Have you ever experienced an improvement in your symptoms after taking a pill, only to realize that it was just a placebo? The mysterious and fascinating phenomenon of the placebo effect has long intrigued scientists and medical professionals. In this article, we will explore the various risk factors that can influence the power of the placebo effect, as well as the precautions that can be taken to minimize its impact. Whether you’re a curious individual or a healthcare provider looking to better understand this intriguing aspect of human psychology, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s dive into the world of the placebo effect and uncover its secrets.
Risk Factors for Placebo Effect
The placebo effect, a phenomenon in which a patient experiences an improvement in symptoms or a perceived benefit from a treatment that has no pharmacological effect, can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these risk factors is crucial in interpreting the outcomes of clinical trials and ensuring the accuracy of medical research.
Individual Factors
Individual factors play a significant role in determining the susceptibility to the placebo effect. Psychological characteristics such as personality traits, suggestibility, and level of optimism can impact an individual’s response to placebo treatments. Additionally, patients with a strong desire to please their healthcare providers or to conform to societal expectations may be more likely to experience the placebo effect. This highlights the importance of considering individual differences when analyzing the effectiveness of medical interventions.
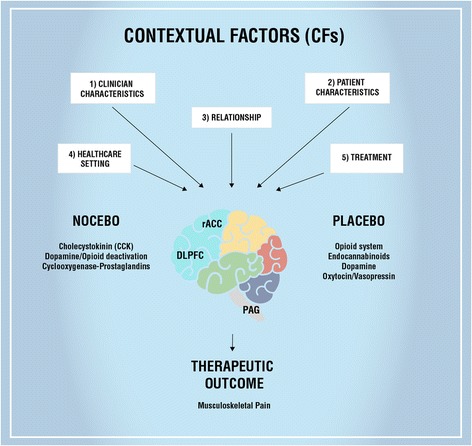
Contextual Factors
The context in which a treatment is administered can have a significant impact on the placebo effect. Environmental factors, such as the physical setting of the healthcare facility, the demeanor of the healthcare provider, and the perceived level of expertise and credibility of the provider, can influence patients’ expectations and beliefs about the treatment’s efficacy. Furthermore, cultural and social factors, including societal beliefs and norms surrounding healthcare, can shape individuals’ responses to placebos.
Healthcare Provider Factors
Healthcare providers also play a role in influencing the placebo effect. Factors such as the provider’s communication style, level of empathy, and ability to establish a therapeutic relationship can impact patients’ expectations and beliefs about the treatment. Moreover, the provider’s level of confidence and enthusiasm when discussing the treatment may influence the patient’s perception of its effectiveness. It is essential for healthcare providers to be aware of these factors and strive to maintain a balanced approach in their interactions with patients.
Precautions to Minimize Placebo Effect
While the placebo effect can complicate the evaluation of medical treatments, taking precautions can help minimize its influence and improve the accuracy of research findings.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should always be at the forefront when designing and conducting clinical trials and medical research. Researchers must consider the potential implications of inducing a placebo effect in study participants and ensure that their welfare is prioritized. This includes providing clear and accurate information about the nature of the study, potential risks and benefits, and the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a crucial aspect of any medical research involving human subjects. By providing participants with comprehensive information about the study’s objectives, procedures, and potential use of placebos, researchers allow individuals to make fully informed decisions about their participation. Informed consent ensures that participants have a clear understanding of the study’s purpose and the possibility of receiving a placebo.
Blinding Methods
Blinding, also known as masking, is a technique commonly used in clinical trials to minimize bias and the placebo effect. Blinding involves withholding information about the treatment assignment from both the participants and the researchers involved in the study. This can be achieved through various methods, such as using identical-looking placebos, using a double-blind design where neither the participant nor the researcher knows the treatment assignment, or employing a single-blind design where only the participant is unaware of the treatment.
Control Groups
Including control groups in clinical trials is essential for evaluating the true effectiveness of a treatment. Control groups receive either a placebo or standard-of-care treatment, enabling researchers to compare the outcomes between the experimental group receiving the active treatment and the control group. By using control groups, researchers can account for the placebo effect and better understand the actual therapeutic effects of the treatment being studied.

Impact of Placebo Effect on Clinical Trials
The placebo effect can have a profound impact on the outcomes of clinical trials, affecting various aspects of study design, measurement tools, and data interpretation.
Study Design
The presence of the placebo effect must be considered when designing clinical trials. Researchers need to carefully select appropriate control groups and blinding methods to minimize the potential for biased results. Well-designed studies take into account the potential influence of the placebo effect and strive to isolate the treatment’s true effects from those attributable to the placebo.
Measurement Tools
Accurate measurement of treatment outcomes is crucial in determining the efficacy of a medical intervention. However, the placebo effect can complicate the interpretation of these measurements. Depending on the nature of the condition or symptoms being assessed, it can be challenging to differentiate between the placebo effect and the actual treatment effects. Researchers must employ reliable and validated measurement tools to minimize potential confounding factors and accurately assess treatment outcomes.
