. When levels of uric acid become too high, sharp urate crystals can form in the joints, leading to gout attacks.
Dietary Factors
Your diet plays a crucial role in the development of gout. Certain foods that are high in purines can increase the production of uric acid in the body. Examples of purine-rich foods include organ meats, seafood, red meat, and certain types of alcohol, such as beer and whiskey. Sugar-sweetened beverages and fructose consumption have also been associated with an increased risk of gout. Additionally, inadequate water intake can contribute to higher levels of uric acid.
Medical Conditions
Several underlying medical conditions can increase your risk of developing gout. Individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome are more prone to gout. Chronic kidney disease can also lead to impaired uric acid excretion, resulting in higher levels of uric acid in the blood. High cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease have also been associated with gout.
Medications
Certain medications can interfere with the body’s ability to excrete uric acid, leading to an increased risk of gout. Diuretics, commonly prescribed for hypertension, can promote uric acid retention. Aspirin, cyclosporine, niacin, levodopa, and chemotherapy drugs have also been linked to gout development. If you are taking any of these medications, it is important to discuss the potential risks with your healthcare provider.
Gender and Age
Gout is more common in men than in women, especially before menopause. However, after menopause, women’s risk of developing gout increases. The female hormone estrogen helps to lower uric acid levels, but after menopause, estrogen levels decline, making women more susceptible to gout attacks.
Precautions for Gout
While certain risk factors for gout may be beyond your control, there are proactive precautions you can take to reduce your risk or manage the condition effectively.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly reduce your risk of developing gout. By maintaining a healthy body weight, you can lower uric acid levels, decreasing the likelihood of gout attacks. Aim for a gradual and sustainable weight loss through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise.
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Following a balanced diet is essential in preventing gout. Limit your intake of purine-rich foods, such as organ meats, seafood, and red meat. Instead, focus on consuming a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Incorporate low-fat dairy products, as they have been shown to reduce the risk of gout.
Limit Intake of Purine-Rich Foods
Purine-rich foods should be consumed in moderation to maintain healthy uric acid levels. Instead of eliminating these foods entirely, consider reducing your portion sizes and frequency of consumption. It is crucial to strike a balance between enjoying your favorite foods and minimizing the risk of gout attacks.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol, especially beer, is known to be a significant trigger for gout attacks. Limit your alcohol intake, particularly beer and spirits, as they are known to increase uric acid levels. If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation and ensure you stay well-hydrated.
Avoid High-Fructose Corn Syrup
High-fructose corn syrup, commonly found in sugary beverages and processed foods, has been linked to an increased risk of gout. Choose natural sweeteners and limit your consumption of sugary foods and drinks. Opt for healthier alternatives like water, herbal teas, and fresh fruit juices.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for maintaining healthy uric acid levels. Proper hydration helps to dilute uric acid, decreasing the risk of crystal formation in the joints. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily and increase your fluid intake during hot weather or vigorous physical activity.
Manage Medical Conditions
If you have underlying medical conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease, it is crucial to manage them effectively. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, take prescribed medications as directed, and attend regular check-ups to ensure your conditions are well-controlled. By managing these conditions, you can minimize their impact on gout development.
Avoid Certain Medications
If possible, avoid medications that can increase your risk of gout or worsen existing gout symptoms. If you are taking diuretics, aspirin, cyclosporine, niacin, levodopa, or chemotherapy drugs, discuss alternative treatment options with your healthcare provider. They may be able to prescribe alternative medications or adjust your current regimen to minimize the risk of gout attacks.
Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health and can also reduce the risk of gout. Engage in moderate aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises as part of your fitness routine. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes better blood flow, all of which contribute to a lower risk of gout.
Quit Smoking
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of gout and can worsen gout symptoms. If you are a smoker, consider quitting to protect your overall health and decrease your risk of gout attacks. Seek support from healthcare professionals, use nicotine replacement therapy if needed, and explore different strategies to help you quit smoking successfully.
By understanding these risk factors and taking necessary precautions, you can reduce your risk of developing gout or manage the condition effectively if you already have it. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider to establish a personalized plan that addresses your specific needs and circumstances. Take charge of your health, make positive lifestyle changes, and enjoy a life free from the pain and discomfort of gout.