Data Interpretation
Analyzing and interpreting data from clinical trials require careful consideration of the placebo effect. It is vital to distinguish between the treatment’s true effects and the placebo response when examining the effectiveness of an intervention. Statistical methods can help identify and account for the placebo effect in order to draw accurate conclusions from the data. Failure to account for the placebo effect can lead to misleading interpretations and potentially ineffective medical treatments.
Psychological and Neurobiological Mechanisms of the Placebo Effect
Understanding the psychological and neurobiological mechanisms underlying the placebo effect is crucial for unraveling its complexities and harnessing its potential benefits in medical treatments.
Expectancy and Belief
The placebo effect is strongly influenced by patients’ expectations and beliefs regarding the treatment. Positive expectations and a belief in the treatment’s effectiveness can lead to the activation of reward pathways in the brain, resulting in physiological changes and a perceived improvement in symptoms. The brain’s response to these expectations and beliefs can trigger the release of endogenous opioids and other neurotransmitters, further influencing the placebo effect.
Conditioning
Conditioning, a process by which associations are formed between a neutral stimulus and a response, plays a significant role in the placebo effect. Through repeated pairing of a placebo treatment with positive outcomes or relief from symptoms, individuals can develop conditioned responses to the placebo. These conditioned responses can elicit physiological changes similar to those produced by the active treatment, contributing to the placebo effect.
Neurotransmitters and Brain Activity
The placebo effect is closely linked to changes in neurotransmitter activity and brain functioning. Neuroimaging studies have shown alterations in various regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and basal ganglia, during placebo responses. Dopamine, endogenous opioids, and other neurotransmitters are thought to play a significant role in modulating the placebo effect. Understanding the neurobiological mechanisms can provide valuable insights into the potential therapeutic applications of the placebo effect.

Placebo Effect in Pain Management
Pain management is an area in which the placebo effect has been widely studied and demonstrated to have a substantial impact on outcomes.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as patients’ expectations, beliefs, and emotional state, can significantly influence the placebo response in pain management. Studies have shown that patients with higher levels of optimism and greater treatment expectations are more likely to experience a placebo analgesic effect. Additionally, the quality of the patient-provider relationship and the level of empathy demonstrated by healthcare providers can contribute to the placebo effect in pain management.
Neurobiological Factors
Neurobiological processes play a vital role in mediating the placebo effect in pain management. Activation of endogenous opioid systems, release of neurotransmitters, and modulation of pain pathways are among the mechanisms involved. Placebo analgesia has been observed in various pain conditions, including acute and chronic pain, highlighting the potential of harnessing the placebo effect to enhance pain management strategies.
Psychosocial Factors
Psychosocial factors, such as social support, the therapeutic context, and the influence of cultural expectations, can significantly impact the placebo effect in pain management. Patients who perceive higher levels of social support and experience a supportive therapeutic environment may be more likely to respond to placebo interventions. Additionally, cultural beliefs and social norms surrounding pain can shape patients’ responses to treatments and contribute to the placebo effect.
Placebo Effect in Mental Health Treatments
The placebo effect is not limited to physical conditions but can also influence outcomes in mental health treatments.
Psychological Interventions
Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychotherapy, can be susceptible to the placebo effect. Patients’ expectations, the therapeutic relationship, and the perceived credibility and effectiveness of the interventions can influence treatment outcomes. By understanding the mechanisms underlying the placebo effect in mental health treatments, clinicians can optimize their approaches and enhance the therapeutic benefits for patients.
Pharmacological Treatments
Placebo responses can also play a role in the effectiveness of pharmacological treatments for mental health conditions. Patients’ beliefs and perceptions of the medication’s efficacy can contribute to the placebo effect and influence treatment outcomes. Furthermore, the response to placebos in clinical trials can complicate the evaluation and approval of new psychiatric medications. Careful consideration of the placebo effect is crucial to accurately assess the true benefits of pharmacological interventions.
Therapeutic Relationships
The patient-provider relationship and the quality of communication between the two parties can impact the placebo effect in mental health treatments. A strong therapeutic relationship characterized by empathy, trust, and collaboration can enhance treatment outcomes, potentially augmenting the placebo effect. Conversely, a poor therapeutic relationship characterized by inadequate communication and a lack of trust can minimize the placebo response and hinder treatment effectiveness.

Placebo Effect in Alternative Medicine
The placebo effect is frequently observed in the context of alternative medicine practices.
Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements, often used in traditional medicine systems, can elicit a significant placebo effect. Patients’ beliefs and expectations regarding the effectiveness of these supplements can lead to the perception of symptom improvement or overall well-being. It is important to distinguish between the placebo effect and any actual therapeutic benefits derived from the active components of the supplements when evaluating their efficacy.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice involving the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body, has been shown to elicit placebo responses. Patients’ beliefs and expectations play a central role in the placebo effect associated with acupuncture. The ritualistic nature of the treatment, the involvement of a skilled practitioner, and the perceived effectiveness of the procedure can contribute to the placebo response.
Homeopathy
Homeopathy, a system of alternative medicine based on the concept of “like cures like,” often involves highly diluted remedies. The placebo effect is believed to play a significant role in the observed effects of homeopathic treatments. Patients’ beliefs in the principles of homeopathy and their expectations regarding the remedies’ effectiveness can contribute to the placebo response. Critical evaluation of homeopathic treatments is essential to distinguish between the placebo effect and any potential therapeutic effects.
Ethical Considerations in Exploiting Placebo Effect
While the placebo effect can have practical applications in clinical practice, it is essential to navigate the ethical considerations associated with its potential exploitation.
Use in Clinical Practice
In clinical practice, healthcare providers must carefully consider the use of placebos and the potential for inducing placebo effects. The administration of placebo treatments without the patient’s knowledge or consent can raise ethical concerns. However, under certain circumstances, such as when standard treatments are unavailable or ineffective, open-label placebos may be used while maintaining transparency and informed consent.
Use in Research
In the design and execution of medical research, ethical guidelines must be followed to safeguard the well-being of study participants. Researchers should be transparent about the potential use of placebos and ensure that participants fully understand the study’s objectives and potential risks. It is essential to strike a balance between scientific rigor and ethical considerations when involving placebos in research protocols.
Educating Patients
Educating patients about the placebo effect is an ethical responsibility of healthcare providers. Patients should be provided with accurate information about the concept, potential benefits, and limitations of placebos. By promoting patient education and open communication, healthcare providers can empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their treatments and minimize any unintended exploitation of the placebo effect.

Placebo Effect in Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine aims to tailor treatment approaches to individual patients, considering their unique characteristics and needs. The placebo effect can influence outcomes in personalized medicine settings.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors are thought to contribute to individual differences in placebo responses. Variations in genes involved in neurotransmitter systems, the immune system, and other biological pathways may predispose individuals to different placebo effects. Understanding these genetic factors can help personalize treatments and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Psychosocial Factors
Psychosocial factors, including personality traits, social support networks, and patients’ expectations and beliefs, can significantly impact placebo responses. Consideration of these psychosocial factors is crucial in personalized medicine to ensure a comprehensive understanding of individual patients’ treatment responses and potential placebo effects.
Treatment Expectations
Personalized medicine involves tailoring treatments based on patients’ individual characteristics, including their treatment expectations. Understanding patients’ treatment expectations and beliefs about the intervention can help healthcare providers optimize treatment outcomes and account for any potential placebo effects. Open communication and shared decision-making can empower patients to contribute to their treatment plans and enhance their engagement in the therapeutic process.
Placebo Effect in Patient-Provider Communication
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing the potential influence of the placebo effect.
Enhancing Communication Skills
Healthcare providers can improve patient-provider communication skills by actively listening, displaying empathy, and fostering a collaborative therapeutic relationship. By establishing a supportive and respectful environment, healthcare providers can enhance treatment outcomes and potentially amplify the beneficial effects of the placebo response.
Addressing Patient Expectations
Openly discussing and addressing patient expectations can help manage the potential placebo effect. Healthcare providers must listen attentively to patients’ concerns, provide accurate information about treatment options, and explain the potential benefits and limitations of both active treatments and placebos. By keeping patients informed and involved in the decision-making process, healthcare providers can promote transparency and minimize any potential exploitation of the placebo effect.
Shared Decision Making
Shared decision making, a collaborative approach in which healthcare providers and patients jointly make treatment decisions, can help optimize outcomes and account for the potential placebo effect. By engaging patients in meaningful discussions about their treatment options, considering their values and preferences, and educating them about potential placebo responses, healthcare providers can empower patients to become active participants in their own care.
In conclusion, the placebo effect is a complex phenomenon that can have a significant impact on clinical trials, medical treatments, and patient outcomes. Various risk factors, such as individual differences, contextual factors, and healthcare provider characteristics, can contribute to the placebo effect. However, precautions such as ethical considerations, informed consent, blinding methods, and control groups can help minimize its influence. Understanding the psychological and neurobiological mechanisms of the placebo effect can provide insights into its potential therapeutic applications. Additionally, recognizing the placebo effect’s role in pain management, mental health treatments, alternative medicine, personalized medicine, and patient-provider communication is crucial for providing optimal care and optimizing treatment outcomes. By navigating the ethical considerations and implementing evidence-based practices, healthcare providers can harness the potential benefits of the placebo effect while ensuring patient well-being and maintaining scientific rigor.